Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Nurs > Volume 40(3); 2010 > Article
-
Original Article
- The Life of Adolescent Patients with Complex Congenital Heart Disease
- Sunhee Lee, So-Sun Kim
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2010;40(3):411-422.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2010.40.3.411
Published online: June 30, 2010
1Instructor, College of Nursing, Eulji University, Seongnam, Korea.
2Professor, College of Nursing · Researcher, The Nursing Policy Research Institute, Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Kim, So-Sun. College of Nursing, Yonsei University, 134 Sinchon-dong, Seodaemun-gu, Seoul 120-752, Korea. Tel: 82-2-2228-3254, Fax: 82-2-392-5440, soskim@yuhs.ac
Copyright © 2010 Korean Society of Nursing Science
Abstract
-
Purpose
- In the present study, an analysis of the life of adolescents with complex congenital heart disease (CHD) was done using grounded theory. Consideration was given to the socio-cultural context of Korea.
-
Methods
- After approval from the institutional review board of Y hospital, 12 patients ranging in age from 14 to 35 were recruited. Data were gathered using in-depth interviews. Theoretical sampling was performed until the concepts were saturated.
-
Results
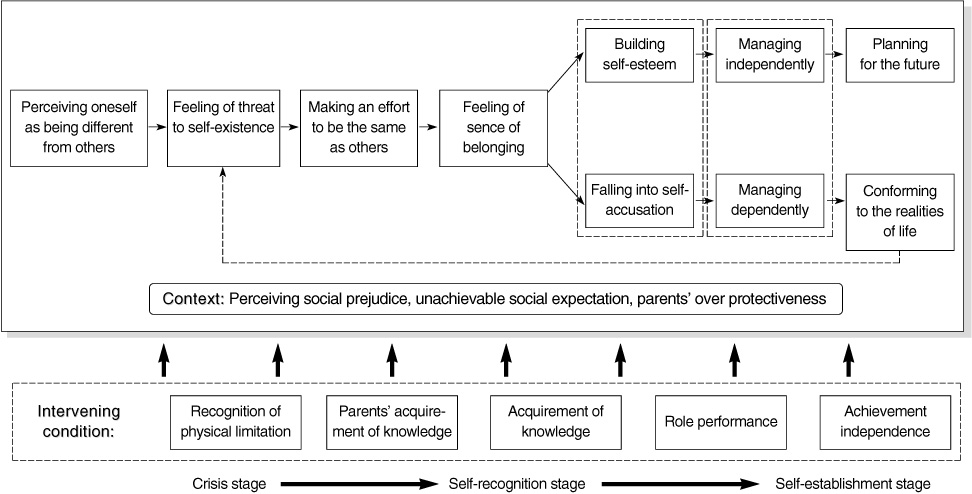
- The results confirmed the life of adolescents with complex CHD as a 'journey to finding uniqueness of oneself as a person with CHD'. The life consisted of 3 stages. In the crisis stage, participants had a feeling of threat to self-existence, and made an effort to be the same as others. In the self-recognition stage, participants who had sufficient role-performance built self-esteem while those who did not fell into self-accusation. In the self-establishment stage, participants who reached sufficiency in independence and knowledge planned the future, whereas those who did not conformed to the realities of life.
-
Conclusion
- The results of present study provide help in understanding the experiences of adolescents with CHD and provide a basis for developing nursing intervention strategies for these patients.
- 1. Berghammer M, Dellborg M, Ekman I. Young adults experiences of living with congenital heart disease. International Journal of Cardiology. 2006;110:340–347.ArticlePubMed
- 2. Branden N. The power of self esteem. 1992;Deerfield Beach, Health Communication. Inc..
- 3. Cabinno MM. Health care issues facing adolescents withcongenital heart disease. Journal of Pediatric Nursing. 2001;16:363–370.Article
- 4. Casey FA, Sykes DH, Craig BG, Power R, Connor Mulholland H. Behavioral adjustment of children with surgically palliated complex congenital heart disease. Journal of Pediatric Psychology. 1996;21:335–352.ArticlePubMed
- 5. Claessens P, Moons P, Dierckx de Casterle B, Cannaerts N, Budts W, Gewiling M. What does it mean it live with congenital heart disease? A qualitative study on the lived experiences of adult patients. European Journal of Cardiovascular Nursing. 2005;4:3–10.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 6. Deanfield J, Thaulow E, Warnes C, Webb G, Kolbel F, Hoffman A, et al. Management of grown up congenital heart disease. European Heart Journal. 2003;24:1035–1084.ArticlePubMed
- 7. Erickson EH. Identity and the life cycle. 1980;New York, NY, W. W. Norton % Co.
