-
Variables associated with compliance with standard precautions among hospital nurses: a systematic review and meta-analysis
-
Song Hee Park, Seok Hee Jeong, Chang Seop Lee, Young Man Kim
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2026;56(1):1-26. Published online February 27, 2026
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25114
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
- Purpose
This study aimed to conduct a systematic review and meta-analysis to identify variables associated with standard precautions compliance among hospital nurses and to comprehensively examine their effect sizes.
Methods
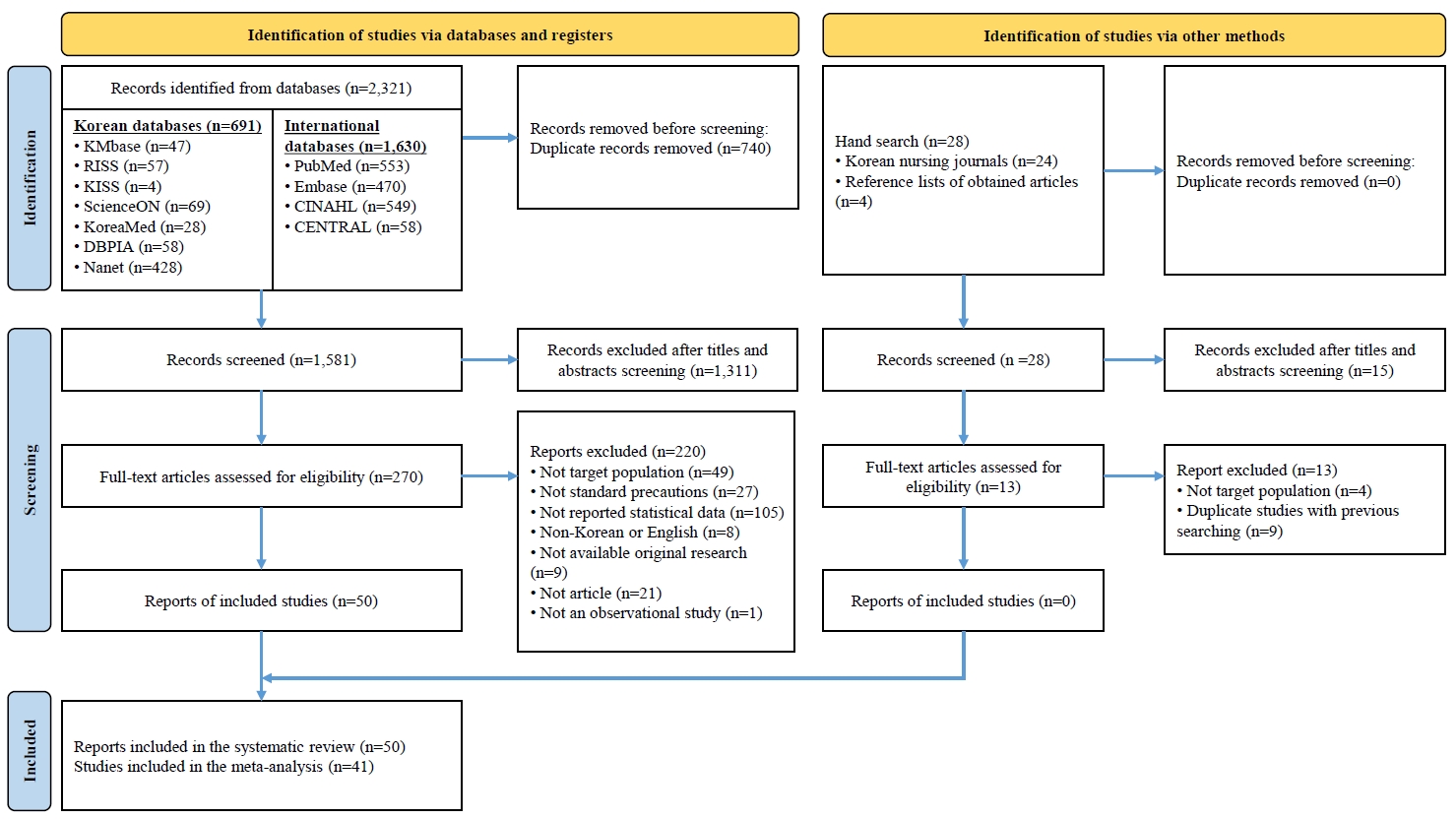
A systematic review and meta-analysis were reported in accordance with the PRISMA and MOOSE guidelines. Studies published in English or Korean were retrieved from KMbase, KoreaMed, KISS, ScienceON, RISS, Nanet, DBpia, PubMed, Embase, CINAHL, and CENTRAL. Data collection was conducted from July 6 to July 16, 2024. To ensure a comprehensive search, no restrictions were placed on the publication period, and studies published up to June 2024 were included in the literature search. Analyses were performed using R ver. 4.4.1.
Results
Of the 2,321 studies screened, 50 were included in the systematic review and 41 were included in the meta-analysis. Variables were categorized according to the ecological model. Among individual-level factors, variables with medium correlation effect sizes (ESr ≥.30) included self-efficacy (ESr=.41; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.24 to 0.56), perceived barriers (ESr=−.35; 95% CI, −0.59 to −0.05), cues to action (ESr=.34; 95% CI, 0.07 to 0.57), and perceived benefits (ESr=.30; 95% CI, 0.13 to 0.46). Among organizational factors, organizational culture for infection control (ESr=.47; 95% CI, 0.39 to 0.54) and patient safety culture (ESr=.44; 95% CI, 0.35 to 0.53) demonstrated medium effect sizes. Other statistically significant variables with small effect sizes were also identified. No variables were identified within the interpersonal, community, or public policy domains.
Conclusion
This study identified self-efficacy and organizational culture for infection control as key determinants of compliance with standard precautions. Strengthening these factors may reduce healthcare-associated infections and promote safer nursing care (PROSPERO registration number: CRD42024566518).
-
Effects of presenteeism on turnover intention in clinical nurses through the serial mediating roles of missed nursing care and job satisfaction: a cross-sectional predictive correlational study
-
Hyeonseon Cheon, Seok Hee Jeong, Hyun Kyung Kim, Hyoung Eun Chang
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(4):584-597. Published online November 10, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25015
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF ePub ePub
- Purpose
This study aimed to investigate the two-mediator serial mediation effect of missed nursing care and job satisfaction on the relationship between presenteeism and turnover intention in clinical nurses.
Methods
A cross-sectional predictive correlational study was conducted, and the participants were 208 clinical nurses working in advanced general hospitals in South Korea. Data were collected from October 6 to November 7, 2023 using self-reported questionnaires, including general characteristics, presenteeism, missed nursing care, job satisfaction, and turnover intention. Data were analyzed using IBM SPSS/WIN ver. 29.0 and PROCESS macro ver. 4.2.
Results
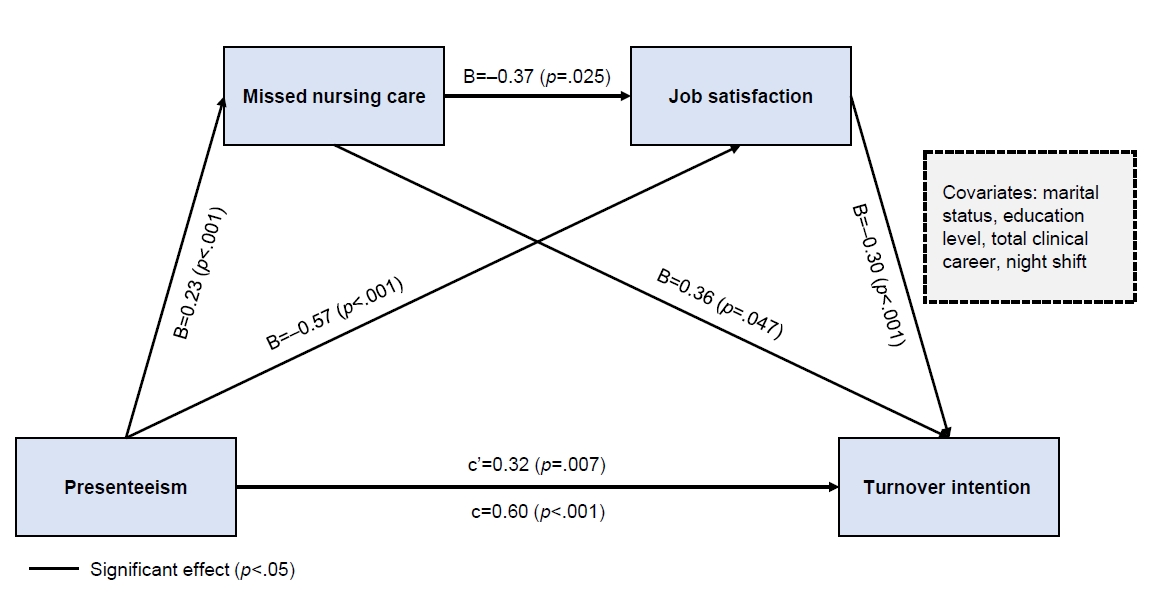
Missed nursing care and job satisfaction exhibited a double mediating effect on the relationship between presenteeism and clinical nurses’ turnover intention. In addition, missed nursing care showed a mediating effect on the relationship between presenteeism and clinical nurses’ turnover intention. Job satisfaction had a mediating effect on the relationship between presenteeism and clinical nurses’ turnover intention. Presenteeism had a direct effect on missed nursing care, job satisfaction, and turnover intention. Missed nursing care exerted a direct effect on job satisfaction and turnover intention among clinical nurses. Job satisfaction had a direct effect on turnover intention.
