Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Nurs > Volume 41(6); 2011 > Article
-
Original Article
- Heart Rate Variability and Metabolic Syndrome in Hospitalized Patients with Schizophrenia
- Kyunghee Lee, Jeongeon Park, Jeongim Choi, Chang Gi Park
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2011;41(6):788-794.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2011.41.6.788
Published online: December 31, 2011
1Professor, College of Nursing, Keimyung University, Daegu, Korea.
2Full-time Lecturer, Department of Nursing, Gyeongsan University College, Gyeongsan, Korea.
3Staff Nurse, Keimyung University Dongsan Medical Center, Daegu, Korea.
4Statistian, College of Nursing, University of Illinois at Chicago, USA.
- Address reprint requests to: Lee, Kyunghee. College of Nursing, Keimyung University, 1095 Dalgubeoldae-ro, Dalseo-gu, Daegu 704-701, Korea. Tel: +82-53-580-3927, Fax: +82-53-580-3916, khl645@kmu.ac.kr
© 2011 Korean Society of Nursing Science
Abstract
-
Purpose
- Reduced heart rate variability significantly increases cardiovascular mortality. Metabolic syndrome increases the cardiac autonomic dysfunction. Recently, increasing cardiovascular mortality has been reported in patients with schizophrenia. This study was done to compare heart rate variability between adults with and without schizophrenia and to compare the relationship of heart rate variability to metabolic syndrome in hospitalized patients with schizophrenia.
-
Methods
- This was a descriptive and correlational study in which 719 adults without schizophrenia and 308 adults with schizophrenia took part between May and June 2008. We measured the following: five-minute heart rate variability; high-frequency, low-frequency, the ratio of low-frequency to high-frequency, and the Standard Deviation of all the normal RR intervals. Data was also collected on metabolic syndrome, abdominal obesity, triglycerides, HDL cholesterol, blood pressure and fasting glucose.
-
Results
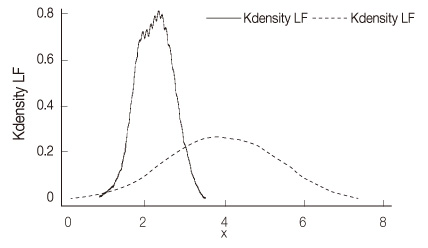
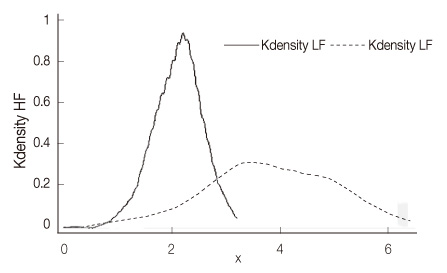
- The Standard Deviation of all the normal RR intervals values of heart rate variability indices were 1.53±0.18. The low-frequency and high-frequency values of heart rate variability indices were significantly higher in hospitalized patients with schizophrenia (3.89±1.36; 3.80±1.20) than those in the healthy participants (2.20±0.46; 2.10±0.46). There were no significant differences between the schizophrenic patients with and without metabolic syndrome.
-
Conclusion
- The results of this study indicate that schizophrenia patients have significantly lower cardiac autonomic control, but they have significantly higher low-frequency and high-frequency values than those of healthy adults. Use of antipsychotic drug may affect the autonomic nervous system in schizophrenic patients. Metabolic syndrome was not associated with cardiac autonomic control in schizophrenia patients.
