Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Nurs > Volume 43(6); 2013 > Article
-
Original Article
- Structural Equation Modeling on Case Management Outcomes and Factors Influencing Outcomes in the Community-dwelling Vulnerable Elders
- Hyunjung Moon, In-Sook Lee
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2013;43(6):791-800.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2013.43.6.791
Published online: December 31, 2013
1Department of Nursing, Far East University, Eumseong, Korea.
2College of Nursing, The Research Institute of Nursing Science, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Lee, In-Sook. College of Nursing, Seoul National University, 28 Yeongeon-dong, Chongro-gu, Seoul 110-799, Korea. Tel: +82-2-740-8828, Fax: +82-2-741-1574, lisook@snu.ac.kr
© 2013 Korean Society of Nursing Science
Abstract
-
Purpose
- This study was done to test a structural equation modeling of case management outcomes in order to identify parameters affecting case management outcomes for the community-dwelling vulnerable elders.
-
Methods
- Data were collected from 309 nurses (case managers) and community-dwelling vulnerable elders (clients) from public health centers. For data analysis, descriptive statistics, Pearson correlation analysis, factor analysis, and covariance structure analysis were performed using SPSS Version 18.0 for Windows and Amos 16.0.
-
Results
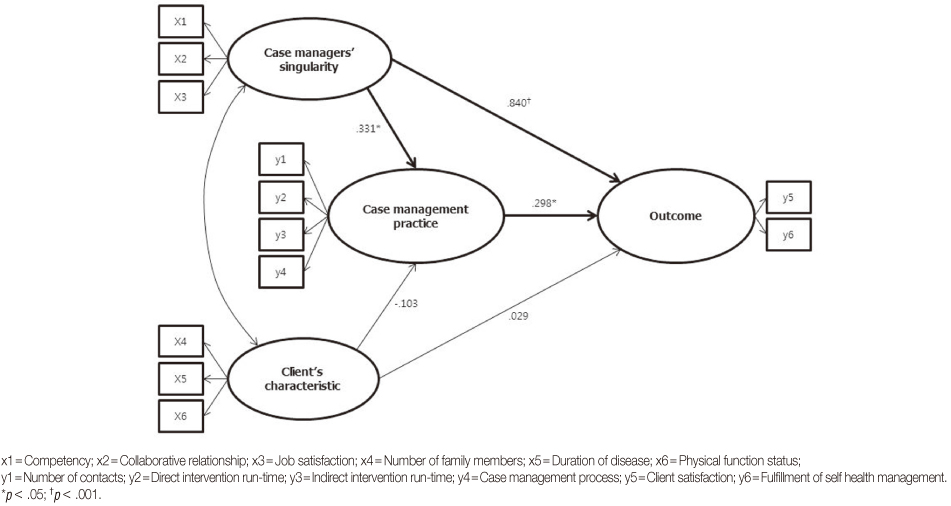
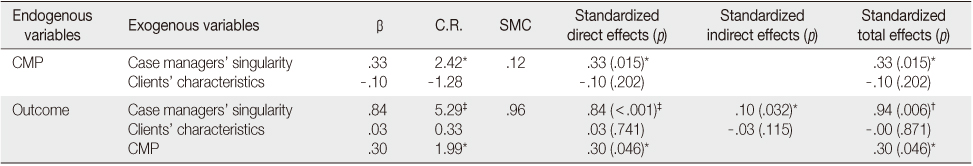
- The hypothetical model had an acceptable fit: GFI=.97, CFI=.95, RMSEA=.02, SRMR=.05. The factor "case managers' singularity" had the greatest impact on case management outcomes in this model. In addition, the factor "case management practice" influenced case management outcomes; however, client characteristics did not. Case managers' singularity affected case management outcomes directly and indirectly, with case management practice mediating the latter effect.
-
Conclusion
- These results suggest that the causal relationship between case management outcomes and factors influencing these outcomes should be clarified through longitudinal research including a variety of client characteristics. In addition, in future studies, analysis of the effects of programs to improve manpower quality and examine the relationships among case management outcomes should be done.
This manuscript is based on a part of the first author's doctoral dissertation from Seoul National University.
This study was supported by Sigma Theta Tau International, Honor Society of Nursing Lambda Alpha Chapter-at-Large (Korea) in 2011.
