Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Nurs > Volume 38(5); 2008 > Article
-
Original Article
- The Mediating Effect of Depression in the Relationship between Muscle Strength of Extremities and Falls among Community-Dwelling Elderly
- Hyoung-Sook Park1, Kyung-Yeon Park2
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2008;38(5):730-738.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2008.38.5.730
Published online: October 12, 2008
1Professor, College of Nursing, Pusan National University, Busan, Korea
2Full-time Lecturer, Department of Nursing, Silla University, Busan, Korea
1Professor, College of Nursing, Pusan National University, Busan, Korea
2Full-time Lecturer, Department of Nursing, Silla University, Busan, Korea
- Address reprint requests to : Park, Kyung-Yeon Department of Nursing, Silla University, San 1-1 Gwaebeop-dong, Sasang-gu, Busan 617-736, Korea Tel: 82-51-999-5461 Fax: 82-51-999-5470 E-mail: kypark@silla.ac.kr
Copyright © 2008 Korean Society of Nursing Science
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Abstract
-
Purpose
- The purpose of this study was to identify the mediating effect of depression in the relationship between muscle strength of extremities and falls among community-dwelling elderly.
-
Methods
- Two hundred forty-seven participants were recruited from a public health center, a hall for the aged and a school for the aged in B city. Face-to-face interviews were conducted using questionnaires from May to September of 2007. Data was analyzed with descriptive statistics, Pearson correlation, and multiple regression using the SPSS WIN 14.0 program.
-
Results
- There was a significantly negative relationship between muscle strength of lower extremities and falls, muscle strength of left upper extremity and falls, and muscle strength of right upper extremity and falls. Depression positively correlated with falls. Depression showed mediating effects between muscle strength of extremities and falls. Weakness of muscle strength of extremities increased depression and the increased depression increased the frequencies of falls.
-
Conclusion
- For the effective management and prevention of community-dwelling older adults’ falls, exercise programs including depression-decreasing strategies should be established. These exercise programs can decrease depression which is the mediator role between the degrees of muscle strength of extremities and falls.
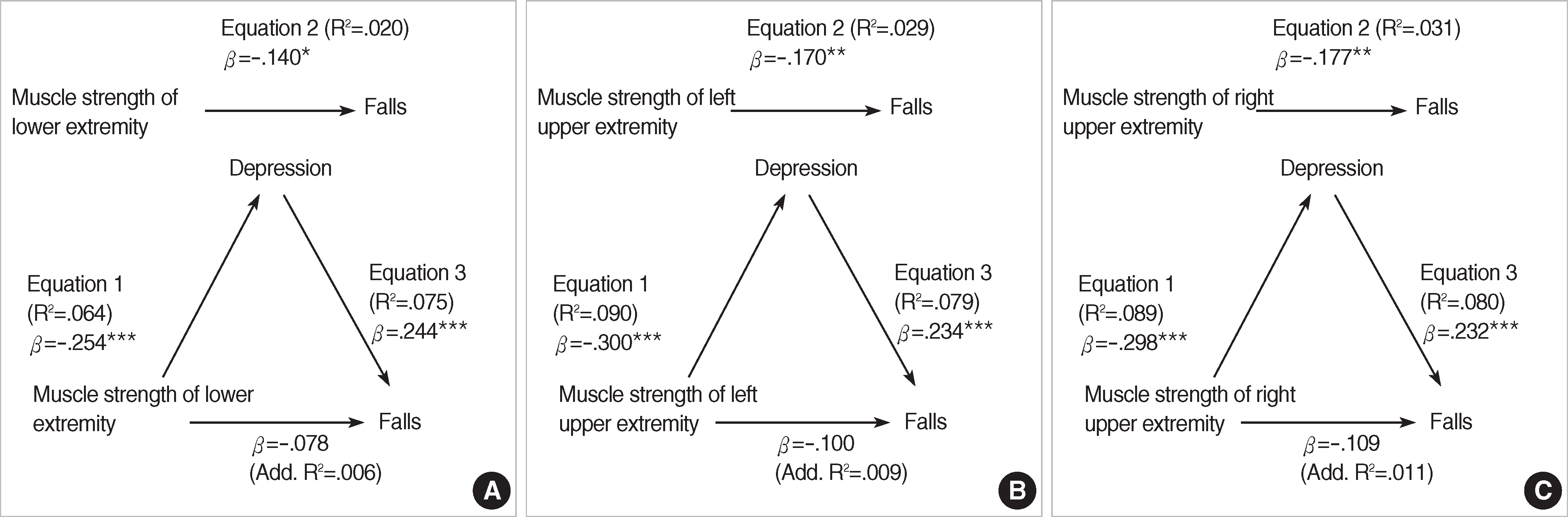
| Predictors | F | β | R2 | Additional R2 | Mediating effect |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Muscle strength of lower extremity (MSLE) | |||||
| Equation 1. MSLE → depression | 16.877*** | -.254*** | .064 | - | |
| Equation 2. MSLE → falls | 4.914* | -.140* | .020 | - | |
| Equation 3. Depression → falls | 9.941*** | .244*** | .075 | - | |
| MSLE → falls | -.078 | .006 | Yes | ||
| Muscle strength of left upper extremity (MSLUE) | |||||
| Equation 1. MSLUE → depression | 24.161*** | -.300*** | .090 | - | |
| Equation 2. MSLUE → falls | 7.294** | -.170** | .029 | - | |