INTRODUCTION
METHODS
Abdominal obesity (waist circumference male ≥90 cm, female ≥80 cm) (WHO, IASO, & IOTF, 2000)
Triglycerides ≥150 mg/dL
HDL cholesterol ≤40 mg/dL (men) and ≤50 mg/dL (women)
Blood pressure: ≥130/ ≥85 mmHg
Fasting glucose: ≥110 mg/dL
RESULTS
DISCUSSION
CONCLUSIONS
- 1. Agelink MW, Majewski T, Wurthmann C, Lukas K, Ullrich H, Linka T, et al. Effects of newer atypical antipsychotics on autonomic neurocardiac function: A comparison between amisulpride, olanzapine, sertindole, and clozapine. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology. 2001;21:8–13.ArticlePubMed
- 2. Astrup AS, Tarnow L, Rossing P, Hansen BV, Hilsted J, Parving HH. Cardiac autonomic neuropathy predicts cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in type 1 diabetic patients with diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes Care. 2006;29:334–339. doi: 10.2337/diacare.29.02.06.dc05-1242.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 3. Bar KJ, Letzsch A, Jochum T, Wagner G, Greiner W, Sauer H. Loss of efferent vagal activity in acute schizophrenia. Journal of Psychiatric Research. 2005;39:519–527.ArticlePubMed
- 4. Birkhofer A, Alger P, Schmid G, Forstl H. The cardiovascular risk of schizophrenic patients. Neuropsychiatr. 2007;21:261–266.PubMed
- 5. Boettger S, Hoyer D, Falkenhahn K, Kaatz M, Yeragani VK, Bar KJ. Altered diurnal autonomic variation and reduced vagal information flow in acute schizophrenia. Clinical Neurophysiology. 2006;117:2715–2722. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2006.08.009.ArticlePubMed
- 6. Cohen H, Loewenthal U, Matar M, Kotler M. Association of autonomic dysfunction and clozapine. Heart rate variability and risk for sudden death in patients with schizophrenia on long-term psychotropic medication. The British Journal of Psychiatry. 2001;179:167–171.PubMed
- 7. Grundy SM, Cleeman JI, Merz CN, Brewer HB Jr, Clark LT, Hunninghake DB, et al. Implications of recent clinical trials for the National Cholesterol Education Program Adult Treatment Panel III guidelines. Circulation. 2004;110:227–239.ArticlePubMed
- 8. Henry BL, Minassian A, Paulus MP, Geyer MA, Perry W. Heart rate variability in bipolar mania and schizophrenia. Journal of Psychiatric Research. 2010;44:168–176. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2009.07.011.ArticlePubMed
- 9. Ikawa M, Tabuse H, Ueno S, Urano T, Sekiya M, Murakami T. Effects of combination psychotropic drug treatment on heart rate variability in psychiatric patients. Psychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences. 2001;55:341–345. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1819.2001.00873.x.ArticlePubMed
- 10. Karason K, Molgaard H, Wikstrand J, Sjostrom L. Heart rate variability in obesity and the effect of weight loss. American Journal of Cardiology. 1999;83:1242–1247. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9149(99)00066-1.ArticlePubMed
- 11. Kelly DL, McMahon RP, Liu F, Love RC, Wehring HJ, Shim JC, et al. Cardiovascular disease mortality in patients with chronic schizophrenia treated with clozapine: A retrospective cohort study. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry. 2010;71:304–311. doi: 10.4088/JCP.08m04718yel.PubMed
- 12. Kim JA, Park YG, Cho KH, Hong MH, Han HC, Choi YS, et al. Heart rate variability and obesity indices: Emphasis on the response to noise and standing. Journal of the American Board of Family Practice. 2005;18:97–103. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.01275.2005.ArticlePubMed
- 13. Kuch B, Hense HW, Sinnreich R, Kark JD, von Eckardstein A, Sapoznikov D, et al. Determinants of short-period heart rate variability in the general population. Cardiology. 2001;95:131–138.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 14. Kudat H, Akkaya V, Sozen AB, Salman S, Demirel S, Ozcan M, et al. Heart rate variability in diabetes patients. Journal of International Medical Research. 2006;34:291–296.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 15. La Rovere MT, Bigger JT Jr, Marcus FI, Mortara A, Schwartz PJ. Baroreflex sensitivity and heart-rate variability in prediction of total cardiac mortality after myocardial infarction. ATRAMI (Autonomic Tone and Reflexes After Myocardial Infarction) Investigators. Lancet. 1998;351:478–484. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(97)11144-8.PubMed
