Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Nurs > Volume 40(5); 2010 > Article
-
Original Article
- The Effects of a Cognitive Enhancement Group Training Program for Community-dwelling Elders
- Young Ran Han, Mi Sook Song, Ji Young Lim
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2010;40(5):724-735.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2010.40.5.724
Published online: October 31, 2010
1Associate Professor, Department of Nursing, Dongguk University, Gyeongju, Korea.
2Professor, College of Nursing, Ajou University, Suwon, Korea.
3Associate Professor, Department of Nursing, Inha University, Incheon, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Han, Young Ran. Department of Nursing, Dongguk University, 707 Sukjang-dong, Gyeongju 780-714, Korea. Tel: 82-54-770-2625, Fax: 82-54-770-2616, hanyr@dongguk.ac.kr
Copyright © 2010 Korean Society of Nursing Science
Abstract
-
Purpose
- In this study a cognitive enhancement group training program of 10 sessions was provided for community-dwelling elders and the effects on cognitive function, depression and quality of life were tested.
-
Methods
- A quasi-experimental study using a nonequivalent control group, pre-post design was used. The participants were 87 elders whose cognitive function was within the normal range. Of these elders, 45 were assigned to the experimental group and 42 to the control group. The intervention was conducted once a week for 10 weeks. Chi-square test, t-test, paired t-test, Wilcoxon rank sum test and Wilcoxon signed rank test were used to analyze the data.
-
Results
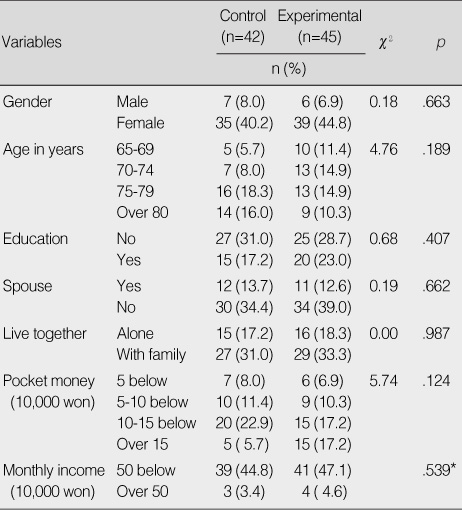
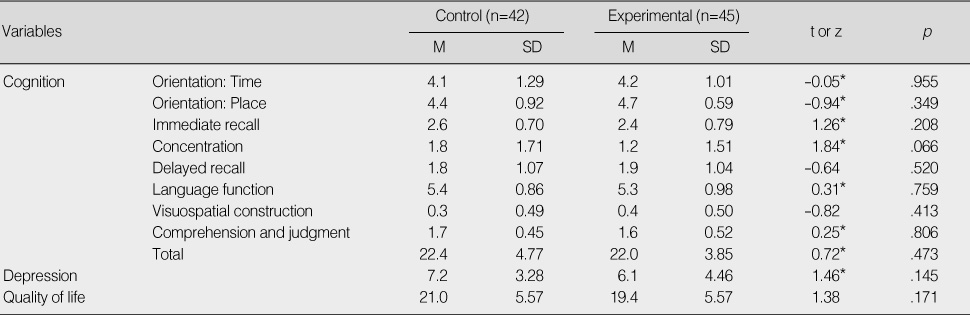
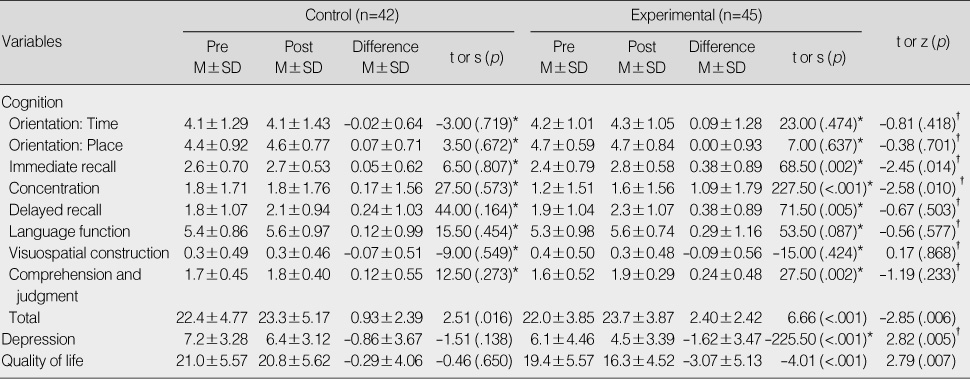
- After the program, the cognitive function (t=-2.85, p=.006), depression (z=2.82, p=.005) and quality of life (t=2.79, p=.007) of the experimental group was significantly better than those of the control group. Especially, immediate recall (z=2.45, p=.014) and concentration (z=2.58, p=.010) in the subcategory of cognitive function were significantly better than that of the control group.
