-
Analysis of the relative importance of key factors in nursing workforce management for pandemic response in general hospitals and long-term care hospitals
-
Jeong Eun Cha, Eun Kyoung Yun
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(2):236-248. Published online May 14, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24112
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF ePub ePub
- Purpose
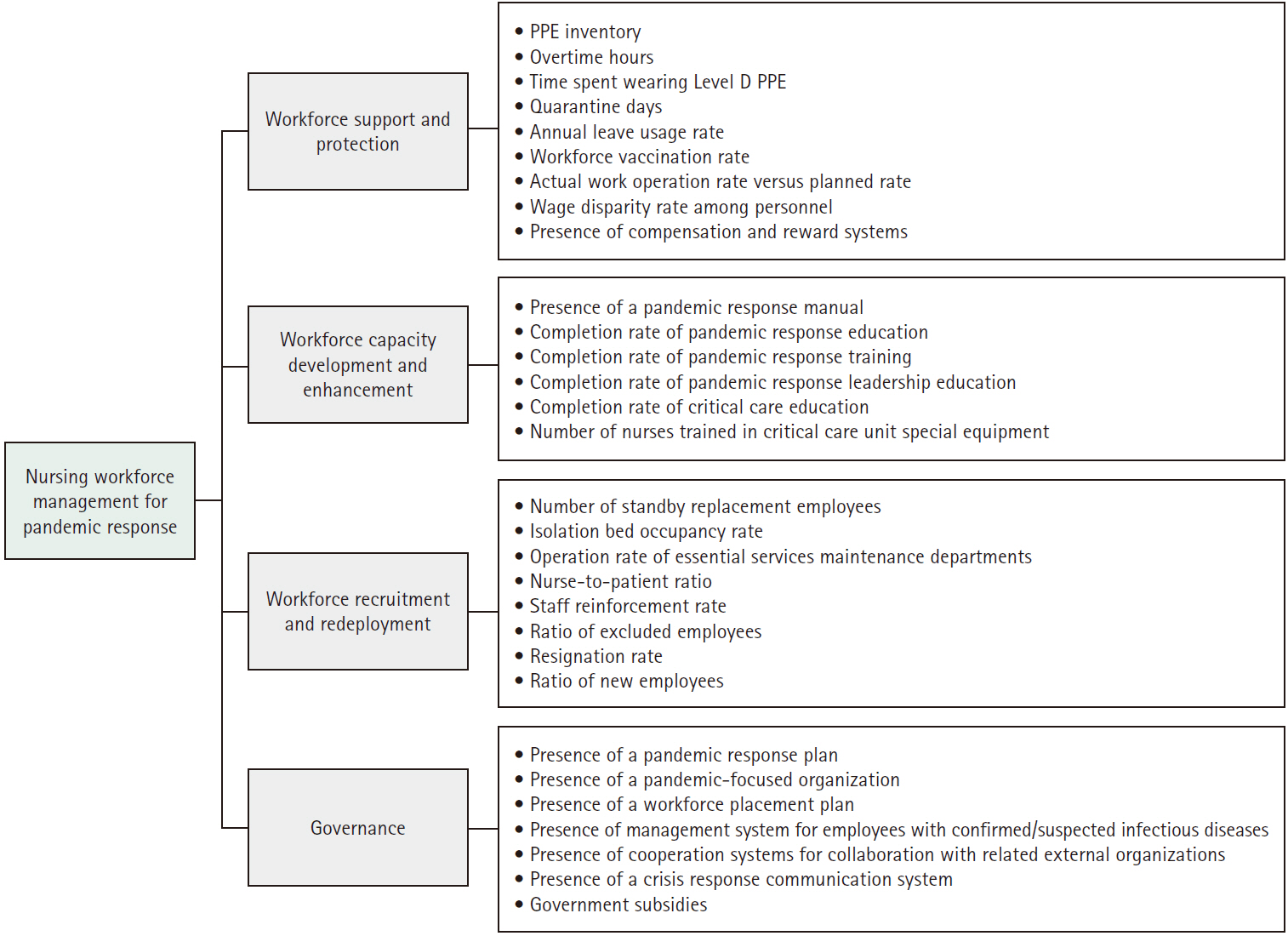
This study aimed to identify the key factors in nursing workforce management for pandemic response in general hospitals and long-term care hospitals and to analyze the relative importance of these factors.
