Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Nurs > Volume 45(5); 2015 > Article
-
Original Article
- Disturbance in ADL from Chemotherapy-induced Peripheral Neuropathy and Quality of Life in Cancer Patients: The Mediating Effect of Psychological Distress
- Kyung Yeon Kim, Seung Hee Lee, Jeong Hye Kim, Pok Ja Oh
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2015;45(5):661-670.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2015.45.5.661
Published online: October 30, 2015
1Korea Institude of Radiological & Medical Science, Seoul, Korea.
2Department of Clinical Nursing, University of Ulsan, Seoul, Korea.
3Department of Nursing, Sahmyook University, Seoul, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Oh, Pok-Ja. Department of Nursing, Sahmyook University, 815 Hwarang-ro, Nowon-gu, Seoul 01795, Korea. Tel: +82-2-3399-1589, Fax: +82-2-3399-1594, ohpj@syu.ac.kr
© 2015 Korean Society of Nursing Science
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NoDerivs License. (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nd/4.0/) If the original work is properly cited and retained without any modification or reproduction, it can be used and re-distributed in any format and medium.
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Predictors of distress among individuals with cancer reporting physical problems
McKinzey Dierkes, Yilin Cai, Victoria Trotta, Patricia Policicchio, Sijin Wen, Gwendolyn Dzwil, Nicholas Davis, Nicole L. Stout
Supportive Care in Cancer.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Associated with Quality of Life in Cancer Patients Experiencing Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy (CIPN) : Scoping review
Minah Cho, Injung Hyun, Jiyeon Lee
Asian Oncology Nursing.2025; 25(2): 75. CrossRef - Sex differences of the association between handgrip strength and health-related quality of life among patients with cancer
Jihye Kim, Yujin Kim, Jae Won Oh, San Lee
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and Effects of a Mobile Application-based Self-Management Program for Chemotherapy-induced Peripheral Neuropathy in Colorectal Cancer Patients
Pok-Ja Oh, Jung Ran Lee
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2022; 34(3): 258. CrossRef - The impact of peripheral neuropathy symptoms, self-care ability, and disturbances to daily life on quality of life among gynecological cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy: a cross-sectional survey
Sohee Mun, Hyojung Park
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2022; 28(4): 296. CrossRef - The mediation and interaction of depressive symptoms in activities of daily living and active aging in rural elderly: A cross-sectional survey
Xuelian Fu, Yinli Su, Chunyan Zeng, Liqiong Liu, Yang Guo, Yuanyuan Wu
