Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Nurs > Volume 41(3); 2011 > Article
-
Original Article
- Quality of Sleep and Serum Lipid Profile in Patients with Restless Legs Syndrome
- Yeon-Gyung Bak, Hyoung-Sook Park
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2011;41(3):344-353.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2011.41.3.344
Published online: June 13, 2011
1Doctoral Student, College of Nursing, Pusan National University, Busan, Korea.
2Professor, College of Nursing, Pusan National University, Busan, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Park, Hyoung-Sook. Yangsan Campus of Pusan National University, College of Nursing, Beomeo-ri, Mulgeum-eup, Yangsan 626-770, Korea. Tel: +82-51-510-8336, Fax: +82-51-510-8308, haedang@pusan.ac.kr
© 2011 Korean Society of Nursing Science
Abstract
-
Purpose
- The purpose of this study was to compare the quality of sleep with the serum lipid profile in patients who have restless legs syndrome (RLS).
-
Methods
- The data were obtained from 116 patients with RLS through questionnaires and blood sampling.
-
Results
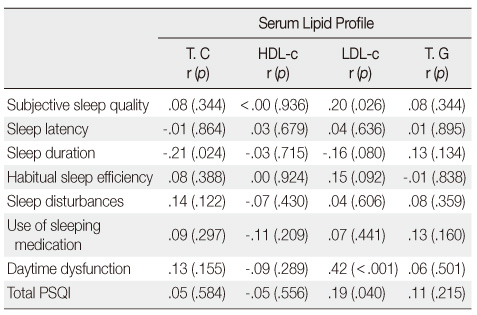
- The results of this study showed correlations between lower quality of sleep and serum lipid profile (LDL Cholesterol) in patients with RLS (r=.19, p=.040). There were correlations for scores of quality of sleep from the, Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI) sub-region between lower subjective sleep quality and serum lipid profile (LDL Cholesterol) (r=.20, p=.026), between fewer hours of sleep duration and serum lipid profile (Total Cholesterol) (r=-.21, p=.024), and, between higher daytime dysfunction and serum lipid profile (LDL Cholesterol) (r=.42, p<.001) of patients with RLS.
-
Conclusion
- Patients with RLS have sleep disorders with lower quality of sleep and changes in the serum lipid profile for total cholesterol and LDL cholesterol. That is, patients with RLS have lower quality of sleep and dyslipidemia compared to persons without RLS. Further research is needed to monitor serum the lipid profile in early stage symptoms of midlife adult patients with RLS and especially older women.
This article is based on a part of the first author's master's thesis from Pusan National University.
- 1. Allen RP, Walters AS, Montplaisir J, Hening W, Myers A, Bell TJ, et al. Restless legs syndrome prevalence and impact: REST (re-stless legs syndrome epidemiology, symptoms and treatment) general population study. Archives of Internal Medicine. 2005;165:1286–1292.PubMed
- 2. Ayas NT, White DP, Manson JE, Manson JE, Stampfer MJ, Speizer FE, et al. A prospective study of sleep duration and coronary heart disease in women. Archives of Internal Medicine. 2003;163:205–209.ArticlePubMed
- 3. Berger K, Leudemann J, Trenkwalder C, John U, Kessler C. Sex and the risk of restless legs syndrome in the general population. Archives of Internal Medicine. 2004;164:196–202.ArticlePubMed
- 4. Buysse D, ReynoldsIII CF, Monk TS, Berman SR, Kupfer DJ. The Pittsburgh sleep quality index: A new instrument for psychiatric and research. Psychiatry Research. 1989;28:193–213. doi:10.1016/0165-1781(89)90047-4.ArticlePubMed
- 5. Cho YW, Lee H, Lee JH, Shin WC, Han SY, Lee MY. Sleep disorders in maintenance dialysis patients with end-stage renal disease. Journal of the Korean Neurological Association. 2003;21:492–497.
- 6. Cho YW, Shin WC, Yun CH, Hong SB, Kim JH, Allen RP, et al. Epidemiology of restless legs syndrome in Korean adults. Sleep. 2008;31:219–233.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 7. Cho YW, Suh YS. Restless legs syndrome: An update in diagnosis and management. Journal of the Korean Academy of Family Medicine. 2008;29:241–250.
- 8. Choi HS, Kang SG, Boo CS, Lee HJ, Cho WY, Kim HK. Restless legs syndrome and quality of life in hemodialysis patients. Sleep Medicine and Psychophysiology. 2007;14:99–106.
