Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Nurs > Volume 40(5); 2010 > Article
-
Original Article
- Aggression and Related Factors in Elementary School Students
- Eun Sun Ji, Mi Heui Jang
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2010;40(5):642-649.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2010.40.5.642
Published online: October 31, 2010
1Post Doctoral Fellow, College of Nursing, University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee, Milwaukee, Wisconsin, USA.
2Assistant Professor, Department of Nursing, Daewon University College, Jecheon, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Jang, Mi Heui. Department of Nursing, Daewon University College, Sinwol-dong, Jecheon 390-702, Korea. Tel: 82-43-649-3283, Fax: 82-43-649-3284, mhjang2006@hanmail.net
• Received: May 4, 2010 • Revised: May 7, 2010 • Accepted: October 14, 2010
Copyright © 2010 Korean Society of Nursing Science
Abstract
-
Purpose
- This study was done to explore the relationship between aggression and internet over-use, depression-anxiety, self-esteem, all of which are known to be behavior and psychological characteristics linked to "at-risk" children for aggression.
-
Methods
- Korean-Child Behavior Check List (K-CBCL), Korean-Internet Addiction Self-Test Scale, and Self-Esteem Scale by Rosenberg (1965) were used as measurement tools with a sample of 743, 5th-6th grade students from 3 elementary schools in Jecheon city. Chi-square, t-test, ANOVA, Pearson's correlation and stepwise multiple regression with SPSS/Win 13.0 version were used to analyze the collected data.
-
Results
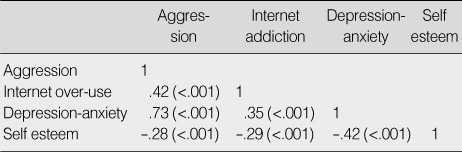
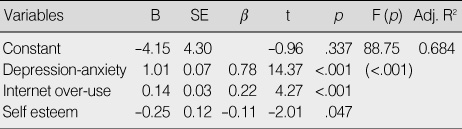
- Aggression for the elementary school students was positively correlated with internet over-use and depression-anxiety, whereas self-esteem was negatively correlated with aggression. Stepwise multiple regression analysis showed that 68.4% of the variance for aggression was significantly accounted for by internet over-use, depression-anxiety, and self-esteem. The most significant factor influencing aggression was depression-anxiety.
-
Conclusion
- These results suggest that earlier screening and intervention programs for depression-anxiety and internet over-use for elementary student will be helpful in preventing aggression.
- 1. Achenbach TM, Edelbrock C. Manual for the child behavior checklist and revised child behavior profile. 1983;Burlington, VM, University of Vermont.
- 2. Anderson CA, Shibuya A, Ihori N, Swing EL, Bushman BJ, Sakamoto A, et al. Violent video game effects on aggression, empathy, and prosocial behavior in eastern and western countries: A meta-analytic review. Psychological Bulletin. 2010;136:151–173.ArticlePubMed
- 3. Bowie BH. Relational aggression, gender, and the developmental process. Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychiatric Nursing. 2007;20:107–115.ArticlePubMed
- 4. Bushman BJ, Huesmann LR. Short-term and long-term effects of violent media on aggression in children and adults. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine. 2006;160:348–352.Article
- 5. Choi AN. The effects of music therapy on the aggression and self-esteem of children for various-income group. 2007;Seoul, Hanyang University. Unpublished doctoral dissertation.
- 6. Council on Communications and Media. Policy statementmedia violence. Pediatrics. 2009;124:1495–1503.PubMed
- 7. Dalgas-Pelish P. Effects of a self-esteem intervention program on school-age children. Pediatric Nursing. 2006;32:341–348.PubMed
- 8. Eisenberg N, Fabes RA, Guthrie IK, Reiser M. Dispositional emotionality and regulation: Their role in predicting quality of social functioning. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology. 2000;78:136–157.ArticlePubMed
- 9. Erdfelder E, Faul F, Buchner A. GPOWER: A general power analysis program. Behavior Research Methods, Instruments, & Computers. 1996;28:1–11.ArticlePDF
- 10. Han SS, Kim KM. Influencing factors on self-esteem in adolescents. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2006;36:37–44.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 11. Kim HS. Development of a sublimation program for Korean adolescents' aggression. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2004;34:81–92.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 12. Ko CH, Yen JY, Liu SC, Huang CF, Yen CF. The associations between aggressive behaviors and internet addiction and online activities in adolescents. Journal of Adolescent Health. 2009;44:598–605.Article
- 13. Kovacs M, Sherrill J, George CJ, Pollock M, Tumuluru RV, Ho V. Contextual emotion-regulation therapy for childhood depression: Description and pilot testing of a new intervention. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry. 2006;45:892–903.ArticlePubMed
- 14. Lam LT, Peng ZW, Mai JC, Jing J. Factors associated with internet addiction among adolescents. Cyberpsychology & Behavior. 2009;12:551–555.Article
- 15. Lee EO. A study of the level of elementary school student's aggression and it's related factors. 2005;Daejon, Chungnam National University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 16. Lee ES. Construction of a structural model about male and female adolescents' alienation, depression, and suicidal thoughts. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2007;37:576–585.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 17. Lee H, Oh KJ, Hong KE, Ha EH. Clinical validity study of Korean CBCL through item analysis. Journal of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry. 1991;2:138–149.