Methods
A validity test was conducted with experts to select four categories and 30 key factors related to nursing workforce management for pandemic response. Surveys were collected from 25 nursing managers in general hospitals and 21 nursing managers in long-term care hospitals, and the relative importance of the key factors was analyzed using the analytic hierarchy process method.
Results
Differences were found between the two groups in the relative importance of nursing workforce management for pandemic response. Specifically, the highest-ranking category was “workforce recruitment and redeployment” for general hospitals, but “workforce support and protection” for long-term care hospitals. The most important factor regarding nursing workforce management was the “nurse-to-patient ratio” for both general and long-term care hospitals.
Conclusion
General and long-term care hospitals need to establish nursing workforce management strategies to effectively respond to pandemics with appropriate consideration of the relative importance and prioritization of key factors based on hospital characteristics.
-
An Exploratory Study on Non-Contact Nursing Experiences of Clinical Nurses during the COVID-19 Pandemic
-
Hye Min Byun, Eun Kyoung Yun
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(3):446-458. Published online August 31, 2024
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24045
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Purpose
This study aimed to understand the non-contact nursing experiences of clinical nurses during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Methods
A qualitative research design applying thematic analysis was used. The participants were purposive sampled from three institutes: a tertiary hospital, a general hospital, and a residential treatment center in Seoul. Data were collected between December 2021 and January 2022 through individual in-depth interviews with 12 clinical nurses. The data were analyzed using Braun and Clarke’s method to identify the meaning of the participants’ experiences.
Results
During the COVID-19 pandemic, the fields where the participants performed non-contact nursing included intensive care units and isolation wards of hospitals, a residential treatment center, and home cares. Their tasks in non-contact nursing commonly involved remote monitoring using digital devices or equipment, consultation and education. From their experiences performing tasks in these fields, the four theme clusters and nine themes were derived. The four theme clusters are as follows: (1) Confusion of nursing role; (2) Conflict due to insufficient support system; (3) Concern about the quality of nursing; (4) Reflection on the establishment of nursing professionalism.
Conclusion
This study highlights the necessity for institutionalizing professional nursing areas, nursing education, and practical support by clarifying the purpose and goals of non-contact nursing and developing nursing knowledge through frameworks.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - A systematic review of pulmonary rehabilitation nursing interventions for patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Da-Jung Kim
Journal of Exercise Rehabilitation.2025; 21(5): 234. CrossRef - Telecare legislation priorities: A Delphi study grounded in ethical challenges
Seongyu Han, Eun Kyoung Yun
Nursing Ethics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
-
1,825
View
-
87
Download
-
2
Web of Science
-
2
Crossref
-
Topic Modeling and Keyword Network Analysis of News Articles Related to Nurses before and after “the Thanks to You Challenge” during the COVID-19 Pandemic
-
Eun Kyoung Yun, Jung Ok Kim, Hye Min Byun, Guk Geun Lee
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(4):442-453. Published online August 31, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20287
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Purpose
This study was conducted to assess public awareness and policy challenges faced by practicing nurses.
Methods
After collecting nurse-related news articles published before and after ‘the Thanks to You Challenge’ campaign (between December 31, 2019, and July 15, 2020), keywords were extracted via preprocessing. A three-step method keyword analysis, latent Dirichlet allocation topic modeling, and keyword network analysis was used to examine the text and the structure of the selected news articles.
Results
Top 30 keywords with similar occurrences were collected before and after the campaign. The five dominant topics before the campaign were: pandemic, infection of medical staff, local transmission, medical resources, and return of overseas Koreans. After the campaign, the topics ‘infection of medical staff’ and ‘return of overseas Koreans’ disappeared, but ‘the Thanks to You Challenge’ emerged as a dominant topic. A keyword network analysis revealed that the word of nurse was linked with keywords like thanks and campaign, through the word of sacrifice. These words formed interrelated domains of ‘the Thanks to You Challenge’ topic.