Conclusion
To reduce nurses’ turnover intention, it is essential to develop and implement programs focused on preventing presenteeism. Additionally, organizational initiatives should prioritize active support for nurses’ health management, alleviating the shortage of nursing staff, augmenting job satisfaction, and improving the overall working environment.
-
Research trends in generative artificial intelligence in nursing: a scoping review
-
Myung Jin Choi, Myoung Hee Seo, Jihun Kim, Sunmi Kim, Seok Hee Jeong
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(3):468-487. Published online August 5, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25006
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF ePub ePub
- Purpose
Generative artificial intelligence (AI) has yet to be comprehensively analyzed in the nursing literature. This study aimed to identify research trends in generative AI within the nursing field through a scoping review and propose strategies for its effective utilization in nursing.
Methods
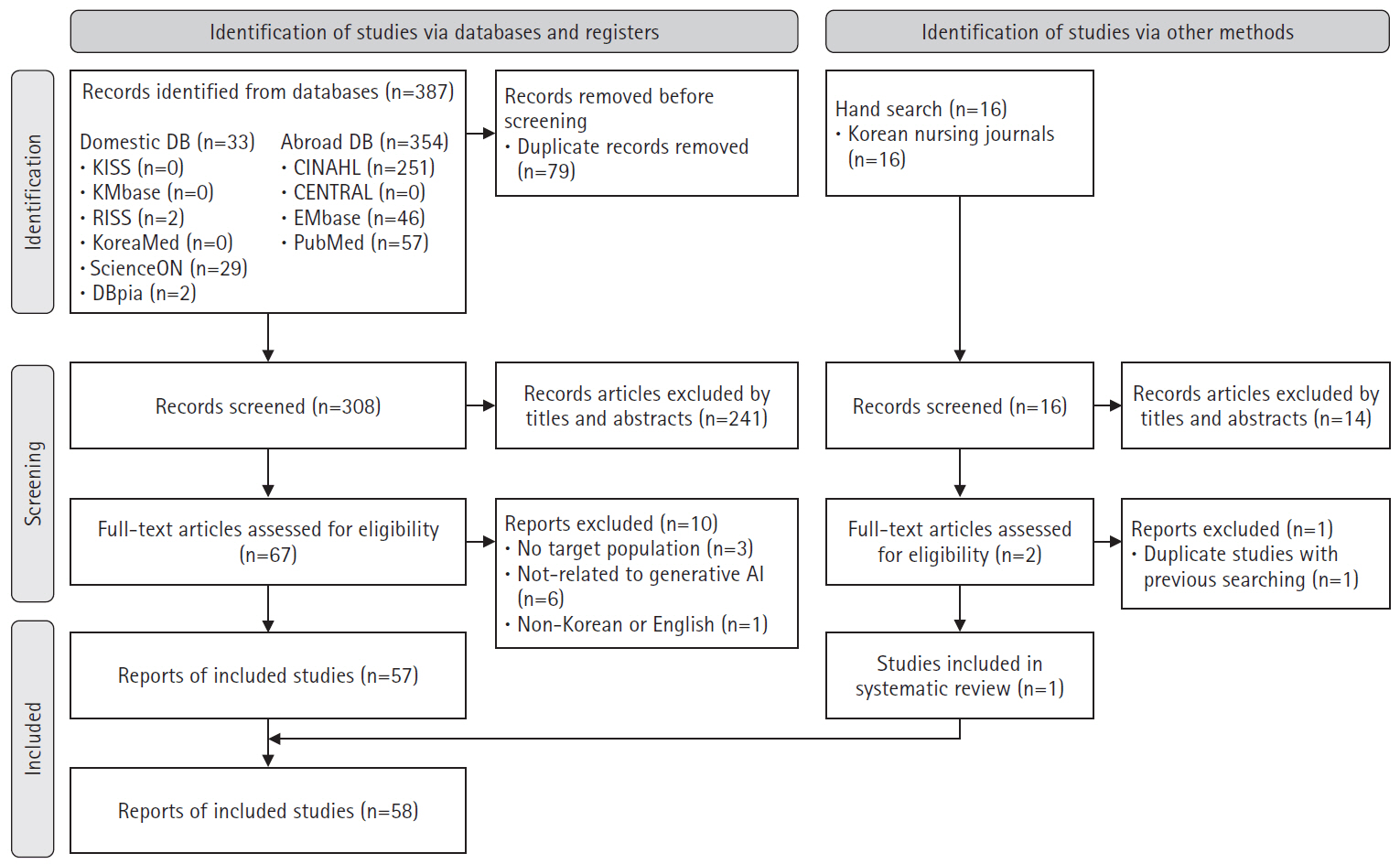
A scoping review was conducted following Arksey and O’Malley’s six-stage framework. The inclusion criteria included: (1) studies conducted in nursing; (2) research related to generative AI; and (3) original research articles, theses, communications, editorials, letters, or commentaries published in academic journals. Database used PubMed, Embase, CENTRAL, CINAHL, KMbase, KoreaMed, KISS, ScienceON, RISS, DBpia, and 27 nursing-specific journals.
Results
In total, 403 studies were initially identified, and 58 were included in the final analysis. In the care domain, strengths included rapid information retrieval and improved nurse-patient communication, while limitations included the irreplaceable human element and low reliability. The administration domain had no relevant studies. In the research domain, generative AI exhibited strengths such as enhanced efficiency in the paper writing process and improved dissemination speed, but its weaknesses included lack of ethical and legal accountability and a risk of inaccurate or biased information. In the education domain, generative AI was effective in saving time in educational design and implementation, as well as supporting content creation, but challenges included algorithmic bias and risks of plagiarism.
Conclusion
This study identified potential benefits and limitations of generative AI across nursing domains. For effective application, it is essential to develop comprehensive guidelines and policies, provide user education and support, and create opportunities for nurses, educators, and students to learn about strengths and risks of generative AI.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Nursing Students' Perspectives on the Use of Artificial Intelligence in Psychiatric Nursing Education: A Qualitative Meta-Synthesis
Sukyung Son, Eunyoung Park
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2025; 34(Special Is): 9. CrossRef
-
6,919
View
-
505
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
Effects of a nursing leadership program on self-leadership, interpersonal relationships, clinical performance, problem-solving abilities, and nursing professionalism among nursing students in South Korea: a quasi-experimental study
-
Sunmi Kim, Young Ju Jeong, Hee Sun Kim, Seok Hee Jeong, Eun Jee Lee
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(1):137-151. Published online February 25, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24110
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF ePub ePub
- Purpose
This study investigated the effects of a nursing leadership program on self-leadership, interpersonal relationships, clinical performance, problem-solving abilities, and nursing professionalism among nursing students in South Korea.
Methods
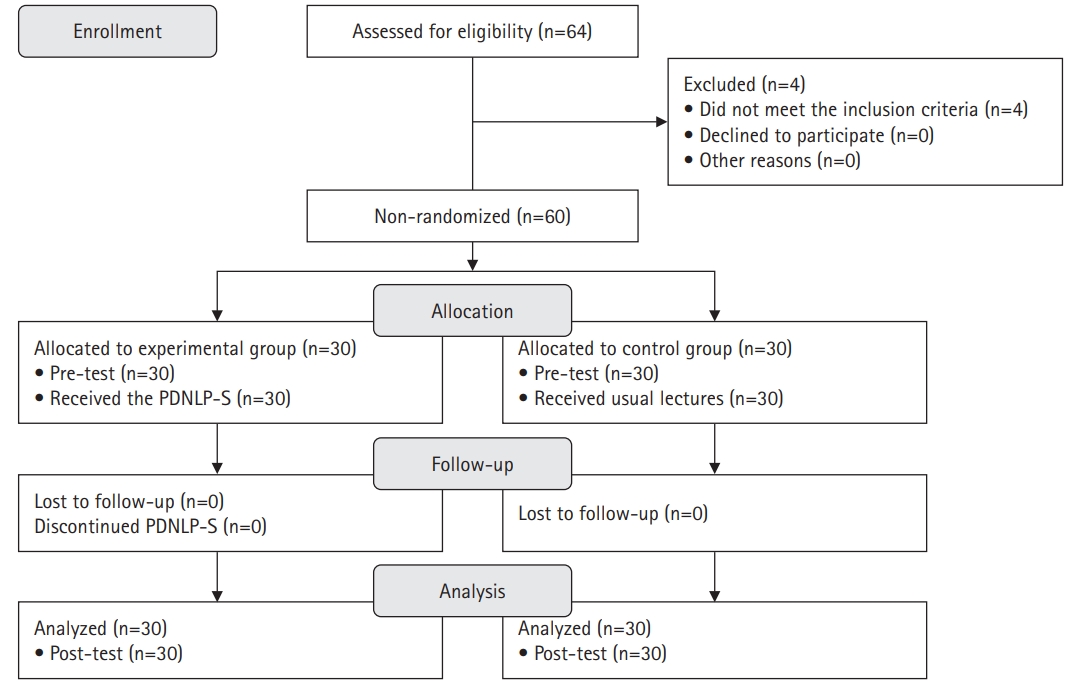
A quasi-experimental study was conducted. The Practice-Driven Nursing Leadership Program for Students (PDNLP-S) was developed based on the ADDIE model (analysis, design, development, implementation, and evaluation). This quasi-experimental study design included 60 nursing students. The experimental group (n=30) participated in the PDNLP-S for 120-minute sessions over 5 weeks, while the control group (n=30) received usual lectures. The PDNLP-S included lectures, discussions, and individual and group activities to cultivate core nursing leadership competencies such as individual growth, collaboration, nursing excellence, creative problem-solving, and influence. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, the Mann-Whitney U-test, and the independent t-test with IBM SPSS Windows ver. 26.0.