- 1. Aliotta SL. Focus on case management: Linking outcomes and accountability. Top Health Inf Manage. 2000;20(3):11–16.PubMed
- 2. Austin CD. Case management: Who needs it? Does it work? Care Manag J. 2002;3(4):178–184.ArticlePubMed
- 3. Björkman T, Hansson L. Client satisfaction with case management: A study of 10 pilot services in Sweden. J Ment Health. 2001;10(2):163–174. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/09638230123831Article
- 4. Chamberlain R, Rapp CA. A decade of case management: A methodological review of outcome research. Community Ment Health J. 1991;27(3):171–188.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 5. Draine J, Solomon P. Case manager alliance with clients in an older cohort. Community Ment Health J. 1996;32(2):125–134.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 6. Drennan V, Goodman C. Nurse-led case management for older people with long-term conditions. Br J Community Nurs. 2004;9(12):527–533.ArticlePubMed
- 7. Frich LM. Nursing interventions for patients with chronic conditions. J Adv Nurs. 2003;44(2):137–153.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 8. Hadjistavropoulos HD, Sagan M, Bierlein C, Lawson K. Development of a case management quality questionnaire. Care Manag J. 2003;4(1):8–17.ArticlePubMed
- 9. Hallberg IR, Kristensson J. Preventive home care of frail older people: A review of recent case management studies. J Clin Nurs. 2004;13(6B):112–120.ArticlePubMed
- 10. Han MH. A study of the role conflict and job satisfaction of public health nurses in Seoul health centers. Seoul, Yonsei University. 1987;Unpublished master's thesis.
- 11. Horvath AO, Greenberg LS. Development and validation of the working alliance inventory. J Couns Psychol. 1989;36(2):223–233. http://dx.doi.org/10.1037/0022-0167.36.2.223Article
- 12. Jang KS. A study on establishment of clinical career development model of nurses. Seoul, Yonsei University. 2000;Unpublished doctoral dissertation.
- 13. June KJ, Lee JY, Yoon JL. Effects of case management using resident assessment instrument-home care (RAI-HC) in home health services for older people. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2009;39(3):366–375. http://dx.doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2009.39.3.366ArticlePubMed
- 14. Kang HY. An analysis of differences in working alliance by counselor experience level. Seoul, Seoul National University. 1995;Unpublished master's thesis.
- 15. Kim GS. Structural equation modeling with AMOS 18.0. Seoul: Hannarae Publishing Co; 2010.
- 16. Kim SB, Jung MY, Jung HS, Jin JG. Organizational behavior. 3rd ed. Seoul: Minyoungsa; 2001.
- 17. Kim SJ, Choi MS, Sung KW. Variables affecting competency of nurses in nursing homes. J Korean Gerontol Nurs. 2010;12(1):29–39.
- 18. King R, Meadows G, Le Bas J. Compiling a caseload index for mental health case management. Aust N Z J Psychiatry. 2004;38(6):455–462. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1614.2004.01388.xArticlePubMedPDF
- 19. Luker KA, Chalmers KI. Gaining access to clients: The case of health visiting. J Adv Nurs. 1990;15(1):74–82.ArticlePubMed
- 20. Melis RJ, van Eijken MI, Teerenstra S, van Achterberg T, Parker SG, Borm GF, et al. A randomized study of a multidisciplinary program to intervene on geriatric syndromes in vulnerable older people who live at home (Dutch EASYcare Study). J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2008;63(3):283–290.PubMed
- 21. Ministry of Health & Welfare. Family health program guidelines. Seoul: Author; 2010.
- 22. Nakatani H, Shimanouchi S. Factors in care management affecting client outcomes in home care. Nurs Health Sci. 2004;6(4):239–246. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1442-2018.2004.00201.xArticlePubMed
- 23. Neale MS, Rosenheck RA. Therapeutic alliance and outcome in a VA intensive case management program. Psychiatr Serv. 1995;46(7):719–721.ArticlePubMed
- 24. Oeseburg B, Wynia K, Middel B, Reijneveld SA. Effects of case management for frail older people or those with chronic illness: A systematic review. Nurs Res. 2009;58(3):201–210. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/NNR.0b013e3181a30941PubMed
- 25. Park EJ. Review of patient satisfaction with case management. J Korean Acad Nurs Adm. 2007;13(3):311–320.
- 26. Reimanis CL, Cohen EL, Redman R. Nurse case manager role attributes: Fifteen years of evidence-based literature. Lippincotts Case Manag. 2001;6(6):230–239. quiz 240-2.ArticlePubMed
- 27. Rosati RJ, Marren JM, Davin DM, Morgan CJ. The linkage between employee and patient satisfaction in home healthcare. J Healthc Qual. 2009;31(2):44–53.Article
- 28. Shin SA. Evaluating a community-based case management program for people with diabetes in Korea. Bundoora, VIC, Australia, La Trobe University. 2009;Unpublished doctoral dissertation.
