Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Nurs > Volume 42(1); 2012 > Article
-
Original Article
- Effects of Nurses' Perception of Servant Leadership on Leader Effectiveness, Satisfaction and Additional Effort: Focused on the Mediating Effects of Leader Trust and Value Congruence
- Sang Sook Han, Nam Eun Kim
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2012;42(1):85-94.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2012.42.1.85
Published online: February 29, 2012
1Professor, College of Nursing Science/East-West Nursing Research Institute, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea.
2Doctoral Students, College of Nursing Science, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Kim, Nam Eun. College of Nursing Science, Kyung Hee University, East-West NEO Medical Center 9A, #149 Sangil-dong, Gangdong-gu, Seoul 134-090, Korea. Tel:+ 82-2-440-8072, Fax: +82-2-440-6870, kne159@naver.com
© 2012 Korean Society of Nursing Science
- 1,341 Views
- 9 Download
- 6 Crossref
Abstract
-
Purpose
- This study was done to examine the effects of nurses' perception of servant leadership on leader effectiveness, satisfaction and promoting additional effort. The focus was the mediating effects of leader trust and value congruence.
-
Methods
- Data were collected from 361 RN-BSN students and nurses participating in nationally attended in-service training programs. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics and structural analysis with SPSS 17.0 windows program and Amos 7.0.
-
Results
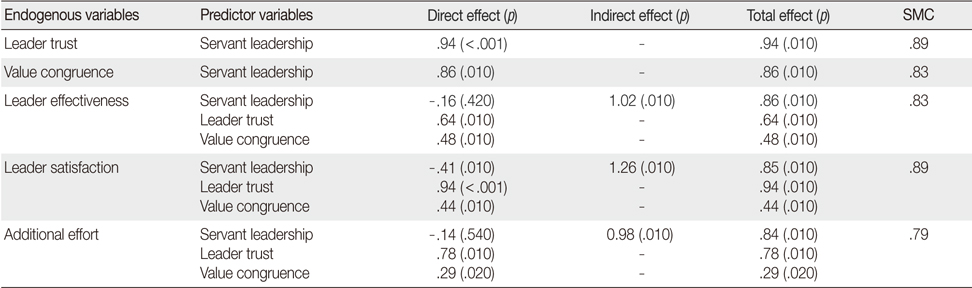
- Direct effects of nurses' perception of servant leadership were negative, but mediating effects of trust and value congruency were positively correlated with leader effectiveness, satisfaction and additional effort, that is servant leadership should be effective through mediating factors.
-
Conclusion
- The study results indicate that if the middle managers of nurses can build leader trust and value congruency between nurses through servant leadership, leader effectiveness, satisfaction and additional effort on the part of the nurses could result in a positive change in the long term.
- 1. Anderson J.C., Gerbing D.W. Structural equation modeling in practice: A review and recommended two-step approach. Psychological Bulletin. 1988;103(3):411–423. http://dx.doi.org/10.1037//0033-2909.103.3.411.Article
- 2. Bass B.M. Bass and Stogdill's handbook of leadership: Theory, research & managerial applications. 1990;New York, NY, The Free Press.
- 3. Calantone R.T., Zhao Y.S. Joint ventures in China: A comparative study of Japanese, Korean, and U. S. partners. Journal of International Marketing. 2001;9(1):1–23.ArticlePDF
- 4. Chae S.H. Transformational, leadership, empowerment, trust and organizational commitment: Multidimensional approach. 2004;Gyeongsan, Yeungnam University. Unpublished doctoral dissertation.
- 5. Choi D.J. A relation of servant leadership, leader trust, and organizational citizenship behavior. Journal of Hotel and Resort. 2008;7(2):159–175.
- 6. Girard S.H. Servant leadership qualities exhibited by Illinois public school district superintendents. 2000;St. Louis, USA, Saint Louis University. Unpublished doctoral dissertation.
- 7. Gorsuch R. Factor analysis. 1983;2nd ed. New Jersesy, NJ, Erlbaum.
- 8. Ha N.S., Choi J. The relationship among leadership styles of nurse managers, job satisfaction, organizational commitment and turn-over intention. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2002;32:812–822.ArticlePDF
- 9. Jeong S.M., Kim K.S. The effects of the servant leadership on the leader trust and organizational trust. Zeitschrift für Wirtschaftswissenschaften. 2008;26(4):57–75.
- 10. Kang Y.Y. The influence of nurse managers' servant leadership on organizational effectiveness. 2008;Seoul, Kyung Hee University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 11. Kim D.H., Jung S.H. Literature review on servant leadership. Industrial Management Review. 2006;29(4):127–148.