| Equation 3. Depression → falls | 10.422*** | .234*** | .079 | - | |
| MSLUE → falls | -.100 | .009 | Yes | ||
| Muscle strength of right upper extremity (MSRUE) | |||||
| Equation 1. MSRUE → depression | 23.800*** | -.298*** | .089 | - | |
| Equation 2. MSRUE → falls | 7.966** | -.177** | .031 | - | |
| Equation 3. Depression → falls | 10.659*** | .232*** | .080 | - | |
| MSRUE → falls | -.109 | .011 | Yes |
- Arfken C. L., Lach H. W., Birge S. J., Miller J.P. 1994;The prevalence and correlates of fear of falling in elderly persons living in the community. American Journal of Public Health. 84:565–570.ArticlePubMedPMC
- Biderman A., Cwikel J., Fried A. V., Galinsky, D. 2002;Depression and falls among community dwelling elderly people: A search for common risk factors. Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health. 56:631–636.ArticlePubMedPMC
- Chang C. M., Kang H.S. 2004;Physical function and physiological status in the elderly those who experienced a fall or not. Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing. 7:48–57.
- Chu L. W., Chi I., Chiu A.Y. 2005;Incidence and predictors of falls in the Chinese elderly. Annals of the Academy of Medicine, Singapore. 34:60–72.ArticlePubMed
- Evans G. W., Lepore S.J. 1997.Moderating and mediating processes in environment behavior research. In: Moore G.T., Marans R.W., editors. Advances in environment, behavior, and design. 4. New York, NY: Plenum.Article
- Ga mann, K. G., Rupprecht, R., Freiberger, E., & for the IZG Study Group. 2008;Predictors for occasional and recurrent falls in . community-dwelling older people. Zeitschrift fur Gerontologie und . Geriatrie: Organ der Deutschen Gesellschaft fur Gerontologie und Geriatrie. 41:1–8.
- Gerety M. B., Williams J. Jr., Mulrow C. D., Cornell J. E., Kadri A. A., Rosenberg J., et al. 1994;Performance of case-finding tools for depression in the nursing home: Influence of clinical and functional characteristics and selection of optimal threshold scores. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society. 42:1103–1109.ArticlePubMed
- Gu M. O., Jeon M. Y., Eun, Y. 2006;The development and effect of an tailed falls prevention exercise for older adults. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 36:341–352.PubMed
- Gu M. O., Jeon M. Y., Kim H. J., Eun, Y. 2005;A review of exercise interventions for fall prevention in the elderly. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 35:1101–1112.ArticlePubMedPDF
- Hybels C. F., Blazer D.G. 2003;Epidemiology of late-life men-taldisorders. Clinics in Geriatric Medicine. 19:663–696.ArticlePubMed
- Jeon M. Y., Jeong H. C., Choe M.A. 2001;A study on the elderly patients hospitalized by the fracture from the fall. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 31:443–453.ArticlePDF
- Kannus P., Sievanen H., Palvanen M., Jarvinen T., Parkkari, J. 2005;Prevention of falls and consequent injuries in elderly people. Lancet. 26:1885–1893.Article
- Kim H.S. 2001.Senior fitness test manual. Seoul: Daehan Media.
- Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2005;Injury surveillance monthly report. 1:1–5. Retrieved July 9, 2008, from. http://www.cdc.go.kr/kcdchome.portal?_nfpb=true&_pageLa-bel=HPPUNI130&rootmenuid=20010&targetmenuid=20202&boardid=170&boardtype=BRDTYPE01&rootcmsid=&con-tentid=
- Lee H. J., Park K. Y., Park H.S. 2005;Self care activity, metabolic control, and cardiovascular risk factors in accordance with the levels of depression of clients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 35:283–291.ArticlePubMedPDF
- MacRae P. G., Feltner M. E., Reinsch, S. 1994;A 1-year exercise program for older women: Effects on falls, injuries, and physical performance. Journal of Aging and Physical Activity. 2:127–142.Article
- Min H.S. 1999.The Effects of personal characteristics and metamem-ory on the old adults’ memory performance. Unpublished doctoral dissertation. Seoul National University; Seoul.
- Park E. Y., Lee J.H. 2005;The effect of complex exercise program for prevention of falls on fitness in elderly. Exercise Science. 14:181–192.
- Park S.W. 1997.Effect of reminiscence therapy on depression for elder-lypatient. Unpublished master’s thesis. Yonsei University; Seoul.
- Robinson-Smith G., Johnston M. V., Allen, J. 2000;Self care, self-efficacy, quality of life, and depression after stroke. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. 81:460–464.ArticlePubMed
- Rubenstein L. Z., Josephson K.R. 2002;The epidemiology of falls and syncope. Clinics in Geriatric Medicine. 18:141–158.ArticlePubMed
- Schoenfelder D.P. 2000;A fall prevention for elderly individuals-Exercise in long term care settings. Journal of Gerontological Nursing. 26:43–51.PubMed
- Sheikh J. I., Yesavage J.A. 1986;Geriatric depression scale (GDS): Recent evidence and development of a shorter version. Clinical Gerontologist. 5:165–173.Article
- Shin K. R., Kang Y., Jung D., Choi K.A. 2007;A studyon the depression, somatic symptom, activities of daily living forthe elder-lywomen in an urban area. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 37:1131–1138.ArticlePubMedPDF
- Stalenhoef P. A., Diederiks J. P., Knottnerus J. A., Kester A. D., Crebolder H.F. 2002;A risk model for the prediction of recurrent falls in community-dwelling elderly: A prospective cohort study. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology. 55:1088–1094.ArticlePubMed