- 29. Stamps PL, Piedmont EB, Slavitt DB, Haase AM. Measurement of work satisfaction among health professionals. Med Care. 1978;16(4):337–352.ArticlePubMed
- 30. Statistics Korea. Elderly statistics 2010. Daejeon: Author; 2010.
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Perceived Barriers to Rural Elderly Women’s Health-Promoting Behaviors: An Ecological Perspective
Hyunjung Moon, Sunkyung Cha, Eunyoung Park
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(17): 6107. CrossRef
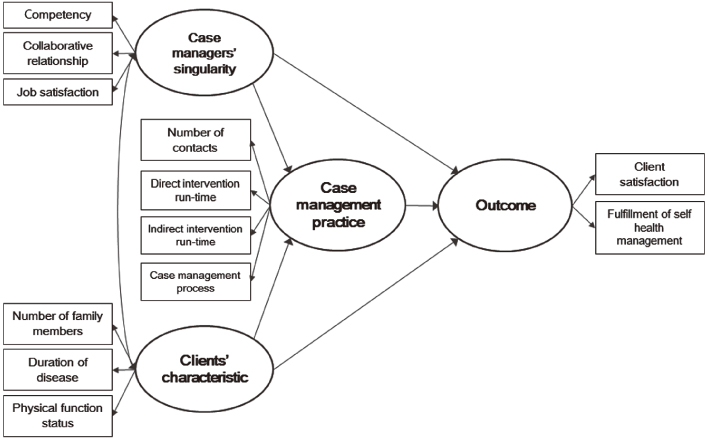
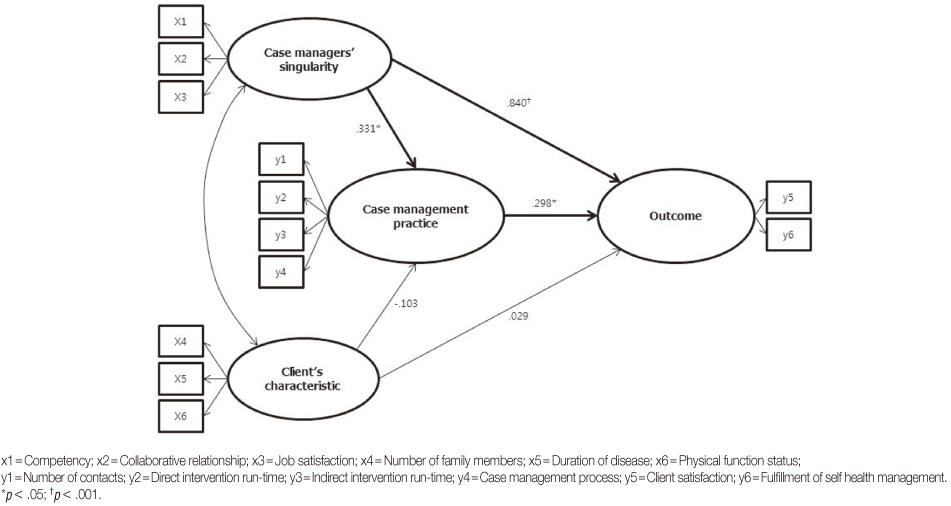
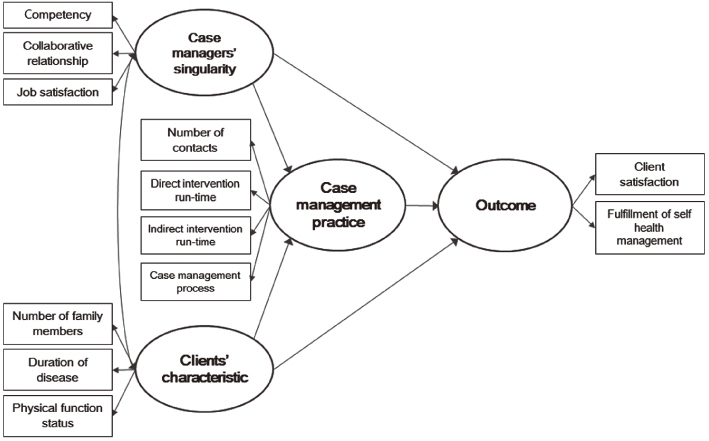
Figure 1
Figure 2
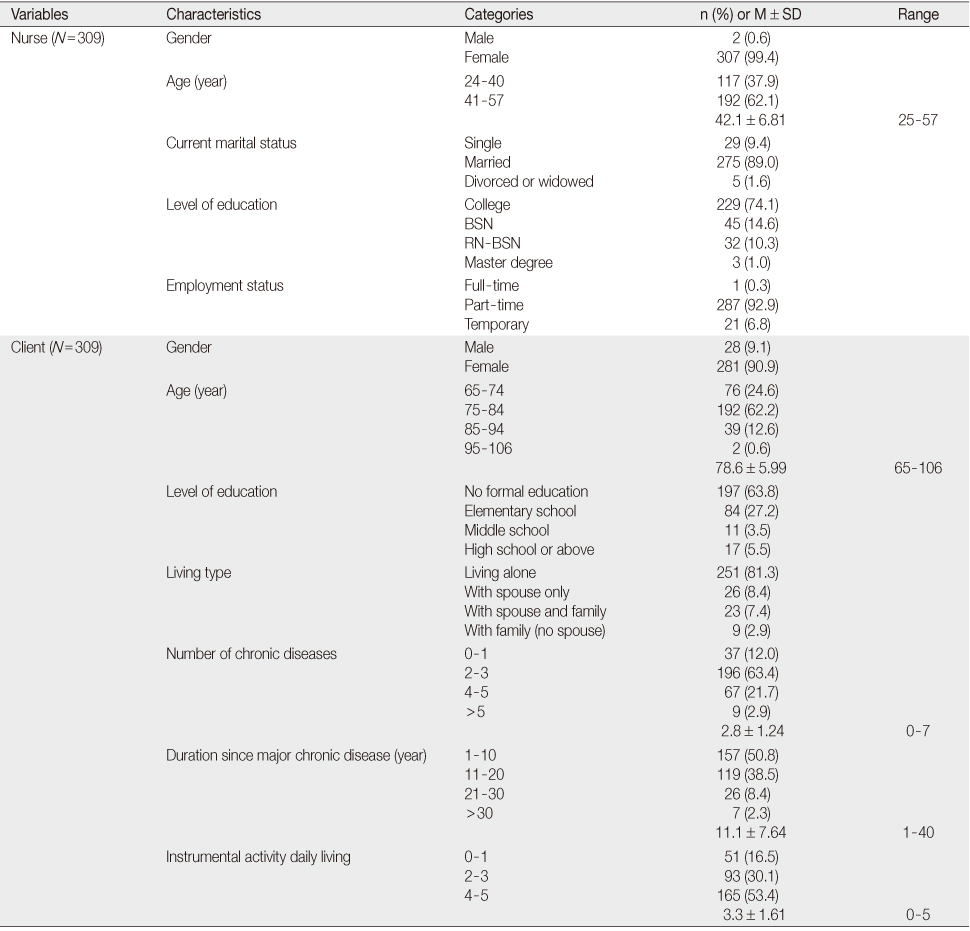
General and Health related Characteristics of the Participants (N=309)
