Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Nurs > Volume 43(6); 2013 > Article
-
Original Article
- Construction of the Addiction Prevention Core Competency Model for Preventing Addictive Behavior in Adolescents
- Hyun Sook Park, Sun Young Jung
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2013;43(6):714-725.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2013.43.6.714
Published online: December 31, 2013
College of Nursing, The Research Institute of Nursing Science, Catholic University of Daegu, Daegu, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Jung, Sun Young. College of Nursing, Catholic University of Daegu, 3056-6 Daemyeong 4-dong, Nam-gu, Daegu 705-718, Korea. Tel: +82-53-650-4977, Fax: +82-53-650-4392, jungsy@cu.ac.kr
• Received: August 7, 2013 • Accepted: October 18, 2013
© 2013 Korean Society of Nursing Science
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- Effects of a Strength Based I-Change Smoking Cessation Program for Smoking Middle School Boys
Jung Hee Kim, Yeon Hee Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2017; 47(2): 164. CrossRef - Health Behaviors and Related Demographic Factors among Korean Adolescents
YunHee Shin, Sook Jung Kang
Asian Nursing Research.2014; 8(2): 150. CrossRef - Predictors of Protective Factors for Internet Game Addiction in Middle School Students using Data Mining Decision Tree Analysis
Young-Ran Kweon, Se-Young Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2014; 23(1): 12. CrossRef - Development of Expert Competency Model for Preventing Adolescent Addictive Behavior and Educational Needs of Psychiatric Mental Health Nurses
Hyun Sook Park, Sun Young Jung
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2014; 23(4): 199. CrossRef
Construction of the Addiction Prevention Core Competency Model for Preventing Addictive Behavior in Adolescents
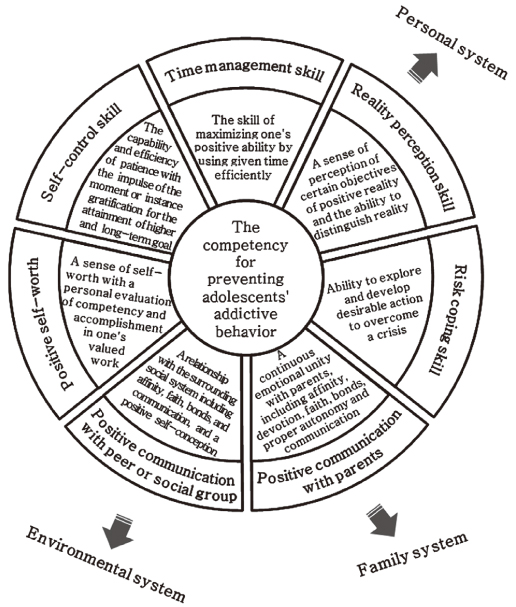
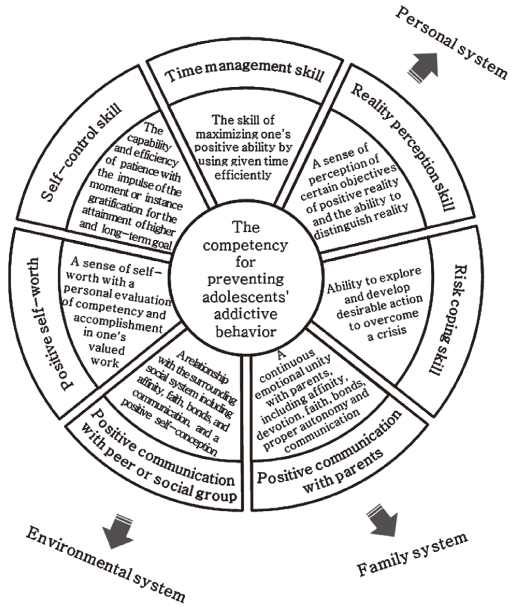
Figure 1
The competency model for preventing adolescents' addictive behavior.