- 9. Choi SH, Kim R, Suh KY. A study on the sleep pattern of the general adult population in Seoul Korean adults. Journal of Korean Neuropsychiatric Association. 1992;31:289–309.
- 10. Ghorayeb I, Bioulac B, Scribans C, Tison F. Perceived severity of restless legs syndrome across the female life cycle. Sleep Medicine. 2008;9:799–802. doi:10.1016/j.sleep.2007.07.018.ArticlePubMed
- 11. Hall MH, Muldoon MF, Jennings JR, Buysse DJ, Flory JD, Manuck SB. Self-reported sleep duration is associated with the metabolic syndrome in midlife adults. Sleep. 2008;31:635–643.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 12. Happe S, Reese JP, Stiasny-Kolster K, Peglau I, Mayer G, Klotsche J, et al. Assessing health related quality of life in patients with restless legs syndrome. Sleep Medicine. 2009;10:295–305. doi:10.1016/j.sleep.2008.01.002.ArticlePubMed
- 13. Hening W, Walters AS, Allen RP, Montplaisir J, Mayers A, Ferini-Strambi L. Impact, diagnosis and treatment of restless legs syndrome (RLS) in primary care population: The REST (restless legs syndrome epidemiology, symptoms and treatment) primary care study. Sleep Medicine. 2004;5:237–246. doi:10.1016/j.sleep.2004.03.006.ArticlePubMed
- 14. Jennings JR, Muldoon MF, Hall M, Buysse DJ, Manuck SB. Self-reported sleep quality is associated with the metabolic syndrome. Sleep. 2007;30:219–233.ArticlePubMed
- 15. Kaneita Y, Uchiyama M, Yoshiike N, Ohida T. Associations of usual sleep duration with serum lipid and lipoprotein levels. Sleep. 2008;31:645–652.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 16. Kim JY, Choi CR, Shin KR, Yi HY, Park MY, Cho NH, et al. Prevalence of restless legs syndrome and association factors in the Korean adult population: The Korean health and genome study. Psychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences. 2005;59:350–353. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1819.2005.01381.x.PubMed
- 17. Kushida CA, Allen RP, Atkinson MJ. Modeling the causal relationships between symptoms associated with restless legs syndro-me and the patient reported impact of RLS. Sleep Medicine. 2004;5:485–488. doi:10.1016/j.sleep.2004.04.004.ArticlePubMed
- 18. Lee EJ. Rest-activity rhythm, sleep pattern and quality of life in patients with restless legs syndrome. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2009;39:422–432.ArticlePubMed
- 19. Lee ERG. A study on quality of women's sleeping by their age group. 2004;Seoul, Ewha Womans University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 20. Lee HS. Dietary and clinical factors affecting serum lipid levels in Korean women. 2003;Seoul, Ewha Womans University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 21. Russell M. Massage therapy and restless legs syndrome. Journal of Bodywork and Movement Therapies. 2007;11:146–150. doi:10.1016/j.jbmt.2006.12.001.Article
