Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Nurs > Volume 45(4); 2015 > Article
-
Review Article
- Effects of Nursing Interventions for Fall Prevention in Hospitalized Patients: A Meta-analysis
- Yoon Lee Kim, Seok Hee Jeong
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2015;45(4):469-482.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2015.45.4.469
Published online: August 31, 2015
1Department of Quality Improvement, Jesus Hospital, Jeonju, Korea.
2College of Nursing · Research Institute of Nursing Science, Chonbuk National University, Jeonju, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Jeong, Seok Hee. College of Nursing, Chonbuk National University, 567 Baekje-daero, Deokjin-gu, Jeonju 54896, Korea. Tel: +82-63-270-3117, Fax: +82-63-270-3127, awesomeprof@jbnu.ac.kr
© 2015 Korean Society of Nursing Science
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NoDerivs License. (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nd/4.0/) If the original work is properly cited and retained without any modification or reproduction, it can be used and re-distributed in any format and medium.
Abstract
-
Purpose
- The purpose of this study was to identify which nursing interventions are the most effective in fall prevention for hospitalized patients.
-
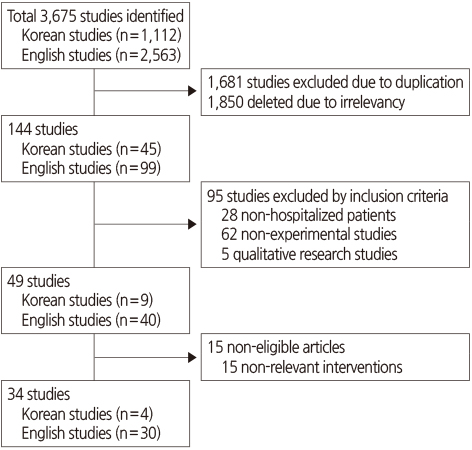
Methods
- From 3,675 papers searched, 34 were selected for inclusion in the meta-analysis. Number of fallers, falls, falls per 1,000 hospital-days, and injurious falls, fall protection activity, knowledge related to falls, and self-efficacy about falls were evaluated as outcome variables. Data were analyzed using the Comprehensive Meta Analysis (CMA) 2.2 Version program and the effect sizes were shown as the Odd Ratio (OR) and Hedges's g.
-
Results
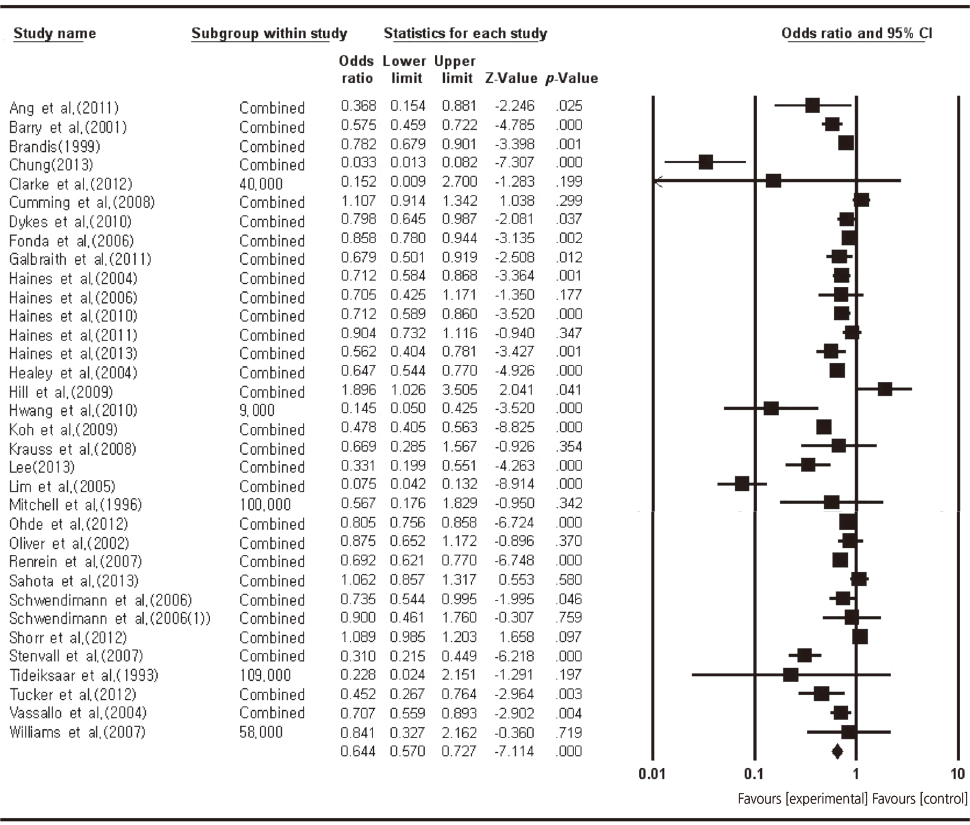
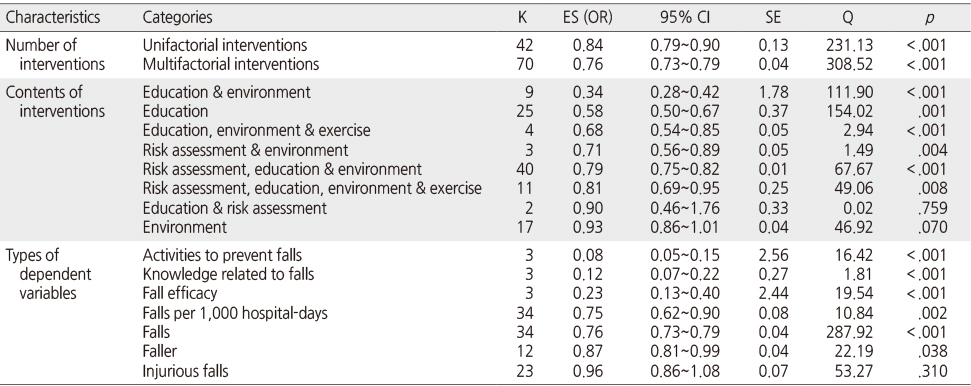
- Overall effect size of nursing interventions for fall prevention was OR=0.64 (95% CI: 0.57~0.73, p <.05) and Hedges's g= - 0.24. The effect sizes (OR) of each intervention ranged from 0.34 to 0.93, and the most effective nursing intervention was the education & environment intervention (OR=0.34, 95% CI: 0.28~0.42, p <.001), followed by education intervention (OR=0.57, 95% CI: 0.50~0.67, p =.001). Subgroup analyses showed that multifaceted interventions (OR=0.76, 95% CI: 0.73~0.79, p <.001) were more effective than unifactorial interventions, and that activities for prevention of falls (OR=0.08, 95% CI: 0.05~0.15, p <.001) showed the largest effect size among outcome variables.
-
Conclusion
- Falls in hospitalized patients can be effectively prevented using the nursing interventions identified in this study. These findings provide scientific evidence for developing and using effective nursing interventions to improve the safety of hospitalized patients.
This manuscript is based on a part of the first author's doctoral dissertation from Chonbuk National University.
- 1. Hayes N. Prevention of falls among older patients in the hospital environment. Br J Nurs. 2004;13(15):896–901. ArticlePubMed