-
Conclusion
- The findings indicate that the cognitive enhancement group training program was effective in enhancing the cognitive function, depression and quality of life for elders and could therefore be considered as a positive program for emotional and cognitive support for community-dwelling elders.
- 1. Chin YR, Lee IS, Chang HS. Analysis of the effects and nursing intervention of home health care in public health centers. Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing. 2004;15:353–363.
- 2. Chu SK, Yoo JH, Lee CY. The effects of a cognitive behavior program on cognition, depression, and activities of daily living in elderly with cognitive impairment. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2007;37:1049–1060.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 3. Cohen J. Statistical power analysis for the behavioral science. 1988;2nd ed. Hillsdale, NJ, Lawrence Erlbaum Association Pub.
- 4. Comijs HC, Jonker C, Beekman AT, Deeg DJ. The association between depressive symptoms and cognitive decline in community-dwelling elderly persons. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry. 2001;16:361–367.ArticlePubMed
- 5. Han JH, Ko SK, Kweon JH, Jo IH, Ahn SM, Han CS, et al. Efficacy of a multifactorial cognitive ability enhancement program for MCI (Mild Cognitive Impairment) group. Korean Journal of Clinical Psychology. 2008;27:805–821.
- 6. Hwang RI, Lim JY, Lee YW. A comparison of the factors influencing the life satisfaction of the elderly according to their cognitive impairment level. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2009;39:622–631.ArticlePubMed
- 7. Jeong WM. The effects of group occupational therapy program for improvement of cognitive abilities in mild case of dementia. Journal of Society of Occupational Therapy for the Aged and Dementia. 2007;1:46–55.
- 8. Jhoo JH, Kim KW, Lee DY, Youn JC, Lee TJ, Choo IH, et al. Comparison of the performance in two differentKorean versions of Mini-Mental State Examination: MMSE-KC and K-MMSE. Journal of Korean Neuropsychiatric Association. 2005;44:98–104.
- 9. Ji HR. The effects of dementia nursing intervention program on cognitive function, depression, activities of daily living and social behavior. 2003;Gwangju, Chonnam National University. Unpublished doctoral dissertation.
- 10. Kauppila T, Pesonen A, Tarkkila P, Rosenberg PH. Cognitive dysfunction and depression may decrease activities in daily life more strongly than pain in community-dwelling elderly adults living with persistent pain. Pain Practice. 2007;7:241–247.ArticlePubMed
- 11. Kee BS. A preliminary study for the standardization of geriatric depression scale short form-Korea version. Journal of Korean Neuropsychiatric Association. 1996;35:298–307.
- 12. Kim DY, Kim IS, Kim TY, Park RJ, Park JM, Son KC, et al. Dementia prevention and cognitive rehabilitation program. 2004;Seoul, Seohyeonsa.
- 13. Kim JH. Effects of a memory training program using efficacy sources on memory improvement in elderly people. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2000;30:1170–1180.ArticlePDF
- 14. Kim JS, Jung JS. The effects of a folk play program on cognition, ADL, and problematic behavior in the elderly with dementia. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2005;35:1153–1162.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 15. Ko SG, Kwon JH. Efficacy of a multifactorial memory enhancement program for older adults in the community. Korean Journal of Clinical Psychology. 2007;26:545–572.Article
- 16. Korean Dementia Association. Dementia: A clinical approach. 2006;Seoul, Academia.
