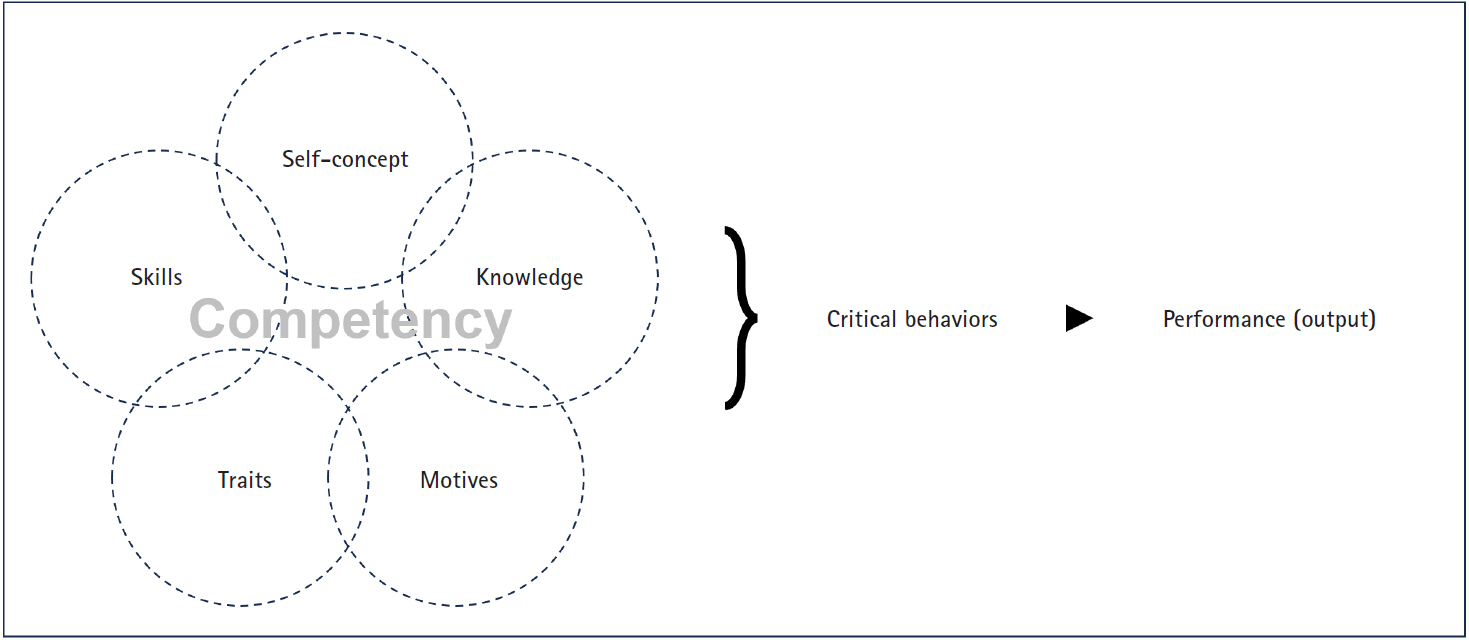
-
Core domains for pre-registered nurses based on program outcomes and licensing competencies
-
Soyoung Yu, Hye Young Kim, Jeung-Im Kim, JuHee Lee, Ju-Eun Song, Hyang Yuol Lee
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(2):249-268. Published online May 27, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25017
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF ePub ePub
- Purpose
This study aimed to identify core domains for pre-registered nurses by comparing licensing competencies with program outcomes (POs) in undergraduate nursing education. This was accomplished in preparation for the transition of the Korean Nurse Licensing Examination (KNLE) from a tradition seven-subject format to a newly integrated, competency-based single-subject format that reflects current trends in nursing assessment.
Methods
A literature review and survey were conducted. From 828 studies retrieved via PubMed, CINAHL, and Google Scholar using keywords such as “newly graduated registered nurses” and “competency OR competence,” 18 were selected according to pre-established inclusion and exclusion criteria. Documents from national and international nursing organizations were included to extract relevant licensing competencies. We also reviewed POs from all undergraduate nursing schools in South Korea to align educational outcomes with the identified core domains.
Results
The core domains identified were clinical performance and decision-making, professional attitudes and ethics, communication and interpersonal skills, leadership and teamwork, quality improvement and safety, health promotion and prevention, and information technology and digital health. These domains showed strong alignment with POs under the fourth-cycle accreditation standards.
Conclusion
It concludes the seven core domains will be appropriate for evaluating pre-registered nurses in the integrated KNLE. Based on the seven identified core domains, expert consensus should be sought in the next phase to support the development of integrated, competency-based test items grounded in these domains.