- 16. La Rovere MT, Pinna GD, Hohnloser SH, Marcus FI, Mortara A, Nohara R, et al. Baroreflex sensitivity and heart rate variability in the identification of patients at risk for life-threatening arrhythmias: Implications for clinical trials. Circulation. 2001;103:2072–2077.ArticlePubMed
- 17. Lee WY, Park JS, Noh SY, Rhee EJ, Kim SW, Zimmet PZ. Prevalence of the metabolic syndrome among 40,698 Korean metropolitan subjects. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice. 2004;65:143–149.ArticlePubMed
- 18. Liao D, Carnethon M, Evans GW, Cascio WE, Heiss G. Lower heart rate variability is associated with the development of coronary heart disease in individuals with diabetes: The atherosclerosis risk in communities (ARIC) study. Diabetes. 2002;51:3524–3531.PubMed
- 19. Mann K, Rossbach W, Muller MJ, Muller-Siecheneder F, Ru H, Dittmann RW. Heart rate variability during sleep in patients with schizophrenia treated with olanzapine. International Clinical Psychopharmacology. 2004;19:325–330.ArticlePubMed
- 20. McEvoy JP, Meyer JM, Goff DC, Nasrallah HA, Davis SM, Sullivan L, et al. Prevalence of the metabolic syndrome in patients with schizophrenia: Baseline results from the Clinical Antipsychotic Trials of Intervention Effectiveness (CATIE) schizophrenia trial and comparison with national estimates from NHANES III. Schizophrenia Research. 2005;80:19–32. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2005.07.014.ArticlePubMed
- 21. Meyer JM. Effects of atypical antipsychotics on weight and serum lipid levels. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry. 2001;62:27–34.
- 22. Meyer JM, Nasrallah HA, McEvoy JP, Goff DC, Davis SM, Chakos M, et al. The Clinical Antipsychotic trials Of Intervention Effectiveness (CATIE) Schizophrenia trial: Clinical comparison of subgroups with and without the metabolic syndrome. Schizophrenia Research. 2005;80:9–18. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2005.07.015.ArticlePubMed
- 23. Montano N, Gneddhi RT, Porta A, Lombardi F, Pagani M, Malliani A. Power spectrum analysis of heart rate variability to assess the changes in sympathovagal balance during graded orthostatic tilt. Circulation. 1994;90:1826–1831.ArticlePubMed
- 24. Oh JY, Hong YS, Sung YA, Barrett-Connor E. Prevalence and factor analysis of metabolic syndrome in an urban Korean population. Diabetes Care. 2004;27:2027–2032. doi: 10.2337/diacare.27.8.2027.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 25. Sugawara N, Yasui-Furukori N, Sato Y, Kishida I, Yamashita H, Saito M, et al. Comparison of prevalence of metabolic syndrome in hospital and community-based Japanese patients with schizophrenia. Annals of General Psychiatry. 2011;10:21. doi: 10.1186/1744-859X-10-21.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 26. Suvisaari JM, Saarni SI, Perala J, Suvisaari JV, Harkanen T, Lonnqvist J, et al. Metabolic syndrome among persons with schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders in a general population survey. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry. 2007;68:1045–1055.ArticlePubMed
- 27. Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology and the North American Society of Pacing and Electrophysiology. Heart rate variability: Standards of measurement, physiological interpretation, and clinical use. Circulation. 1996;93:1043–1065.ArticlePubMed
- 28. Van Ravenswaaij-Arts CM, Kollee LA, Hopman JC, Stoelinga GB, van Geijn HP. Heart rate variability. Annals of Internal Medicine. 1993;118:436–447.ArticlePubMed
- 29. WHO, IASO, & IOTF. The Asia-Pacific perspective: Redefining obesity and its treatment. 2000;Australia, Health Communications. 1–56.
- 30. Wang YC, Yang CC, Bai YM, Kuo TB. Heart rate variability in schizophrenic patients switched from typical antipsychotic agents to amisulpride and olanzapine: 3-month follow-up. Neuropsychobiology. 2008;57:200–205. doi: 10.1159/000149818.ArticlePubMedPDF
REFERENCES
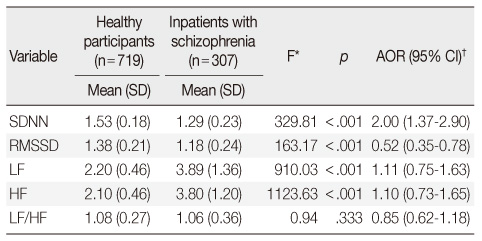
*Covariate: Age; †Logistic regression analyses adjusted with all above variables.