- Stel V. S., Smit J. H., Pluijm S. M., Lips, P. 2004;Consequences of falling in older men and women and risk factors for health ser-viceuse and functional decline. Age Ageing. 33:58–65.ArticlePubMed
- Tabachnick B. G., Fidell L.S. 2001.Using multivariate statistics. 4th ed.Boston: Allyn & Bacon.
- Tinetti M. E., Speechley M., Ginter S.F. 1988;Risk factors for falls among elderly persons living in the community. The New England Journal of Medicine. 319:1701–1707.ArticlePubMed
- Whooley M. A., Kip K. E., Cauley J. A., Ensrud K. E., Nevitt M. C., Browner W.S. 1999;Depression, falls, and risk of fracture in older women. Study of Osteoporotic Fractures Research Group. Archives of Internal Medicine. 159:484–490.PubMed
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- A Study on the Depression, Family Support and Life Satisfaction in the Elderly
Sunsook Sim, Miran Bang
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2017; 20(2): 122. CrossRef - The Effects of a Regular Walking Program on Body Composition, Functional Fitness, and Anxiety and Depression in Elderly Women
Samcheol Lee
Journal of The Korean Society of Integrative Medicine.2016; 4(2): 67. CrossRef - Study on the Preference Survey for Developing the Fall Impact Protective Clothing - Targeting Women ages of 50s to 70s -
Jung Hyun Park, Jeong Ran Lee
Fashion & Textile Research Journal.2014; 16(1): 101. CrossRef - Unhealthy and unsafe practices associated with symptoms of depression among injured patients
Sara L. Cooper, Allan W. Graham, Cynthia W. Goss, Carolyn DiGuiseppi
International Journal of Injury Control and Safety Promotion.2011; 18(3): 243. CrossRef - Impact of depression and activities of daily living on the fear of falling in Korean community‐dwelling elderly
Kyung Rim Shin, Younhee Kang, Mi Young Kim, Dukyoo Jung, Jeong Soo Kim, Chong Min Hong, Eun Suk Yun, Rye Won Ma
Nursing & Health Sciences.2010; 12(4): 493. CrossRef - Prevalence and Predictors of Geriatric Depression in Community-Dwelling Elderly
Jeung-Im Kim, Myoung-Ae Choe, Young Ran Chae
Asian Nursing Research.2009; 3(3): 121. CrossRef - Força muscular de idosos com e sem depressão participantes de um programa de ginástica
Vanessa Helena Santana Dalla Déa, Edison Duarte, José Rubens Rebelatto, Alessandra Paiva de Castro
Acta Ortopédica Brasileira.2009; 17(6): 322. CrossRef
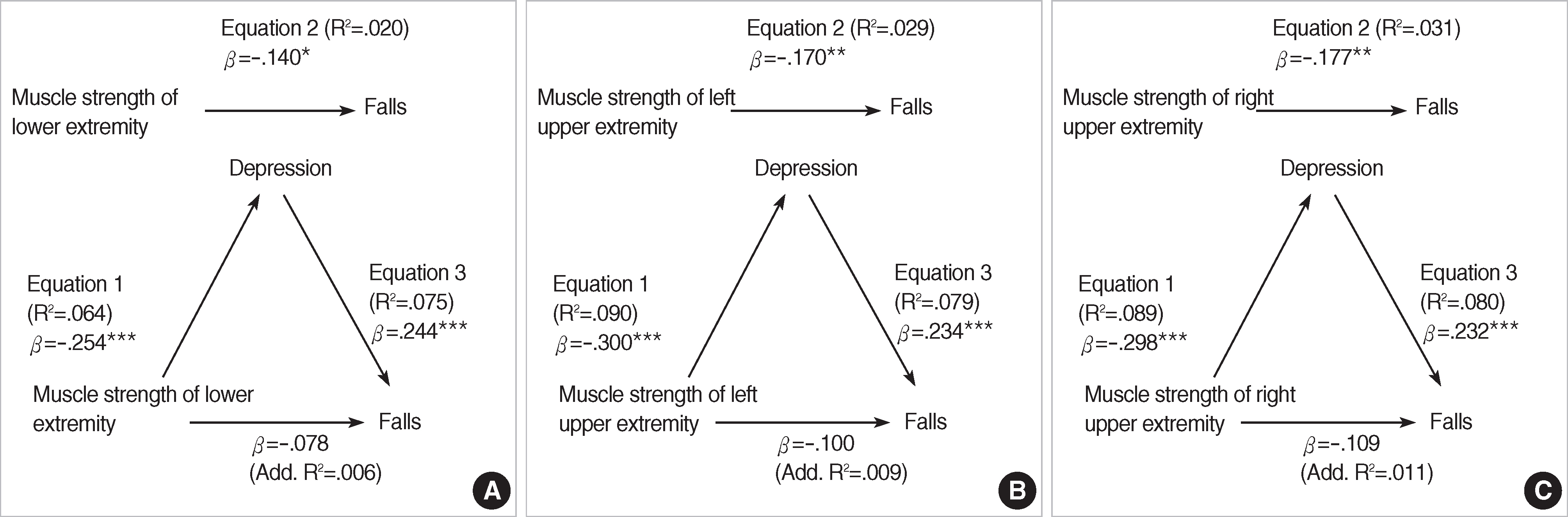
Figure 1.
