Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Nurs > Volume 43(4); 2013 > Article
-
Original Article
- Effects of a Family Education Program for Families of Pathological Gamblers
- Jungah Hong, Soo Yang
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2013;43(4):497-506.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2013.43.4.497
Published online: August 30, 2013
College of Nursing, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Yang, Soo. College of Nursing, The Catholic University of Korea, 505 Banpo-dong, Seocho-gu, Seoul 137-701, Korea. Tel: +82-2-2258-7407, Fax: +82-2-2258-7772, sooy@catholic.ac.kr
© 2013 Korean Society of Nursing Science
Abstract
-
Purpose
- This study was done to examine the intervention effects on the family of a family education program for pathological gamblers based on Community Reinforcement and Family Training (CRAFT).
-
Methods
- A quasi-experimental, nonequivalent control group pretest-posttest design was used. The participants were 44 families of pathological gamblers from G center in Gyung-gi Province and 5 Gam-Anon groups in Seoul City and Gyung-gi Province. The experimental group (n=22) attended the 6 weekly 2 hour-long CRAFT family education program. The control group (n=22) attended the 12-step program of Gam-Anon. Data were collected from November, 2011 to May, 2012.
-
Results
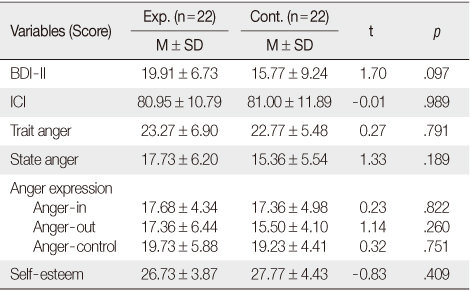
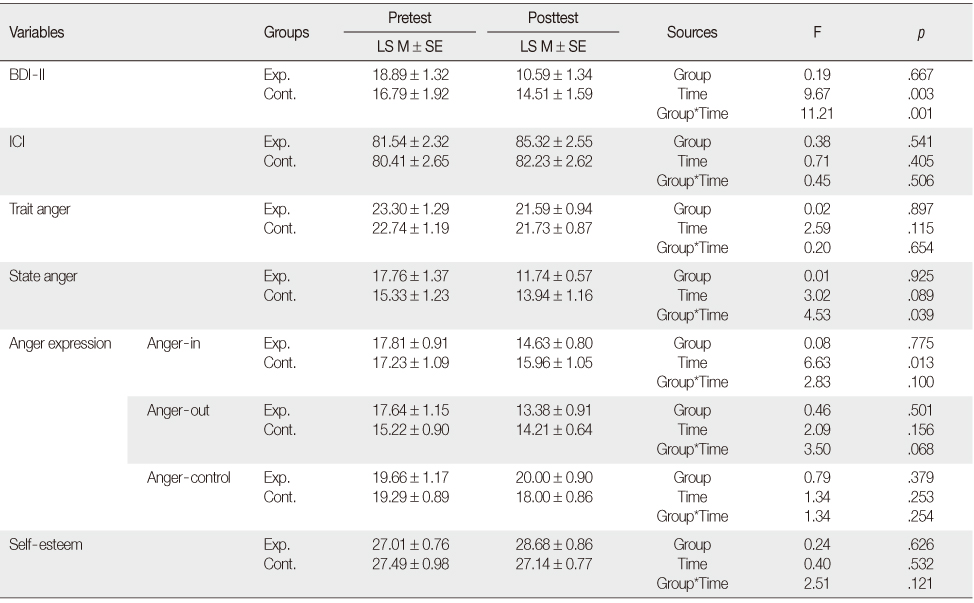
- Compared with the control group, the experimental group showed significant decrease in depression (p=.001) and state anger (p=.039). There were no significant differences between groups in the level of interpersonal communication, trait anger, the mode of anger expression and self-esteem.
-
Conclusion
- Findings from this study suggest that the CRAFT family education program is effective in decreasing depression and state anger in families of pathological gamblers.
This manuscript is based on a part of the first author's doctorial dissertation from The Catholic University of Korea.
- 1. Abbott DA, Cramer SL, Sherrets SD. Pathological gambling and the family: Practice implications. Fam Soc. 1995;76(4):213–219.ArticlePDF
- 2. Beck AT, Steer RA, Brown GK. Manual for the Beck depression inventory-II. 2nd ed. San Antonio, TX: Psychological Corporation; 1996.