AOR=Adjusted odds ratio; 95% CI=95% confidence interval; SDNN= Standard deviation of all normal RR intervals; RMSSD=Root mean square of successive differences; LF=Low-frequency; HF=High-frequency; LF/HF: The ratio of low to high frequency.
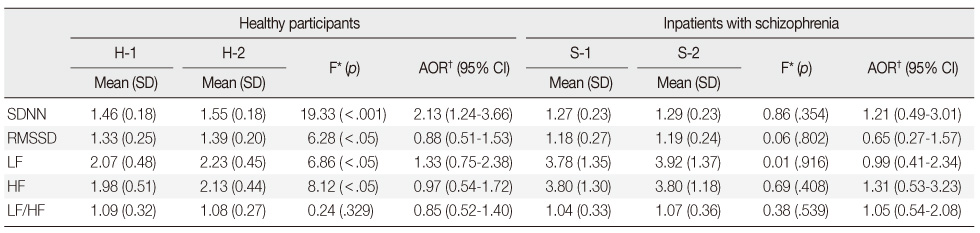
*Covariate: Age; †Logistic regression analyses adjusted with all above variables.
AOR=Adjusted odds ratio; 95% CI=95% confidence interval; SDNN=Standard deviation of all normal RR intervals; RMSSD=Root mean square of successive differences; LF=Low-frequency; HF=High-frequency; LF/HF: The ratio of low to high frequency; H-1 group: Healthy participants with metabolic syndrome, n=115; H-2 group: Healthy participants without metabolic syndrome, n=604; S-1group: Inpatients with schizophrenia with metabolic syndrome, n=61; S-2 group: Inpatients with schizophrenia without metabolic syndrome, n=246.
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Altered Heart Rate Variability During Rest in Schizophrenia: A State Marker
Anjum Datta, Sandeep Choudhary, Sunaina Soni, Rajesh Misra, Kiran Singh
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Autonomic nervous system dysfunction in schizophrenia: impact on cognitive and metabolic health
Nicolette Stogios, Alexander Gdanski, Philip Gerretsen, Araba F. Chintoh, Ariel Graff-Guerrero, Tarek K. Rajji, Gary Remington, Margaret K. Hahn, Sri Mahavir Agarwal
npj Schizophrenia.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Resting vagal activity in schizophrenia: Meta-analysis of heart
rate variability as a potential endophenotype
Annika Clamor, Tania M. Lincoln, Julian F. Thayer, Julian Koenig
British Journal of Psychiatry.2016; 208(1): 9. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Metabolic Syndrome among Mental Health Facility Patients with Schizophrenia
Sun-Hye Lee, Sunhee Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2016; 25(1): 1. CrossRef - Impact of metabolic syndrome and its components on heart rate variability during hemodialysis: a cross-sectional study
Yu-Ming Chang, Chih-Chung Shiao, Ya-Ting Huang, I-Ling Chen, Chuan-Lan Yang, Show-Chin Leu, Hung-Li Su, Jsun-Liang Kao, Shih-Ching Tsai, Rong-Na Jhen, Ching-Cherng Uen
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Heart rate variability and vagal tone in schizophrenia: A review
Julian M. Montaquila, Benjamin J. Trachik, Jeffrey S. Bedwell
Journal of Psychiatric Research.2015; 69: 57. CrossRef - Association and interaction analysis of excess weight and chronic kidney disease for cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy in the general Chinese population
Yan Zhang, Nai-Jia Liu, Jin Zhang, Hong Yang, Zi-Hui Tang
Renal Failure.2015; 37(7): 1111. CrossRef - Evaluation of autonomic nervous system by salivary alpha-amylase level and heart rate variability in patients with schizophrenia
Masa Ieda, Tsuyoshi Miyaoka, Rei Wake, Kristian Liaury, Keiko Tsuchie, Michiyo Fukushima, Tomoko Araki, Satoko Ezoe, Takuji Inagaki, Jun Horiguchi
