Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Nurs > Volume 46(6); 2016 > Article
-
Original Article
- Decision Making Experience on Breast Reconstruction for Women with Breast Cancer
- Myungsun Yi, Woo Joung Joung, Eun Young Park, Eun Jin Kwon, Haejin Kim, Ji Young Seo
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2016;46(6):894-904.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2016.46.6.894
Published online: December 30, 2016
1College of Nursing·Research Institute of Nursing Science, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
2Research Institute of Nursing Science, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
3College of Nursing, Gachon University, Inchon, Korea.
4Department of Nursing, Bucheon University, Bucheon, Korea.
5College of Nursing, Dankook University, Cheonan, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Joung, Woo Joung. Research Institute of Nursing Science, Seoul National University, 103 Daehak-ro, Jongno-gu, Seoul 03080 ,Korea. Tel: +82-2-740-8460, Fax: +82-2-740-8837, kimsoft1@snu.ac.kr
© 2016 Korean Society of Nursing Science
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NoDerivs License. (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nd/4.0/) If the original work is properly cited and retained without any modification or reproduction, it can be used and re-distributed in any format and medium.
Abstract
-
Purpose
- The purpose of this study was to explore decision making experiences of Korean women with breast cancer who underwent breast reconstruction with/after a mastectomy.
-
Methods
- Data were collected during 2015-2016 through individual in-depth interviews with 10 women who had both mastectomy and breast reconstruction, and analyzed using phenomenological method to identify essential themes on experiences of making a decision to have breast reconstruction.
-
Results
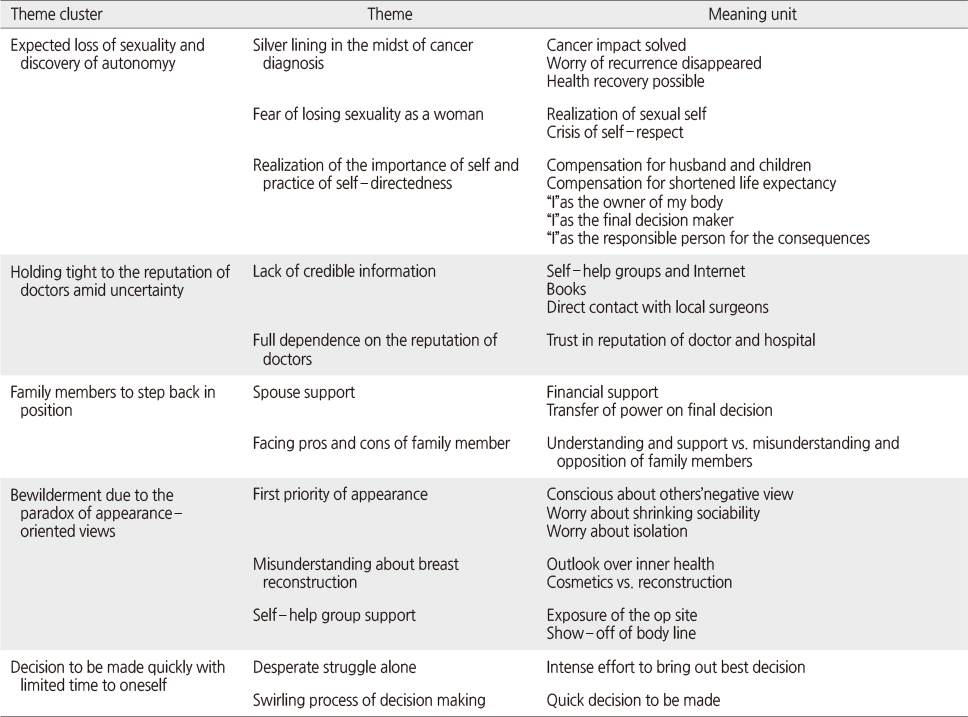
- Five theme clusters emerged. First, “expected loss of sexuality and discovery of autonomy” illustrates various aims of breast reconstruction. Second, “holding tight to the reputation of doctors amid uncertainty” specifies the importance of a trust relationship with their physician despite a lack of information. Third, “family members to step back in position” describes support or opposition from family members in the decision making process. Fourth, “bewilderment due to the paradox of appearance-oriented views” illustrates paradoxical environment, resulting in confusion and anger. Lastly, “decision to be made quickly with limited time to oneself” describes the crazy whirling process of decision making.