- 22. Schlesinger I, Ekikh I, Avizohar O, Sprecher E, Yarnitsky D. Cardiovascular risk factors in restless legs syndrome. Movement disorders. 2009;24:1587–1592. doi:10.1002/mds.22486.ArticlePubMed
- 23. Suh YK. The association between sleep duration, obesity and metabolic syndrome in Korean adult. 2009;Seoul, Ewha Womans University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 24. Tings T, Schettler V, Canelo M, Paulus W, Trenkwalder C. Impact of regular LDL apheresis on the development of restless legs syndrome. Movement Disorders. 2004;19:1072–1075. doi:10.1002/mds.20102.ArticlePubMed
- 25. Tison F, Crochard A, Leger D, Bouee S, Lainey E, EI Hasnaoui A. Epidemiology of restless legs syndrome in French adults: A nationwide survey: The INSTANT study. Neurology. 2005;65:239–246. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000168910.48309.4a.ArticlePubMed
- 26. Third report of the national cholesterol education program (NCEP) expert pannel on detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood cholesterol in adult (adult treatment pannel III). Final report. Circulation. 2002;106:3143–3421.ArticlePubMed
- 27. Walters A, Aldrich M, Allen R, Ancoli-Israel S, Buchholz D, Chokroverty S, et al. International restless legs syndrome study group: Towards a better definition of the restless leg syndrome. Movement Disorders. 1995;10:634–642. doi:10.1002/mds.870100517.PubMed
- 28. Winkelman JW, Shahar E, Sharief I, Gottlieb DJ. Association of restless legs syndrome and cardiovascular disease in the sleep heart health study. Neurology. 2008;70:35–42. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000287072.93277.c9.ArticlePubMed
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Relationship of Restless Legs Syndrome Symptom, Sleep Disturbance and Depression in Middle-aged Women
Yeon Ok Suh, Sun-Sook Moon, Kyung-Woo Lee
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2018; 21(2): 91. CrossRef - Sleep Duration and Risk of Atrial Fibrillation (from the Physicians' Health Study)
Owais Khawaja, Akmal Sarwar, Christine M. Albert, John Michael Gaziano, Luc Djoussé
The American Journal of Cardiology.2013; 111(4): 547. CrossRef - Factors related to the Quality of Sleep in the Elderly Women
Young-Hee Kim, Jin-Sook Han
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2011; 12(10): 4467. CrossRef
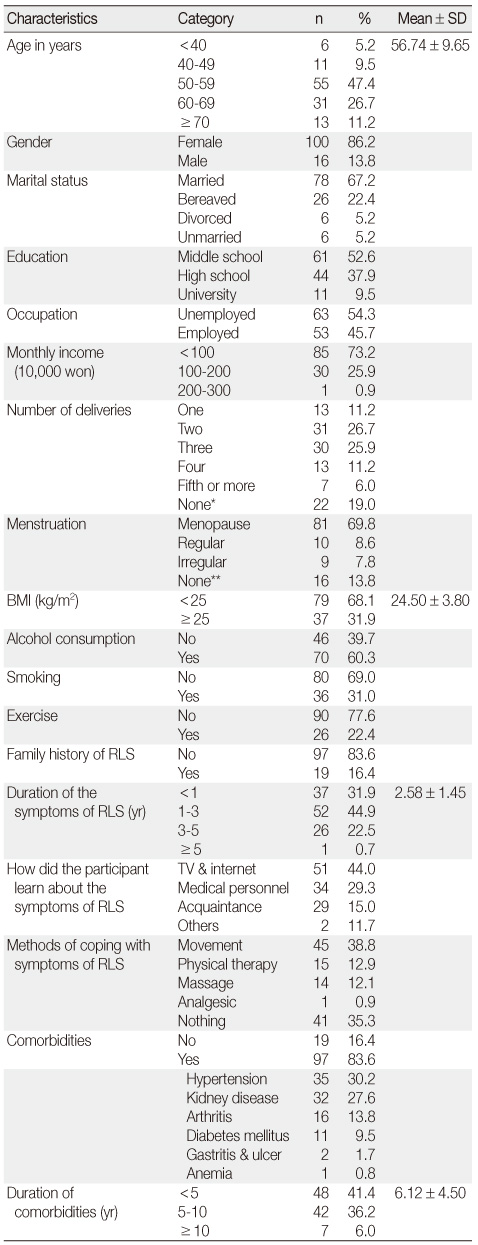
General Characteristics and Disease Related Characteristics of Participants (N = 116)
*Unmarried female: 6, Male: 16; **male 16.
BMI=body mass index; RLS=restless leg syndrome.
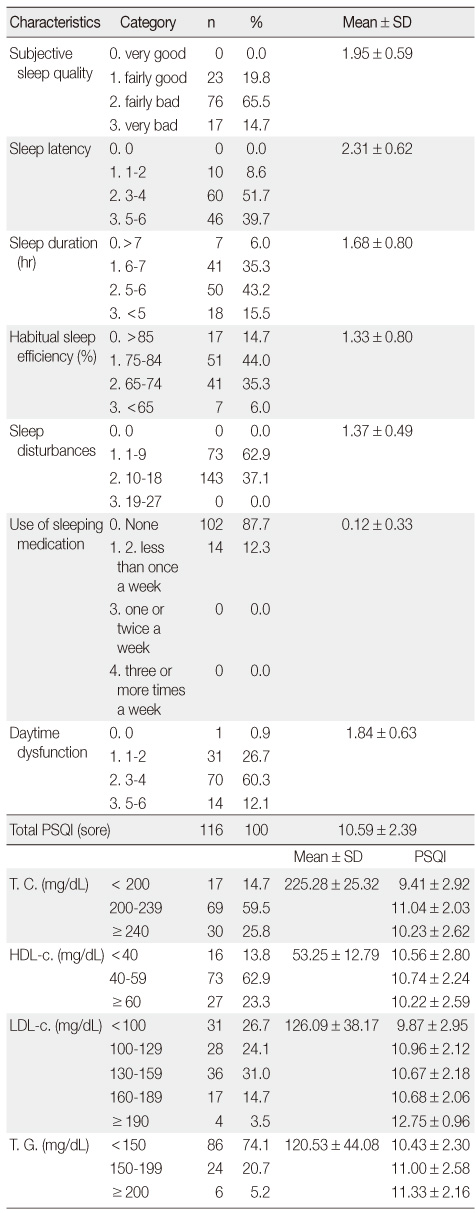
Quality of Sleep and Serum Lipid Profile of Participants (N = 116)
PSQI=pittsburgh sleep quality index; T. C.=total cholesterol; HDL-c.=high density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL-c=low density lipoprotein cholesterol; T. G.= triglycerides.