- 2. Kim YS, Choi-Kwon S. Fall risk factors and fall risk assessment of inpatients. Korean J Adult Nurs. 2013;25(1):74–82.ArticlePDF
- 3. Hendrich AL, Bender PS, Nyhuis A. Validation of the Hendrich II fall risk model: A large concurrent case/control study of hospitalized patients. Appl Nurs Res. 2003;16(1):9–21. ArticlePubMed
- 4. Oliver D, Papaioannou A, Giangregorio L, Thabane L, Reizgys K, Foster G. A systematic review and meta-analysis of studies using the STRATIFY tool for prediction of falls in hospital patients: How well does it work? Age Ageing. 2008;37(6):621–627. ArticlePubMed
- 5. Korea Consumer Agency. Press release: The 'fall accident' takes up most among the medical accidents by improper safety management in the hospital [Internet]. Eumseong-gun, Author. 2006;cited 2014 January 30. Available from: http://www.kca.go.kr/brd/m_32/view.do?seq=749&multi_itm_seq=2
- 6. Schwendimann R, Bühler H, De Geest S, Milisen K. Characteristics of hospital inpatient falls across clinical departments. Gerontology. 2008;54(6):342–348. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 7. Joint Commission International. International patient safety goals [Internet]. Oak Brook, IL, Author. 2011;cited 2014 January 7. Available from: http://www.jointcommissioninternational.org/improve/international-patient-safety-goals/
- 8. Korea Institute for Healthcare Accreditation. Standard of healthcare accreditation for tertiary hospital: Ver2.0 [Internet]. Seoul, Author. 2014;cited 2014 May 7. Available from: https://www.koiha.or.kr/home/data/data/doList.act?boardtype=05
- 9. American Nurses Association. NDNQI indicators and reported rates [Internet]. Silver Spring, MD, Author. 2011;cited 2014 January 7. Available from: http://www.nursingquality.org/data.aspx
- 10. Goodwin VA, Abbott RA, Whear R, Bethel A, Ukoumunne OC, Thompson-Coon J, et al. Multiple component interventions for preventing falls and fall-related injuries among older people: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Geriatr. 2014;14:15ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 11. Lee DCA, Pritchard E, McDermott F, Haines TP. Falls prevention education for older adults during and after hospitalization: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Health Educ J. 2014;73(5):530–544. ArticlePDF
- 12. Sherrington C, Whitney JC, Lord SR, Herbert RD, Cumming RG, Close JC. Effective exercise for the prevention of falls: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2008;56(12):2234–2243. ArticlePubMed
- 13. Choi M, Hector M. Effectiveness of intervention programs in preventing falls: A systematic review of recent 10 years and meta-analysis. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2012;13(2):188.e13–188.e21. ArticlePubMed
- 14. Coussement J, De Paepe L, Schwendimann R, Denhaerynck K, Dejaeger E, Milisen K. Interventions for preventing falls in acute- and chronic-care hospitals: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2008;56(1):29–36. ArticlePubMed