-
Conclusion
- Findings highlight aims, worries, barriers, and facilitators that women with breast cancer experience when making a decision about breast reconstruction. Deciding on breast reconstruction was not only a burden for women in a state of shock with a diagnosis of breast cancer, but also an opportunity to decide to integrate their body, femininity, and self which might be wounded from a mastectomy. These findings will help oncology professionals provide effective educational counselling before the operation to promote higher satisfaction after the operation.
- 1. National Cancer Information Center. Cancer information service [Internet]. Goyang, Author. 2016;cited 2016 January 20. Available from:http://www.cancer.go.kr/mbs/cancer/subview.jsp?id=cancer_100100000000
- 2. Chung IY, Kang E, Yang EJ, Lim JY, Kim EK, Kim HA, et al. Survey of psychosocial problems facing breast cancer survivors after undergoing a mastectomy and their awareness of breast reconstruction. J Breast Cancer. 2011;14:Suppl 1. S70–S76. Article
- 3. Piot-Ziegler C, Sassi ML, Raffoul W, Delaloye JF. Mastectomy, body deconstruction, and impact on identity: A qualitative study. Br J Health Psychol. 2010;15(Pt 3):479–510. ArticlePubMed
- 4. Furlan VLA, Sabino Neto M, Abla LEF, Oliveira CJR, Lima ACD, Ruiz BFDO, et al. Quality of life and self-esteem after mastectomy in patients who did or did not undergo breast reconstruction. Revista Brasileira de Cirurgia Plástica. 2013;28(2):264–269.
- 5. Nam S, Park S, Lee DW, Song SY, Park HS, Kim SI, et al. Clinical outcome of immediate breast reconstruction after mastectomy for breast cancer. J Breast Dis. 2014;2(2):44–50. Article
- 6. Nissen MJ, Swenson KK, Kind EA. Quality of life after postmastectomy breast reconstruction. Oncol Nurs Forum. 2002;29(3):547–553. ArticlePubMed
- 7. Fernández-Delgado J, López-Pedraza MJ, Blasco JA, Andradas-Aragones E, Sánchez-Méndez JI, Sordo-Miralles G, et al. Satisfaction with and psychological impact of immediate and deferred breast reconstruction. Ann Oncol. 2008;19(8):1430–1434. ArticlePubMed
- 8. Kang HJ, Kim SW, Noh DY, Youn YK, Oh SK, Choe KJ, et al. Immediate breast reconstruction after a mastectomy for breast cancer. J Korean Surg Soc. 2000;59(5):584–589.
- 9. Ceradini DJ, Levine JP. Breast cancer reconstruction: More than skin deep. Prim Psychiatry. 2008;15(10):72–80.
- 10. Korean Breast Cancer Society. Breast cancer facts & figures [Internet]. Seoul, Author. 2015;cited 2016 June 10. Available from:http://www.kbcs.or.kr/journal/file/2015_Breast_Cancer_Facts_and_Figures_updated.pdf
- 11. Lee CN, Hultman CS, Sepucha K. What are patients’ goals and concerns about breast reconstruction after mastectomy? Ann Plast Surg. 2010;64(5):567–569. ArticlePubMed
- 12. Wolf L. The information needs of women who have undergone breast reconstruction. Part I: Decision-making and sources of information. Eur J Oncol Nurs. 2004;8(3):211–223. ArticlePubMed
- 13. Wolf L. The information needs of women who have undergone breast reconstruction. Part II: Information giving and content of information. Eur J Oncol Nurs. 2004;8(4):315–324. ArticlePubMed
- 14. Sheehan J, Sherman KA, Lam T, Boyages J. Association of information satisfaction, psychological distress and monitoring coping style with post-decision regret following breast reconstruction. Psychooncology. 2007;16(4):342–351. ArticlePubMed
- 15. Nissen MJ, Swenson KK, Kind EA. Quality of life after postmastectomy breast reconstruction. Oncol Nurs Forum. 2002;29(3):547–553. ArticlePubMed
- 16. Harcourt DM, Rumsey NJ, Ambler NR, Cawthorn SJ, Reid CD, Maddox PR, et al. The psychological effect of mastectomy with or without breast reconstruction: A prospective, multicenter study. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2003;111(3):1060–1068. ArticlePubMed
- 17. Finlay L. Ambiguous encounters: A relational approach to phenomenological research. Indo-Pac J Phenomenol. 2009;9(1):1–17. Article
- 18. Patton MQ. Qualitative research methods. Newbury Park, CA: Sage; 1980. p. 1–381.