Results
The experimental group demonstrated significant improvements in self-leadership (t=3.28, p=.001), interpersonal relationships (t=3.07, p=.002), clinical performance (U=268.50, p=.004), and problem-solving abilities (t=2.20, p=.017) compared to the control group. No significant difference was observed in nursing professionalism (t=0.50, p=.311).
Conclusion
This study demonstrates that the PDNLP-S improved nursing students’ self-leadership, interpersonal relationships, clinical performance, and problem-solving abilities. The PDNLP-S can play a significant role in cultivating future nurse leaders by enhancing these nursing leadership competencies among nursing students.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Self-Determination Theory in Return to Work Interventions: A Scoping Review
Kexin Chen, Ling Yang, Jiajia Tu
Journal of Multidisciplinary Healthcare.2025; Volume 18: 7539. CrossRef
-
7,373
View
-
300
Download
-
1
Web of Science
-
1
Crossref
-
National Petition Analysis Related to Nursing: Text Network Analysis and Topic Modeling
-
HyunJung Ko, Seok Hee Jeong, Eun Jee Lee, Hee Sun Kim
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(6):635-651. Published online December 31, 2023
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23052
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Purpose
This study aimed to identify the main keyword, network structure, and main topics of the national petition related to “nursing” in South Korea.
Methods
Data were gathered from petitions related to the national petition in Korea Blue House related to the topic “nursing” or “nurse” from August 17, 2017, to May 9, 2022. A total of 5,154 petitions were searched, and 995 were selected for the final analysis. Text network analysis and topic modeling were analyzed using the Netminer 4.5.0 program.
Results
Regarding network characteristics, a density of 0.03, an average degree of 144.483, and an average distance of 1.943 were found. Compared to results of degree centrality and betweenness centrality, keywords such as “work environment,” “nursing university,” “license,” and “education” appeared typically in the eigenvector centrality analysis. Topic modeling derived four topics: (1) “Improving the working environment and dealing with nursing professionals,” (2) “requesting investigation and punishment related to medical accidents,” (3) “requiring clear role regulation and legislation of medical and nonmedical professions,” and (4) “demanding improvement of healthcare-related systems and services.” Conclusion: This is the first study to analyze Korea's national petitions in the field of nursing. This study's results confirmed both the internal needs and external demands for nurses in South Korea. Policies and laws that reflect these results should be developed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Voice of Customer Analysis of Nursing Care in a Tertiary Hospital: Text Network Analysis and Topic Modeling
Hyunjung Ko, Nara Han, Seulki Jeong, Jeong A Jeong, Hye Ryoung Yun, Eun Sil Kim, Young Jun Jang, Eun Ju Choi, Chun Hoe Lim, Min Hee Jung, Jung Hee Kim, Dong Hyu Cho, Seok Hee Jeong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(5): 529. CrossRef - A Study on Internet News for Patient Safety Campaigns: Focusing on Text Network Analysis and Topic Modeling
Sun-Hwa Shin, On-Jeon Baek
Healthcare.2024; 12(19): 1914. CrossRef
-
2,789
View
-
44
Download
-
1
Web of Science
-
2
Crossref
-
Factors Affecting Radiation Protective Behaviors in Perioperative Nurses Applying the Theory of Planned Behavior: Path Analysis
-
Se Young Jang, Hee Sun Kim, Seok Hee Jeong, Young Man Kim
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(2):222-235. Published online April 30, 2023
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22099
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Purpose
The aim of this study was to identify the factors explaining protective behaviors against radiation exposure in perioperative nurses based on the theory of planned behavior.
Methods
This was a cross-sectional study. A total of 229 perioperative nurses participated between October 3 and October 20, 2021. Data were analyzed using SPSS/WIN 23.0 and AMOS 23.0 software. The three exogenous variables (attitude toward radiation protective behaviors, subjective norm, and perceived behavioral control) and two endogenous variables (radiation protective intention and radiation protective behaviors) were surveyed.
Results
The hypothetical model fit the data (χ2/df = 1.18, SRMR = .02, TLI = .98, CFI = .99, RMSEA = .03). Radiation protective intention (β = .24, p = .001) and attitude toward radiation protective behaviors (β = .32, p = .002) had direct effects on radiation protective behaviors. Subjective norm (β = .43, p = .002) and perceived behavior control (β = .24, p = .003) had direct effects on radiation protective intention, which explained 38.0% of the variance. Subjective norm (β = .10, p = .001) and perceived behavior control (β = .06, p = .002) had indirect effects via radiation protective intention on radiation protective behaviors. Attitude toward radiation protective behaviors, subjective norm, and perceived behavioral control were the significant factors explaining 49.0% of the variance in radiation protective behaviors.
Conclusion
This study shows that the theory of planned behavior can be used to effectively predict radiation protective behaviors in perioperative nurses. Radiation safety guidelines or education programs to enhance perioperative nurses’ protective behaviors should focus on radiation protective intention, attitude toward radiation protective behaviors, subjective norm, and perceived behavioral control.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Health Protective Behavior in Occupational Health Practice: A Concept Analysis
Fenggang Liu, Juanjuan Wang, Weeraporn Suthakorn, Li Liao
Health Science Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors related to preventive measures towards PM2.5 exposure: A systematic review
Jeevan Bhatta, Orapin Laosee, Cheerawit Rattanapan
Global Transitions.2024; 6: 212. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Radiation Protection Behavior of Nurses in Intensive Care Units
Seo Jeong Kim, Yun Hee Kim
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2024; 17(3): 1. CrossRef - A Review of the Relationship between Health Behaviors and Career Adaptability among University Students
Dongming Jia, Xia Yuan
Journal of Medicine and Health Science.2024; 2(4): 43. CrossRef
-
2,609
View
-
98
Download
-
2
Web of Science
-
4
Crossref
-
Effects of Leadership Styles of Nursing Managers on Turnover Intention of Hospital Nurses: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
-
Yunjeong Cho, Seok Hee Jeong, Hee Sun Kim, Young Man Kim
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(5):479-498. Published online October 31, 2022
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22039
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Purpose
This study aimed to examine effect sizes of leadership styles of nursing managers on turnover intention of hospital nurses.
Methods
A systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted in accordance with the PRISMA and MOOSE guidelines. Participants were nurses working in hospitals. The intervention involved nursing managers’ leadership styles; the outcome assessed was nurses’ turnover intention. This was an observational study design. Eleven databases were searched to obtain articles published in Korean or English. Of the 14,428 articles reviewed, 21 were included in systematic review and meta-analysis. Comprehensive Meta-Analysis and R software programs were used.
Results
The total effect size r (ESr) was - 0.25 (95% confidence interval: - 0.29 to - 0.20). Effect sizes of each leadership style on turnover intention were as follows: ethical leadership (ESr = - 0.34), transformational leadership (ESr = - 0.28), authentic leadership (ESr = - 0.23), transactional leadership (ESr = - 0.21), and passive avoidant leadership (ESr = 0.13). Ethical leadership was the most effective style in decreasing turnover intention of hospital nurses.
