Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Nurs > Volume 44(5); 2014 > Article
-
Original Article
- Predictors of Hospitalization for Alcohol Use Disorder in Korean Men
- Hae-Sook Hong, Jeong-Eun Park, Wan-Ju Park
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2014;44(5):552-562.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2014.44.5.552
Published online: October 31, 2014
College of Nursing, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Park, Wan-Ju. College of Nursing, Kyungpook National University, 680 Gukchaebosang-ro, Jung-gu, Daegu 700-422, Korea. Tel: +82-53-420-4977, Fax: +82-53-421-2758, wanjupark@knu.ac.kr
© 2014 Korean Society of Nursing Science
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NoDerivs License. (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nd/4.0/) If the original work is properly cited and retained without any modification or reproduction, it can be used and re-distributed in any format and medium.
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Associations among Addiction Risk, Life Satisfaction, Depression, and Suicidal Ideation in Korean Adults
Mi Nam Bae, Mihyoung Lee, Sihyun Park, Eun Jin Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2019; 28(2): 133. CrossRef - Structural Equation Model for the Analysis of Alcohol-related Problem of Alcohol Use Disorders
Hee Jung Son, Won Kee Lee, Young Shin Park, Hae Sook Hong
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2017; 42(2): 192. CrossRef - One Year Clinical Correlates of EtG Positive Urine Screening in Alcohol-Dependent Patients: A Survival Analysis
Pablo Barrio, Silvia Mondon, Lídia Teixidor, Lluisa Ortega, Eduard Vieta, Antoni Gual
Alcohol and Alcoholism.2017; 52(4): 460. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Social Problem-solving Ability in Male Alcohol Dependent Patients
Mi Young Kim, Eun Kyung Byun