- 18. Lee JS. The relationship between the over-use of internet and aggressiveness an impulsiveness of children. 2004;Daejon, Kong-Ju National University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 19. Lee KE, Park K. The influence between internet addiction, interpersonal relations disposition and depression in elementary school student. Psychotherapy. 2008;8:31–48.
- 20. Mcleod JD, Shanahan MJ. Trajectories of poverty and children's mental health. Journal of Health and Social Behavior. 1996;37:207–220.ArticlePubMed
- 21. Mehroof M, Griffiths MD. Online gaming addiction: The role of sensation seeking, self-control, neuroticism, aggression, state anxiety, and trait-anxiety. Cyberpsychology & Behavior. 2009;10:[e-pub ahead of print].
- 22. Screening test for school mental health in 2006. Ministry of Health & Welfare. 2006;Retrieved March 31, 2010. from http://www.mw.go.kr/front/index.jsp.
- 23. A study of internet addiction proneness scale for adult. National Information Society Agency of Korea. 2005;Retrieved March 31, 2010. from http://www.nia.or.kr/Index.aspx?PortalID=ko.
- 24. Rosenberg M. Conceiving the self. 1965;Malabar, FL, Krieger.
- 25. Report of school violence trend and an urgent countermeasure in 2010. The Foundation for Preventing Youth Violence. 2010;Retrieved March 31, 2010. from http://www.jikim.net/bbs/index.php?action=bbs_view&backto=bbs_list&pageno=1&bbs_code=blue_board_bodo&bbs_bid=74&menu=1&s_m=4.
- 26. Naked graduation ceremony. The Korea Herald. 2010;Retrieved March 29, 2010. fromhttp://biz.heraldm.com/common/Detail.jsp?newsMLId=20100217001316.
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- The Role of Individuals’ Need for Online Social Interactions and Interpersonal Incompetence in Digital Game Addiction
Sarbottam Bhagat, Eui Jun Jeong, Dan J. Kim
International Journal of Human–Computer Interaction.2020; 36(5): 449. CrossRef - Why Do Some People Become Addicted to Digital Games More Easily? A Study of Digital Game Addiction from a Psychosocial Health Perspective
Eui Jun Jeong, Dan J. Kim, Dong Min Lee
International Journal of Human–Computer Interaction.2017; 33(3): 199. CrossRef - Relationships Between the Appraisal Type of Competencies and Aggression in Elementary School Students
Hyun-kyung Yoon, Myung-goo Choi
Journal of Digital Convergence.2016; 14(7): 485. CrossRef - Online Game Addiction and Adolescent's Delinquency: Verification of the Moderating Effect of Depression and Anxiety
Mi-Na KO
Journal of Fisheries and Marine Sciences Education.2015; 27(3): 644. CrossRef - A longitudinal study for child aggression with Korea Welfare Panel Study data
Nayeon Choi, Jib Huh
Journal of the Korean Data and Information Science Society.2014; 25(6): 1439. CrossRef - Family Function and Internet Addiction in Lower Grade Elementary School Students
Eun-Sook Jung, Moon-Sook Shim
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2012; 26(2): 328. CrossRef
Aggression and Related Factors in Elementary School Students
Aggression and Related Factors in Elementary School Students
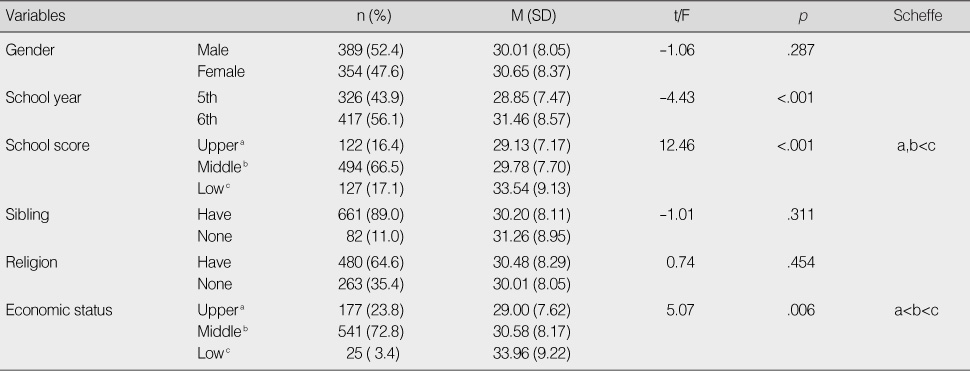
Difference of Aggression according to Subject Characteristics (N=743)
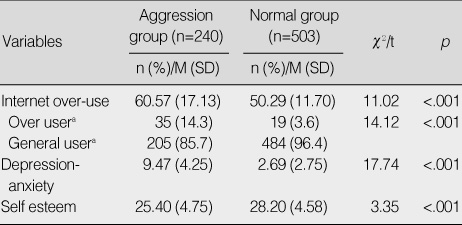
Differences in Predictor Variables by Aggression Group (N=743)
an (%).
Correlation Between Aggression and Variables (N=743)
Factors Influence Aggression (N=743)
Table 1
Difference of Aggression according to Subject Characteristics (N=743)
Table 2
Differences in Predictor Variables by Aggression Group (N=743)
an (%).
Table 3
Correlation Between Aggression and Variables (N=743)
Table 4
Factors Influence Aggression (N=743)
 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION
 Cite
Cite