- 3. Bienvenu MJ. An interpersonal communication inventory. J Commun. 1971;21(4):381–388. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-2466.1971.tb02937.xArticle
- 4. Choi KH. The effect of a parent group education on parents' interpersonal communication and children's perception to their parents. Ulsan, Ulsan University. 1993;Unpublished master's thesis.
- 5. Choi MK, Lee YH. Depression, powerlessness, social support, and socioeconomic status in middle aged community residents. J Korean Acad Psychiatr Ment Health Nurs. 2010;19(2):196–204.Article
- 6. Chon KK. Development of the Korean state-trait anger expression inventory (II). Korean J Rehabil Psychol. 1996;3(1):53–69.
- 7. Ciarrocchi JW. Counselling problem gamblers: A self-regulation manual for individual and family therapy. San Diego, CA: Academic Press; 2002.
- 8. Ciarrocchi JW, Reinert DF. Family environment and length of recovery for married male members of Gamblers Anonymous and female members of GamAnon. J Gambl Stud. 1993;9(4):341–352.ArticlePDF
- 9. Grant JE, Kushner MG, Kim SW. Pathological gambling and alcohol use disorders. Alcohol Res Health. 2002;26(2):143–150.PMC
- 10. Han YO, Jeong JY, Kim HW. Preliminary study for developing of pathological gambler's family intervention program. Korean J Health Psychol. 2011;16(2):263–277.Article
- 11. Heineman M. A comparison: The treatment of wives of alcoholics with the treatment of wives of pathological gamblers. J Gambl Behav. 1987;3(1):27–40.ArticlePDF
- 12. Jang MH, Won JS. Association of anger and anger expression, social support, self-esteem, and depression in elderly. J Korean Acad Psychiatr Ment Health Nurs. 2009;18(3):259–268.ArticlePDF
- 13. Jon BJ. Self-esteem: A test of its measurability. Yonsei Nonchong. 1974;11(1):107–130.
- 14. Kim KH, Kwon SJ. Psychological characteristics and predictors of pathological gamblers. Korean J Health Psychol. 2003;8(2):261–277.
- 15. Kim MS, Lee IS, Lee CS. The validation study I of Korean BDI-II: In female university students sample. Korean J Clin Psychol. 2007;26(4):997–1014.
- 16. Lee JS. A study on the development and effectiveness of a coping skill improvement program for significant family members of alcoholics. Seoul, Ewha Womans University. 2004;Unpublished doctoral dissertation.
- 17. Lorenz VC, Shuttlesworth DE. The impact of pathological gambling on the spouse of the gambler. J Community Psychol. 1983;11(1):67–76. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/1520-6629(198301)11:1<67::AID-JCOP2290110107>3.0.CO;2-OArticle
- 18. Lorenz VC, Yaffee RA. Pathological gambling: Psychosomatic, emotional and marital difficulties as reported by the spouse. J Gambl Behav. 1988;4(1):13–26.ArticlePDF
- 19. Makarchuk K, Hodgins DC, Peden N. Development of a brief intervention for concerned significant others of problem gamblers. Addict Disord Their Treat. 2002;1(4):126–134.Article
- 20. Mazzoleni MH, Gorenstein C, Fuentes D, Tavares H. Wives of pathological gamblers: Personality traits, depressive symptoms and social adjustment. Rev Bras Psiquiatr. 2009;31(4):332–337.ArticlePubMed
- 21. Robson PJ. Self-esteem-a psychiatric view. Br J Psychiatry. 1988;153:6–15.ArticlePubMed
- 22. Rosenberg M. Society and adolescent self-image. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press; 1965.
- 23. Rychtarik RG, McGillicuddy NB. Preliminary evaluation of a coping skills training program for those with a pathological-gambling partner. J Gambl Stud. 2006;22(2):165–178. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10899-006-9008-6ArticlePubMedPDF
- 24. Seo SG. Cognitive factors related to anger and their therapeutic implications. Seoul, Seoul National University. 2004;Unpublished doctoral dissertation.
- 25. Shin KC, Choi YS, Park EJ, Choi YS, Chung SY, Kim SH. Research for family treatment program of pathological gambler. Seoul: The National Gambling Control Commission; 2010.