- 15. Kim CG. Effects on multifactorial fall prevention program of elderly living at home in Korea: Meta-analysis. J Health Med Sci. 2013;2(1):31–38.
- 16. Park SM. Meta-analysis of the interventions for preventing falls by the elderly in the eight countries: Comparison between aged 70's and 80's. J Korean Gerontol Soc. 2010;30(1):49–63.
- 17. Son YJ. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the effects of exercise for fall prevention in the elderly [master's thesis]. Suwon, Ajou University. 2013.
- 18. Park M, Song R. Effects of Tai Chi on fall risk factors: A meta-analysis. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2013;43(3):341–351. ArticlePubMed
- 19. Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow C, Gøtzsche PC, Ioannidis JP, et al. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate healthcare interventions: Explanation and elaboration. BMJ. 2009;339:b2700ArticlePubMedPMC
- 20. Higgins JPT, Green S. In: Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions: Version 5.1.0 [Internet]. London, UK, The Cochrane Collaboration. 2011;cited 2014 January 7. Available from: www.cochrane-handbook.org.
- 21. Kim SY, Park JE, Seo HJ, Lee YJ, Son HJ, Jang BH, et al. NECA's guidance for undertaking systematic reviews and meta-analyses for intervention. Seoul: National Evidence-based Healthcare Collaborating Agency; 2011.
- 22. Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ. 2003;327(7414):557–560. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 23. Hwang SD. Meta-analysis. Seoul: Hakjisa Corp.; 2014.
- 24. Hedges LV, Olkin I. Statistical methods for meta-analysis. Orlando, FL: Academic Press, Inc.; 1985.
- 25. Sutton AJ, Duval SJ, Tweedie RL, Abrams KR, Jones DR. Empirical assessment of effect of publication bias on meta-analyses. BMJ. 2000;320(7249):1574–1577.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 26. Lee YK. The effect of education for the prevention of falls on the knowledge related to falls, the activity of preventing falls, and fall efficacy among the hospitalized elderly patients [master's thesis]. Seoul, Ewha Womans University. 2013.
- 27. Chai KJ. A literature review a program of intervention for prevention of falling in the patients with dementia. J Soc Occup Ther Aged Dement. 2010;4(2):27–34.
- 28. Kim JH, Kim AK. A quality assessment of meta-analyses of nursing in South Korea. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2013;43(6):736–745. ArticlePubMed
- 29. Vaapio S, Salminen M, Vahlberg T, Sjösten N, Isoaho R, Aarnio P, et al. Effects of risk-based multifactorial fall prevention on health-related quality of life among the community-dwelling aged: A randomized controlled trial. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2007;5:20ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 30. Kim SN. Effects of a multifactorial fall prevention program on physical · psychological function and home environmental hazards in community dwelling low-income elderly. J Korean Gerontol Soc. 2012;32(2):377–395.
