Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Nurs > Volume 43(4); 2013 > Article
-
Original Article
- Development and Effects of a Simulation-based Education Program for Newborn Emergency Care
- So Young Yoo
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2013;43(4):468-477.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2013.43.4.468
Published online: August 30, 2013
Department of Nursing, Baekseok University, Cheonan, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Yoo, So Young. Department of Nursing, Baekseok University, 76 Munam-ro, Dongnam-gu, Cheonan 330-704, Korea. Tel: +82-41-550-2185, Fax: +82-41-550-2829, ku-ru@bu.ac.kr
• Received: January 25, 2013 • Accepted: June 13, 2013
© 2013 Korean Society of Nursing Science
Abstract
-
Purpose
- This study was conducted to develop a simulation-based education program for newborn emergency care based on most needed topics found from the needs assessment. This study consisted of two phases: developing the program and evaluating its effectiveness.
-
Methods
- The effectiveness of the program was tested in July, 2012, with 49 junior nursing students from C Nursing College in Seoul, who did not have any clinical experience in newborn care. The experimental group was given a three-hour lecture, three hours of clinical training, and a two-hour simulation program, whereas the control group only had the three-hour lecture.
-
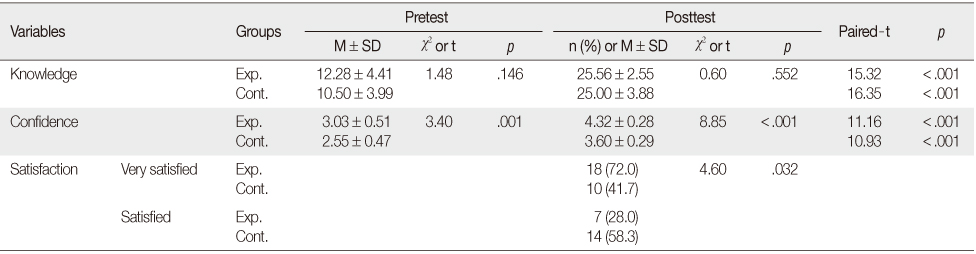
Results
- There was significant improvement in knowledge in both groups, but no significant differences according to educational methods. The experiment group was more confident of their care (4.32±.29) than the control group (3.60±.29) with the difference being significant (t=8.85, p<.001), and the experimental group was also more satisfied with the program (χ2=4.60, p=.032).
-
Conclusion
- As the results indicate 'the neonatal emergency care program' increased learners' knowledge, confidence and satisfaction with the program, it should be integrated into clinical training in pediatric nursing curriculum and in-service programs for nurses. To increase generalization further verification studies with various learner groups are needed.
This manuscript is based on a part of the author's doctoral dissertation from Ewha Womans University.
- 1. In: Ahn HS. editor. Hong Chang Yee textbook of pediatrics. 9th ed. Seoul: Daehan Printing & Publishing Co., Ltd.; 2007.
- 2. Anderson JM, Warren JB. Using simulation to enhance the acquisition and retention of clinical skills in neonatology. Semin Perinatol. 2011;35(2):59–67. http://dx.doi.org/10.1053/j.semperi.2011.01.004ArticlePubMed
- 3. Arnold J. The neonatal resuscitation program comes of age. J Pediatr. 2011;159(3):357–358. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jpeds.2011.05.053ArticlePubMed
- 4. Chang S, Kwon E, Kwon YO, Kwon HK. The effects of simulation training for new graduate critical care nurses on knowledge, selfefficacy, and performance ability of emergency situations at intensive care unit. J Korean Acad Adult Nurs. 2010;22(4):375–383.
- 5. Cheung N, Song Y. Clinical application of objective structured clinical examination (OSCE) for novice nurses. J Korean Acad Fundam Nurs. 2006;13(3):334–342.