- 26. Spielberger CD. Professional manual for the State Trait Anger Expression Inventory (STAXI). Odessa, FL: Psychological Assessment Resources; 1988.
- 27. The National Gambling Control Commission. The service system establishment plan for national gambling addiction prevention and recovery. Seoul: Author; 2012.
- 28. Yoo CY, Park SY, Son HI. Smith JE Meyers RJ . Motivating substance abusers to enter treatment. Goyang: Dragon Publishing Co; 2009.(Original work published 2004).
- 29. Zion MM, Tracy E, Abell N. Examining the relationship between spousal involvement in Gam-Anon and relapse behaviors in pathological gamblers. J Gambl Stud. 1991;7(2):117–131.ArticlePubMedPDF
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Telemedicine as bridge to the offline world for person affected with problematic internet use or internet use disorder and concerned significant others
Laura Bottel, Bert Theodor te Wildt, Matthias Brand, Magdalena Pape, Stephan Herpertz, Jan Dieris-Hirche
DIGITAL HEALTH.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Delphi Analysis of Gambling Addiction Rehabilitation Service Model
신성만, Sun Jung Kwon, 정여주
Korea Journal of Counseling.2015; 16(6): 157. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Family-function in Families of Pathological Gamblers
Soo Yang, Jung Ah Hong
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2015; 24(3): 196. CrossRef
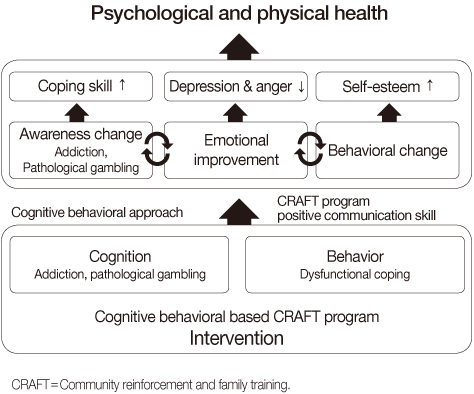
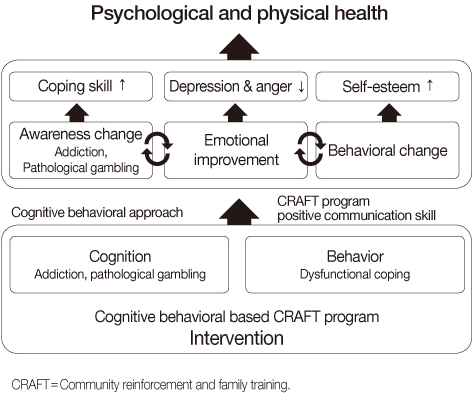
Figure 1
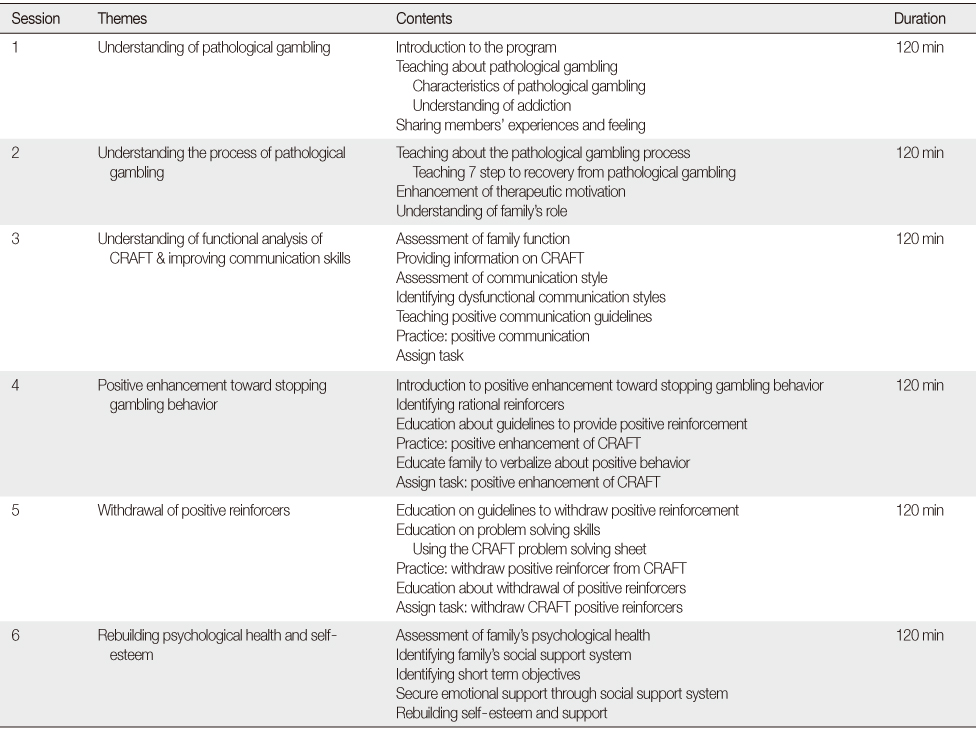
Contents of Family Education Program for Families of Pathological Gamblers
min=Minutes; CRAFT=Community reinforcement and family training.