Conclusion
Positive leadership styles of nurse managers effectively decrease turnover intention of hospital nurses, and negative leadership styles of nurse managers effectively increase turnover intention of hospital nurses. The ethical leadership style is the most effective in decreasing turnover intention of hospital nurses; however, it requires careful interpretation as its effects are reported by only two studies. This study contributes to addressing the high turnover rate of hospital nurses and developing positive leadership styles of nurse managers in hospital settings.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - The effect of organizational communication and grit on turnover intention of rehabilitation hospital nurses: A cross-sectional correlation study
Inji Ha, Heeok Park, Ji Hun Joung
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2025; 27(1): 35. CrossRef - Influence of Leadership Styles on Turnover Intentions in Technology Startups
Sheeza Fayyaz, Saima Majeed
Journal of Professional & Applied Psychology .2025; 6(1): 36. CrossRef - Protecting Workers From Rude Customers to Enhance Organizational Identification in Emotional Labor Environments: A Study With Call Center Agents
Hyojeong Kim, Nagesh N Murthy, Anurag Agarwal, Kwangtae Park
Production and Operations Management.2025; 34(10): 3250. CrossRef - Humanistic nursing care management strategies: from formulation to implementation
Jing Lv, Yajie Su, Hongmei Tang, Xiaolin Jiang, Xiaojuan Chen
Frontiers in Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - When Leadership Drives Nurses Away: Empirical Research Qualitative on High Turnover Rates Reasons
Saleem Al‐Rjoub
Nursing Open.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Relationship between different leadership styles of nursing managers and nurses’ turnover intention in hospitals: an integrative review
Alicia Jimenez-Caceres, Anna Agusti-Boada, Conxi Caro-Benito, Olga Monistrol
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Structured Subjective Readiness in Situational Leadership: Validating the 4D Model as an Associative Predictor
Dino Giergia, Nikola Drašković, Mario Fraculj
Administrative Sciences.2025; 15(12): 488. CrossRef - Mediating Effect of Leader-Member Exchange on the Ethical Leadership of Nursing Unit Managers and Turnover Intention of Clinical Nurses: A Nationwide Survey using Proportional Quota Sampling
Jihun Kim, Sunmi Kim, Nara Han, Seok Hee Jeong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(1): 42. CrossRef - Effects of Resilience, Nursing Managers’ Empowering Leadership on Turnover Intention among New Nurses: Mediating role of Transition Shock
Hyun Jin Jung, Hyun Kyung Kim, Seok Hee Jeong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(3): 212. CrossRef - Investigation of the relationship between nurses' perception of toxic leadership and their organizational trust levels and turnover intentions
Sultan Türkmen Keskin, Meltem Özduyan Kiliç
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2024; 80(5): 1859. CrossRef - The structural relationship of job stress, job satisfaction, organizational commitment, and turnover intention among youth sports education leaders in Korea
Myung Kyu Jung, Tae Gyeom Jung, Min Woo Jeon, Ji Hae Lee
Frontiers in Psychology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Patient Safety Management System, Leadership, and Communication Types on Nurse’ Patient Safety Management Activities
Eunji Lee, Haejung Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(4): 367. CrossRef - Nursing-sensitive Indicators in East Asian Hospitals: A Scoping Review
Jae Jun Lee, Won Jin Seo, Dong Ah Park, Hwa Yeong Oh, Seung Eun Lee
Quality Improvement in Health Care.2024; 30(2): 88. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Nurses Turnover in Saudi Arabia: A Systematic Review
Abdulmajeed M. Albalawi, Glezzeelyne P. Pascua, Sameer A. Alsaleh, Walaa Sabry, Sitti Nursa Ahajan, Jeseela Abdulla, Amal Abdulalim, Suad S. Salih, Sulaiman Al Sabei
Nursing Forum.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Nursing Unit Managers’ Authentic Leadership, Transformational Leadership, and Transactional Leadership on Turnover Intention in Advanced Beginner Nurses: Mediation Effects of Positive Psychological Capital
Eun Jeong Kim, Eungyung Kim, Son Ja Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2023; 29(4): 409. CrossRef - Factors related to the organizational silence of Korean nurses: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Kyungja Kang, Jeong-Hee Kim
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2023; 29(3): 302. CrossRef
-
7,753
View
-
491
Download
-
8
Web of Science
-
16
Crossref
-
Patient Safety Management Activities of Korean Nurses: A Meta-Analytic Path Analysis
-
Seohee Jeong, Seok Hee Jeong
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(4):363-377. Published online August 31, 2022
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22022
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Purpose
This study aimed to test a hypothetical model of Korean nurses’ patient safety management activities using meta-analytic path analysis.
Methods
A systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-analytic path analysis were conducted following the PRISMA and MOOSE guidelines. Seventy-four studies for the meta-analysis and 92 for the meta-analytic path analysis were included. The R software program (Version 3.6.3) was used for data analysis.
Results
Four variables out of 49 relevant variables were selected in the meta-analysis. These four variables showed large effect sizes (ESr = .54) or median effect sizes (ESr = .33∼.40) with the highest k (number of studies) in the individual, job, and organizational categories. The hypothetical model for the meta-analytic path analysis was established using these variables and patient safety management activities. Twelve hypothetical paths were set and tested. Finally, the perception of the importance of patient safety management and patient safety competency directly affected patient safety management activities. In addition, self-efficacy, the perception of the importance of patient safety management, patient safety competency, and patient safety culture, indirectly affected patient safety management activities.
Conclusion
Self-efficacy, the perception of the importance of patient safety management, patient safety competency, and the organization’s patient safety culture should be enhanced to improve nurses’ patient safety management activities.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Development and validation of patient safety educational booklet to empower anesthesia process owners to improve safety compliance before, during and after anesthesia
Fatemeh Asadi, Azam Saei, Shanam Sedigh Maroufi, Jamileh Abolghasemi
Journal of Education and Health Promotion.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Development of a patient safety management protocol for nurses in long-term care hospitals
Soon-Ock Kim
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of Clinical Nurses' Patient Safety Competency, Psychological Safety, and Nursing Unit Manager's Safety-Specific Transformational Leadership on Intention to Report Near Misses
Young hyun Cho, Seung Eun Lee, Mi Jeong Kwak, Hyun Joo Lee
Quality Improvement in Health Care.2025; 31(2): 60. CrossRef - The influencing factors of pediatric nurses’ perception of patient safety culture and partnership with patients’ parents on patient safety nursing activities in South Korea: a descriptive study
Seo Jin Lee, Young Ran Han
Child Health Nursing Research.2024; 30(4): 255. CrossRef - Effects of Nurse-Nurse Collaboration and Nurse-Physician Collaboration on Nursing Performance in Nurses: The Mediating Effect of Patient Safety Management Activities
JaHyun Kim, Seok Hee Jeong, Hee Sun Kim, Sunmi Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(4): 343. CrossRef - Mediating Effects of Job Satisfaction between Nurses’ Perceptions of Patient Safety Culture and Their Safety Nursing Activities
I Jung Han, Young Ran Han
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2023; 30(1): 46. CrossRef - The Effects of Professional Autonomy, Job Satisfaction, and Perceived Patient-Safety Culture on Nurses' Patient-Safety Management Activities: A Cross-Sectional Study
Bokja Koak, Junglim Seo, Eunji Song, Haneul Shin, Jaehee Jeon
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2023; 35(2): 117. CrossRef
-
3,900
View
-
196
Download
-
3
Web of Science
-
7
Crossref
-
Images of Nurses Appeared in Media Reports Before and After Outbreak of COVID-19: Text Network Analysis and Topic Modeling
-
Min Young Park, Seok Hee Jeong, Hee Sun Kim, Eun Jee Lee
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(3):291-307. Published online June 30, 2022
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22002
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Purpose
The aims of study were to identify the main keywords, the network structure, and the main topics of press articles related to nurses that have appeared in media reports.
Methods
Data were media articles related to the topic “nurse” reported in 16 central media within a one-year period spanning July 1, 2019 to June 30, 2020. Data were collected from the Big Kinds database. A total of 7,800 articles were searched, and 1,038 were used for the final analysis. Text network analysis and topic modeling were performed using NetMiner 4.4.