BSN=Bachelor of science in nursing; RN-BSN=Registered nurse to bachelor of science in nursing.
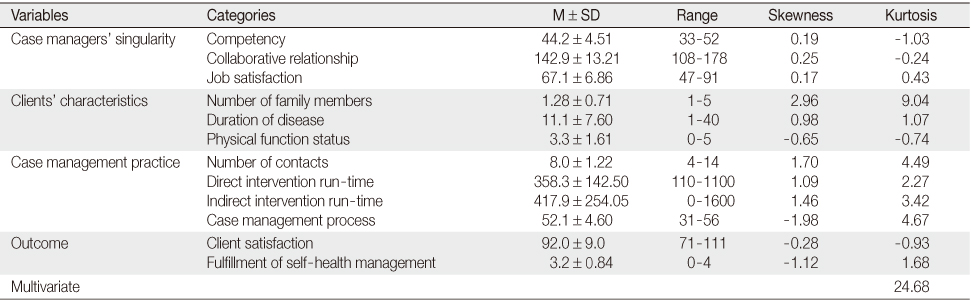
Descriptive Statistics of the Observed Variables (N=309)
Effects of Predictive Variables on Endogenous Variables in the Model
CMP=Case management practice; β=Standardized regression weight; C.R.=Critical ratio; SMC=Squared multiple correlation (R2).
*p<.05; †p<.01; ‡p<.001.
BSN=Bachelor of science in nursing; RN-BSN=Registered nurse to bachelor of science in nursing.
CMP=Case management practice; β=Standardized regression weight; C.R.=Critical ratio; SMC=Squared multiple correlation (R2). *
 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION
 Cite
Cite