- 6. Chung SH, Choi YS, Bae CW. Changes in the neonatal and infant mortality rate and the causes of death in Korea. Korean J Pediatr. 2011;54(11):443–455. http://dx.doi.org/10.3345/kjp.2011.54.11.443ArticlePubMedPMC
- 7. Erdfelder E, Faul F, Buchner A. GPOWER: A general power analysis program. Behav Res Methods Instrum Comput. 1996;28(1):1–11.ArticlePDF
- 8. Hur HK, Park SM. Effects of simulation based education, for emergency care of patients with dyspnea, on knowledge and performance confidence of nursing students. J Korean Acad Soc Nurs Educ. 2012;18(1):111–119.Article
- 9. Jeffries PR. A framework for designing, implementing, and evaluating simulations used as teaching strategies in nursing. Nurs Educ Perspect. 2005;26(2):96–103.PubMed
- 10. Jho MY. An analysis of research on nursing practice education in Korea. J Korean Acad Soc Nurs Educ. 2010;16(2):239–248.Article
- 11. Kassab M, Kenner C. Simulation and neonatal nursing education. Newborn Infant Nurs Rev. 2011;11(1):8–9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1053/j.nainr.2010.12.006Article
- 12. Kattwinkel J, Bloom RS. American Academy of Pediatrics & American Heart Association. Textbook of neonatal resuscitation. 6th ed. Elk Grove Village, IL: American Academy of Pediatrics; 2011.
- 13. Kim HR, Choi EJ. Development of a scenario and evaluation for SimBaby simulation learning of care for children with fever in emergency units. J Korea Contents Assoc. 2011;11(6):279–288.Article
- 14. Kim UO, Brousseau DC, Konduri GG. Evaluation and management of the critically ill neonate in the emergency department. Clin Pediatr Emerg Med. 2008;9(3):140–148.Article
- 15. Kim YH, Jang KS. Effect of a simulation-based education on cardio-pulmonary emergency care knowledge, clinical performance ability and problem solving process in new nurses. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2011;41(2):245–255. http://dx.doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2011.41.2.245ArticlePubMed
- 16. Kim YM, Oh YM, Kim HJ, Lee WJ, Im TH, Chung HS, et al. Development and pilot applications of simulation-based comprehensive emergency airway management courses. J Korean Soc Emerg Med. 2007;18(1):1–9.
- 17. Korean Academy of Nursing. The great encyclopedia of nursing science. Seoul: Korea Dictionary Research Publishing; 1996.
- 18. Lee SJ, Roh YS, Kim JO, Jang KI, Ryoo EN, Park YM. Comparison of multi-mode simulation and SimMan(R) simulation on evaluation of nursing care for patients with dyspnea. J Korean Acad Soc Nurs Educ. 2010;16(1):51–60.Article
- 19. Lee WS, Cho KC, Yang SH, Roh YS, Lee GY. Effects of problem-based learning combined with simulation on the basic nursing competency of nursing students. J Korean Acad Fundam Nurs. 2009;16(1):64–72.
- 20. Lee WS, Kim M. Effects and adequacy of high-fidelity simulation- based training for obstetrical nursing. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2011;41(4):433–443. http://dx.doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2011.41.4.433ArticlePubMed
- 21. Lindamood KE, Rachwal C, Kappus L, Weinstock P, Doherty EG. Development of a neonatal intensive care multidisciplinary crisis resource training program. Newborn Infant Nurs Rev. 2011;11(1):17–22.Article
- 22. Park JY. Self-assessment, self-efficacy and satisfaction after OSCE using smart phone. J Korean Acad Soc Nurs Educ. 2012;18(1):119–129.Article
- 23. Patel D, Piotrowski ZH, Nelson MR, Sabich R. Effect of a statewide neonatal resuscitation training program on Apgar scores among high-risk neonates in illinois. Pediatrics. 2001;107(4):648–655.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 24. Sanford PG. Simulation in nursing education: A review of the research. Qual Rep. 2010;15(4):1006–1011.Article
- 25. Shin HS, Shim KK. Nursing students' experiences on pediatric nursing simulation practice. J East West Nurs Res. 2010;16(2):147–155.
- 26. Sung MH. Correlations between motivation to achieve, clinical competency and satisfaction in clinical practice for diploma and baccalaureate nursing students. J Korean Acad Fundam Nurs. 2010;17(1):90–98.