-
Assessment of Risk Factors for Postoperative Delirium in Older Adults Who Underwent Spinal Surgery and Identifying Associated Biomarkers Using Exosomal Protein
-
Wonhee Baek, JuHee Lee, Yeonsoo Jang, Jeongmin Kim, Dong Ah Shin, Hyunki Park, Bon-Nyeo Koo, Hyangkyu Lee
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(4):371-384. Published online August 31, 2023
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22146
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Purpose
With an increase in the aging population, the number of patients with degenerative spinal diseases undergoing surgery has risen, as has the incidence of postoperative delirium. This study aimed to investigate the risk factors affecting postoperative delirium in older adults who had undergone spine surgery and to identify the associated biomarkers.
Methods
This study is a prospective study. Data of 100 patients aged ≥ 70 years who underwent spinal surgery were analyzed. Demographic data, medical history, clinical characteristics, cognitive function, depression symptoms, functional status, frailty, and nutritional status were investigated to identify the risk factors for delirium. The Confusion Assessment Method, Delirium Rating Scale-R-98, and Nursing Delirium Scale were also used for diagnosing deliri-um. To discover the biomarkers, urine extracellular vesicles (EVs) were analyzed for tau, ubiquitin carboxy-terminal hydrolase L1 (UCH-L1), neurofilament light, and glial fibrillary acidic protein using digital immunoassay technology.
Results
Nine patients were excluded, and data obtained from the remaining 91 were analyzed. Among them, 18 (19.8%) developed delirium. Differences were observed between partici-pants with and without delirium in the contexts of a history of mental disorder and use of benzodiazepines (p = .005 and p = .026, respectively). Tau and UCH-L1—concentrations of urine EVs—were comparatively higher in participants with severe delirium than that in partici-pants without delirium (p = .002 and p = .001, respectively).
Conclusion
These findings can assist clinicians in accurately identifying the risk factors before surgery, classifying high-risk patients, and predicting and detecting delirium in older patients. Moreover, urine EV analysis revealed that postoperative delirium following spinal surgery is most likely associated with brain damage.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Emerging biomarkers of postoperative delirium at the intersection of neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration
Kun Leng, Mervyn Maze, Odmara L. Barreto Chang
Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
-
1,777
View
-
61
Download
-
1
Web of Science
-
1
Crossref
-
Factors Affecting Clinical Practicum Stress of Nursing Students: Using the Lazarus and Folkman's Stress-Coping Model
-
Sung Hae Kim, JuHee Lee, MiRa Jang
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(4):437-448. Published online August 29, 2019
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.4.437
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
-
Purpose
This study was conducted to test a path model for the factors related to undergraduate nursing students' clinical practicum stress, based on Lazarus and Folkman's stress-coping model.
Methods
This study utilized a path analysis design. A total of 235 undergraduate nursing students participated in this study. The variables in the hypothetical path model consisted of clinical practicum, emotional intelligence, self-efficacy, Nun-chi, and nursing professionalism. We tested the fit of the hypothetical path model using SPSS/WIN 23.0 and AMOS 22.0.
Results
The final model fit demonstrated a satisfactory statistical acceptance level: goodness-of-fit-index=.98, adjusted goodness-of-fit-index=.91, comparative fit index=.98, normed fit index=.95, Tucker-Lewis index=.92, and root mean square error of approximation=.06. Self-efficacy (β=−.22, p=.003) and Nun-chi behavior (β=−.17, p=.024) were reported as significant factors affecting clinical practicum stress, explaining 10.2% of the variance. Nursing professionalism (β=.20, p=.006) and self-efficacy (β=.45, p<.001) had direct effects on emotional intelligence, explaining 45.9% of the variance. Self-efficacy had indirect effects on Nun-chi understanding (β=.20, p<.001) and Nun-chi behavior (β=.09, p=.005) through emotional intelligence. Nursing professionalism had indirect effects on Nun-chi understanding (β=.09, p=.005) and Nun-chi behavior (β=.09, p=.005) through emotional intelligence. The variables for self-efficacy and nursing professionalism explained 29.1% of the Nun-chi understanding and 18.2% of the Nun-chi behavior, respectively.