- 12. Kim G.S. Analysis of structural equation model. 2007;Seoul, Hannarae Publishing.
- 13. Kouzes J.M., Posner B.Z. The leadership challenge. 1995;California, CA, Jossey-Bass.
- 14. Laub J. Assessing the servant organization: Development of the servant organizational leadership (SOLA) instrument. Dissertation Abstracts International. 1999;60(02):308.
- 15. Lee J.G., Park J.H. The role of trust and value congruence as a mediator between superiors' transformational, transactional leadership and outcomes. Korean Management Review. 2003;32(4):925–954.
- 16. Lee Y.H. An influence on the servant leadership of social welfare organization leader to social workers' job satisfaction and organization absorption. 2008;Cheongju, Cheongju University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 17. Lewicki R.J., Bunker B.B. Kramer R.M., Tyler T.R. Developing and maintaining trust in work relationship. In: Trust in organizations: Frontiers of theory and research. 1996;California, CA, Sage.
- 18. Oh J.C., Yang T.S. An effects of servant leadership of manager on self-efficacy, trust and service orientation: Focused on public administration service organization. Daehan Journal of Business. 2009;22(3):1245–1268.
- 19. Park J.K. A trend analysis of servant leadership. Journal of Tourism Sciences. 2008;137–149.
- 20. Podsakoff P.M., MaCkenzie S.B., Bommer W.H. Transformational leader behaviors and substitutes for leadership as determinants of employee satisfaction, commitment, trust, and organizational citizenship behaviors. Journal of Management. 1996;22(2):259–298. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/014920639602200204.ArticlePDF
- 21. Posner B.Z. Person-organization values congruence: No support for individual difference as a moderating influence. Human Relationship. 1992;45(4):351–361. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/001872679204500403.
- 22. Russell R.F. The role of values in servant leadership. Leadership & Organization Development Journal. 2001;22(2):76–84. http://dx.doi.org/10.1108/01437730110382631.Article
- 23. Shapiro D.L., Sheppard B.H., Cheraskin L. Business on a handshake. Negotiational Journal. 1992;8(4):365–377. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1571-9979.1992.tb00679.x.Article
- 24. Spears L.C. In: Insights on leadership: Service, stewardship, spirit and servant-leadership. 1995;New york, NY, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
- 25. Yoo E.J. A study on the relationship of servant leadership of nursing unit manager on trust in leader and organizational citizenship behavior of nursing staff. 2008;Seoul, Yonsei University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 26. Yoon C.W. The effects of servant leadership on job attitude and job performance in hospitals. 2009;Busan, Dong-eui University. Unpublished doctoral dissertation.
- 27. Yoon D.G. A study on the influence of servant leadership in hotel organization on the attitude of employees. 2005;Gyeongsan, Daegu University. Unpublished doctoral dissertation.
- 28. Yoon D.G., Jang B.J. A study on the influence of leader's servant leadership on leader effect - centered on hotel enterprise. Korean Journal of Tourism Research. 2005;20(1):137–153.
- 29. Yoon D.G., Jang B.J. A study on the influence of servant leadership in hotel organization on the attitude of employees. Journal of Korean Academy of Marketing Science. 2006;16(3):107–123.
- 30. Yukl G.A., Fleet D.D.V. Dunnette M.D., Hough Leaetta M. Theory and research on leadership in organization. In: Handbook of industrial and organizational psychology. 1992;2nd ed. Palo Alto, Consulting Psychologist Press. 147–198.