REFERENCES
Appendix
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Characteristics and Effects of Fall Prevention Interventions among the Korean Older Adults: A Systematic Review
Jeong Ha Park, Hee Ju Kim
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2022; 24(1): 65. CrossRef - Internet-Delivered Cognitive Behavioral Therapy in Patients With Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Hyunjung Kim, Younjae Oh, Sun Ju Chang
Journal of Medical Internet Research.2022; 24(6): e35260. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of Turkish Version of the Self- Awareness of Falls in Elderly Scale Among Elderly Inpatients
Fatma Birgili, Seda Kılınç, Nezihe Bulut Uğurlu
Cyprus Journal of Medical Sciences.2022; 7(7): 69. CrossRef - Validity of the Morse Fall Scale and the Johns Hopkins Fall Risk Assessment Tool for fall risk assessment in an acute care setting
Young Ju Kim, Kyoung‐Ok Choi, Suk Hyun Cho, Seok Jung Kim
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2022; 31(23-24): 3584. CrossRef - An Educational Intervention to Improve Staff Collaboration and Enhance Knowledge of Fall Risk Factors and Prevention Guidelines
Kimberly A. DiGerolamo, Mei Lin Chen-Lim
Journal of Pediatric Nursing.2021; 57: 43. CrossRef - Trends of Nursing Research on Accidental Falls: A Topic Modeling Analysis
