Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Nurs > Volume 43(5); 2013 > Article
-
Original Article
- Effects of a Cultural Competence Promotion Program for Multicultural Maternity Nursing Care: Case-based Small Group Learning
- Myung-Sook Park, Young-Ran Kweon
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2013;43(5):626-635.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2013.43.5.626
Published online: October 31, 2013
Department of Nursing, Chosun University, Gwangju, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Kweon, Young-Ran. Department of Nursing, Chosun University, 375 Seosuk-dong, Dong-gu, Gwangju 501-759, Korea. Tel: 82-62-230-6325, Fax: 82-62-230-6329, yrk@chosun.ac.kr
• Received: March 23, 2013 • Accepted: August 19, 2013
© 2013 Korean Society of Nursing Science
Abstract
-
Purpose
- The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of a cultural competence improvement program for maternity nurses.
-
Methods
- A quasi-experimental study using a non-equivalent control group pre and posttest design was used. Participants were 67 maternity nurses caring for multicultural pregnant women in G city. The cultural competence improvement program was developed based on the 3-D Puzzle Model and was provided using case-based small group learning methods for the experimental group (n=31). The control group (n=36) did not receive any intervention. Data were collected using self-report structured questionnaires at two time points: prior to the intervention and after the intervention and were analyzed with descriptive statistics, χ2-test, and t-test.
-
Results
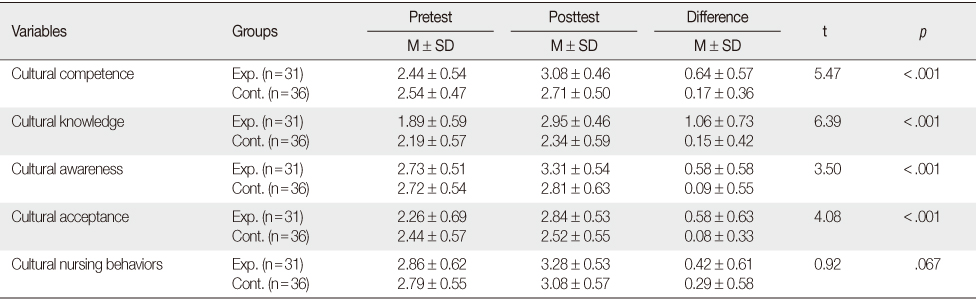
- Compared to the control group, the experimental group reported significant positive changes for cultural knowledge (t=6.39, p<.001), cultural awareness (t=3.50, p<.001), and cultural acceptance (t=4.08, p<.001). However, change in cultural nursing behaviors (t=0.92, p=.067) was not significantly different between the two groups.
-
Conclusion
- Findings from this study indicate that a cultural competence improvement program with case-based small group learning is a useful intervention strategy to promote multicultural maternity care. Further, strategies to improve cultural nursing behavior should be developed to promote culturally congruent nursing care.
- 1. American Association of Colleges of Nursing. Cultural competency in baccalaureate nursing education. 2008;Retrieved September 20, 2012. from http://www.aacn.nche.edu/leading-initiatives/education-resources/competency.pdf
- 2. Amerson R. The impact of service-learning on cultural competence. Nurs Educ Perspect. 2010;31(1):18–22.
- 3. Andrews MM, Boyle JS. Transcultural concepts in nursing care. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; 2012.
- 4. Benkert R, Templin T, Schim SM, Doorenbos AZ, Bell SE. Testing a multi-group model of culturally competent behaviors among underrepresented nurse practitioners. Res Nurs Health. 2011;34(4):327–341. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/nur.20441ArticlePubMedPMC
- 5. Berlin A, Nilsson G, Törnkvist L. Cultural competence among Swedish child health nurses after specific training: A randomized trial. Nurs Health Sci. 2010;12(3):381–391. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1442-2018.2010.00542.xPubMed
- 6. Caffrey RA, Neander W, Markle D, Stewart B. Improving the cultural competence of nursing students: Results of integrating cultural content in the curriculum and an international immersion experience. J Nurs Educ. 2005;44(5):234–240.ArticlePubMed
- 7. Campinha-Bacote J. Cultural competence in nursing curricula: How are we doing 20 years later? J Nurs Educ. 2006;45(7):243–244.ArticlePubMed
- 8. Castro A, Ruiz E. The effects of nurse practitioner cultural competence on Latina patient satisfaction. J Am Acad Nurse Pract. 2009;21(5):278–286. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-7599.2009.00406.xArticlePubMed
- 9. Chae DH, Park YH, Kang KH, Lee TH. A study on factors affecting cultural competency of general hospital nurses. J Korean Acad Nurs Adm. 2012;18(1):76–86. http://dx.doi.org/10.11111/jkana.2012.18.1.76Article
- 10. Choi SY. A study on the development of cultural competence measure for helping professions. J Community Welf. 2010;35:23–53.