Conclusion
The findings of this study can provide useful information for understanding various issues and social perspectives on COVID-19 nursing. The major themes of news reports lagged behind the real problems faced by nurses in COVID-19 crisis. While the press tends to focus on heroism and whole society, issues and policies mutually beneficial to public and nursing need to be further explored and enhanced by nurses.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Effect of Nursing Professionalism on Turnover Intention among Nurses: The Mediating Effect of Job Embeddedness
Ja In Kim, Seok Hee Jeong, Hyoung Eun Chang, Sunmi Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(4): 446. CrossRef - Patent Technology Trends of Oral Health: Application of Text Mining
Hee-Kyeong Bak, Yong-Hwan Kim, Han-Na Kim
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2024; 24(1): 9. CrossRef - Agendas on Nursing in South Korea Media: Natural Language Processing and Network Analysis of News From 2005 to 2022
Daemin Park, Dasom Kim, Ah-hyun Park
Journal of Medical Internet Research.2024; 26: e50518. CrossRef - Analysis of issues related to nursing law: Examination of news articles using topic modeling
JooHyun Lee, Hyoung Eun Chang, Jaehyuk Cho, Seohyun Yoo, Joonseo Hyeon, Andrea Cioffi
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(8): e0308065. CrossRef - Research Trends on Cancer-Related Cognitive Impairment in Patients with Non-Central Nervous System Cancer: Text Network Analysis and Topic Modeling
Hee-Jun Kim, Sun Hyoung Bae, Jin-Hee Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2023; 30(3): 313. CrossRef - Perspectives of Frontline Nurses Working in South Korea during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Combined Method of Text Network Analysis and Summative Content Analysis
SangA Lee, Tae Wha Lee, Seung Eun Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2023; 53(6): 584. CrossRef - Nurses’ Experience in COVID-19 Patient Care
Soojin Chung, Mihyeon Seong, Ju-young Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2022; 28(2): 142. CrossRef - A topic modeling analysis for Korean online newspapers: Focusing on the social perceptions of nurses during the COVID-19 epidemic period
Soo Jung Chang, Sunah Park, Yedong Son
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2022; 28(4): 444. CrossRef - Images of Nurses Appeared in Media Reports Before and After Outbreak of COVID-19: Text Network Analysis and Topic Modeling
Min Young Park, Seok Hee Jeong, Hee Sun Kim, Eun Jee Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2022; 52(3): 291. CrossRef - Experience of Nurses in Charge of COVID-19 Screening at General Hospitals in Korea
Boo Young Ha, Yun-Sook Bae, Han Sol Ryu, Mi-Kyeong Jeon
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2022; 52(1): 66. CrossRef - An Exploratory Study on Current Nursing Issues in the COVID-19 era through Newspaper Articles: The Application of Text Network Analysis
Young Joo Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2022; 28(3): 307. CrossRef - Analysis of Headline News about Nurses Before and After the COVID-19 Pandemic
Su-Mi Baek, Myonghwa Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2022; 28(4): 319. CrossRef - Warmth and competence perceptions of key protagonists are associated with containment measures during the COVID-19 pandemic: Evidence from 35 countries
Maria-Therese Friehs, Patrick F. Kotzur, Christine Kraus, Moritz Schemmerling, Jessica A. Herzig, Adrian Stanciu, Sebastian Dilly, Lisa Hellert, Doreen Hübner, Anja Rückwardt, Veruschka Ulizcay, Oliver Christ, Marco Brambilla, Jonas De keersmaecker, Feder
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
-
2,098
View
-
25
Download
-
7
Web of Science
-
13
Crossref
-
An Exploratory Study on the Policy for Facilitating of Health Behaviors Related to Particulate Matter: Using Topic and Semantic Network Analysis of Media Text
-
Hye Min Byun, You Jin Park, Eun Kyoung Yun
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(1):68-79. Published online February 28, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20213
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Purpose
This study aimed to analyze the mass and social media contents and structures related to particulate matter before and after the policy enforcement of the comprehensive countermeasures for particulate matter, derive nursing implications, and provide a basis for designing health policies.
Methods
After crawling online news articles and posts on social networking sites before and after policy enforcement with particulate matter as keywords, we conducted topic and semantic network analysis using TEXTOM, R, and UCINET 6.
Results
In topic analysis, behavior tips was the common main topic in both media before and after the policy enforcement. After the policy enforcement, influence on health disappeared from the main topics due to increased reports about reduction measures and government in mass media, whereas influence on health appeared as the main topic in social media. However semantic network analysis confirmed that social media had much number of nodes and links and lower centrality than mass media, leaving substantial information that was not organically connected and unstructured.