Conclusion
In undergraduate nursing education, it is important to identify and manage factors that affect clinical practicum stress. The findings of this study emphasize the importance of Nun-chi, self-efficacy, emotional intelligence, and nursing professionalism in the development of an educational strategy for undergraduate nursing students.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Relationships between demographic variables and stress coping strategies in sample of Iranian teenage girls
Nasibe Farmani Qasabe, Gholamreza Garmaroudi, Ehsan Kazemnezhad Leyli, Hassan Farrahi
BMC Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The role of professional identity, psychological resilience, and coping styles in mitigating compassion fatigue among geriatric services and management interns
Li-Hong Fan, Guo-Hao Wang, Jin-Mei Lei, Chao Shi, Li-Juan Yi
Geriatric Nursing.2025; 64: 103372. CrossRef - The Impact of Dietary Habits and Nutrition Knowledge on Harmful Alcohol Use and Nicotine Dependence Among Medical Students: A Single-Center, Cross-Sectional Study
Aureliusz Andrzej Kosendiak, Bartosz Bogusz Adamczak, Zofia Kuźnik, Szymon Makles, Weronika Hariasz
Nutrients.2025; 17(11): 1788. CrossRef - Cerrahi Klinik Uygulamasına Çıkan Hemşirelik Öğrencilerinde Klinik Stres Düzeyi ve Etkileyen Faktörler
Tuğba Çam Yanık, Canan Kanat, Merve Nur Tanrıverdi, Hatice Ural
Mersin Üniversitesi Tıp Fakültesi Lokman Hekim Tıp Tarihi ve Folklorik Tıp Dergisi.2025; 15(2): 721. CrossRef - Environmental and Individual Factors Associated with Clinical Practice Stress in Korean Nursing Students: A Scoping Review
Ui Rim Song
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2025; 37(4): 355. CrossRef - Effect of structured community-based older people education program on empathy, emotional intelligence, and caring behavior among nursing students
Jing Ma, PingLei Chui, Mei Chan Chong, Jingru Yuan, Yongyan Zhu, Luyao Liu, Zhenqing Sun
Frontiers in Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of stress on burnout among infection control nurses during the COVID-19 pandemic: the mediating effects of social support and self-efficacy
Su-jin Lee, Ju-Young Park, Seo-Hyeon Kim
BMC Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of verbal violence, clinical practice stress, and coping with stress on nursing students’ major satisfaction during clinical practice
Heejung Heo, Yeoungsuk Song
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2023; 29(2): 190. CrossRef - Examining Students’ Experience with the Nursing Management Practicum Based on the Service Design
Yoomi Jung, Myungja Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2022; 28(3): 214. CrossRef - Effects of a group poetry therapy program on stress, anxiety, ego-resilience, and psychological well-being of nursing students
Jung Hyun Park, Ji Young Kim, Hyeon Ok Kim
Archives of Psychiatric Nursing.2022; 41: 144. CrossRef - The mediating effect of media usage on the relationship between anxiety/fear and physician–patient trust during the COVID-19 pandemic
Yidi Chen, Jianhui Wu, Jinjin Ma, Huanya Zhu, Wenju Li, Yiqun Gan
Psychology & Health.2022; 37(7): 847. CrossRef - A Cross-Sectional Study: What Contributes to Nursing Students’ Clinical Reasoning Competence?
Soomin Hong, JuHee Lee, Yeonsoo Jang, Yoonju Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(13): 6833. CrossRef
-
3,209
View
-
141
Download
-
8
Web of Science
-
12
Crossref
-
Relationship between Expectations Regarding Aging and Physical Activity among Middle Aged Adults in Urban Areas: Based on the Pender's Health Promotion Model
-
Sung-Hye Cho, MoonKi Choi, JuHee Lee, Hyewon Cho
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2015;45(1):14-24. Published online February 27, 2015
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2015.45.1.14
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
-
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to measure the level of expectations regarding aging (ERA) and identify relationship between ERA and physical activity of middle aged adults.
Methods
Participants were middle aged adults who resided in the community in three cities in Korea. Data were collected using questionnaires that contained items on individual characteristic, International Physical Activity Questionnaires (IPAQ), and behavior-specific cognitive factors including ERA-12. Hierarchical multiple regression was conducted to examine whether ERA would predict physical activity by controlling other factors.
Results
The mean age of the participants was 51.1±6.9 years. The mean score for ERA (possible range=0 to 100) was 40.04±14.31. More than half of the participants (62.6%) were not engaged in health promoting physical activity. Gender, employment status and exercise confidence were associated with level of physical activity (F=7.14, p<.001, R2=.36). After controlling for individual factors and behavior-specific cognitive factors, ERA was independently related to physical activity (F=7.19, p<.001, R2=.38).