Frontiers in Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Changes in Chemotherapy-induced Peripheral Neuropathy, Sleep Quality, and Quality of Life following Chemotherapy in Stomach Cancer Patients: a Prospective Study
Pok Ja Oh, Jin Lee, Jeong Hye Kim
Asian Oncology Nursing.2020; 20(2): 72. CrossRef - Changes in chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy, disturbance in activities of daily living, and depression following chemotherapy in patients with colorectal cancer: A prospective study
Pok-Ja Oh, Jung Ran Lee, Sook-Kyoung Kim, Jeong-Hye Kim
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2020; 44: 101676. CrossRef - Effects of aroma self-foot reflexology on peripheral neuropathy, peripheral skin temperature, anxiety, and depression in gynaecologic cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy: A randomised controlled trial
Gie Ok Noh, Kyung Sook Park
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2019; 42: 82. CrossRef - Oxaliplatin-induced Peripheral Neuropathy, Symptoms, Distress and Quality of Life among Korean Patients with Gastrointestinal Cancer
Hye Jeong Jung, Soo jung Ahn, Yoo Ri Yang, Kyoung A Kim, Sang Joon Shin, Min Kyu Jung, Sang Hui Chu
Asian Oncology Nursing.2019; 19(4): 204. CrossRef - Neuropathic symptoms, physical and emotional well-being, and quality of life at the end of life
Cindy Tofthagen, Constance Visovsky, Sara Dominic, Susan McMillan
Supportive Care in Cancer.2019; 27(9): 3357. CrossRef - Dolor neuropático en pacientes oncológicos en tratamiento con bortezomib
S. Expósito Vizcaíno, J. Casanova-Mollà, L. Escoda, S. Galán, J. Miró
Neurología.2018; 33(1): 28. CrossRef - Chemotherapy Induced Peripheral Neuropathy, Sleep and Quality of Life among Patients with Gastric Cancer Receiving Chemotherapy
Hyemi Kim, Hyojung Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2018; 25(3): 176. CrossRef - Neuropathic pain in cancer patients treated with bortezomib
S. Expósito Vizcaíno, J. Casanova-Mollà, L. Escoda, S. Galán, J. Miró
Neurología (English Edition).2018; 33(1): 28. CrossRef - Predicting health-related quality of life in cancer patients receiving chemotherapy: a structural equation approach using the self-control model
Yu-Ri Park, Eun-Young Park, Jung-Hee Kim
BMC Health Services Research.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - The psychometric properties of the Turkish version of the Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy Assessment Tool (CIPNAT)
Sevinç Kutlutürkan, Elif Sözeri Öztürk, Fatma Arıkan, Burcu Bayrak Kahraman, Keziban Özcan, Mürvet Artuk Uçar
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2017; 31: 84. CrossRef
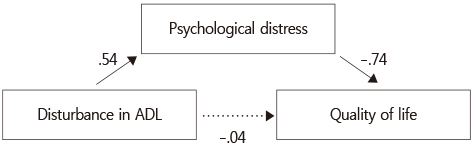
Figure 1
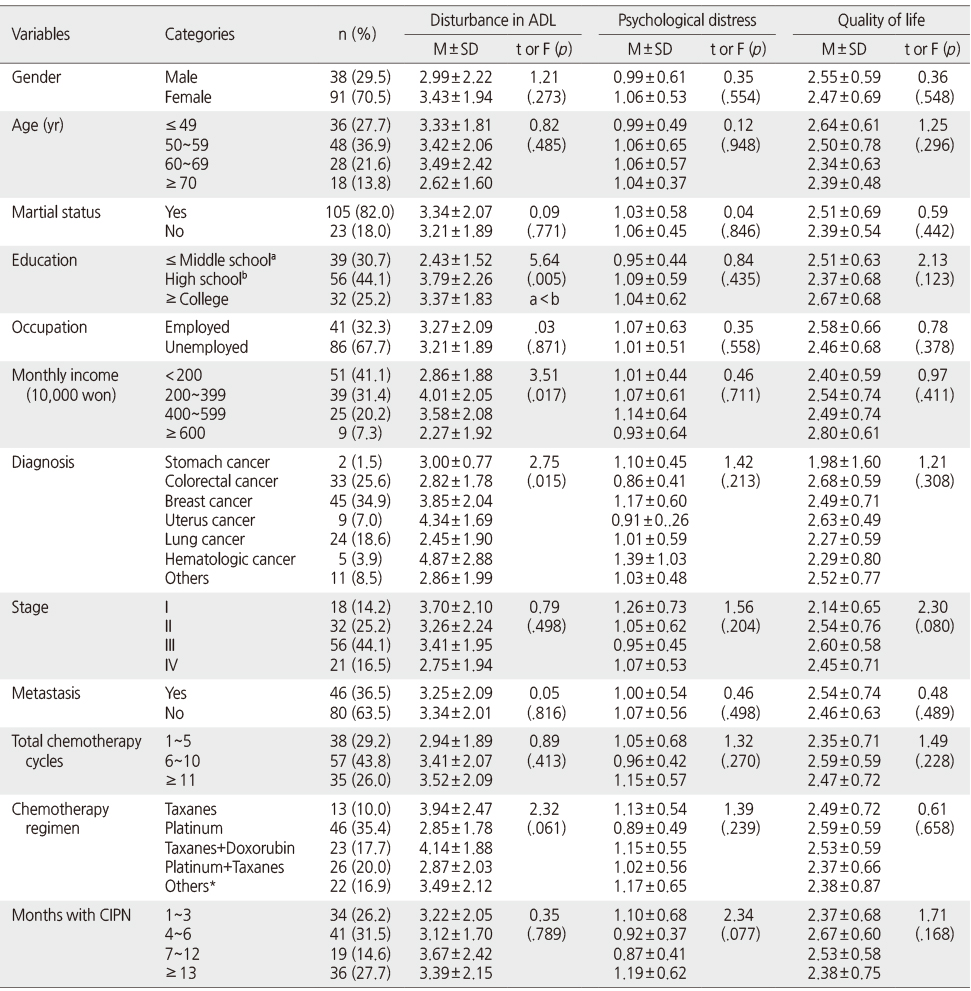
Disturbance in ADL, Psychological Distress, and Quality of Life according to General Characteristics of the Participants (N=130)
*Vinka-alkaloid, vincristine, velcade; a, b=Scheffé test; CIPN=Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy.
