Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Nurs > Volume 41(4); 2011 > Article
-
Original Article
- Analysis of Cost and Efficiency of a Medical Nursing Unit Using Time-Driven Activity-Based Costing
- Ji Young Lim, Mi Ja Kim, Chang Gi Park
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2011;41(4):500-509.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2011.41.4.500
Published online: August 31, 2011
1Associate Professor, Department of Nursing, Inha University, Incheon, Korea.
2Professor, College of Nursing, University of Illinois at Chicago, Chicago, USA.
3Senior Health Economist, College of Nursing, University of Illinois at Chicago, Chicago, USA.
- Address reprint requests to: Lim, Ji Young. Department of Nursing, Inha University, 253 Younghyun-dong, Nam-gu, Incheon 402-751, Korea. Tel: +82-32-860-8210, Fax: +82-32-874-5880, lim20712@inha.ac.kr
• Received: August 11, 2010 • Accepted: August 4, 2011
© 2011 Korean Society of Nursing Science
Abstract
-
Purpose
- Time-driven activity-based costing was applied to analyze the nursing activity cost and efficiency of a medical unit.
-
Methods
- Data were collected at a medical unit of a general hospital. Nursing activities were measured using a nursing activities inventory and classified as 6 domains using Easley-Storfjell Instrument. Descriptive statistics were used to identify general characteristics of the unit, nursing activities and activity time, and stochastic frontier model was adopted to estimate true activity time.
-
Results
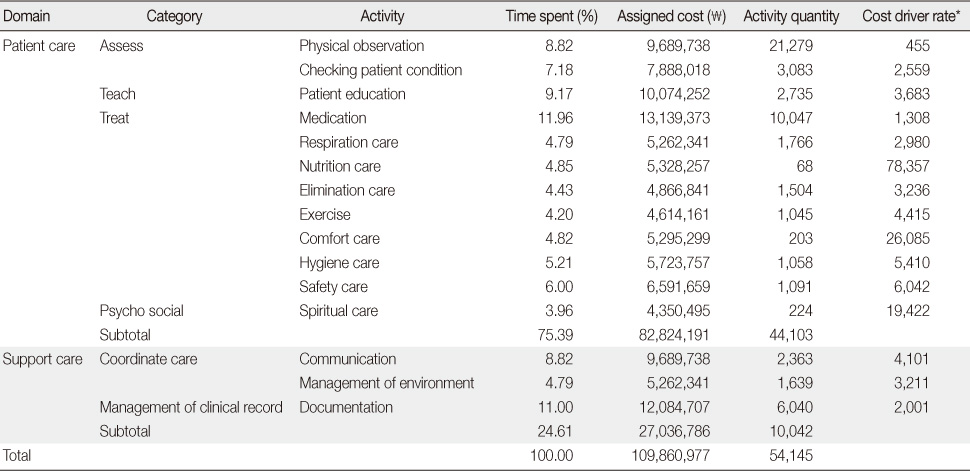
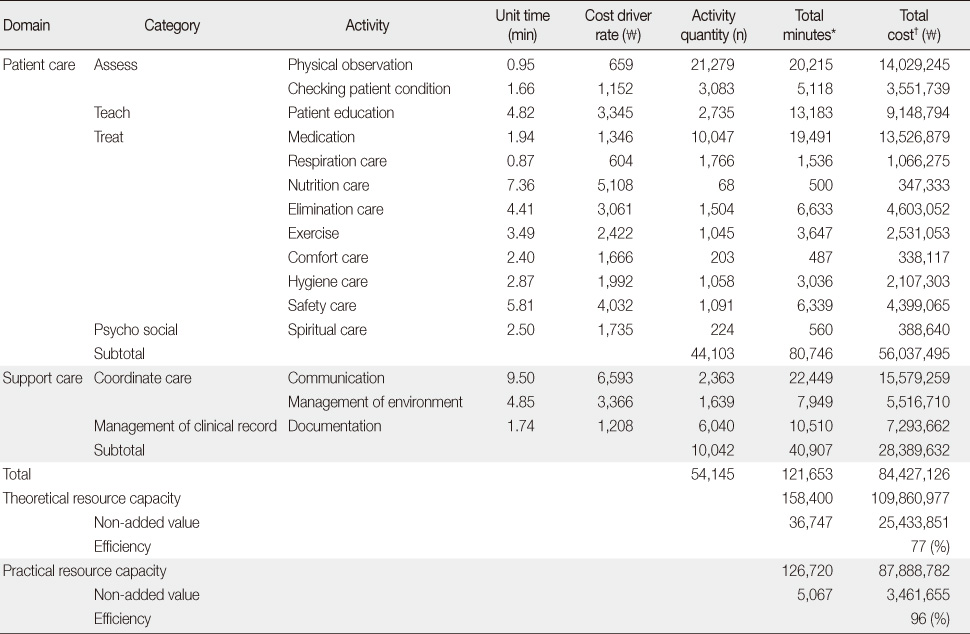
- The average efficiency of the medical unit using theoretical resource capacity was 77%, however the efficiency using practical resource capacity was 96%. According to these results, the portion of non-added value time was estimated 23% and 4% each. The sums of total nursing activity costs were estimated 109,860,977 won in traditional activity-based costing and 84,427,126 won in time-driven activity-based costing. The difference in the two cost calculating methods was 25,433,851 won.
-
Conclusion
- These results indicate that the time-driven activity-based costing provides useful and more realistic information about the efficiency of unit operation compared to traditional activity-based costing. So time-driven activity-based costing is recommended as a performance evaluation framework for nursing departments based on cost management.