- 27. Yang JJ. The effects of a simulation-based education on the knowledge and clinical competence for nursing students. J Korean Acad Soc Nurs Educ. 2012;18(1):14–24.Article
- 28. Yoo SY, Kim SH, Lee JH. Educational needs in the development of a simulation based program on neonatal emergency care for nursing students. J Korean Acad Child Health Nurs. 2012;18(4):170–176. http://dx.doi.org/10.4094/jkachn.2012.18.4.170Article
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- Preparedness training programs improved the emergency response and crucial outcomes among nursing students: a scoping review
Budi Mulyana, Rian Adi Pamungkas, Widia Sari, Anita Sukarno, Ernalinda Rosya, Wiwik Wariani
Frontiers of Nursing.2024; 11(2): 159. CrossRef - Sustained Effect of Simulation-Based Resuscitation Education on Knowledge, Self-Confidence, and Performance Ability of Neonatal Intensive Care Unit Nurses
Cho Yeon Lim, Mi Ryeong Song
The Journal of Continuing Education in Nursing.2024; 55(2): 79. CrossRef - Effects of gamification on academic motivation and confidence of undergraduate nursing students: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Young K. Seo, Chan M. Kang, Kun H. Kim, Ihn S. Jeong
Nurse Education Today.2024; 143: 106388. CrossRef - Development and Effectiveness of a Rapid Cycle Deliberate Practice Neonatal Resuscitation Simulation Program: A Quasi-Experimental Study
Sun-Yi Yang, Yun-Hee Oh
Healthcare.2024; 12(1): 104. CrossRef - Development and evaluation of simulation‐based scenario education program for professional oral hygiene care in intubated patient
Ma‐I Choi, Hie‐Jin Noh, Sun‐Young Han, Sung‐Suk Bae, GiYon Kim, So‐Jung Mun
Journal of Dental Education.2023; 87(11): 1512. CrossRef - The Effectiveness of Learning to Use HMD-Based VR Technologies on Nursing Students: Chemoport Insertion Surgery
Ae-Ri Jung, Eun-A Park
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(8): 4823. CrossRef - The effects of neonatal resuscitation gamification program using immersive virtual reality: A quasi-experimental study
Sun-Yi Yang, Yun-Hee Oh
Nurse Education Today.2022; 117: 105464. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Debriefing for Meaningful Learning-based simulation training on high-risk neonatal care: A randomized controlled simulation study
Sun-Yi Yang, Yun-Hee Oh
Clinical Simulation in Nursing.2021; 61: 42. CrossRef - Effectiveness of neonatal emergency nursing education through simulation training: Flipped learning based on Tanner’s Clinical Judgement Model
Sun‐Yi Yang
Nursing Open.2021; 8(3): 1314. CrossRef - Simulation-based education program on postpartum hemorrhage for nursing students
Miok Kim, Juyoung Ha
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2020; 26(1): 19. CrossRef - Developing Nursing Standard Guidelines for Nurses in a Neonatal Intensive Care Unit: A Delphi Study
Hanna Lee, Da-Jung Kim, Jeong-Won Han
Healthcare.2020; 8(3): 320. CrossRef - An Analysis of Pediatric Emergency Nursing Practice and Nursing Competence among Emergency Department Nurses
Heekyung Jeon, YeoJin Im
Child Health Nursing Research.2019; 25(2): 143. CrossRef - The Effects of Simulation Education for New Nurses on Emergency Management Using Low-fidelity Simulator
Young Hee Lee, Hye Young Ahn
Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2019; 25(3): 331. CrossRef - Effects of Simulation-Based Education before Clinical Experience on Knowledge, Clinical Practice Anxiety, and Clinical Performance Ability in Nursing Students
Eun Jeong Ko, Eun Jung Kim
Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2019; 25(3): 289. CrossRef - Development and Effects a Simulation-based Emergency Airway Management Education Program for Nurses in a Neonatal Intensive Care Unit
Minjung Kim, Sunghee Kim