- 17. Korean Society of Biological Nursing Science. Mosby's medical, nursing & allied health dictionary. 2002;Seoul, Mosby & Hyunmoosa.
- 18. Lee DY, Lee KU, Lee JH, Kim KW, Jhoo JH, Youn JC, et al. A normative study of the Mini-Mental State Examination in the Korean elderly. Journal of Korean Neuropsychiatric Association. 2002;41:508–525.
- 19. Lee HS, Kim HS, Jung YM. Depression and quality of life in Korean elders. Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing. 2009;20:12–22.
- 20. Lim ES. Effects of physical ability, depression and social support on quality of life in low income elders living at home. 2002;Seoul, Yonsei University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 21. 2008 National health statistics: National health and nutrition survey. Ministry for Health, Welfare and Family Affairs, & Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2009;12;Retrieved March 2, 2010. from http://knhanes.cdc.go.kr.
- 22. 2008 Customized visiting health service guidebook, 117-118. Ministry of Health and Welfare. 2008;Retrieved March 2, 2010. from http://www.mw.go.kr/front/sch/search.jsp.
- 23. Rapp S, Brenes G, Marsh AP. Memory enhancement training for older adults with mild cognitive impairment: A preliminary study. Aging & Mental Health. 2002;6:5–11.Article
- 24. Park MH, Kwon DY, Seo WK, Lim KS, Song MS. The effects of cognitive training on community-dwelling elderly Koreans. Journal of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing. 2009;16:904–909.ArticlePubMed
- 25. Schalock RL, Siperstein GN. Quality of life: Conceptualization and measurement. 1996;Washington DC, American Association on Mental Retardation.
- 26. Shin KR, Byeon YS, Kang YH, Oak J. A study on physical symptom, activity of daily living, and health-related quality of life (HRQoL) in the community-dwelling older adults. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2008;38:437–444.ArticlePubMed
- 27. Shin MK. Effects of an exercise program on frontal lobe cognitive function in elders. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2009;39:107–115.ArticlePubMed
- 28. Song MS, Song HJ. Development of community-based intensive health care program for the community dwelling elderly. Journal of Korean Gerontological Society. 2009;29:37–50.
- 29. Won JS, Kim JH. Influencing factors on cognitive function and depression in elderly. Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing. 2003;12:148–154.ArticlePDF
- 30. Won JS, Kim KH. Evaluation of cognitive functions, depression, life satisfaction among the elderly receiving visiting nursing services. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2008;38:1–10.ArticlePubMed
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- The Mediating Effect of Depressive Symptoms on the Relationship between Activity Engagement and Cognitive Function among Older Adults
Da Eun Kim, Bokyoung Kim
Research in Community and Public Health Nursing.2025; 36: 328. CrossRef - Development and effectiveness of a cognitive enhancement program based on a mobile application for preventing dementia: a study focusing on older adults who use senior citizen centers
Mi-Ra Jung, Eun Jeong, Chang-Gyeong Lee
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2023; 25(2): 113. CrossRef - The Effect of Cognitive Rehabilitation Program Combined with Physical Exercise on Cognitive Function, Depression, and Sleep in Chronic Stroke Patients
SoHyun Kim, SungHyoun Cho
Physical Therapy Rehabilitation Science.2022; 11(1): 32. CrossRef - The Effects of a Recollection-Based Occupational Therapy Program of Alzheimer’s Disease: A Randomized Controlled Trial
DeokJu Kim
Occupational Therapy International.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - Effectiveness of integrative medicine program for dementia prevention on cognitive function and depression of elderly in a public health center
Hae In Ahn, Min Kyung Hyun
Integrative Medicine Research.2019; 8(2): 133. CrossRef - Development and validation of exercise rehabilitation program for cognitive function and activity of daily living improvement in mild dementia elderly
Mi-Ri Choi, Ji-Youn Kim, Eun-Surk Yi
Journal of Exercise Rehabilitation.2018; 14(2): 207. CrossRef - Effects of a Memory and Visual-Motor Integration Program for Older Adults Based on Self-Efficacy Theory