Yeji Seo, Kyunghee Kim, Ji-Su Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(8): 3963. CrossRef - Analysis of Fall Incident Rate among Hospitalized Korean Children Using Big Data
Eun Joo Kim, Anna Lee
Journal of Pediatric Nursing.2021; 61: 136. CrossRef - Development and Effect of a Fall Prevention Program Based on the King's Goal Attainment Theory for Fall High-Risk Elderly Patients in Long-Term Care Hospital
Bom Mi Park, Ho Sihn Ryu, Kyeung Eun Kwon, Chun Young Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2019; 49(2): 203. CrossRef - Use of the Nursing Outcomes Classification for Falls and Fall Prevention by Nurses in South Korea
Eunjoo Lee
International Journal of Nursing Knowledge.2019; 30(1): 28. CrossRef - Development and Validation of the Self-Awareness of Falls in Elderly Scale Among Elderly Inpatients
Meei-Ling Shyu, Hui-Chuan Huang, Mei-Jung Wu, Hsiu-Ju Chang
Clinical Nursing Research.2018; 27(1): 105. CrossRef - The effectiveness of intervention programs for preventing patients from falls
Jana Horová, Iva Brabcová, Jitka Krocová
Kontakt.2017; 19(2): e105. CrossRef - Effect of Strength Exercise on Patient Fall Prevention Program: Focusing on the Fall High Risk Group Elderly Patients