- 11. Choi WH, Choi HJ, Choi YS. An explorative study on the cultural competence of social work practice setting. J Community Welf. 2008;26:89–113.
- 12. Doorenbos AZ, Lindhorst T, Schim SM, Van Schaik E, Demiris G, Wechkin HA, et al. Development of a web-based educational intervention to improve cross-cultural communication among hospice providers. J Soc Work End Life Palliat Care. 2010;6(3-4):236–255. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/15524256.2010.529022ArticlePubMedPMC
- 13. Ganann R, Sword W, Black M, Carpio B. Influence of maternal birthplace on postpartum health and health services use. J Immigr Minor Health. 2012;14(2):223–229. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10903-011-9477-2ArticlePubMedPDF
- 14. Giger JN, Davidhizar RE. Transcultural nursing: Assessment and intervention. St. Louis, MO: Mosby; 2008.
- 15. Grant LF, Lentzring TD. Status of cultural competence in nursing education: A literature review. J Multicult Nurs Health. 2003;9(2):6–13.
- 16. Hawala-Druy S, Hill MH. Interdisciplinary: Cultural competency and culturally congruent education for millennials in health professions. Nurse Educ Today. 2012;32(7):772–778. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.nedt.2012.05.002ArticlePubMed
- 17. Jeong SJ. A study on the development and the effect of group counseling program for improving early childhood teachers' multicultural education competency. Jeonju, Chonbuk National University. 2012;Unpublished doctoral dissertation.
- 18. Jin KN, Kim J, Sung D, Hwang S, Jung WW. Cultural competence of global healthcare providers in healthcare setting: Case study of Seoul area. Health Soc Welf Rev. 2010;30(2):581–598.Article
- 19. Kim EY. Cultural competence enhancement programs for social workers working with culturally diverse families. Seoul, Ewha Womans University. 2012;Unpublished doctoral dissertation.
- 20. Kim YJ, Lee JY, Cho SH. An explorative study of perceived cultural competency of medical social workers in Korea. Health Soc Welf Rev. 2011;31(3):251–283.Article
- 21. In: Michaelsen LK, Parmelee DX, McMahon KK, Levine RE. editors. Team-based learning for health professions education: A guide to using small groups for improving learning. Sterling, VA: Stylus Publishing; 2007.
- 22. Munoz CC, DoBroka CC, Mohammad S. Development of a multidisciplinary course in cultural competence for nursing and human service professions. J Nurs Educ. 2009;48(9):495–503. http://dx.doi.org/10.3928/01484834-20090610-03ArticlePubMed
- 23. Park JS. Study on cultural competence of nurses working in general hospital. Daegu, Keimyung University. 2011;Unpublished master's thesis.