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2016; 25(4): 316. CrossRef - Effect of alcohol consumption on peripheral bloodAlumethylation in Korean men
Dong-Sun Kim, Young Hun Kim, Won Kee Lee, Yeon Kyung Na, Hae Sook Hong
Biomarkers.2016; 21(3): 243. CrossRef
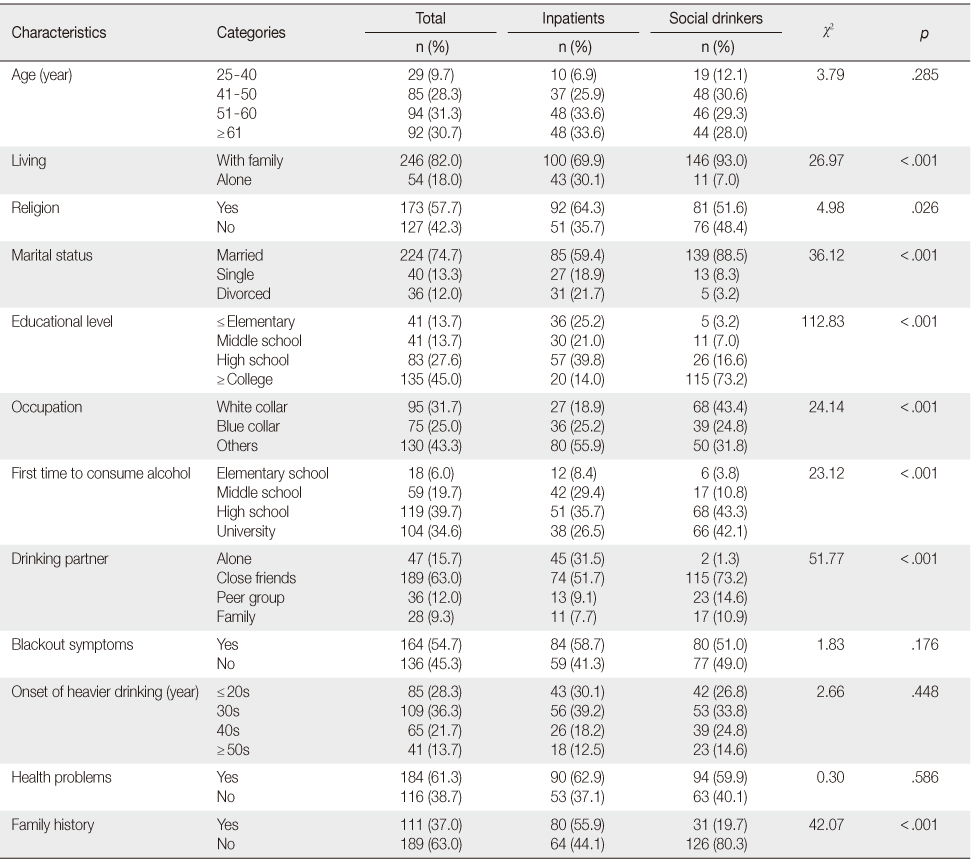
Demographic and Clinical Characteristics of Participants (N=300)
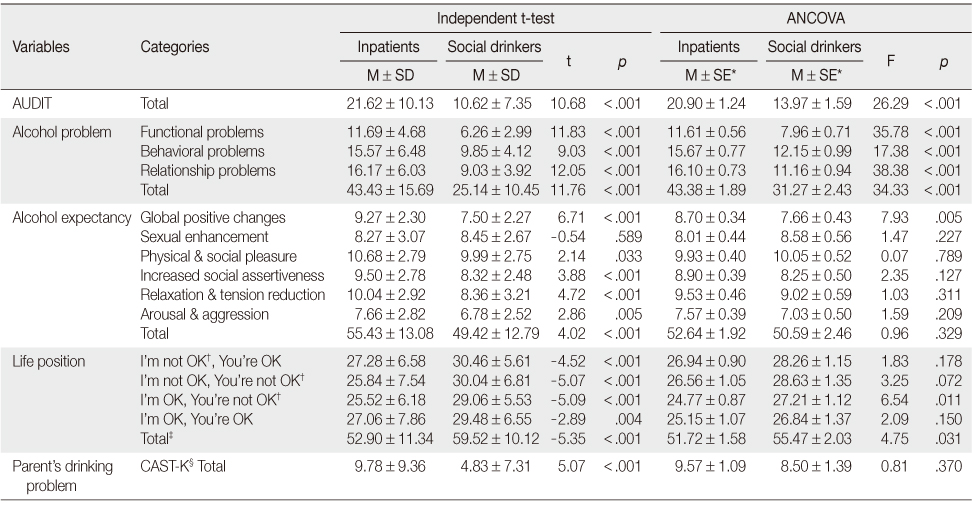
Comparisons of Study Variables between Inpatients and Social Drinkers (N=300)
*Mean values were estimated using least squared method, adjusted for living, religion, marital status, educational level, and occupation. first time of drinking, drinking partner, family history;
†Life position subtotal scores were calculated after reversed coding; ‡Life position total scores were calculated after reversed coding for negative items; §The Korean version of the Children of Alcoholics Screening Test; AUDIT=The Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test.
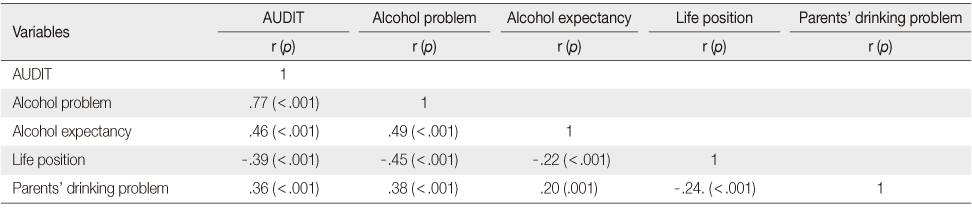
Correlations among Study Variables (N=300)
AUDIT=The Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test.
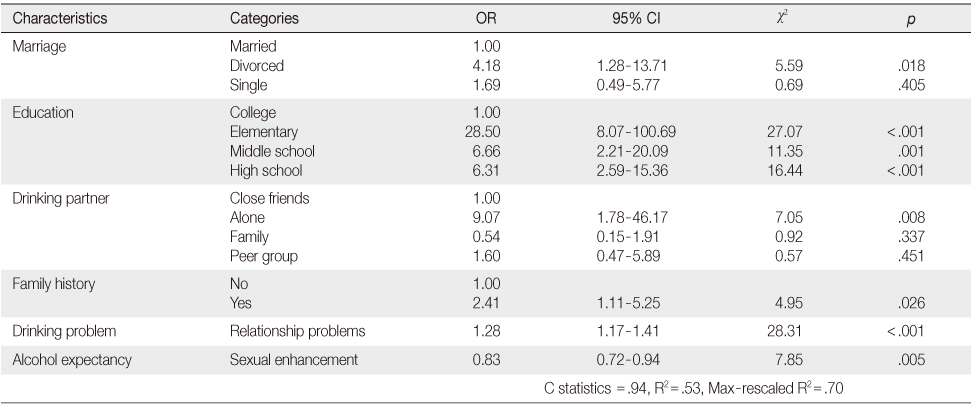
Predictors of Hospitalization by Multiple Logistic Regression Analysis (N=300)
*Mean values were estimated using least squared method, adjusted for living, religion, marital status, educational level, and occupation. first time of drinking, drinking partner, family history; †Life position subtotal scores were calculated after reversed coding; ‡Life position total scores were calculated after reversed coding for negative items; §The Korean version of the Children of Alcoholics Screening Test; AUDIT=The Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test.
AUDIT=The Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test.
 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION
 Cite
Cite