- 8. Foster E, Graham TP, Driscoll DJ, Reid GJ, Reiss JG, Russel IA, et al. Task force 2: Special health care needs of adults with congenital heart disease. Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 2001;37:1176–1183.ArticlePubMed
- 9. Guba EG, Lincoln YS. Effective evaluation: Improving the usefulness of evaluation results through responsive and naturalistic approaches. 1981;San Francisco, CA, Jossey-Bass.
- 10. Gutgesell HP, Gessner IH, Vetter VL, Yabek SM, Norton JB Jr. Recreational and occupational recommendations for young patients with heart disease. A statement for physician by the Committee on congenital cardiac defects of the council on cardiovascular disease in the young, American Heart Association. Circulation. 1986;74:1195–1198.PubMed
- 11. Han SS, Kim KM. Influencing factors in self-esteem in adolescents. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2006;36:37–44.PubMed
- 12. Immer FF, Althaus SM, Berdat PA, Saner H, Carrel TP. Quality of life and specific problems after cardiac surgery in adolescents and adults with congenital heart diseases. European Journal of Cardiovascular Prevention and Rehabilitation. 2004;12:138–143.Article
- 13. Kamphuis M, Ottenkamp J, Vliegen HW, Vogels T, Zwinderman KH, Kamphuis RP, et al. Health related quality of life and health status in adult survivors with previously operated complex congenital heart disease. Heart. 2002;87:356–362.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 14. Kools S, Gilliss CL, Tong EM. Family transition in congenital heart disease management: The impact of hospitalizationin early adulthood. Journal of Family Nursing. 1999;5:404–423.
- 15. Lane DA, Lip GYH, Millane TA. Quality of life in adults with congenital heart disease. Heart. 2002;88:71–75.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 16. Lee CS. Influences of home environment, school environment and self-esteem on adolescent's ego-identity in Cheju. Journal of College Education. 2000;2:109–136.
- 17. Lee ES. Construction of a structural model about male and female adolescent's alienation, depression, and suicidal thought. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2007;37:576–585.PubMed
- 18. Lee H, Kim MH, Jung JW, Kim SH, Choi BY. Prevalence of congenital heart disease from the elementary student heart disease screening program. Korean Journal of Preventive Medicine. 2001;34:427–436.
- 19. Lee HJ. Congenital heart disease after childhood experience of "grown up congenital heart clinic (GUCH Clinic)". Korean Circulation Journal. 2001;31:537–541.Article
- 20. Masi G, Brovedani P. Adolescents with congenital heartdisease: Psychopathological implications. Adolescence. 1999;34:185–191.PubMed
- 21. Saunders CP, Roberts GJ. Dental attitudes, knowledge, and health practices of parents of children with congenital heart disease. Archives of Disease in Childhood. 1997;76:539–540.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 22. Spijkerboer AW, Utens EM, De Koning WB, Bogers AJ, Helbing WA, Verhulst FC. Health related quality of life in children and adolescents after invasive treatment for congenital heart disease. Quality of Life Research. 2006;15:663–673.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 23. Strauss A, Corbin J. Basics of qualitative research techniques and procedures for developing grounded theory. 1998;2nd ed. London, Sage, Publications.