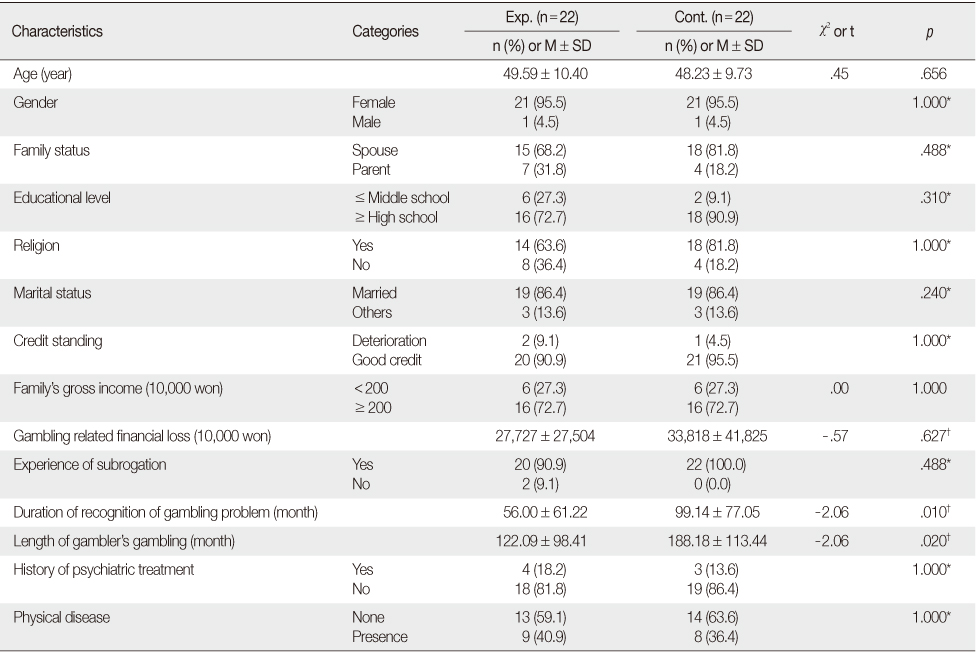
General Characteristics of Participants (N=44)
Exp.=Experimental group; Cont.=Control group.
*Fisher's exact test; †Wilcoxon rank sum test.
Homogeneity of Measurement Variables between Groups (N=44)
Exp.=Experimental group; Cont.=Control group; BDI-II=Beck depression inventory-II; ICI=Interpersonal communication inventory.
Comparison of Changes in Measurement Variables between Groups (N=44)
Exp.=Experimental group (n=22); Cont.=Control group (n=22); BDI-II=Beck depression inventory-II; ICI=Interpersonal communication inventory.
LS M±SE=Least square mean±standard error.
min=Minutes; CRAFT=Community reinforcement and family training.
Exp.=Experimental group; Cont.=Control group. *Fisher's exact test; †Wilcoxon rank sum test.
Exp.=Experimental group; Cont.=Control group; BDI-II=Beck depression inventory-II; ICI=Interpersonal communication inventory.
Exp.=Experimental group (n=22); Cont.=Control group (n=22); BDI-II=Beck depression inventory-II; ICI=Interpersonal communication inventory. LS M±SE=Least square mean±standard error.
 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION
 Cite
Cite