- 24. Schim SM, Doorenbos AZ. A three-dimensional model of cultural congruence: Framework for intervention. J Soc Work End Life Palliat Care. 2010;6(3-4):256–270. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/15524256.2010.529023ArticlePubMedPMC
- 25. Schim SM, Doorenbos AZ, Borse NN. Cultural competence among Ontario and Michigan healthcare providers. J Nurs Scholarsh. 2005;37(4):354–360.ArticlePubMed
- 26. Schim SM, Doorenbos AZ, Miller J, Benkert R. Development of a cultural competence assessment instrument. J Nurs Meas. 2003;11(1):29–40.ArticlePubMed
- 27. Starr S, Wallace DC. Self-reported cultural competence of public health nurses in a Southeastern U.S. Public health department. Public Health Nurs. 2009;26(1):48–57. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1525-1446.2008.00753.xArticlePubMed
- 28. The Korea Institute for Health and Social Affairs. International marriage migrant women's reproductive health status and policy challenges. 2008;Retrieved August 10, 2012. from https://www.kihasa.re.kr/html/jsp/publication/policy/view.jsp?bid=12&ano=398&key=&query=&ryear_value=0&content_type=1&queryString
- 29. The Ministry of Security and Public Administration. Research situation analysis of foreign population. 2011;Retrieved September 20, 2012. from http://www.mopas.go.kr
- 30. Yeo TP, Phillips J, Delengowski A, Griffiths M, Purnell L. Oncology nursing: Educating advanced practice nurses to provide culturally competent care. J Prof Nurs. 2011;27(4):245–254. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.profnurs.2011.03.004ArticlePubMed
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- Nursing educators' experiences of cultural competence in the nursing education program: A qualitative descriptive study
Fatemeh Darban, Jamileh Farokhzadian, Monirsadat Nematollahi, Nastaran Heydarikhayat, Motahareh Faramarzpour
Journal of Professional Nursing.2024; 54: 142. CrossRef - Effect of Case-Based Small-Group Learning on Care Workers’ Emergency Coping Abilities
Soon-Ok Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(21): 11458. CrossRef - Effectiveness of cultural competence educational interventions on health professionals and patient outcomes: A systematic review
Duckhee Chae, Jinhee Kim, Suhee Kim, Jina Lee, Seojin Park
Japan Journal of Nursing Science.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Organisational cultural competence needed to care for foreign patients: A focus on nursing management
Duckhee Chae, Yunhee Park
Journal of Nursing Management.2019; 27(1): 197. CrossRef - Agreement on Core Components of an E-Learning Cultural Competence Program for Public Health Workers in South Korea: A Delphi Study
Duckhee Chae, Hyunlye Kim, Jae Yong Yoo, Jina Lee