Eun-Hwi Kim, Soon-Rim Suh
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2017; 47(3): 431. CrossRef - The Effect of a Dementia Preventive Intervention based on Motivational Interviewing among the Elderly over 75 Years of Age in Nursing Homes
Hyun Mi Jo, Suk-Sun Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2017; 28(3): 260. CrossRef - Effects of Social Support and Psychological Well-being on Intention to Exercise Maintenance of Elderly Pilates Participants
Seok-Il Kim, Hyun-Ok Oh
The Korean Journal of Physical Education.2017; 56(1): 167. CrossRef - Depression and Cognitive Function of the Community-dwelling Elderly
Seong Ok Seo, Ae Young So
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2016; 27(1): 1. CrossRef - Experiences of Participation in Dementia Prevention Program for Older Adults in Nursing Homes
Sun Ok Lim, Hyun Mi Jo
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2016; 19(2): 128. CrossRef - The systemic contemplation of sadness mediation program applied to internal senior citizens
Kyung-Mi Kim, Hyun-Young Kim
Journal of Digital Convergence.2015; 13(12): 391. CrossRef - The Effects of a Positive Psychology Improvement Program on Elders' Depression and Death Anxiety
Seung Joo Lim, Hung Sa Lee, Chunmi Kim, Young Go
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2015; 26(3): 238. CrossRef - Developing a Community Capacity Builded Exercise Maintenance Program for Frail Elderly Women
Yeon Hee Choi, Sun Yi Hong
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2015; 18(2): 153. CrossRef - Factors associated with Cognitive Decline in the Elderly in Community
Young-Sook Kwon, Kyung-Shin Paek
Journal of Digital Convergence.2014; 12(2): 587. CrossRef - The Effects of Community-Based Visiting Care on the Quality of Life
Ji Young Lim, Geun Myun Kim, Eun-Joo Kim, Kyung Won Choi, Sang Suk Kim
Western Journal of Nursing Research.2013; 35(10): 1280. CrossRef - The Effects of an Exercise Program using a Resident Volunteer as a Lay Health Leader for Elders' Physical Fitness, Cognitive Function, Depression, and Quality of Life
Yeon-Hee Choi, Na-Young Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2013; 24(3): 346. CrossRef - The Effects of the Activity Program for Preventing Dementia Against Depression, Cognitive Function, and Quality of Life for the Elderly
Kum-Sook Park, Heon-Young Jeong, Sun-Yoe So, Young-Hee Park, Hee-Jung Yang, Kyoung-Ran Jung, Soon-Joo Moon, Hae-Kyoung Kim, Jung-Hee Cho, Kyung-Hee Yang
Journal of Oriental Neuropsychiatry.2013; 24(4): 353. CrossRef - Effects of Art Therapy on Cognition, Depression, and Quality of Life in Elderly
Yeon Hee Choi, En Young Jeon
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2013; 24(3): 323. CrossRef - Non-specialist health worker interventions for the care of mental, neurological and substance-abuse disorders in low- and middle-income countries
Nadja van Ginneken, Prathap Tharyan, Simon Lewin, Girish N Rao, SM Meera, Jessica Pian, Sudha Chandrashekar, Vikram Patel
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.2013;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of a Recreational Combination Gymnastics Program for Old-old Women
Yeon Hee Choi, Choon Ji Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2012; 42(6): 843. CrossRef - Nutritional Risk, Perceived Health Status, and Depression of the Young-Old and the Old-Old in Low-Income Elderly Women
Myung-Suk Lee
Journal of agricultural medicine and community health.2012; 37(1): 12. CrossRef - Effects on Salivation, Xerostomia and Halitosis in Elders after Oral Function Improvement Exercises
Young Jin Kim, Kyung Min Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2012; 42(6): 898. CrossRef

Figure 1
Cognitive Enhancement Group Training Program for Elders
Demographic Characteristics of Participants
*Fisher's exact test.
Homogeneity Test of Cognition, Depression and Quality of Life between Groups
*Wilcoxon rank sum test.
Difference of Cognition, Depression and Quality of Life between Groups
*Wilcoxon signed rank test; †Wilcoxon rank sum test.
*Fisher's exact test.
*Wilcoxon rank sum test.
*Wilcoxon signed rank test; †Wilcoxon rank sum test.
 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION


 Cite
Cite