Child Health Nursing Research.2019; 25(4): 518. CrossRef - Effects of nursing process-based simulation for maternal child emergency nursing care on knowledge, attitude, and skills in clinical nurses
Sunghee Kim, Gisoo Shin
Nurse Education Today.2016; 37: 59. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Student Learning with a Simulation Program focusing on Cardiac Arrest in Knowledge, Self-confidence, Critical Thinking, and Clinical Performance Ability
Min-Jeong Chae, Soon-Hee Choi
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2016; 28(4): 447. CrossRef - Effects of Direct Practice of Newborn Health Assessment on Students’ Nursing Clinical Competence and Self-Efficacy
Seol Hui Park, Se Ang Ryu
Child Health Nursing Research.2016; 22(2): 117. CrossRef - Development and Effects of Integrated Simulation Program (Maternal-Child) for Nursing Students
Hyun Jung Park, Sun Hee Lee
Child Health Nursing Research.2015; 21(4): 293. CrossRef - Effects of Integrated Nursing Practice Simulation-based Training on Stress, Interest in Learning, and Problem-Solving Ability of Nursing Students*
Sun-Nam Park, Min-Sun Chu, Yoon-Young Hwang, Sun-Hee Kim, Sun-Kyoung Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2015; 22(4): 424. CrossRef - Effects of the Use of High-Fidelity Human Simulation in Nursing Education: A Meta-Analysis
Jin Lee, Pok-Ja Oh
Journal of Nursing Education.2015; 54(9): 501. CrossRef - Stress and Satisfaction from Simulation-based Practice and Clinical Practice on High-risk Newborn Nursing
Sun-Nam Park, Yunsoo Kim
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2015; 21(1): 86. CrossRef - The Effects of Video-based Peer assisted Learning in Standardized Patients Simulation: Pre and Post Operative Care
In-Hee Park, Sujin Shin
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2015; 27(1): 73. CrossRef - Effects of a Colonoscopy based Simulation Education Program on Knowledge and Clinical Performance in Nursing Students
Hyo-Youn Kim, Hae-Ran Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2015; 27(2): 135. CrossRef - Effect of Simulation-based Advanced Cardiopulmonary Life Support Education for Nursing Students Hospitals
Hyo-Ju Jung, Min-Jeong Chae
The Korean Journal of Health Service Management.2015; 9(3): 127. CrossRef - A Review on the Use of Effect Size in Nursing Research
Hyuncheol Kang, Kyupil Yeon, Sang-Tae Han
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2015; 45(5): 641. CrossRef
- We recommend
- Related articles
-
- Development and effects of a media-based reproductive health promotion program for male high school students at male high school: a quasi-experimental study
- Development and Effectiveness of Progressive Simulation Education Program on Medication Safety for Nursing Students
- Effectiveness of Simulation-Based Education for Caring Patients with COVID-19
- Development and Effectiveness Evaluation of Comprehensive Mobile-Based, Breastfeeding Promotion Program for Mothers with Gestational Diabetes
Development and Effects of a Simulation-based Education Program for Newborn Emergency Care
Development and Effects of a Simulation-based Education Program for Newborn Emergency Care
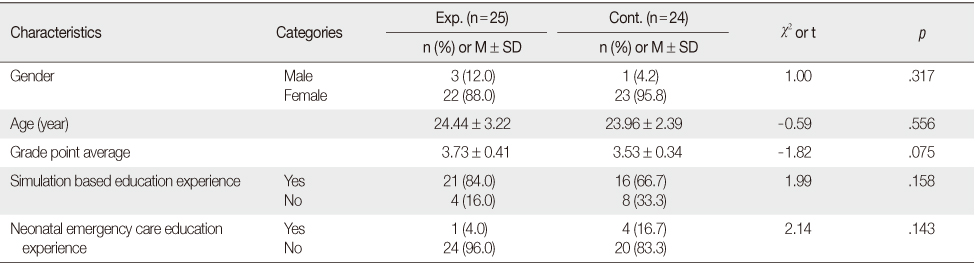
General Characteristics and Homogeneity of Experimental and Control Groups (N=49)
Exp.=Experimental group; Cont.=Control group.
Comparison between Experimental Group and Control Group for Mean Scores for Variables (N=49)
Exp.=Experimental group(n=25); Cont.=Control group (n=24).
Performance Test Scores for Each Module (N=25)
Table 1
General Characteristics and Homogeneity of Experimental and Control Groups (N=49)
Exp.=Experimental group; Cont.=Control group.
Table 2
Comparison between Experimental Group and Control Group for Mean Scores for Variables (N=49)
Exp.=Experimental group(n=25); Cont.=Control group (n=24).
Table 3
Performance Test Scores for Each Module (N=25)
 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 Cite
Cite