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Servant Leadership and Organizational Citizenship Behavior in Indonesian Christian Higher Education: Direct and Indirect Effects
Zummy Anselmus Dami, Ali Imron, Burhanuddin, Achmad Supriyanto
Journal of Research on Christian Education.2024; 33(1-2): 58. CrossRef - Servant leadership and job satisfaction: The mediating role of trust and leader-member exchange
Zummy Anselmus Dami, Ali Imron, Burhanuddin Burhanuddin, Achmad Supriyanto
Frontiers in Education.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - A meta-analytic review of the consequences of servant leadership: The moderating roles of cultural factors
Yucheng Zhang, Yuyan Zheng, Long Zhang, Shan Xu, Xin Liu, Wansi Chen
Asia Pacific Journal of Management.2021; 38(1): 371. CrossRef - Effects of nurses’ emotional intelligence on their organizational citizenship behavior, with mediating effects of leader trust and value congruence
So‐Hee Lim, Sang‐Sook Han, Yun‐Su Joo
Japan Journal of Nursing Science.2018; 15(4): 363. CrossRef - Leadership Experience of Clinical Nurses: Applying Focus Group Interviews
Byoung-Sook Lee, Yong-Sook Eo, Mi-Aie Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2015; 45(5): 671. CrossRef - Factors related to Nurses' Patient Identification Behavior and the Moderating Effect of Person-organization Value Congruence Climate within Nursing Units
Young Mee Kim, Seung-Wan Kang, Se Young Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2014; 44(2): 198. CrossRef
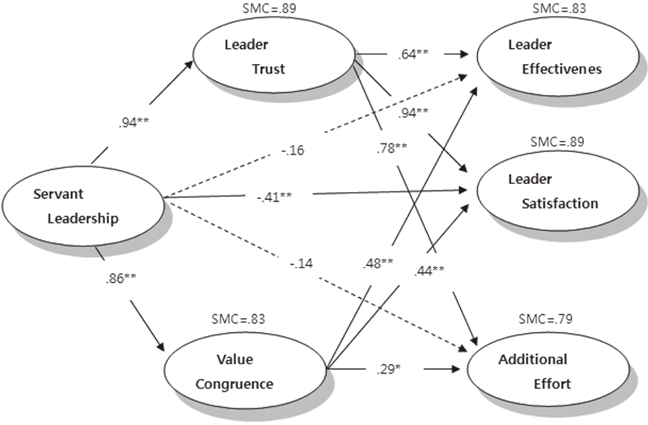
Figure 1
Figure 2
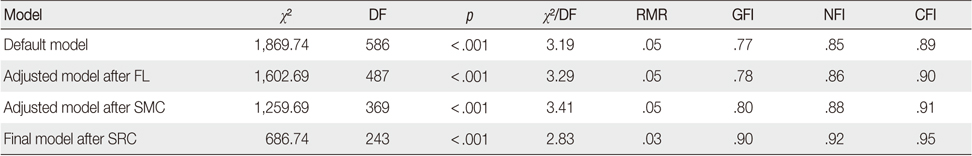
The Convergent Validity of the Model (N=361)
RMR=Root mean square residual; GFI=Goodness of fit index; NFI=Normed fit index; CFI=Goodness of fit index; FL=Factor loading; SMC=Squared multiple correlation; SRC=Standardized residual covariance.
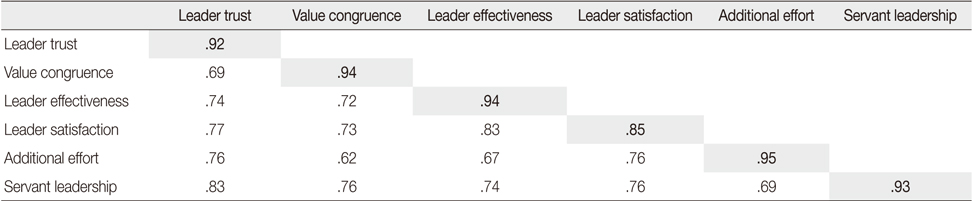
The Discriminant Validity of the Model (N=361)
The shaded section; Average variance extracted. The non-shaded section; Correlation
SMC=Squared multiple correlation(Non shaded section); AVE=Average variance extracted(Shaded section).
Effects of Predictor Variables in the Modified Model
SMC=Squared multiple correlation.
RMR=Root mean square residual; GFI=Goodness of fit index; NFI=Normed fit index; CFI=Goodness of fit index; FL=Factor loading; SMC=Squared multiple correlation; SRC=Standardized residual covariance.
The shaded section; Average variance extracted. The non-shaded section; Correlation SMC=Squared multiple correlation(Non shaded section); AVE=Average variance extracted(Shaded section).
SMC=Squared multiple correlation.
 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION
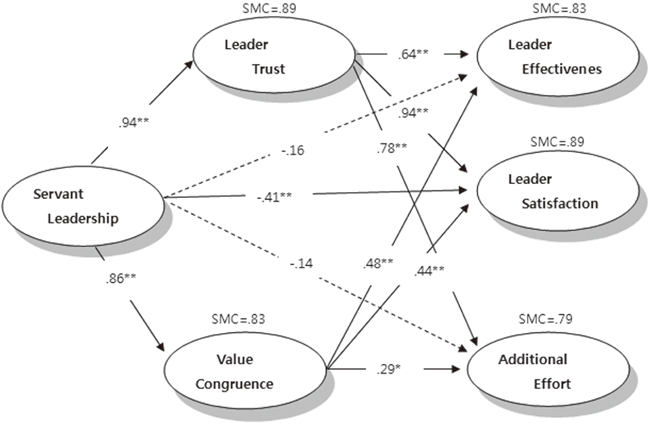
 Cite
Cite