- 24. Swan L, Hillis S. Exercise prescription in adult with congenital heart disease: A long way to go. Heart. 2000;83:685–687.PubMedPMC
- 25. Uzark K, vonBargen Mazza P, Messiter E. Health education needs of adolescents with congenital heart disease. Journal of Pediatric Health Care. 1989;3:137–143.ArticlePubMed
- 26. Viner R. Transition from paediatric to adult care. Bridging the gaps or passing the buck? Archives of Disease in Childhood. 1999;81:271–275.ArticlePubMedPMC
REFERENCES
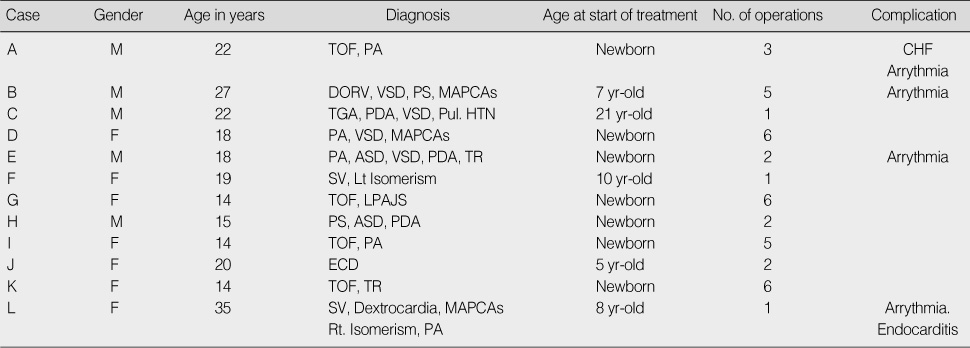
TOF=Tetralogy of Fallot; PA=Pulmonary atresia; CHF=Congestive heart failure; DORV=Double outlet right ventricle; VSD=Ventriclular septal defect; PS=Pulmonary stenosis; TGA=Transposition of the great arteries; PDA=Patent ductus arteiosus; Pul. HTN=Pulmonary hypertension; MAPCAs=Major aorto pulmonary collateral arteries; ASD=Atrial septal defect; TR=Tricuspid regurgitation; SV=Single ventricle; LPAJS=Left pulmonary artery junctional stenosis; ECD=Endocardial cushion defect.
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Workplace Harassment in Patients with Congenital Heart Disease
Efrén Martínez-Quintana, Beatriz Déniz-Alvarado, Carlos Gallego-Sosa, Javier Pardo-Maiza, Jesús María González-Martín, Fayna Rodríguez-González
International Journal of Bullying Prevention.2025; 7(1): 36. CrossRef - Multifaceted Assessment of Quality of Life in Hospitalized Adolescents Aged 11–18 with Cardiological Problems
Agnieszka Pluta, Alicja Marzec, Monika Chojnowska, Mariola Głowacka
Children.2025; 12(12): 1661. CrossRef - Management of Caustic Esophageal Injury: A Survey Study in Türkiye and Review of the Literature
Sümeyye Sözduyar, Denizcan İnal, Ergun Ergün, Gülnur Göllü, Ahmet Murat Çakmak, Ufuk Ateş
Journal of Ankara University Faculty of Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Familial Relationships on School Adjustment of Adolescents and Young Adults With Congenital Heart Disease
Youngji Moon, Jo Won Jung, Sunhee Lee
Journal of Cardiovascular Nursing.2023; 38(1): 52. CrossRef - Quality of Life in Congenital Heart Disease Patients According to Their Anatomical and Physiological Classification