Conclusion
The results demonstrate that individuals' belief about aging has effects on physical activity in Korean middle aged adults. Thus, nursing interventions which focused on ERA could help enhance physical activity in middle aged adults.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - The Relationship Among Stress, Sense of Coherence and Sleep Quality in Middle-aged Women
So Hyeon Kim, So Young Choi
Journal of Korean Maternal and Child Health.2025; 29(3): 137. CrossRef - Family care and health-promoting behaviors among community elders: The chain mediating effect of self-efficacy and aging expectations
Yian Chen, Lin Zhang, Jiashuang Xu, Miaojing Song, Pengjuan Ji, Qiqi Ji, Leilei Guo
Geriatric Nursing.2025; 66: 103606. CrossRef - The Effects of Health Status and Social Support on Happiness in MiddleAged Women
Bok Hui Baek, So Young Choi
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2024; 38(1): 16. CrossRef - Impact of WhatsApp-Based Self-Care Education on Self-Care Behaviors and Lifestyle in Overweight and Obese Pregnant Women with Diabetes: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Fatemeh Salarkarimi, Majid Karandish, Mehrnoosh Zakerkish, Zahra Abbaspoor
Jundishapur Journal of Chronic Disease Care.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Level of Expectations Regarding Aging Among Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Lunwei Lin, Shunqi Liao, Zhangrong Yan, Chaofan Liu, Qi Wang, Fang Wang
Journal of the American Medical Directors Association.2024; 25(3): 410. CrossRef - The Effect of a Training Intervention Based on Pender’s Health Promotion Model on the Lifestyle of Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis
Hossein Hassannezhad, Hasan Robabi, Fatihe Kerman Saravi
Medical-Surgical Nursing Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of Persian Version of the 12-Item Expectations Regarding Aging Survey
Hamid Sharif Nia, Long She, Sotheeswari Somasundram, Fatemeh Khoshnavay Fomani, Omolhoda Kaveh, Lida Hosseini
The International Journal of Aging and Human Development.2023; 96(2): 248. CrossRef - Health-Related Expectations Regarding Aging among Middle-Aged and Older Japanese: Psychometric Performance and Novel Findings from the ERA-12-J
Michael Annear, Yasuo Shimizu, Tetsuhiro Kidokoro
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(20): 13509. CrossRef - Factors Influencing the Physical Activity of Foreign Workers: Based on a Health Promotion Model
Jeong Eui Cho, Yeongmi Ha
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2021; 32(3): 344. CrossRef - Lower serum levels of alpha tocopherol and lycopene are associated with higher pain and physical disability in subjects with primary knee osteoarthritis: A case-control study
Bina Eftekharsadat, Dawood Aghamohammadi, Neda Dolatkhah, Maryam Hashemian, Halale Salami
International Journal for Vitamin and Nutrition Research.2021; 91(3-4): 304. CrossRef - Effects of a Daily Life-Based Physical Activity Enhancement Program for Middle-Aged Women at Risk for Cardiovascular Disease
Kyung Ae Kim, Seon Young Hwang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2019; 49(2): 113. CrossRef - Applying the theory of planned behavior to determine factors associated with physical activity by women with hypertension in rural areas of Iran
Effat Hatefnia, Kobra Alizadeh, Mostafa Ghorbani
Asian Biomedicine.2019; 12(2): 83. CrossRef - Factors Affecting the Successful Aging of Late Middle-Aged Adults
YonJi Kim, JuHee Lee, Young Joo Lee
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2018; 18(2): 90. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Exercise Behavior of the Male Manual Worker and Office Worker based on Health Promotion Model
SeungKyoung Yang, Yeongmi Ha, Mi-Ra Jung
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2015; 24(3): 235. CrossRef
-
1,138
View
-
18
Download
-
14
Crossref
-
Transforming nursing education to enhance integrated nursing competency: a Delphi-based methodological study on symptom-based clinical reasoning
-
Jeung-Im Kim, Soyoung Yu, Jin-Hee Park, Ju-Eun Song, Eunjung Ryu, JuHee Lee, YeoJin Im
-
Received November 7, 2025 Accepted December 10, 2025 Published online December 23, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25151
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
- Purpose
This study aimed to address the shift toward competency-based education and the planned 2028 “Integrated Nursing” National Licensing Examination (NLE), this study aimed to establish structural alignment among NLE domains, the seven integrated nursing competencies (INCs), and curriculum goals, with a particular focus on implementing symptom-based clinical reasoning (SBCR).
Methods
This Delphi-based methodological study included seven content experts for content validity index (CVI) assessment and 24 nursing education experts who participated in a consensus workshop. The item-level CVI and the scale-level CVI/average were calculated to confirm the linkage between INCs and NLE domains. In addition, qualitative analysis of workshop materials and meeting records was conducted to derive 10 integrated learning topics and to develop an SBCR educational model for the key symptom of headache, grounded in Miller’s Clinical Competence Pyramid (levels 2–4).
Results
The analysis confirmed the validity of integrating the INCs within the overall curriculum structure. The resulting framework delineates staged learning objectives and core clinical questions designed to systematically enhance clinical reasoning, promote safe nursing practice, and support professional reflection within a unified curriculum.
Conclusion
This study provides a practical foundation for nursing curriculum redesign by facilitating a transition from fragmented, subject-based instruction to a holistic, patient-centered SBCR model. This approach aligns with the requirements of the integrated NLE and is expected to contribute to meaningful improvements in actual clinical competency.
|