Hyun-Ok Lee, Byung-Hwa Lee, Chang-Hee Lee
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2017; 42(4): 338. CrossRef - The Effect of Pediatric Inpatient Fall Prevention Education on Caregivers' Fall-related Knowledge and Preventive Behaviors
So Yeon Park, Hyeon Ok Ju
Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2017; 23(4): 398. CrossRef
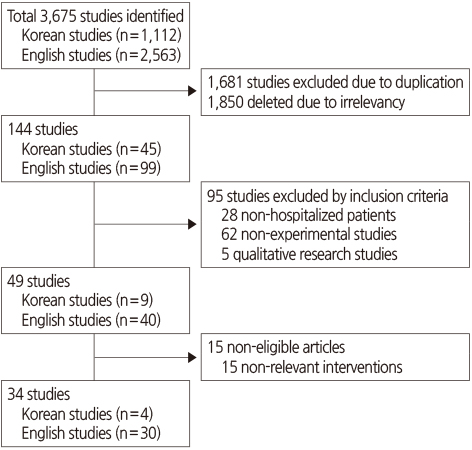
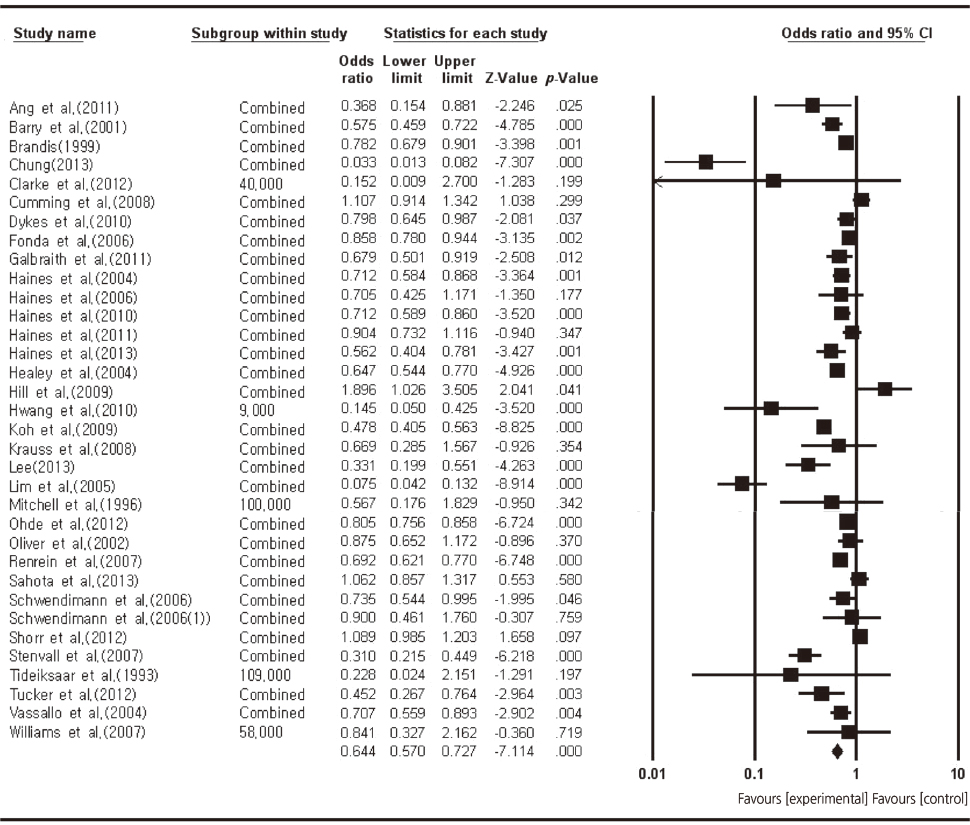
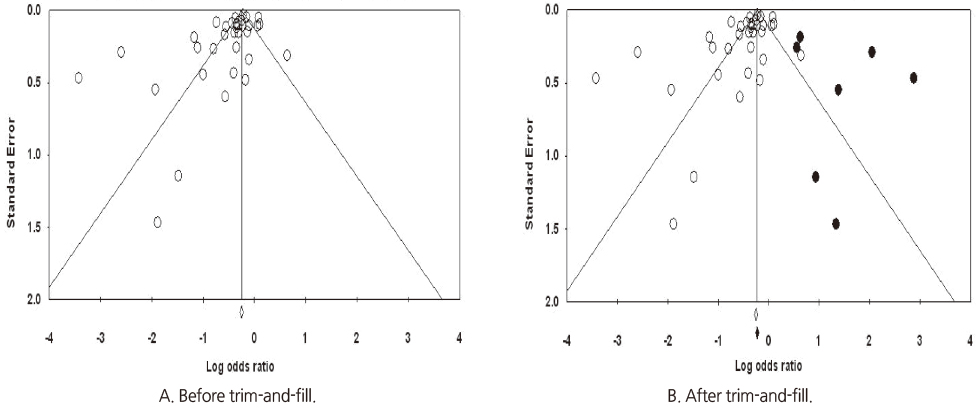
Figure 1
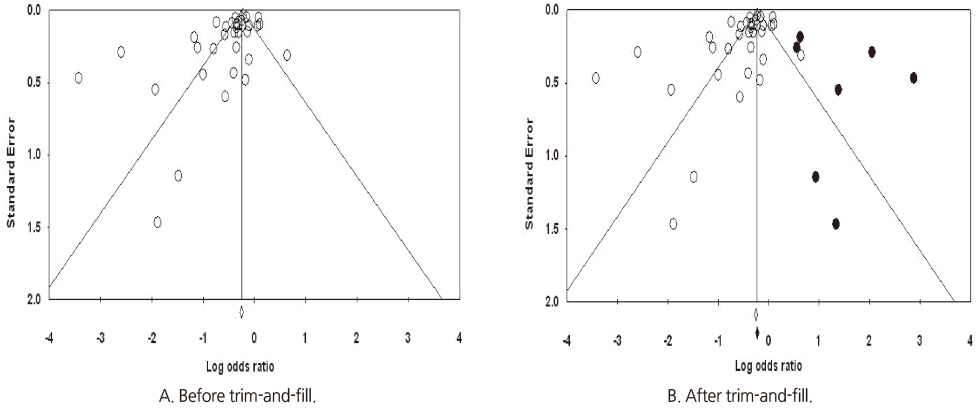
Figure 2
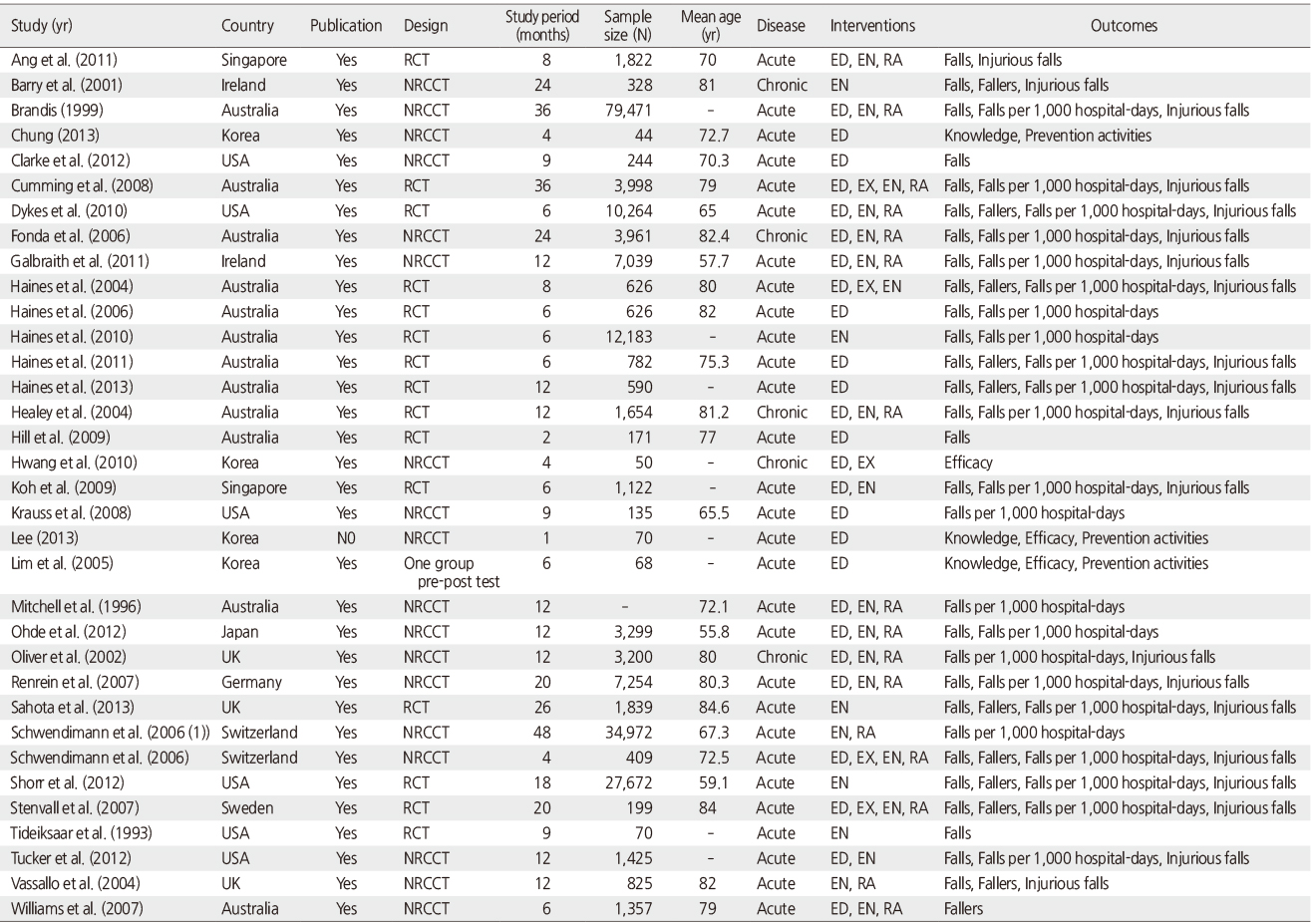
Figure 3
Characteristics of Included Studies (N=34)
ED=Education; EN=Environmental; EX=Exercise; RA=Risk assessment; NRCCT=Non-Randomized controlled clinical trial; RCT=Randomized controlled trial.
Effect Sizes of Interventions by Intervention Characteristics and Dependent Variables
K=Number of effect size; ES=Effect size; OR=Odds ratio; SE=Standard error; Q=Homogeneity.
ED=Education; EN=Environmental; EX=Exercise; RA=Risk assessment; NRCCT=Non-Randomized controlled clinical trial; RCT=Randomized controlled trial.
K=Number of effect size; ES=Effect size; OR=Odds ratio; SE=Standard error; Q=Homogeneity.
 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 Cite
Cite