Results
The number of media reports related to nurses increased by 3.86 times after the novel coronavirus (COVID-19) outbreak compared to prior. Pre- and post-COVID-19 network characteristics were density 0.002, 0.001; average degree 4.63, 4.92; and average distance 4.25, 4.01, respectively. Four topics were derived before and after the COVID-19 outbreak, respectively. Pre-COVID-19 example topics are “a nurse who committed suicide because she could not withstand the Taewoom at work” andf “a nurse as a perpetrator of a newborn abuse case,” while post-COVID-19 examples are “a nurse as a victim of COVID-19,” “a nurse working with the support of the people,” and “a nurse as a top contributor and a warrior to protect from COVID-19.” Conclusion: Topic modeling shows that topics become more positive after the COVID-19 outbreak. Individual nurses and nursing organizations should continuously monitor and conduct further research on nurses’ image.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Honoring donors: medical students’ reflections on cadaveric dissection
Young Gyu Kwon, Myeong Namgung, Song Hee Park, Mi Kyung Kim, Chan Woong Kim, Hyo Hyun Yoo
BMC Medical Education.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of the relative importance of key factors in nursing workforce management for pandemic response in general hospitals and long-term care hospitals
Jeong Eun Cha, Eun Kyoung Yun
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2025; 55(2): 236. CrossRef - Shifting social perceptions of dietitians in Korea after the legislation of nutrition teachers: a keyword network analysis of unstructured data
Yunkyoung Oh, Eunsil Her
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(3): 214. CrossRef - Media Portrayals of Nurse Retention: A Decade of News With Topic Modeling and Network Analysis
Taewha Lee, JooHyun Lee
International Nursing Review.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A Text Network Analysis of Research on the Bereaved After Sudden Death Since 2000
Kyung-Ah Kang, Suk-Jung Han, Jiyoung Chun
Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2025; 28(4): 160. CrossRef - Voice of Customer Analysis of Nursing Care in a Tertiary Hospital: Text Network Analysis and Topic Modeling
Hyunjung Ko, Nara Han, Seulki Jeong, Jeong A Jeong, Hye Ryoung Yun, Eun Sil Kim, Young Jun Jang, Eun Ju Choi, Chun Hoe Lim, Min Hee Jung, Jung Hee Kim, Dong Hyu Cho, Seok Hee Jeong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(5): 529. CrossRef - Impact of a game-based interprofessional education program on medical students’ perceptions: a text network analysis using essays
Young Gyu Kwon, Myeong Namgung, Song Hee Park, Mi Kyung Kim, Sun Jung Myung, Eun Kyung Eo, Chan Woong Kim
BMC Medical Education.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of issues related to nursing law: Examination of news articles using topic modeling
JooHyun Lee, Hyoung Eun Chang, Jaehyuk Cho, Seohyun Yoo, Joonseo Hyeon, Andrea Cioffi
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(8): e0308065. CrossRef - Medical students’ perceptions of improving physician satisfaction and patient care: a text network analysis approach
Young Gyu Kwon, Myeong Namgung, Song Hee Park, Mi Kyung Kim, Hyo Hyun Yoo, Chan Woong Kim
BMC Medical Education.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Socialisation of children to nurse and nursing images: A Goffman‐inspired thematic analysis of children's picture books in a Swedish context
Stinne Glasdam, Hongxuan Xu, Sigrid Stjernswärd
Nursing Inquiry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Agendas on Nursing in South Korea Media: Natural Language Processing and Network Analysis of News From 2005 to 2022
Daemin Park, Dasom Kim, Ah-hyun Park
Journal of Medical Internet Research.2024; 26: e50518. CrossRef - Research trends over 10 years (2010-2021) in infant and toddler rearing behavior by family caregivers in South Korea: text network and topic modeling
In-Hye Song, Kyung-Ah Kang
Child Health Nursing Research.2023; 29(3): 182. CrossRef - The Analysis of Research Trends and Public Awareness of Smart Farms using Text Mining
Sung-Ho Kil, Hye-Mi Park, Eunseok Lee, Jin-Young Kim, Ji-Woo Kim
Journal of People, Plants, and Environment.2023; 26(1): 9. CrossRef - National Petition Analysis Related to Nursing: Text Network Analysis and Topic Modeling
HyunJung Ko, Seok Hee Jeong, Eun Jee Lee, Hee Sun Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2023; 53(6): 635. CrossRef - An analysis of Research Published in the Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing from 2013 to 2022 using Text Network Analysis and Topic Modeling
Eun Jo Kim, Kuem-Sun Han
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2023; 32(2): 188. CrossRef - Chronological Changes in the Portrayal of Korean Nurses in TV Documentaries
Eunjin Kim, Gumhee Baek, Aram Cho, Mijin Byun
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2023; 29(4): 341. CrossRef - A topic modeling analysis for Korean online newspapers: Focusing on the social perceptions of nurses during the COVID-19 epidemic period
Soo Jung Chang, Sunah Park, Yedong Son
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2022; 28(4): 444. CrossRef
-
3,474
View
-
51
Download
-
10
Web of Science
-
17
Crossref
-
Effects of Second Victim Experiences after Patient Safety Incidents on Nursing Practice Changes in Korean Clinical Nurses: The Mediating Effects of Coping Behaviors
-
Seohee Jeong, Seok Hee Jeong
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(4):489-504. Published online August 31, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21089
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Purpose
This study was investigated the mediating effect of coping behaviors in the relationship between the second victim experiences after patient safety incidents and the nursing practice changes.
Methods
A cross-sectional survey was performed using structured questionnaires. Participants were 218 clinical nurses in general tertiary hospitals in South Korea. Data were collected through an online survey and snowball sampling from August 11 to September 6 2020. Data were analyzed using SPSS 23.0 program. A mediation analysis was performed using multiple regression and a simple mediation model applying the PROCESS macro with 95% bias-corrected bootstrap confidence interval.
Results
The mean scores of second victim experiences was 3.41/5. Approach coping (β = .55, p < .001) and the avoidant coping (β = - .23, p = .001) showed mediation effects in the relationship between second victim experiences and constructive change in nursing practice. Avoidant coping (β = .29, p < .001) showed a mediation effect in the relationship between second victim experiences and defensive change in nursing practice.
Conclusion
Coping behaviors has a mediating effect on the relationship between second victim experiences and nursing practice changes. To ensure that nurses do not experience second victim, medical institutions should have a culture of patient safety that employs a systematic approach rather than blame individuals. They also need to develop strategies that enhance approach coping and reducing avoidant coping to induce nurses’ constructive practice changes in clinical nurses in experiencing second victims due to patient safety incidents.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Influences of Clinical Nurses’ Second Victim Experience after Patient Safety Incidents, Individual and Organizational Support, and Job Satisfaction on Turnover Intention
Hyeran Kang, Jeong-Hee Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2026; 32(1): 58. CrossRef - Factors influencing negative outcomes for nurses who experience patient safety incidents: An integrative review
Hanseulgi Lee, Nam‐Ju Lee, Nari Kim
International Nursing Review.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - How does just culture reduce negative work outcomes through second victim distress and demand for support in clinical nurses? A path analysis
Seohee Jeong, Sunmi Kim, Hyoung Eun Chang, Seok Hee Jeong
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Changes in Nursing Practice Among Clinical Nurses After Experiencing a Patient Safety Incident: Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling
Sunmi Kim, Seohee Jeong, Seok Hee Jeong, Majd Mrayyan
Journal of Nursing Management.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Predictors of Nurses' Reporting Level by the Types of Patient Safety Incidents
Ju-Hee Kang, Yeojin Yi
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(4): 434. CrossRef - The Relationship of Medication Safety Competence, Second Victim Experiences, Second Victim Support, and Negative Work Outcomes among Clinical Nurses
Ahlim Chang, Youngjin Lee, Minkyung Kang, Ji Yea Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(5): 493. CrossRef - “Learn from Errors”: Post-traumatic growth among second victims
Huanhuan Huang, Tong Liu, Ying Peng, Xingyao Du, Qi Huang, Qinghua Zhao, Mingzhao Xiao, Yetao Luo, Shuangjiang Zheng
BMC Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Nurse Leader Perspectives and Experiences on Caregiver Support Following a Serious Medical Error
Marie M. Prothero, Madeline Sorhus, Katherine Huefner
JONA: The Journal of Nursing Administration.2024; 54(12): 664. CrossRef - Prevalence of the second victim phenomenon among intensive care unit nurses and the support provided by their organizations
Maria Kappes, Pilar Delgado‐Hito, Verónica Riquelme Contreras, Marta Romero‐García
Nursing in Critical Care.2023; 28(6): 1022. CrossRef - The mediating role of coping styles in the relationship between second victim experience and professional quality of life among nurses: a cross-sectional study
Xizhao Li, Chong Chin Che, Yamin Li, Ling Wang, Mei Chan Chong
BMC Nursing.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Associations among workplace incivility, stress coping, and nursing performance in hospital nurses: A path analysis
Eun Ha Kim, Yeojin Yi
Journal of Nursing Scholarship.2023; 55(4): 834. CrossRef - Influence of Clinical Nurses’ Second-Victim Experience and Second-Victim Support in Relation to Patient Safety Incidents on Their Work-Related Outcomes
Su Jin Jung, Youngjin Lee, Sun Hyoung Bae
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2022; 28(4): 331. CrossRef - Profiles of second victim symptoms and desired support strategies among Korean nurses: A latent profile analysis
Eun Young Choi, Jeehee Pyo, Minsu Ock, Haeyoung Lee
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2022; 78(9): 2872. CrossRef
-
3,494
View
-
81
Download
-
10
Web of Science
-
13
Crossref
-
A Meta-Analytic Path Analysis on the Outcome Variables of Nursing Unit Managers’ Transformational Leadership: Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis
-
Sunmi Kim, Seok Hee Jeong
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(6):757-777. Published online December 31, 2020
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20205
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Purpose
The purpose of this study was to identify the outcome variables of nursing unit managers’ transformational leadership and to test a hypothetical model using meta-analytic path analysis.
Methods
A systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted in accordance with PRISMA guidelines. Data analysis, conducted using R version 3.6.2 software, included 49 studies for the meta-analysis and 119 studies for meta-analytic path analysis.