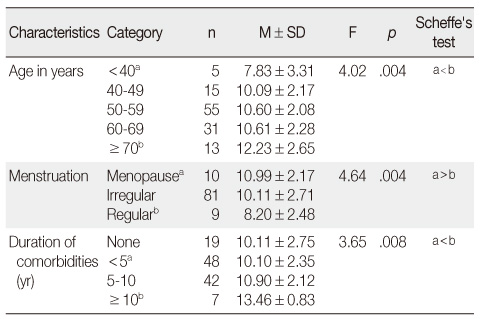
Quality of Sleep of Participants according to General and Disease Related Characteristics
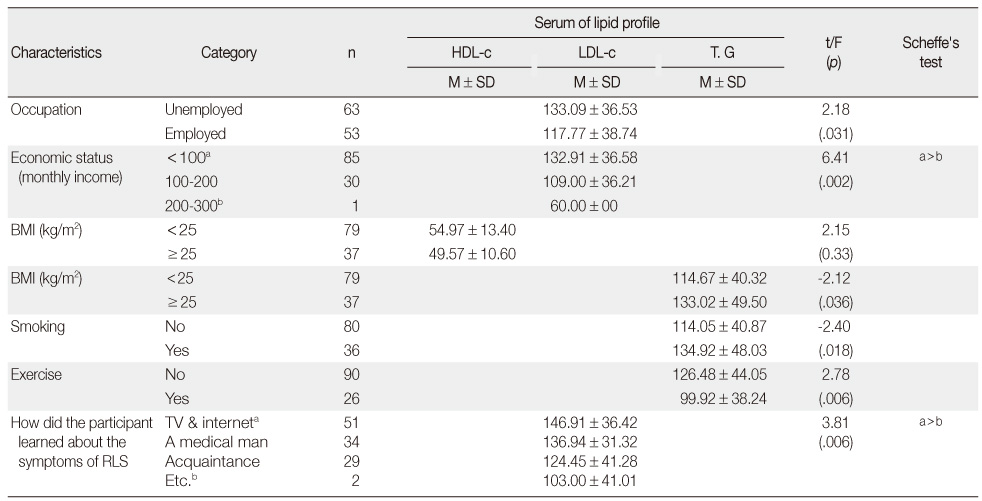
Serum Lipid Profile of Participants according to General and Disease Related Characteristics
Economic status (monthly income)(10,000 won); BMI=body mass index; HDL-c.=high density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL-c.=low density lipoprotein cholesterol; T.G.=triglycerides; RLS=restless legs syndrome; Etc.b: none.
Correlation between Quality of Sleep and Serum Lipid Profile of Participants (N=116)
T. C.=total cholesterol; HDL-c.=high density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL-c. =low density lipoprotein cholesterol; T. G.=triglycerides; PSQI=pittsburgh sleep quality index.
*Unmarried female: 6, Male: 16; **male 16. BMI=body mass index; RLS=restless leg syndrome.
PSQI=pittsburgh sleep quality index; T. C.=total cholesterol; HDL-c.=high density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL-c=low density lipoprotein cholesterol; T. G.= triglycerides.
Economic status (monthly income)(10,000 won); BMI=body mass index; HDL-c.=high density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL-c.=low density lipoprotein cholesterol;
T.G.=triglycerides; RLS=restless legs syndrome; Etc.b: none.
T. C.=total cholesterol; HDL-c.=high density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL-c. =low density lipoprotein cholesterol; T. G.=triglycerides; PSQI=pittsburgh sleep quality index.
 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION
 Cite
Cite