Figure 1
Construction of the Addiction Prevention Core Competency Model for Preventing Addictive Behavior in Adolescents
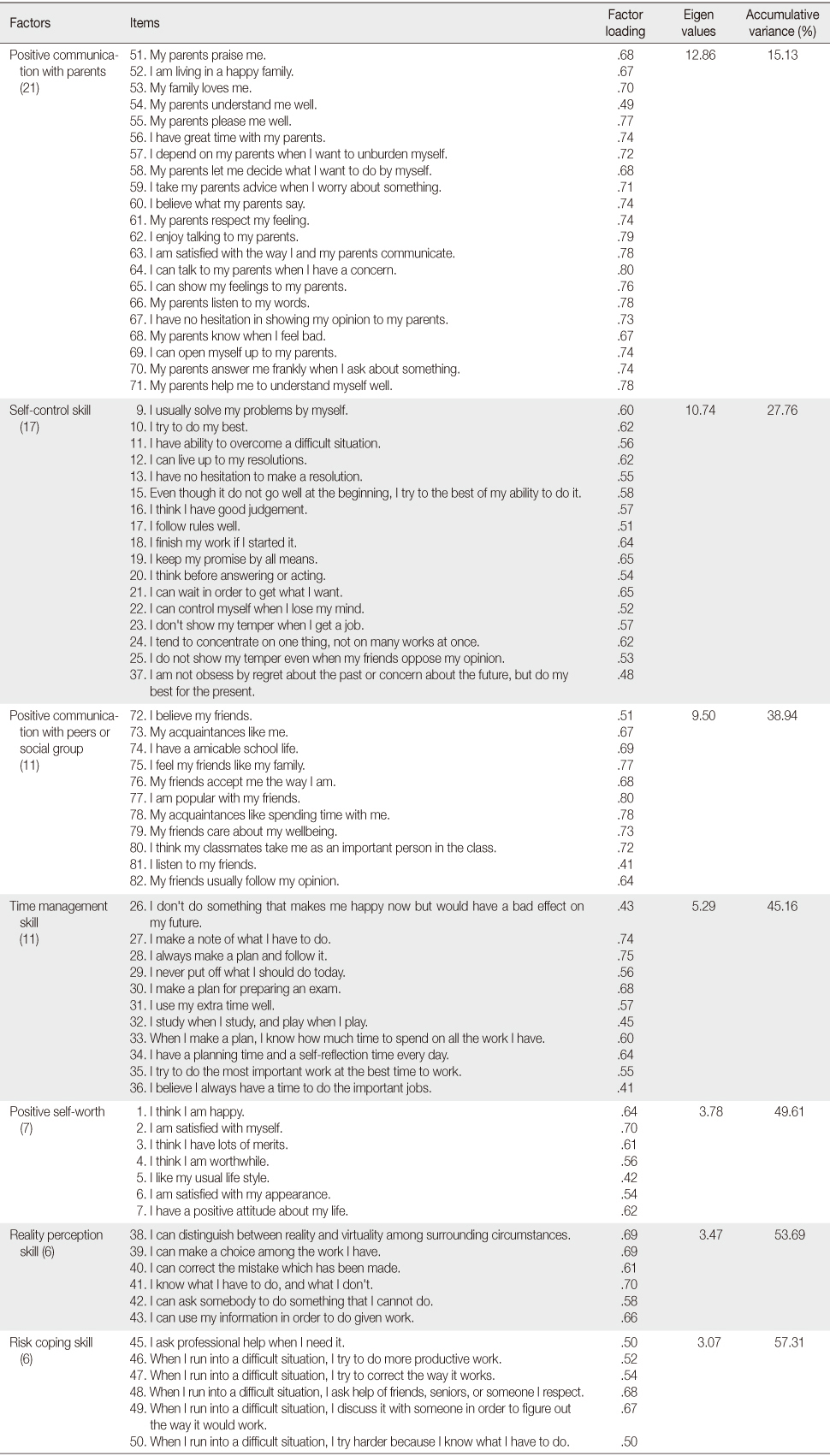
Factor Analysis of Final Items (N=861)
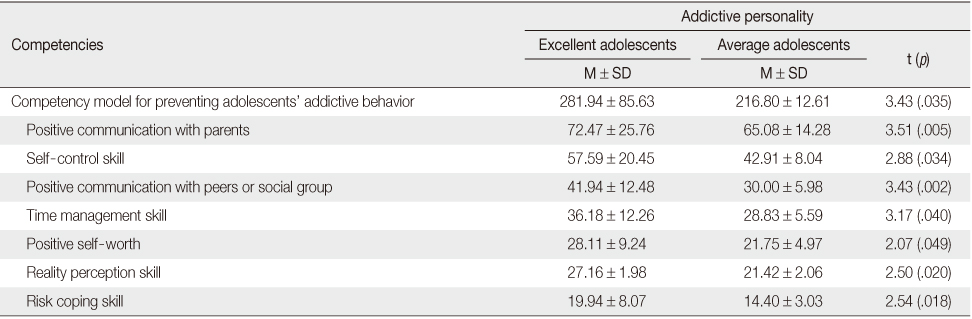
Competency due to Level of Crisis (N=258)
Table 1
Factor Analysis of Final Items (N=861)
Table 2
Competency due to Level of Crisis (N=258)
 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION
 Cite
Cite