Efr閚 Mart韓ez-Quintana, Hiurma Estupi襻n-Le髇, Ana Beatriz Rojas-Brito, Liuva D閚iz-D閚iz, Alejandro Barreto-Mart韓, Fayna Rodr韌uez-Gonz醠ez
Congenital Heart Disease.2023; 18(2): 197. CrossRef - La intervención psicocardiológica en la rehabilitación cardiovascular de niños escolares con cardiopatías congénitas: una revisión sistemática
T. Rodríguez Rodríguez, A. Nohaya Alonso, N. González Vales
Rehabilitación.2022; 56(4): 353. CrossRef - Factor analysis of the Korean version of the Illness Cognition Questionnaire for adolescents with chronic illness
Dasuel Lee, Dae‐Chul Jeong, Nack‐Gyun Chung, Sunhee Lee
International Journal of Nursing Practice.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The effects of rational emotive behavior therapy for depressive symptoms in adults with congenital heart disease
Ju Ryoung Moon, June Huh, Jinyoung Song, I-Seok Kang, Seung Woo Park, Sung-A Chang, Ji-Hyuk Yang, Tae-Gook Jun, Jong-Sook Han
Heart & Lung.2021; 50(6): 906. CrossRef - The adaptation process of mothers raising a child with complex congenital heart disease
Jeong-Ah Ahn, Sunhee Lee
Journal of Child Health Care.2018; 22(4): 520. CrossRef - The Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale is an adequate screening instrument for depression and anxiety disorder in adults with congential heart disease
Ju Ryoung Moon, June Huh, Jinyoung Song, I-Seok Kang, Seung Woo Park, Sung-A Chang, Ji-Hyuk Yang, Tae-Gook Jun
Health and Quality of Life Outcomes.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - The relationship between perceived parental rearing behaviors and school adjustment of adolescent cancer survivors in Korea
Sunhee Lee, Dong Hee Kim
Medicine.2017; 96(32): e7758. CrossRef - The effect of a resilience improvement program for adolescents with complex congenital heart disease
Sunhee Lee, Junga Lee, Jae Young Choi
European Journal of Cardiovascular Nursing.2017; 16(4): 290. CrossRef - Comparison of Physical Activity and Health-related Quality of Life in Adolescents with and without Congenital Heart Disease: A Propensity Matched Comparison