- 19. Colaizzi PF. Psychological research as the phenomenologist views it. In: Valle RS, King M, editors. Existential-phenomenological alternatives for psychology. New York, NY: Oxford University Press; 1978. p. 48–71.
- 20. Guba EG, Lincoln YS. Effective evaluation: Improving the usefulness of evaluation results through responsive and naturalistic approaches. San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass; 1981. p. 1–444.
- 21. Fang SY, Balneaves LG, Shu BC. “A struggle between vanity and life”: The experience of receiving breast reconstruction in women of Taiwan. Cancer Nurs. 2010;33(5):E1–E11. PMC
- 22. Rubin LR. “Does that make me a woman?”: Breast cancer, mastectomy, and breast reconstruction decisions among sexual minority women. Psychol Women Q. 2011;35(3):401–414.
- 23. Sandham C, Harcourt D. Partner experiences of breast reconstruction post mastectomy. Eur J Oncol Nurs. 2007;11(1):66–73. ArticlePubMed
- 24. Osuch JR, Silk K, Price C, Barlow J, Miller K, Hernick A, et al. A historical perspective on breast cancer activism in the United States: From education and support to partnership in scientific research. J Womens Health (Larchmt). 2012;21(3):355–362. ArticlePubMedPMC
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Mental health in female breast cancer survivors post-mastectomy: A structural model based on Roy's adaptation model
Hyeng Sook Yoon, Eunjung Ryu
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2025; 12: 100820. CrossRef - Influence of body image on quality of life in breast cancer patients undergoing breast reconstruction: Mediating of self‐esteem
Yunhee Jang, Mihyeon Seong, Sohyune Sok
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2023; 32(17-18): 6366. CrossRef - Effects of decision aids on breast reconstruction: A systematic review and meta‐analysis of randomised controlled trials
Shu Yang, Lin Yu, Chunmiao Zhang, Mengmeng Xu, Qi Tian, Xuan Cui, Yantong Liu, Shuanghan Yu, Minglu Cao, Wei Zhang
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2023; 32(7-8): 1025. CrossRef - “Struggling to Accept the New Breast as Part of My Body” – The Challenge of Immediate Breast Reconstruction in Women With Breast Cancer
Jeehee Han, Juhye Jin, Sanghee Kim, Dong Won Lee, Sue Kim
Cancer Nursing.2022; 45(4): 262. CrossRef - Do COVID-19–Related Treatment Changes Influence Fear of Cancer Recurrence, Anxiety, and Depression in Breast Cancer Patients?