Results
In the meta-analysis, four out of 32 outcome variables were selected. These four variables were empowerment, nursing performance, job satisfaction, and organizational commitment, which showed larger effect sizes than the median and more than five k. The hypothetical model for the meta-analytic path analysis was established by using these four variables and transformational leadership. A total of 22 hypothetical paths including nine direct effects and 13 indirect effects were set and tested. The meta-analytic path analysis showed that transformational leadership had direct effects on the four variables. Finally, eight direct effects, 12 indirect effects, and six mediating effects were statistically significant, and the hypothetical model was verified.
Conclusion
Nursing unit managers can use the transformational leadership to improve empowerment, nursing performance, job satisfaction, and organizational commitment of nurses. This study empirically showed the importance of transformational leadership of nursing managers. This finding will be used as evidence to develop strategies for enhancing transformational leadership, empowerment, nursing performance, job satisfaction, and organizational commitment in nursing science and practice.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Strategies Employed by Nursing Managers Within a Transformational Approach: A Qualitative Study
Gholamhossein Mahmoudirad, Ayob Akbari, Suja P. Davis
Nursing Research and Practice.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Using Behaviour Diagnostics to Identify Enablers and Barriers to Optimise Nurse and Midwife Manager Leadership Time
Julie Considine, Philippa Blencowe, Naida Lumsden, Jordana Schlieff, Judy Currey, Abdulqadir J. Nashwan
Journal of Nursing Management.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Leadership Development in Undergraduate Nursing Students: A Scoping Review
Patrícia Costa, Joana Pereira Sousa, Tiago Nascimento, Paulo Cruchinho, Elisabete Nunes, Filomena Gaspar, Pedro Lucas
Nursing Reports.2025; 15(5): 160. CrossRef - Effect of Nursing Managers’ Ethical Leadership on Clinical Nurse Empowerment, Performance, and Organizational Commitment
Jihun Kim, Seok Hee Jeong, Hee Sun Kim, Myung Ha Lee
Journal of Nursing Research.2025; 33(4): e400. CrossRef - Transformational Leadership, Psychological Empowerment, and Organizational Citizenship Behaviors among Nursing Workforce: A Single Mediation Analysis
Ibrahim Abdullatif Ibrahim, Ahmed Hashem El-Monshed, Marwan Altheeb, Mohamed Gamal El-Sehrawy, Abdulqadir J. Nashwan
Journal of Nursing Management.2024; 2024: 1. CrossRef - Personal and organisational attributes that support transformational leadership in acute healthcare: scoping review
Julie Considine, Jenny Dempster, Nga Man Wendy Wong, Noelleen Kiprillis, Leanne Boyd
Australian Health Review.2024; 48(3): 274 . CrossRef - Leadership styles and transformational leadership skills among nurse leaders in Qatar, a cross‐sectional study
Amer Al‐Thawabiya, Kalpana Singh, Badriya Abdulla Al‐Lenjawi, Albara Alomari
Nursing Open.2023; 10(6): 3440. CrossRef - Effects of Leadership Styles of Nursing Managers on Turnover Intention of Hospital Nurses: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Yunjeong Cho, Seok Hee Jeong, Hee Sun Kim, Young Man Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2022; 52(5): 479. CrossRef - Patient Safety Management Activities of Korean Nurses: A Meta-Analytic Path Analysis
Seohee Jeong, Seok Hee Jeong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2022; 52(4): 363. CrossRef - Nurses' ethical leadership and related outcome variables: Systematic review and meta‐analysis
Sunmi Kim, Seok Hee Jeong, Myoung Hee Seo
Journal of Nursing Management.2022; 30(7): 2308. CrossRef
-
2,809
View
-
127
Download
-
10
Web of Science
-
10
Crossref
-
Types of Perception toward Ethical Issues in Perioperative Nurses: Q-Methodological Approach
-
Jin Nam Kim, Seok Hee Jeong
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(6):679-691. Published online January 15, 2018
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.6.679
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Abstract
Purpose
This study was aimed at identifying the types of perceptions of ethical issues among perioperative nurses.
Methods
Q-methodology focusing on individual subjectivity was used with data collected in November 2016. Thirty-four Q-statements were selected and scored by the 35 participants on a 9-point scale with normal distribution. Participants were perioperative nurses working in advanced general hospitals and general hospitals. The data were analyzed using the PC-QUANL program.
Results
A total of 35 perioperative nurses were classified into 4 factors based on the following viewpoints: self-centered (type 1), onlooking and avoiding (type 2), patient-centered (type 3), and problem-centered (type 4). The 4 factors accounted for 57.84% of the total variance. Individual contributions of factors 1, 2, 3, and 4 were 41.80%, 7.18%, 5.20%, and 3.66%, respectively.
Conclusion
The major contribution of this study is the clarification of perioperative nurses’ subjective perceptions of ethical issues. These findings can be used in formulating effective strategies for nursing educators, professional nurses, and nursing administrators to improve ethical decision-making abilities and to perform ethical nursing care by the appropriate management of ethical issues in everyday nursing practice.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Ethical issues in the operating room: A scoping review
Heejung Jeon, Sanghee Kim, Yuha Shon
Nursing Ethics.2024; 31(4): 472. CrossRef - The Psychological Responses of Nurses Caring for COVID-19 Patients: A Q Methodological Approach
Kyung Hyeon Cho, Boyoung Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(7): 3605. CrossRef - Development of Ethical Nursing Competence Self-rating Scale for Clinical Nurses
Borah Kang, Heeyoung Oh
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2020; 32(5): 482. CrossRef
-
1,517
View
-
17
Download
-
2
Web of Science
-
3
Crossref
-
Life Experiences of Uninfected Women Living with HIV-Infected Husbands: A Phenomenological Study
-
Myoung Hee Seo, Seok Hee Jeong
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2017;47(6):781-793. Published online December 29, 2017
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.6.781
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
-
Purpose
This study aimed to understand the meaning and essence of the life experiences of uninfected women living with HIV-infected husbands.
Methods
This qualitative study adopted van Manen's hermeneutic phenomenological method. Study participants were 8 females whose husband had been diagnosed with HIV for longer than 6 months, who had known about their husband's infection for more than 6 months, who were in a legal or common-law marriage and were living with their husbands at the time of interview for this study, and whose HIV antibody test results were negative. Data were collected from in-depth individual interviews with the participants from May to August 2016, and from related idiomatic expressions, literature, artwork, and phenomenological references.
Results
The following essential themes were identified regarding the life experiences of uninfected women living with HIV-infected husbands: ‘experiencing an abrupt change that came out of the blue and caused confusion’, ‘accepting one's fate and making desperate efforts to maintain one's family’, ‘dealing with a heavy burden alone’, ‘experiencing the harsh reality and fearful future’, and ‘finding consolation in the ordeal’.
Conclusion
This study provided a holistic and in-depth understanding of the meaning and essence of the life experiences of uninfected women living with HIV-infected husbands. Thus, this study recognizes these unnoticed women as new nursing subjects. Further, the present findings can be used as important basic data for the development of nursing interventions and national policy guidelines for uninfected women living with HIV-infected husbands.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Using decision tree analysis to understand the influence of social networks on disclosure of HIV infection status
Gwang Suk Kim, Mi-So Shim, Jeongmin Yi
AIDS Care.2022; 34(1): 118. CrossRef - Factors Influencing the Initiation of Treatment after the Diagnosis of Korean Patients with HIV
Mi-So Shim, Gwang Suk Kim, Chang Gi Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2018; 29(3): 279. CrossRef
-
1,297
View
-
13
Download
-
2
Crossref
-
Effects of Nursing Interventions for Fall Prevention in Hospitalized Patients: A Meta-analysis
-
Yoon Lee Kim, Seok Hee Jeong
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2015;45(4):469-482. Published online August 31, 2015
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2015.45.4.469
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
-
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to identify which nursing interventions are the most effective in fall prevention for hospitalized patients.
Methods
From 3,675 papers searched, 34 were selected for inclusion in the meta-analysis. Number of fallers, falls, falls per 1,000 hospital-days, and injurious falls, fall protection activity, knowledge related to falls, and self-efficacy about falls were evaluated as outcome variables. Data were analyzed using the Comprehensive Meta Analysis (CMA) 2.2 Version program and the effect sizes were shown as the Odd Ratio (OR) and Hedges's g.
Results
Overall effect size of nursing interventions for fall prevention was OR=0.64 (95% CI: 0.57~0.73, p <.05) and Hedges's g= - 0.24. The effect sizes (OR) of each intervention ranged from 0.34 to 0.93, and the most effective nursing intervention was the education & environment intervention (OR=0.34, 95% CI: 0.28~0.42, p <.001), followed by education intervention (OR=0.57, 95% CI: 0.50~0.67, p =.001). Subgroup analyses showed that multifaceted interventions (OR=0.76, 95% CI: 0.73~0.79, p <.001) were more effective than unifactorial interventions, and that activities for prevention of falls (OR=0.08, 95% CI: 0.05~0.15, p <.001) showed the largest effect size among outcome variables.