Hyun Jeong Kim, Eun Sun Yoon, Soo Jung Lee, Jina Choo, Seong-Ho Kim, Sae Young Jae
The Korean Journal of Sports Medicine.2017; 35(1): 40. CrossRef - Health-related quality of life in adolescents with congenital heart disease
Juliana Bertoletti, Giovana C. Marx, Sérgio P. Hattge, Lúcia C. Pellanda
Cardiology in the Young.2015; 25(3): 526. CrossRef - Comparison of Coping Strategy and Disease Knowledge in Dyads of Parents and Their Adolescent With Congenital Heart Disease
Jeong-Ah Ahn, Sunhee Lee, Jae Young Choi
Journal of Cardiovascular Nursing.2014; 29(6): 508. CrossRef - Coping and Resilience of Adolescents With Congenital Heart Disease
Sunhee Lee, Sue Kim, Jae Young Choi
Journal of Cardiovascular Nursing.2014; 29(4): 340. CrossRef
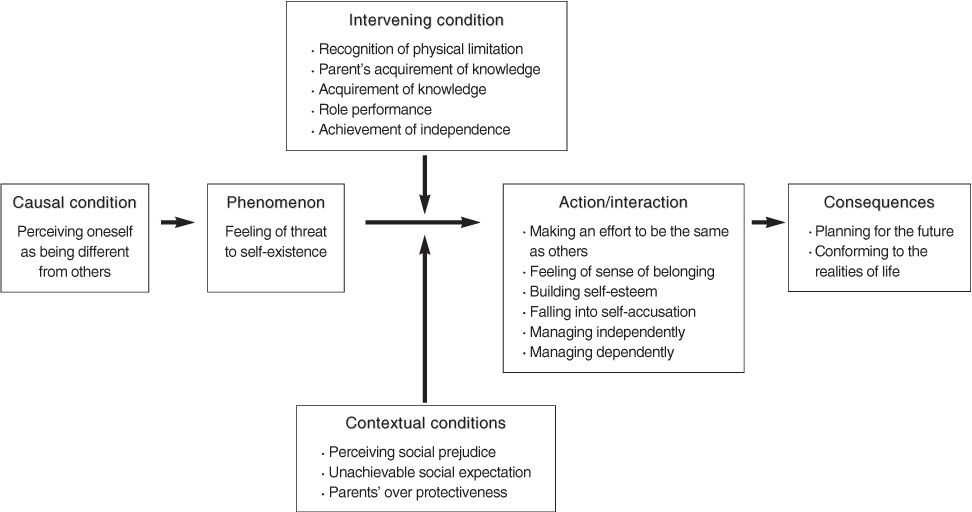
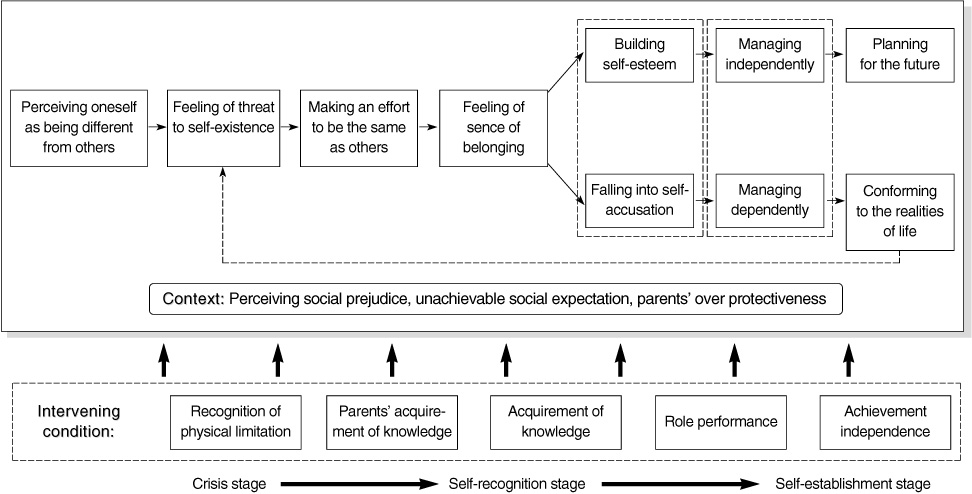
Figure 1
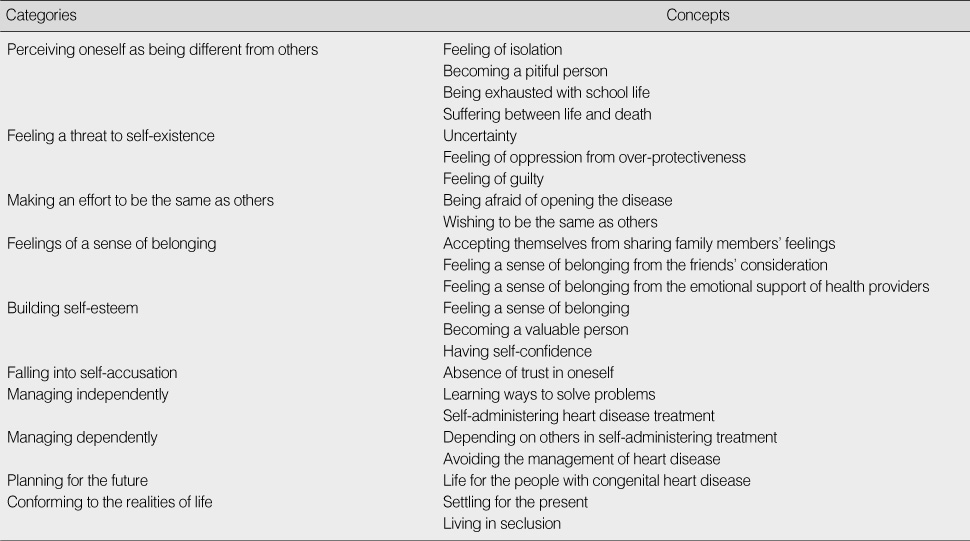
Figure 2
Demographic Characteristics of the Participants
TOF=Tetralogy of Fallot; PA=Pulmonary atresia; CHF=Congestive heart failure; DORV=Double outlet right ventricle; VSD=Ventriclular septal defect; PS=Pulmonary stenosis; TGA=Transposition of the great arteries; PDA=Patent ductus arteiosus; Pul. HTN=Pulmonary hypertension; MAPCAs=Major aorto pulmonary collateral arteries; ASD=Atrial septal defect; TR=Tricuspid regurgitation; SV=Single ventricle; LPAJS=Left pulmonary artery junctional stenosis; ECD=Endocardial cushion defect.
Categories and Concepts
TOF=Tetralogy of Fallot; PA=Pulmonary atresia; CHF=Congestive heart failure; DORV=Double outlet right ventricle; VSD=Ventriclular septal defect; PS=Pulmonary stenosis; TGA=Transposition of the great arteries; PDA=Patent ductus arteiosus; Pul. HTN=Pulmonary hypertension; MAPCAs=Major aorto pulmonary collateral arteries; ASD=Atrial septal defect; TR=Tricuspid regurgitation; SV=Single ventricle; LPAJS=Left pulmonary artery junctional stenosis; ECD=Endocardial cushion defect.
 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION
 Cite
Cite