Conclusion
Understanding of particulate matter policy and implications influence health, as well as gaps in the needs and use of health information, should be integrated with leadership and supports in the nurses’ care of vulnerable patients and public health promotion.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Online community users’ perceptions of particulate matter in South Korea through topic modeling and semantic network analysis
Hansol Choi, Yong Pyo Kim, Yungwook Kim, Ji Yi Lee, Hyemi Lee
Environmental Advances.2025; 20: 100641. CrossRef - Changes in Public Sentiment under the Background of Major Emergencies—Taking the Shanghai Epidemic as an Example
Bowen Zhang, Jinping Lin, Man Luo, Changxian Zeng, Jiajia Feng, Meiqi Zhou, Fuying Deng
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(19): 12594. CrossRef
-
1,450
View
-
17
Download
-
1
Web of Science
-
2
Crossref
-
Development and Analysis of System Dynamics Model for Predicting on the Effect of Patient Transfer Counseling with Nurses
-
Hye Min Byun, Eun Kyoung Yun
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(5):554-564. Published online October 31, 2018
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.5.554
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
-
Purpose
This study aimed to construct a management model for patient transfer in a multilevel healthcare system and to predict the effect of counseling with nurses on the patient transfer process.
Methods
Data were collected from the electronic medical records of 20,400 patients using the referral system in a tertiary hospital in Seoul from May 2015 to April 2017. The data were analyzed using system dynamics methodology.
Results
The rates of patients who were referred to a tertiary hospital, continued treatment, and were terminated treatment at a tertiary hospital were affected by the management fee and nursing staffing in a referral center that provided patient transfer counseling. Nursing staffing in a referral center had direct influence on the range of increase or decrease in the rates, whereas the management fee had direct influence on time. They were nonlinear relations that converged the value within a certain period.
Conclusion
The management fee and nursing staffing in a referral center affect patient transfer counseling, and can improve the patient transfer process. Our findings suggest that nurses play an important role in ensuring smooth transitions between clinics and hospitals.
-
Non-linear System Dynamics Simulation Modeling of Adolescent Obesity: Using Korea Youth Risk Behavior Web-based Survey
-
Hanna Lee, Eun Suk Park, Jae Kook Yu, Eun Kyoung Yun
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2015;45(5):723-732. Published online October 30, 2015
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2015.45.5.723
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
-
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to develop a system dynamics model for adolescent obesity in Korea that could be used for obesity policy analysis.
Methods
On the basis of the casual loop diagram, a model was developed by converting to stock and flow diagram. The Vensim DSS 5.0 program was used in the model development. We simulated method of moments to the calibration of this model with data from The Korea Youth Risk Behavior Web-based Survey 2005 to 2013. We ran the scenario simulation.
Results
This model can be used to understand the current adolescent obesity rate, predict the future obesity rate, and be utilized as a tool for controlling the risk factors. The results of the model simulation match well with the data. It was identified that a proper model, able to predict obesity probability, was established.
Conclusion
These results of stock and flow diagram modeling in adolescent obesity can be helpful in development of obesity by policy planners and other stakeholders to better anticipate the multiple effects of interventions in both the short and the long term. In the future we suggest the development of an expanded model based on this adolescent obesity model.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - In vitro antioxidant and antihypertensive properties of sesame seed enzymatic protein hydrolysate and ultrafiltration peptide fractions
Magdalene M. Aondona, Julius K. Ikya, Moses T. Ukeyima, Tsav‐wua J. A. Gborigo, Rotimi E. Aluko, Abraham T. Girgih
Journal of Food Biochemistry.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors associated with Obesity among Korean Adolescents based on the Seventh Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2016)
Hyun Young Koo, Eun Kyung Lee
Child Health Nursing Research.2019; 25(1): 28. CrossRef - Development and Analysis of System Dynamics Model for Predicting on the Effect of Patient Transfer Counseling with Nurses
Hye Min Byun, Eun Kyoung Yun
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2018; 48(5): 554. CrossRef - A systems thinking approach to explore the structure of urban walking and health promotion in Seoul
Dong Ha Kim, Chang-Kwon Chung, Jihyun Lee, Kwang Kee Kim, Jung JeKarl, Seunghyun Yoo
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2018; 35(5): 1. CrossRef - Parent Involvement Intervention in Developing Weight Management Skills for both Parents and Overweight/Obese Children
Hee Soon Kim, Jiyoung Park, Kye-yeong Park, Myung-Nam Lee, Ok Kyung Ham
Asian Nursing Research.2016; 10(1): 11. CrossRef
-
1,097
View
-
7
Download
-
5
Crossref
-
Model for Unplanned Self Extubation of ICU Patients Using System Dynamics Approach
-
Yu Gil Song, Eun Kyoung Yun
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2015;45(2):280-292. Published online April 30, 2015
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2015.45.2.280
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
-
Purpose
In this study a system dynamics methodology was used to identify correlation and nonlinear feedback structure among factors affecting unplanned extubation (UE) of ICU patients and to construct and verify a simulation model.