Asian Nursing Research.2019; 13(3): 184. CrossRef - Experience of migrant care and needs for cultural competence training among public health workers in Korea
Duckhee Chae, Jina Lee, Keiko Asami, Hyunlye Kim
Public Health Nursing.2018; 35(3): 211. CrossRef - Effects of a Cultural Competence Educational Program for Nursing Students
Hyang-In Cho Chung, Seok-Young Han, Seung-Hee Seo
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2017; 23(4): 406. CrossRef - Cultural Competence of Obstetric and Neonatal Nurses
Ella T. Heitzler
Journal of Obstetric, Gynecologic & Neonatal Nursing.2017; 46(3): 423. CrossRef - Development of a Multicultural Education Program for Nursing Students and Evaluation of its Effects on Multicultural Sensitivity and Efficacy
Myeong Jeong Chae, Jin-il Kim
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2016; 30(1): 70. CrossRef - The Effectiveness of a Cultural Competence Training Program for Public Health Nurses using Intervention Mapping
Yune Kyong Kim, Hyeonkyeong Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2016; 27(4): 410. CrossRef - The Influence of Case-Based Learning using video In Emergency care of infant and toddlers
Hye-Young Cho, Kyoung-Ah Kang
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2016; 17(12): 292. CrossRef - Nursing experience of delivery care for married immigrant women in Korea: An application of focus group interview
Byoung-Sook Lee, Min-Young Kim
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2015; 16(6): 3999. CrossRef - Effects of a Multicultural Course on the Multicultural Acceptability and Competency of Nursing Students
Myeong Jeong Chae, Jin-il Kim, Jin Hee Lee
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2015; 21(3): 373. CrossRef - Development and Effect of a Cultural Competency Promotion Program for Nurses in Obstetrics-Gynecology and Pediatrics
Minji Je, Hyun-Mi Son, Young-Hae Kim
Child Health Nursing Research.2015; 21(2): 151. CrossRef - Cultural competence education for health professionals
Lidia Horvat, Dell Horey, Panayiota Romios, John Kis-Rigo
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.2014;[Epub] CrossRef - A Proposed Teaching Model to Improve Cultural Competency Care for Undergraduate Korean Nursing Students
Kyung Sook Choi, Sarah Morgan, Vipavee Thongpriwan, So Young Lee, Myunghee Jun
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2014; 20(3): 424. CrossRef - The Effect of the Cultural Competence in Multicultural Nursing Education by Action Learning
Yeon-Soon Kim, Jin-Young Kim
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2014; 15(11): 6527. CrossRef
Effects of a Cultural Competence Promotion Program for Multicultural Maternity Nursing Care: Case-based Small Group Learning
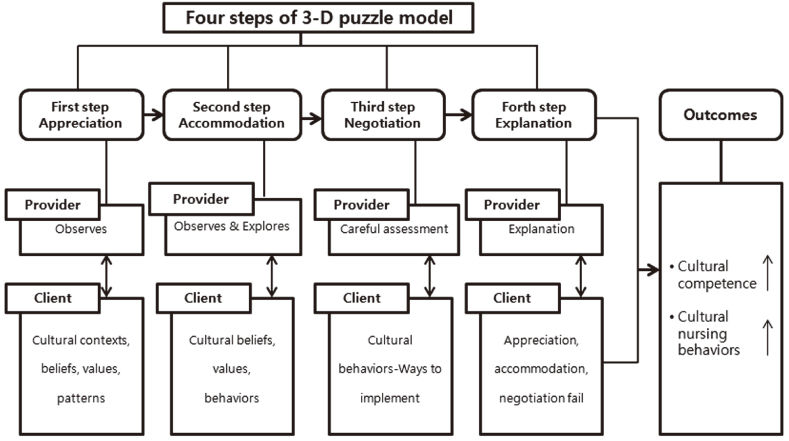
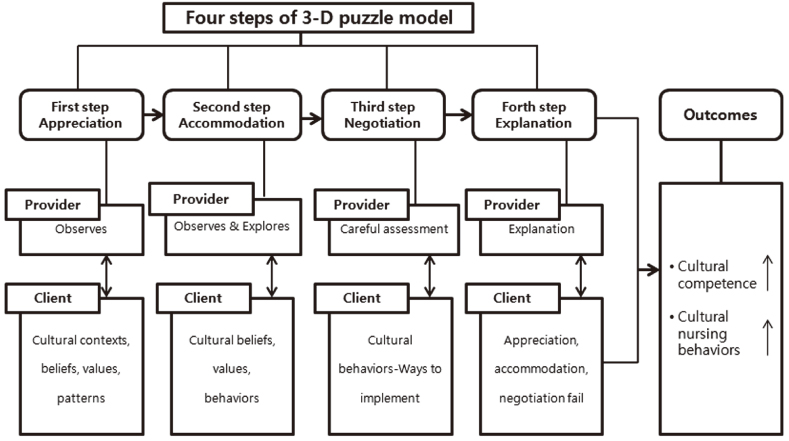
Figure 1
Four steps of 3-D puzzle model.