European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience.2014; 264(1): 83. CrossRef - Heart rate variability and the metabolic syndrome: a systematic review of the literature
Melanie I. Stuckey, Mikko P. Tulppo, Antti M. Kiviniemi, Robert J. Petrella
Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews.2014; 30(8): 784. CrossRef - Unraveling the Mechanisms Responsible for the Comorbidity between Metabolic Syndrome and Mental Health Disorders
Elizabeth K. Nousen, Juliana G. Franco, Elinor L. Sullivan
Neuroendocrinology.2013; 98(4): 254. CrossRef
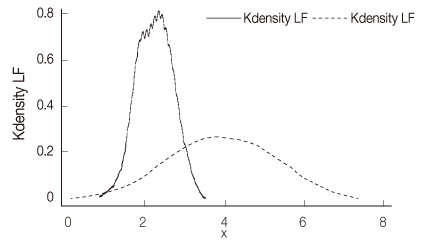
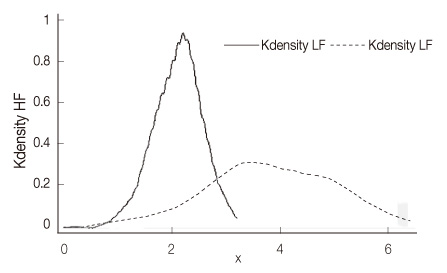
Figure 1
Figure 2
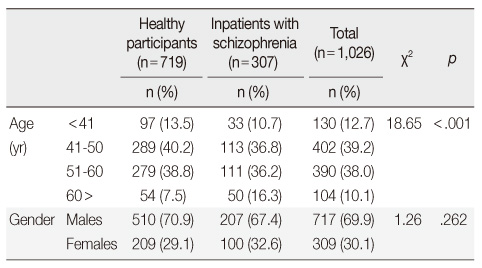
Characteristics of Study Population (N=1,026)
Values of Linear Heart Rate Variability Indices between H Participants and S Participants (N=1,026)
*Covariate: Age; †Logistic regression analyses adjusted with all above variables.
AOR=Adjusted odds ratio; 95% CI=95% confidence interval; SDNN= Standard deviation of all normal RR intervals; RMSSD=Root mean square of successive differences; LF=Low-frequency; HF=High-frequency; LF/HF: The ratio of low to high frequency.
Differences in Heart Rate Variability Indices according to the Metabolic Factor between Healthy Participants and Inpatients with Schizophrenia Groups (N=1,026)
*Covariate: Age; †Logistic regression analyses adjusted with all above variables.
AOR=Adjusted odds ratio; 95% CI=95% confidence interval; SDNN=Standard deviation of all normal RR intervals; RMSSD=Root mean square of successive differences; LF=Low-frequency; HF=High-frequency; LF/HF: The ratio of low to high frequency; H-1 group: Healthy participants with metabolic syndrome, n=115; H-2 group: Healthy participants without metabolic syndrome, n=604; S-1group: Inpatients with schizophrenia with metabolic syndrome, n=61; S-2 group: Inpatients with schizophrenia without metabolic syndrome, n=246.
*Covariate: Age; †Logistic regression analyses adjusted with all above variables. AOR=Adjusted odds ratio; 95% CI=95% confidence interval; SDNN= Standard deviation of all normal RR intervals; RMSSD=Root mean square of successive differences; LF=Low-frequency; HF=High-frequency; LF/HF: The ratio of low to high frequency.
*Covariate: Age; †Logistic regression analyses adjusted with all above variables. AOR=Adjusted odds ratio; 95% CI=95% confidence interval; SDNN=Standard deviation of all normal RR intervals; RMSSD=Root mean square of successive differences; LF=Low-frequency; HF=High-frequency; LF/HF: The ratio of low to high frequency; H-1 group: Healthy participants with metabolic syndrome, n=115; H-2 group: Healthy participants without metabolic syndrome, n=604; S-1group: Inpatients with schizophrenia with metabolic syndrome, n=61; S-2 group: Inpatients with schizophrenia without metabolic syndrome, n=246.
 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION
 Cite
Cite