Methods
Factors affecting UE were identified through a theoretical background established by reviewing literature and preceding studies and referencing various statistical data. Related variables were decided through verification of content validity by an expert group. A causal loop diagram (CLD) was made based on the variables. Stock & Flow modeling using Vensim PLE Plus Version 6.0b was performed to establish a model for UE.
Results
Based on the literature review and expert verification, 18 variables associated with UE were identified and CLD was prepared. From the prepared CLD, a model was developed by converting to the Stock & Flow Diagram. Results of the simulation showed that patient stress, patient in an agitated state, restraint application, patient movability, and individual intensive nursing were variables giving the greatest effect to UE probability. To verify agreement of the UE model with real situations, simulation with 5 cases was performed. Equation check and sensitivity analysis on TIME STEP were executed to validate model integrity.
Conclusion
Results show that identification of a proper model enables prediction of UE probability. This prediction allows for adjustment of related factors, and provides basic data do develop nursing interventions to decrease UE.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Prediction model for unplanned extubation of thoracoabdominal drainage tube in postoperative inpatients: a retrospective study
Yushu Sun, Xiuping Li, Jia Xu, Xiaojie Zhang, Fanglei Gu, Hongying Pan
European Journal of Medical Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical application and evaluation of a new type of tracheal catheter fixation belt
Fang Niu, Qinghua Liu, Xiaohui Li, Xiang Li
Nursing Open.2023; 10(4): 2593. CrossRef - Incidence of Unplanned Extubation and Related Factors of Reintubation in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit
Hee Moon Lim, Hyejung Lee, Mi Jung Park, Jeong Eun Shin
Journal of The Korean Society of Maternal and Child Health.2022; 26(2): 72. CrossRef - Design of assessment tool for unplanned endotracheal extubation of artificial airway patients
Ping Zhang, Li‐Ping Liu
Nursing Open.2021; 8(4): 1696. CrossRef - Critical care nurses’ communication experiences with patients and families in an intensive care unit: A qualitative study
Hye Jin Yoo, Oak Bun Lim, Jae Lan Shim, Liza Heslop
PLOS ONE.2020; 15(7): e0235694. CrossRef
-
1,293
View
-
16
Download
-
5
Crossref
-
A Development and Evaluation of Nursing KMS using QFD in Outpatient Departments
-
Han Na Lee, Eun Kyoung Yun
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2014;44(1):64-74. Published online February 28, 2014
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2014.44.1.64
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
-
Purpose
This study was done to develop and implement the Nursing KMS (knowledge management system) in order to improve knowledge sharing and creation among clinical nurses in outpatient departments.
Methods
This study was a methodological research using the 'System Development Life Cycle': consisting of planning, analyzing, design, implementation, and evaluation. Quality Function Deployment (QFD) was applied to establish nurse requirements and to identify important design requirements. Participants were 32 nurses and for evaluation data were collected pre and post intervention at K Hospital in Seoul, a tertiary hospital with over 1,000 beds.
Results
The Nursing KMS was built using a Linux-based operating system, Oracle DBMS, and Java 1.6 web programming tools. The system was implemented as a sub-system of the hospital information system. There was statistically significant differences in the sharing of knowledge but creating of knowledge was no statistically meaningful difference observed. In terms of satisfaction with the system, system efficiency ranked first followed by system convenience, information suitability and information usefulness.
Conclusion
The results indicate that the use of Nursing KMS increases nurses' knowledge sharing and can contribute to increased quality of nursing knowledge and provide more opportunities for nurses to gain expertise from knowledge shared among nurses.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Evaluation Method of Mobile Commerce
Hae-Sool Yang, Sang-Won Kang
Journal of Digital Convergence.2015; 13(2): 141. CrossRef
-
922
View
-
6
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
Comparison of the Factors Influencing Young Adolescents' Aggression according to Family Structure
-
Eun Kyoung Yun, Sung Hee Shin
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2013;43(3):321-330. Published online June 28, 2013
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2013.43.3.321
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
-
Purpose
This cross-sectional study was done to compare factors influencing young adolescents' aggression according to family structure.