General Characteristics of Participants (N=247)
| Characteristics | n | % |
|---|---|---|
| Gender | ||
| Male | 38 | 15.4 |
| Female | 209 | 84.6 |
| Age (yr) | ||
| 65-69 | 16 | 6.5 |
| 70-79 | 138 | 55.8 |
| 80 or more | 93 | 37.7 |
| Mean±SD | 77.9±5.4 | |
| Education | ||
| None | 133 | 53.9 |
| Elementary school | 65 | 26.3 |
| Middle school or higher | 49 | 19.8 |
| Spouse | ||
| Yes | 58 | 23.5 |
| No | 189 | 76.5 |
| Living arrangement | ||
| Children offspring | 117 | 47.4 |
| Spouse | 43 | 17.4 |
| Solitude | 86 | 34.8 |
| Others | 1 | 0.4 |
| Perceived economic status | ||
| High | 6 | 2.4 |
| Middle | 120 | 48.6 |
| Low | 121 | 49.0 |
| Perceived health status | ||
| Good | 47 | 19.0 |
| Moderate | 81 | 32.8 |
| Poor | 119 | 48.2 |
| Regular exercise | ||
| Yes | 119 | 48.2 |
| No | 128 | 51.8 |
| Pre-existing chronic disease | ||
| Yes | 168 | 68.0 |
| No | 79 | 32.0 |
Descriptive Statistics of Research Variables (N=247
| Variables | Mean | SD | Actual range | Reference range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M. strength of lower ext. (Frequency) | 12.67 | 4.46 | 0-28 | |
| Male | 14.45 | 4.22 | 4-26 | 8-18 |
| Female | 12.35 | 4.43 | 0-28 | 8-16 |
| M. strength of upper ext. (Hand grip) | ||||
| Left hand (kg) | 14.89 | 5.66 | 0-35 | |
| Male | 21.91 | 6.58 | 0-35 | 30-40 |
| Female | 13.61 | 4.42 | 0-24 | 17-24 |
| Right hand (kg) | 15.20 | 5.50 | 0-36 | |
| Male | 21.94 | 6.21 | 0-36 | 30-40 |
| Female | 13.98 | 4.36 | 0-33 | 17-24 |
| Depression | 7.30 | 3.82 | 0-15 | 0-5 |
| Falls | ||||
| Frequency | 0.68 | 1.13 | 0-4 | |
| n | % | |||
| Yes | 84 | 34.01 | ||
| 1 | 38 | 45.24 | ||
| 2 | 20 | 23.81 | ||
| 3 | 15 | 17.86 | ||
| 4 or more | 11 | 13.10 | ||
| No | 163 | 65.99 |
M.=Muscle; Ext.=Extremities.
Correlations among Study Variables (N=247)
| M. strength. of lower ext. r (p) | M. strength of left upper ext. r (p) | M. strength of right upper ext. r (p) | Depression r (p) | Falls r (p) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M. strength of lower ext. | |||||
| M. strength of left upper ext. | .412 (<.001) | ||||
| M. strength of right upper ext. | .444 (<.001) | .781 (<.001) | |||
| Depression | -.254 (<.001) | -.300 (<.001) | -.298 (<.001) | ||
| Falls | -.140 (.028) | -.170 (.007) | -.177 (.005) | .264 (<.001) |
M.=Muscle; Ext.=Extremities.
Mediating Effects of Depression in the Relationship between Muscle Strength of Extremities and Falls (N=247)
| Predictors | F | β | R2 | Additional R2 | Mediating effect |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Muscle strength of lower extremity (MSLE) | |||||
| Equation 1. MSLE → depression | 16.877 |
-.254 |
.064 | - | |
| Equation 2. MSLE → falls | 4.914 |
-.140 |
.020 | - | |
| Equation 3. Depression → falls | 9.941 |
.244 |
.075 | - | |
| MSLE → falls | -.078 | .006 | Yes | ||
| Muscle strength of left upper extremity (MSLUE) | |||||
| Equation 1. MSLUE → depression | 24.161 |
-.300 |
.090 | - | |
| Equation 2. MSLUE → falls | 7.294 |
-.170 |
.029 | - | |
| Equation 3. Depression → falls | 10.422 |
.234 |
.079 | - | |
| MSLUE → falls | -.100 | .009 | Yes | ||
| Muscle strength of right upper extremity (MSRUE) | |||||
| Equation 1. MSRUE → depression | 23.800 |
-.298 |
.089 | - | |
| Equation 2. MSRUE → falls | 7.966 |
-.177 |
.031 | - | |
| Equation 3. Depression → falls | 10.659 |
.232 |
.080 | - | |
| MSRUE → falls | -.109 | .011 | Yes |
*p<.05
**p<.01
***p<.001.
Equation 1. IV → mediator to check beta and R2; Equation 2. IV → DV to check beta and R2 (it should be significant to test mediator effect); Equation 3. Step 1: mediator → DV to check beta and R2; Step 2: IV → DV to check beta and R2.
M.=Muscle; Ext.=Extremities.
M.=Muscle; Ext.=Extremities.
p<.05 p<.01 p<.001. Equation 1. IV → mediator to check beta and R2; Equation 2. IV → DV to check beta and R2 (it should be significant to test mediator effect); Equation 3. Step 1: mediator → DV to check beta and R2; Step 2: IV → DV to check beta and R2.
 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION
 Cite
Cite