Conclusion
Falls in hospitalized patients can be effectively prevented using the nursing interventions identified in this study. These findings provide scientific evidence for developing and using effective nursing interventions to improve the safety of hospitalized patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Characteristics and Effects of Fall Prevention Interventions among the Korean Older Adults: A Systematic Review
Jeong Ha Park, Hee Ju Kim
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2022; 24(1): 65. CrossRef - Internet-Delivered Cognitive Behavioral Therapy in Patients With Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Hyunjung Kim, Younjae Oh, Sun Ju Chang
Journal of Medical Internet Research.2022; 24(6): e35260. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of Turkish Version of the Self- Awareness of Falls in Elderly Scale Among Elderly Inpatients
Fatma Birgili, Seda Kılınç, Nezihe Bulut Uğurlu
Cyprus Journal of Medical Sciences.2022; 7(7): 69. CrossRef - Validity of the Morse Fall Scale and the Johns Hopkins Fall Risk Assessment Tool for fall risk assessment in an acute care setting
Young Ju Kim, Kyoung‐Ok Choi, Suk Hyun Cho, Seok Jung Kim
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2022; 31(23-24): 3584. CrossRef - An Educational Intervention to Improve Staff Collaboration and Enhance Knowledge of Fall Risk Factors and Prevention Guidelines
Kimberly A. DiGerolamo, Mei Lin Chen-Lim
Journal of Pediatric Nursing.2021; 57: 43. CrossRef - Trends of Nursing Research on Accidental Falls: A Topic Modeling Analysis
Yeji Seo, Kyunghee Kim, Ji-Su Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(8): 3963. CrossRef - Analysis of Fall Incident Rate among Hospitalized Korean Children Using Big Data
Eun Joo Kim, Anna Lee
Journal of Pediatric Nursing.2021; 61: 136. CrossRef - Development and Effect of a Fall Prevention Program Based on the King's Goal Attainment Theory for Fall High-Risk Elderly Patients in Long-Term Care Hospital
Bom Mi Park, Ho Sihn Ryu, Kyeung Eun Kwon, Chun Young Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2019; 49(2): 203. CrossRef - Use of the Nursing Outcomes Classification for Falls and Fall Prevention by Nurses in South Korea
Eunjoo Lee
International Journal of Nursing Knowledge.2019; 30(1): 28. CrossRef - Development and Validation of the Self-Awareness of Falls in Elderly Scale Among Elderly Inpatients
Meei-Ling Shyu, Hui-Chuan Huang, Mei-Jung Wu, Hsiu-Ju Chang
Clinical Nursing Research.2018; 27(1): 105. CrossRef - The effectiveness of intervention programs for preventing patients from falls
Jana Horová, Iva Brabcová, Jitka Krocová
Kontakt.2017; 19(2): e105. CrossRef - Effect of Strength Exercise on Patient Fall Prevention Program: Focusing on the Fall High Risk Group Elderly Patients
Hyun-Ok Lee, Byung-Hwa Lee, Chang-Hee Lee
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2017; 42(4): 338. CrossRef - The Effect of Pediatric Inpatient Fall Prevention Education on Caregivers' Fall-related Knowledge and Preventive Behaviors
So Yeon Park, Hyeon Ok Ju
Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2017; 23(4): 398. CrossRef
-
4,026
View
-
108
Download
-
13
Crossref
-
Effects of Blending Oil of Lavender and Thyme on Oxidative Stress, Immunity, and Skin Condition in Atopic Dermatitis Induced Mice
-
Young Mi Seo, Seok Hee Jeong
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2015;45(3):367-377. Published online June 30, 2015
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2015.45.3.367
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
-
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effects of essential oil on oxidative stress, immunity, and skin condition in atopic dermatitis (AD) induced mice.
Methods
This study was a 3×3 factorial design. Factors were oil type (Lavender, Thyme, and 2:1 mixture of lavender and thyme oil [blending oil]) and treatment period (0 day, 7 days, and 21 days). The samples were 45 mice with AD and randomly assigned to nine groups of five mice per group. The dependent variables such as superoxide radical, IgE, degranulated mast cells, and epidermal thickness were measured. Data were collected from February to April in 2014. Descriptive statistics, One-way ANOVA, Two-way ANOVA, and Tukey's HSD test were performed using the SPSS WIN 20.0 program.
Results
Dependent variables were not statistically significantly different by the three oil types (p>.05). Essential oils such as lavender, thyme, and blending oil were all effective in reducing AD symptoms and especially 2:1 blending oil were most effective. There were statistically significant differences by the three treatment periods in all dependent variables (p<.001). There were statistically significant interactions between oil types and treatment periods in all dependent variables (p<.01). For decreasing superoxide radical, degranulated mast cells, and epidermal thickness, 2:1 mixed oil should be applied for at least 21 days. Otherwise to reduce IgE, 2:1 mixed oil should be used for at least 7 days.
Conclusion
These findings provide bases for developing effective interventions for AD patients to manage their AD symptoms.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Essential oils in cosmetics: Antioxidant properties and advancements through nanoformulations
Bongunuri Harsha Vardhan Reddy, Sha Mohammad Sameer Hussain, Mohammad Shahil Hussain, Rajpurohit Narendra Kumar, Jeena Gupta
Pharmacological Research - Natural Products.2025; 6: 100192. CrossRef - Lavender: phytochemistry, pharmacology, cross-disciplinary applications, and clinical efficacy
Boye Jiang, Yun Hou, Sheng Jiang, Fenglan Zhao, Xiaoyan Wei, Qingguo Meng, Feng Li
Phytomedicine.2025; 148: 157274. CrossRef - Harnessing the health perks of underrated spices in bakery products- A review
Hassan Mehmood Sipra, Asad Ali, Qamar Abbas Syed, Muhammad Irfan, Syed Ali Hassan
Food Chemistry Advances.2024; 5: 100790. CrossRef - A comparative study on a biodegradable hyaluronic acid microneedle patch with a needleless patch for dry skin in atopic dermatitis: a single-blinded, split-body, randomized controlled trial
Ji-Hoon Song, Eun Jin An, Chang Yub Sung, Do Hyeon Jeong, Gihyun Lee, Soo-Yeon Park
Archives of Dermatological Research.2022; 315(3): 569. CrossRef - Targeting deregulated oxidative stress in skin inflammatory diseases: An update on clinical importance
Abdul Q. Khan, Maha Victor Agha, Khalid Sultan A.M. Sheikhan, Shahd M. Younis, Maha Al Tamimi, Majid Alam, Aamir Ahmad, Shahab Uddin, Joerg Buddenkotte, Martin Steinhoff
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2022; 154: 113601. CrossRef - A randomized controlled trial of combination of peppermint, lavender, and turmeric oil for antipruritic agent in pregnant women
Fransisca Retno Asih, Farid Husin, Oki Suwarsa, Irda Fidrianny, Dany Hilmanto
Medical Journal of Indonesia.2021; 30(1): 39. CrossRef - Effects of Evening Primrose Oil and Evening Primrose–rosemary Mixed Oil on Atopic Dermatitis-induced Animal Model
Seon Ju Kim, Shin Hee Park
Asian Journal of Beauty and Cosmetology.2017; 15(4): 399. CrossRef - Topical Application of Cudrania tricuspidata Stem Extract Inhibits Atopic Dermatitis-Like Skin Lesions in an NC/Nga Mouse Model: An Experimental Animal Study
Yoo-Sin Park, Shin-Hee Kim, Sang-Yeon Kim, Gae-Myoung Koh, Ju-Hwan Suh, Ju-Seop Kang
Pharmacology & Pharmacy.2016; 07(08): 358. CrossRef
-
1,937
View
-
30
Download
-
8
Crossref
-
Identification of Subgroups with Lower Level of Stroke Knowledge Using Decision-tree Analysis
-
Hyun Kyung Kim, Seok Hee Jeong, Hyun Cheol Kang
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2014;44(1):97-107. Published online February 28, 2014
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2014.44.1.97
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
-
Purpose
This study was performed to explore levels of stroke knowledge and identify subgroups with lower levels of stroke knowledge among adults in Korea.
Methods
A cross-sectional survey was used and data were collected in 2012. A national sample of 990 Koreans aged 20 to 74 years participated in this study. Knowledge of risk factors, warning signs, and first action for stroke were surveyed using face-to-face interviews. Descriptive statistics and decision tree analysis were performed using SPSS WIN 20.0 and Answer Tree 3.1.
Results
Mean score for stroke risk factor knowledge was 7.7 out of 10. The least recognized risk factor was diabetes and four subgroups with lower levels of knowledge were identified. Score for knowledge of stroke warning signs was 3.6 out of 6. The least recognized warning sign was sudden severe headache and six subgroups with lower levels of knowledge were identified. The first action for stroke was recognized by 65.7 percent of participants and four subgroups with lower levels of knowledge were identified.