Soo Yeon Kim, Sue Kim
Cancer Nursing.2022; 45(2): E628. CrossRef - A Decision Tree Model for Breast Reconstruction of Women with Breast Cancer: A Mixed Method Approach
Eun Young Park, Myungsun Yi, Hye Sook Kim, Haejin Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(7): 3579. CrossRef - The Lived Experience of Body Alteration and Body Image with Regard to Immediate Breast Reconstruction among Women with Breast Cancer
Jeonghee Ahn, Eunyoung E Suh
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2021; 51(2): 245. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Quality of Life Among Breast Cancer Patients Following Immediate Breast Reconstruction
A Young Kim, Jeong Hye Kim
Asian Oncology Nursing.2020; 20(1): 1. CrossRef - Korean Translation and Psychometric Evaluation of Korean Version EORTC QLQ-BRECON23
Soo-Kyung Bok, Youngshin Song, Ancho Lim, Hyunsuk Choi, Hyunkyung Shin, Sohyun Jin
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(24): 9163. CrossRef - Operation Experiences of Women with Breast Cancer
Hyeon-Young Kim, Sun Hwa Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2020; 27(2): 129. CrossRef - “Waiting for breast reconstruction”: An interpretative phenomenological analysis of heterosexual couples’ experiences of mastectomy for breast cancer
Kristopher Lamore, Cécile Flahault, Léonor Fasse, Aurélie Untas
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2019; 42: 42. CrossRef - Breast reconstruction statistics in Korea from the Big Data Hub of the Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service
Jae-Won Kim, Jun-Ho Lee, Tae-Gon Kim, Yong-Ha Kim, Kyu Jin Chung
Archives of Plastic Surgery.2018; 45(05): 441. CrossRef
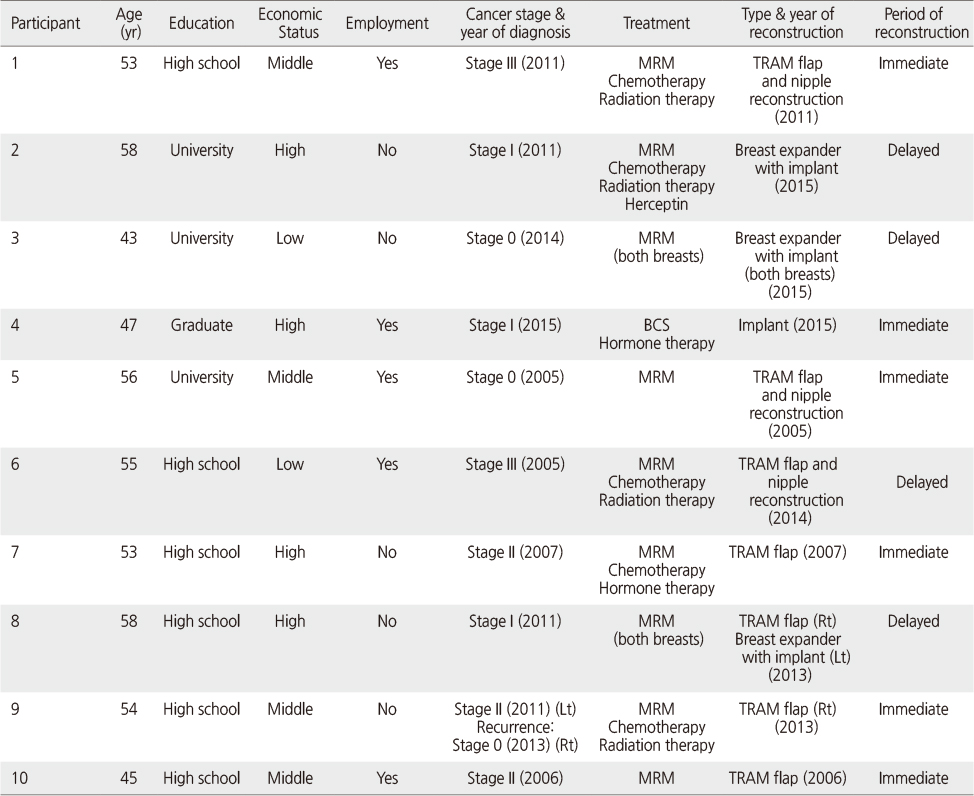
Demographic and Disease-related Characteristics of the Participants
MRM=Modified radical mastectomy; BCS=Breast conservative surgery; TRAM=Transverse rectus abdominis muscle.
Theme Clusters and Themes on Decision Making Experience of Breast Reconstruction
MRM=Modified radical mastectomy; BCS=Breast conservative surgery; TRAM=Transverse rectus abdominis muscle.
 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION
 Cite
Cite