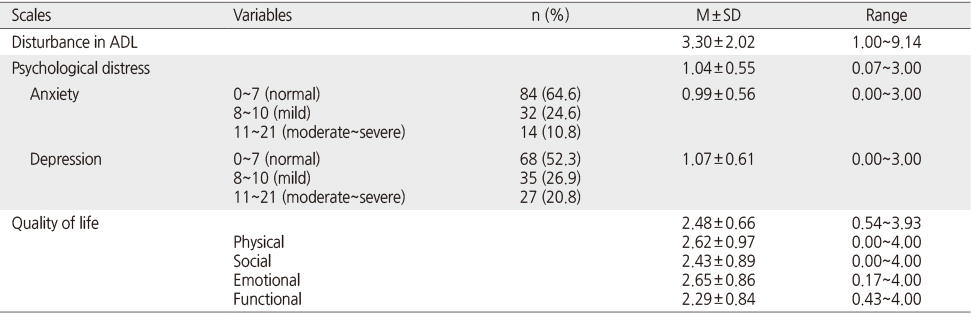
Level of Disturbance in ADL from Chemotherapy induced Peripheral Neuropathy, Depression, Anxiety, and Quality of Life (N=130)
ADL=Activities of daily living.
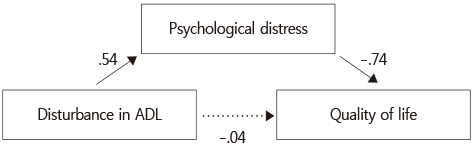
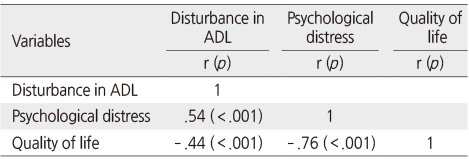
Relationships among Disturbance in ADL from Chemotherapy induced Peripheral Neuropathy, Psychological Distress, and Quality of Life (N=130)
ADL=Activities of daily living.
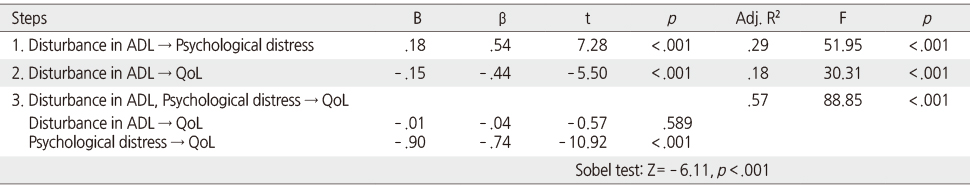
Mediating Effect of Psychological Distress in the Relationship between Disturbance in ADL from Chemotherapy induced Peripheral Neuropathy and Quality of Life (N=130)
ADL=Activities of daily living; QoL=Quality of life.
*Vinka-alkaloid, vincristine, velcade; a, b=Scheffé test; CIPN=Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy.
ADL=Activities of daily living.
ADL=Activities of daily living.
ADL=Activities of daily living; QoL=Quality of life.
 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION
 Cite
Cite