Conclusion
Multi-faceted education should be designed to improve stroke knowledge among Korean adults, particularly focusing on subgroups with lower levels of knowledge and less recognition of items in this study.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Knowledge, practice, and awareness of stroke warning signs and potential risk factors among future rehabilitation specialists in Saudi Arabia
Alaa M. Albishi, Futun Almutairi, Waleed M. Alshehri, Muneera M. Almurdi, Sami S. Alabdulwahab
Frontiers in Medicine.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Global Awareness and Response to Early Symptoms of Acute Stroke: A Systematic Literature Review
Theodoros Vatsalis, Dimitrios Papadopoulos, Vasiliki Georgousopoulou, Prodromos Bostantzis, Jobst Rudolf
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Stroke knowledge and health-promoting behaviors: Mediating effect of patient self-esteem
GyeongChae MUN, JaeLan SHIM
Patient Education and Counseling.2024; 129: 108398. CrossRef - Comparison of Stroke Knowledge, Health Beliefs, and Stroke Prevention Behavior between Early and Middle-Aged Adults
Eun Ko
STRESS.2022; 30(2): 98. CrossRef - Variation in Knowledge of Stroke Warning Signs by Age and Presence of Conventional Risk Factors
Juyeon Oh, Hyun Young Kim, Young Seo Kim, Sun Hwa Kim
Journal of Cardiovascular Nursing.2022; 37(2): 177. CrossRef - Analysis of Subgroups with Lower Level of Patient Safety Perceptions Using Decision-Tree Analysis
Sun Hwa Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2020; 50(5): 686. CrossRef - Stroke Management Awareness and Behavior among Nursing Students in Bangladesh
Shariful Islam, Eui Geum Oh, Tae Wha Lee, Sanghee Kim
Open Journal of Nursing.2017; 07(01): 1. CrossRef - Awareness of Stroke Warning Symptoms and Related Factors among Residents in a Province
Yu-Mi Lee, Keon-Yeop Kim, Ki-Su Kim
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2014; 15(8): 5116. CrossRef
-
1,166
View
-
18
Download
-
8
Crossref
-
Trends of Doctoral Dissertations in Nursing Science: Focused on Studies Submitted Since 2000
-
Hyunsook Shin, Kyung-Mi Sung, Seok Hee Jeong, Dae-Ran Kim
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2008;38(1):74-82. Published online February 29, 2008
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2008.38.1.74
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
-
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to identify the characteristics of doctoral dissertations in nursing science submitted since 2000.
Methods
Three-hundred and five dissertations of six schools of nursing published from 2000 to 2006 in Korea were analyzed with the categories of philosophy, method, body of knowledge, research design, and nursing domain.
Results
In philosophy, 82% of all dissertations were identified as scientific realism, 15% were relativism, and 3% were practicism. Two-hundred and fifty dissertations (82%) were divided into a quantitative methodology and 55 dissertations (18%) were qualitative methodology. Specifically, 45% were experimental, 23% methodological, 13% survey and 17% qualitative designed researches. Prescriptive knowledge was created in 47% of dissertations, explanatory knowledge in 29%, and descriptive knowledge in 24%. Over 50% of all research was studied with a community-based population. In the nursing domain, dissertations of the practice domain were highest (48.2%).
Conclusion
Dissertations since 2000 were markedly different from the characteristics of the previous studies (1982-1999) in the increase of situation-related, prescriptive and community-based population studies. A picture of current nursing science identified in this study may provide a future guideline for the doctoral education for nursing.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Development support as education aid or labor trade? South Korean nurses in West Germany (1965–1976)
Jinyoung Yu, Jungwook Seo
Asia Europe Journal.2024; 22(2): 225. CrossRef - Nitel Araştırma ve Ruh Sağlığı ve Psikiyatri Hemşireliğinin Felsefi Boyutu ve Karakteristik Özellikleri
Mahire Olcay ÇAM, Ece MUTLU SATIL
Ordu Üniversitesi Hemşirelik Çalışmaları Dergisi.2021; 4(3): 436. CrossRef - Development and Analysis of System Dynamics Model for Predicting on the Effect of Patient Transfer Counseling with Nurses
Hye Min Byun, Eun Kyoung Yun
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2018; 48(5): 554. CrossRef - A Historical Trends of Doctoral Nursing Education in Korea
Kasil Oh, Young Sook Park, Ja Hyung Lee, Kyong-Ok Oh, Yang Heui Ahn, Jiyoung Lim
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2014; 20(1): 93. CrossRef - Analysis of Trends and Contents of Nursing Doctoral Dissertations in Korea
Kwang-Ja Lee, Younhee Kang, Mee Ock Gu, Kyunghee Kim, Oksoo Kim, Yeon-Ok Suh, Eunyoung Suh, Soo Yang, Eun-Hyun Lee, Ja Hyung Lee, Myoung-Ae Choe, Yang Sook Hah
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2012; 42(2): 302. CrossRef - Trends in Research on Caregivers Hospitalized Children in Korea-Focus on Knowledge Type
In-soo Kwon, Yeong-mi Seo, Ji-youn Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Child Health Nursing.2012; 18(3): 101. CrossRef - Reviewing the trends of nursing doctoral thesis research in Hong Kong
Yingchun Zeng, Samantha Pang
Open Journal of Nursing.2012; 02(04): 346. CrossRef - Research Trends on Parent-Child Relationships from the Perspective of Nursing
Mi Ran Kim, Young Hee Park, Eun Sook Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Child Health Nursing.2010; 16(4): 249. CrossRef
-
974
View
-
5
Download
-
8
Crossref
-
Trends of Nursing Science Inquiry in Doctoral Dissertations
-
Eui Sook Kim, Gwang Suk Kim, Dae Ran Kim, Eun Jeong Kim, Kyung Mi Sung, Hae Kung Shin, Hyun Sook Shin, Young Ja Lee, Seok Hee Jeong
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2004;34(2):315-323. Published online March 28, 2017
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2004.34.2.315
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
-
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to identify the theoretical characteristics and direction of inquiry in the discipline of nursing by analyzing doctoral dissertations.
Method
The materials used in this study were 277 doctoral dissertations from five universities in Korea. The framework for the study was derived from Kim's(1993) alternative linkage among philosophy, theory, and method in nursing science.
Result
Of the 277 dissertations it was found that there were 13 types of linkages out of a possible 54 types. Most of the dissertations (128 of 277) were done within the linkage of realism/etic/quantitative/explanatory knowledge type. Of the 218 dissertations within scientific realism, 42 were within relativism, and 17 within practicism. There were 134 dissertations of the explanatory knowledge type, 112 descriptive ones, and 31 prescriptive ones. Studies done within the etic quantitative methodology included 209 dissertations and within the emic perspective, 43 with qualitative methodology, and 7 with quantitative.
Conclusion
The results show that it is necessary to develop more alternative linkages for nursing practice and this will lead to expanding nursing knowledge.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Comparison of Domestic and International Research (1992-2011): Intensive Care Nursing Studies
Eun Hee Choi, Eun Hee Jang, Ji Youn Choi, So Jung Lee, Hyo Kuyng Seo, Kyung Sook Park
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2015; 27(4): 384. CrossRef - An Analysis of Nursing Research on Child Rearing in Korea.
Dong Won Lee, In Soo Kwon
Child Health Nursing Research.2014; 20(4): 264. CrossRef - A Historical Trends of Doctoral Nursing Education in Korea
Kasil Oh, Young Sook Park, Ja Hyung Lee, Kyong-Ok Oh, Yang Heui Ahn, Jiyoung Lim
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2014; 20(1): 93. CrossRef - Analysis of Research Trends about Spiritual Care in Korea
Seung-Yeon Yoo
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2013; 25(3): 332. CrossRef - Analysis of Trends and Contents of Nursing Doctoral Dissertations in Korea
Kwang-Ja Lee, Younhee Kang, Mee Ock Gu, Kyunghee Kim, Oksoo Kim, Yeon-Ok Suh, Eunyoung Suh, Soo Yang, Eun-Hyun Lee, Ja Hyung Lee, Myoung-Ae Choe, Yang Sook Hah
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2012; 42(2): 302. CrossRef - Trends in Research on Caregivers Hospitalized Children in Korea-Focus on Knowledge Type
In-soo Kwon, Yeong-mi Seo, Ji-youn Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Child Health Nursing.2012; 18(3): 101. CrossRef - Trends of Occupational Health Nursing Research in Korea
Young-Im Kim, Bok-Im Lee
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2011; 20(2): 195. CrossRef - The Analysis on Published Research in the Journal of Muscle and Joint Health
Nan-Young Lim, Jong-Im Kim, Eun-Nam Lee, Kyung-Sook Lee, In-Ok Lee, Kyung-Sook Cho, Won-Sook Bak, Yoon-Kyoung Lee, Hyun-Sook Kang, Keum-Soon Kim, Mi-Young Chon
Journal of muscle and joint health.2010; 17(1): 79. CrossRef - Trends of Doctoral Dissertations in Nursing Science: Focused on Studies Submitted Since 2000
Hyunsook Shin, Kyung-Mi Sung, Seok Hee Jeong, Dae-Ran Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(1): 74. CrossRef
-
865
View
-
2
Download
-
9
Crossref
|