Methods
Participants were 680 young adolescents aged 11 to 15 years (113 in single father families, 136 in single mother families, 49 in grandparent families, and 382 in both-parent families). All measures were self-administered. Data were analyzed using SPSS 18.0 program and factors affecting young adolescents' aggression were analyzed by stepwise multiple regression.
Results
Levels of young adolescents' aggression and all variables were significantly different among the four family structure groups. Factors influencing young adolescents' aggression were also different according to these 4 groups. For single father families, depression-anxiety and family hardiness significantly predicted the level of young adolescents' aggression (adjusted R square=.37, p<.001). For single mother families, depression-anxiety, gender, and friends' support significantly predicted the level of young adolescents' aggression (adjusted R square=.58, p<.001). For grandparent families, depression-anxiety and family support significantly predicted the level of young adolescents' aggression (adjusted R square=.58, p<.001). For both-parent families, depression-anxiety, family hardiness, and friends' support significantly predicted the level of young adolescents' aggression (adjusted R square=.48, p<.001).
Conclusion
Nurses working with young adolescents should consider family structure-specific factors influencing aggression in this population.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - How do grandparents influence child health and development? A systematic review
Aalyia F.A. Sadruddin, Liliana A. Ponguta, Anna L. Zonderman, Kyle S. Wiley, Alyssa Grimshaw, Catherine Panter-Brick
Social Science & Medicine.2019; 239: 112476. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Adolescents’ Self-control According to Family Structure
In Young Cho, Ja Sook Kim, Ja Ok Kim
Journal of Child and Family Studies.2018; 27(11): 3520. CrossRef - Mediating Effects of Cognitive Emotion Regulation on Influences of Self-differentiation and Family Function in High School Students' Problem Behavior
Jin Joo Chang, Sung Hee Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2017; 26(3): 248. CrossRef - Survey on Foodservice Satisfaction and Dietary Education needs for Improvement of School Foodservice in Middle School Students in Seoul
Kyung-Hee Shin, Youngmee Lee, Wookyoun Cho
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2017; 22(2): 127. CrossRef - Comparison of Boys' and Girls' Families for Actor and Partner Effect of Stress, Depression and Parent-Adolescent Communication on Middle School Students' Suicidal Ideation: Triadic Data Analysis
Sung Hee Shin, Suk Jeong Ko, Yu Jeong Yang, Hyun Su Oh, Mi Young Jang, Joong Myung Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2014; 44(3): 317. CrossRef - A Study on the Relationship among Family Functioning, Empathy, and Aggression by High School Students
Hee Jung Choi, Eun Sun Lim, Jang Hak Yoo
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2013; 24(4): 480. CrossRef
-
1,246
View
-
9
Download
-
6
Crossref
-
Predictors of Employment Intention for Mentally Disabled Persons
-
Sang-Sook Han, Jeong Hye Han, Eun Kyoung Yun
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2008;38(4):541-549. Published online August 31, 2008
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2008.38.4.541
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
-
Purpose
This study was conducted to determine the predictors of employment intention for mentally disabled persons.
Methods
Mentally disabled persons who had participated in rehabilitation programs in one of 16 mental health centers and 9 community rehabilitation centers located in Seoul and Kyunggi province were recruited for this study. A random sampling method was used and 414 respondents were used for final analysis. Data was analyzed by Pearson's correlation, and stepwise multiple regression using the SPSS Win 14.0.
Results
The predictors influencing employment intention of the mentally disabled person were observed as employment desire (β=.48), guardian's expectation (β=.26), professional's support (β=.23), financial management (β=.10), eating habits (β=.07), and quality of life (β=-.01). Six factors explained 61.1% of employment intention of mentally disabled persons.
Conclusion
The employment intention of a mentally disabled person was influenced by employment desire, diet self-efficacy, guardian's expectation, professional's support, quality of life, financial management and eating habits.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Concept Analysis of Motivation for Vocational Rehabilitation in Persons with Mental Disabilities
Eun-Seon An, Ji-Min Seo
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2015; 24(4): 279. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Quality of Life in People with Mental Disabilities using Mental Health Centers
Eun Kyung Byun, Seong-Sook Jun
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2011; 20(2): 157. CrossRef
-
919
View
-
3
Download
-
2
Crossref
|