- 1. Hofler RA, List J. Valuation on the frontier: Calibration actual and hypothetical statements of value. American Journal of Agricultural Economics. 2004;86:213–221. doi: 10.1111/j.0092-5853.2004.00573.x.
- 2. Hong CG. The understanding of two-stage costing system from the economic perspective-with an emphasis on activity-based costing. Korean Accounting Review. 2001;26:1–24.
- 3. Jang JB. Study on estimation of the costs incurred by ED nursing activities by applying the activity based costing. 2004;Seoul, Ewha Womans University. Unpublished master thesis.
- 4. Kang KH. Analysis of nursing activities and cost of nursing service based on the ABC system. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration. 1999;5:389–400.
- 5. Kaplan RS, Anderson SR. Time-driven activity-based costing. Harvard Business Review. 2004;82:131–138.ArticlePDF
- 6. Kaplan RS, Anderson SR. The innovation of time-driven activity-based costing. Journal of Cost Management. 2007;21(2):5–15.
- 7. Kim IS, Kang KH, Lee HJ, Kim MJ, Kang SJ, Joo YM. Cost analysis of nursing services in the delivery room using activity-based costing. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration. 2002;8:17–29.
- 8. Kim J, Ham U, Rhieu S. Analysis of efficiency in hospitals by stochastic frontier approach. Daehan Journal of Business. 2009;22:1867–1889.
- 9. Kim JS. A study on the activity analysis method for activity based costing system: Using existing firm material in service industry. 2000;Incheon, University of Incheon. Unpublished master thesis.
- 10. Lee SD, Lee SH, Seo JH. Hospital cost accounting. 2001;Seoul, Imagination, Publishing.
- 11. Lee SJ. Cost analysis of home health care with activity-based costing (ABC). 2003;Seoul, Yonsei University. Unpublished doctoral dissertation.
- 12. Lim JY. An analysis of cost and profits of a nursing unit using performance-based costing: Case of a general surgical ward in a general hospital. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2008;38:161–171.PubMed
- 13. Louie GH, Ward MM. Sex disparities in self-reported physical functioning: True differences, reporting bias, or incomplete adjustment for confounding? Journal of the American Geriatrics Society. 2010;58:1117–1122. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2010.02858.x.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 14. MaCleod J, Hickman M, Smith GD. Reporting bias and self-reported drug use. Addiction. 2005;100:562–563.ArticlePubMed
- 15. Oh D, Lee J, Min I. Analysis on efficiency and productivity of Korean regional public hospital between before and after the separation of dispensary from medical practice: Using parametric and non-parametric statistical approaches. Korean Journal of Health Economics and Policy. 2007;13:173–198.
- 16. Park JH, Sung YH, Song MS, Cho JS, Sim WH. The classification of standard nursing activities in Korea. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2000;30:1411–1426.ArticlePDF
- 17. Storfjell JL, Omoike O, Ohlson S. The balancing act: Patient care time versus cost. The Journal of Nursing Administration. 2008;38:244–249. doi: 10.1097/01.NNA.0000312771.96610.df.PubMed
- 18. Yoon J, Jung S, Kim J, An S. Cost management using activity based costing in hospitals: A study on the case study in the K hospital. Journal of Taxation and Accounting. 2003;4:295–327.
- 19. Yoon KJ. A comparison of DEA and SFM to evaluate the performance of public department. Korean Public Administration Review. 1998;32:257–273.
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- Cost estimation of preventive dental hygiene care using Time-Driven Activity-Based Costing (TDABC)
Yun-Sook Jung, Bo-Kyoung Oh, Yun-Jung Jang, Sun-Hee Hwang, Seo-Young Yoon, Seong-Eun Baek, Min-Young Kim
Journal of Korean Society of Dental Hygiene.2024; 24(5): 489. CrossRef - Estimated Time to Complete Direct Nursing Interventions Using the Nursing Interventions Classification (NIC) at Eight Hospitals in South Korea
Eunjoo Lee, Hyejin Park
International Journal of Nursing Knowledge.2018; 29(2): 104. CrossRef - Economic Analysis of USN-Based Data Acquisition Systems in Tall Building Construction
Hyunsu Lim, Jin Lee, Taehoon Kim, Kyuman Cho, Hunhee Cho
Sustainability.2017; 9(8): 1360. CrossRef - A Methodological Quality Evaluation of Nursing Cost Analysis Research based on Activity-based Costing in Korea
Ji-Young Lim, Wonjung Noh, Jin-A Mo
The Journal of the Korea Contents Association.2016; 16(7): 279. CrossRef - Financial Ratio Analysis for Developing Nursing Management Strategies in University Hospitals
Ji Young Lim, Wonjung Noh, Seung Eun Oh, Ok Gum Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2013; 19(1): 7. CrossRef - Activity-Based Costing Analysis of Nursing Activities in General Hospital Wards
Ho-Soon Yoon, Jinhyun Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2013; 19(4): 449. CrossRef
Analysis of Cost and Efficiency of a Medical Nursing Unit Using Time-Driven Activity-Based Costing
Analysis of Cost and Efficiency of a Medical Nursing Unit Using Time-Driven Activity-Based Costing
Costs Using Traditional Activity-Based Costing
*assigned cost/activity quantity.
Costs and Efficiency Using Time-Driven Activity-Based Costing
*unit time X activity quantity; †cost driver rate X activity quantity.
Table 1
Costs Using Traditional Activity-Based Costing
*assigned cost/activity quantity.
Table 2
Costs and Efficiency Using Time-Driven Activity-Based Costing
*unit time X activity quantity; †cost driver rate X activity quantity.
 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION
 Cite
Cite