Figure 1
Effects of a Cultural Competence Promotion Program for Multicultural Maternity Nursing Care: Case-based Small Group Learning
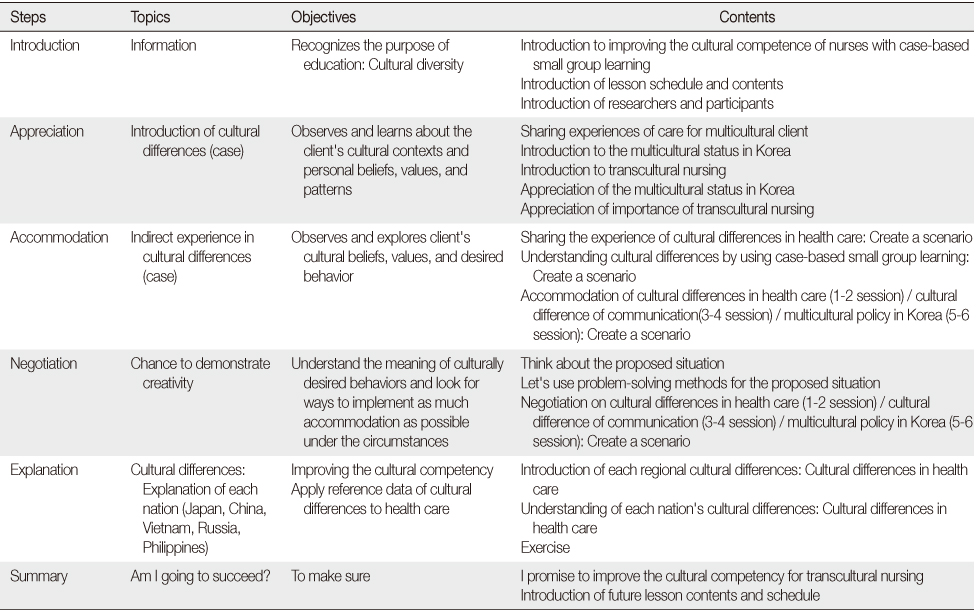
Contents of the Cultural Competence Improving Program with Case-based Small Group Learning
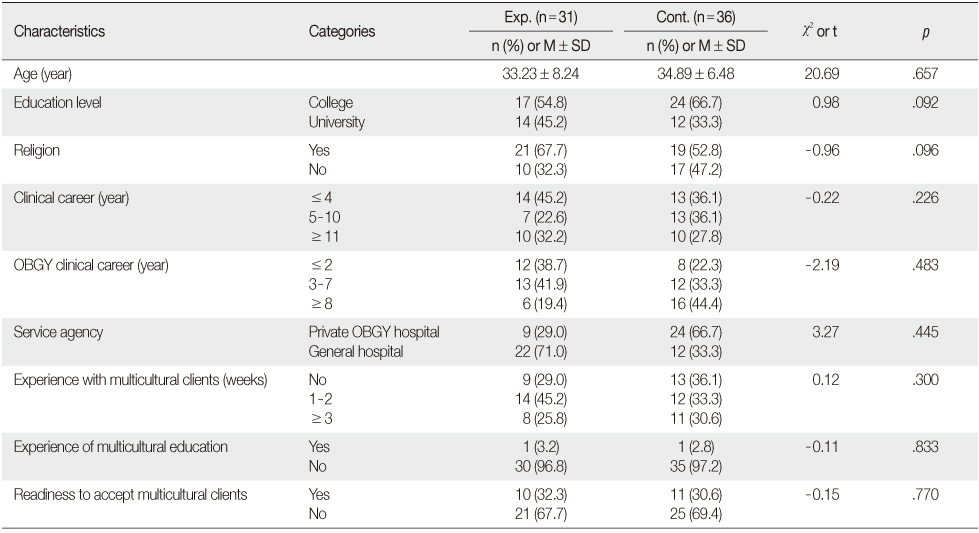
Homogeneity of General Characteristics (N=67)
Exp.=Experimental group; Cont.=Control group; OBGY=Obstetrics and gynecology.
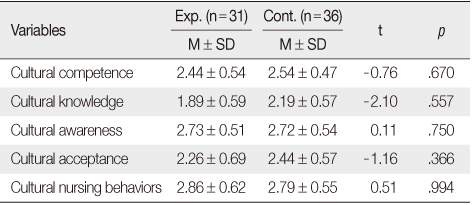
Homogeneity of Dependent Variables (N=67)
Exp.=Experimental group; Cont.=Control group.
Comparison of Dependent Variables between Two Groups after Treatment (N=67)
Exp.=Experimental group; Cont.=Control group.
Table 1
Contents of the Cultural Competence Improving Program with Case-based Small Group Learning
Table 2
Homogeneity of General Characteristics (N=67)
Exp.=Experimental group; Cont.=Control group; OBGY=Obstetrics and gynecology.
Table 3
Homogeneity of Dependent Variables (N=67)
Exp.=Experimental group; Cont.=Control group.
Table 4
Comparison of Dependent Variables between Two Groups after Treatment (N=67)
Exp.=Experimental group; Cont.=Control group.
 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION
 Cite
Cite

