Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Nurs > Volume 40(3); 2010 > Article
-
Original Article
- Comparison for Risk Estimate of Aspiration between the Revised Dysphagia Assessment Tool and Videofluoroscopy in Post-Stroke Patients
- Kyung Hee Moon, Hyun Sook Sohn, Eun Seok Lee, Eun Kyung Paek, Eun Ju Kang, Seung Hee Lee, Na Ri Han, Meen Hye Lee, Deog Young Kim, Chang Gi Park, Ji-Soo Yoo
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2010;40(3):359-366.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2010.40.3.359
Published online: June 30, 2010
1Director, Division of Nursing, Severance Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
2Registered Nurse, Department of Nursing, Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
3Associate Professor, Department and Research Institute of Rehabilitation Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
4Researcher, University of Illinois at Chicago, IL, USA.
5Professor, College of Nursing · Researcher, Nursing Policy Research Institute, Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Yoo, Ji-Soo. College of Nursing, Yonsei University, 250 Seongsan-ro, Seodaemun-gu, Seoul 120-752, Korea. Tel: 82-2-2228-3252, Fax: 82-2-392-5440, yoojs48@yuhs.ac
Copyright © 2010 Korean Society of Nursing Science
Abstract
-
Purpose
- The purpose of this study was to determine the significant factors for risk estimate of aspiration and to evaluate the efficiency of the dysphagia assessment tool.
-
Methods
- A consecutive series of 210 stroke patients with aspiration symptoms such as cough and dysphagia who had soft or regular diet without tube feeding were examined. The dysphagia assessment tool for aspiration was compared with videofluoroscopy using Classification and Regression Tree (CART) analysis.
-
Results
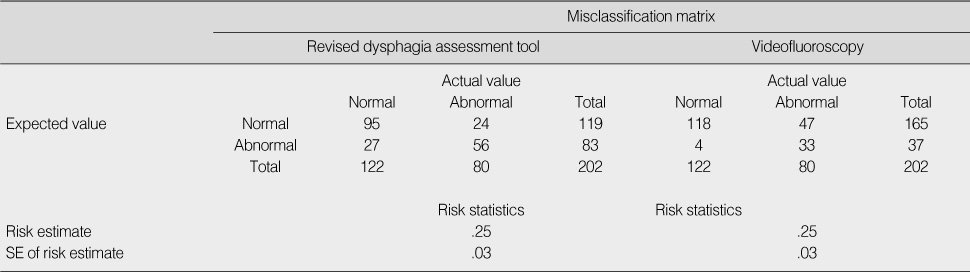
- In CART analysis, of 34 factors, the significant factors for estimating risk of aspiration were cough during swallowing, oral stasis, facial symmetry, salivary drooling, and cough after swallowing. The risk estimate error of the revised dysphagia assessment tool was 25.2%, equal to that of videofluoroscopy.
-
Conclusion
- The results indicate that the dysphagia assessment tool developed and examined in this study was potentially useful in the clinical field and the primary risk estimating factor was cough during swallowing. Oral stasis, facial symmetry, salivary drooling, cough after swallowing were other significant factors, and based on these results, the dysphagia assessment tool for aspiration was revised and complemented.
- 1. Daniels SK, Ballo LA, Mahoney MC. Clinical predictors of dysphagia and aspiration risk: Outcome measures in acute stoke patients. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. 2000;81:1030–1033.ArticlePubMed
- 2. Erdfelder E, Faul F, Buchner A. GPOWER: A general power analysis program. Behavior Research Methods, Instruments, & Computers. 1996;28:1–11.ArticlePDF
- 3. Han TR, Paik NJ, Park JW. The functional dysphagia scale using videofluoroscopic swallowing study in stroke patients. Journal of Korean Academy of Rehabilitation Medicine. 1999;23:1118–1126.
- 4. Han TR, Paik NJ, Park JW. The clinical functional scale for dysphagia in stroke patients. Korean Journal of Stroke. 2001;3:153–157.
- 5. Jung SH, Lee KJ, Hong JB, Han TR. Validation of clinical dysphagia scale: Based on videofluoroscopic swallowing study. Journal of Korean Academy of Rehabilitation Medicine. 2005;29:343–350.
- 6. Martino R, Foley N, Bhogal S, Diamant N, Speechley M, Teasell R. Dysphagia after stroke: Incidence, diagnosis, and pulmonary complications. Stroke. 2005;36:2756–2763.ArticlePubMed
- 7. Massey R, Jedlicka DJ. The massey bedside swallowing screening. Journal of Neuroscience Nursing. 2002;34:257–260.
- 8. Muller R, Möckel M. Logistic regression and CART in the analysis of multimarker studies. Clinica Chimica Acta. 2008;394:1–6.Article
- 9. Nishiwaki K, Tsuji T, Liu M, Hase K, Tanaka N, Fujiwara T. Identification of a simple screening tool for dysphagia in patients with stroke using factor analysis of multiple dysphagia variables. Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine. 2005;37:247–251.ArticlePubMed
- 10. Paek EK, Moon KH, Kim HJ, Lee ES, Sohn HS, Yoo JS, et al. Dysphagia assessment tool for post-stroke patients. Clinical Nursing Research. 2007;13(3):19–30.
- 11. Paik NJ, Kim IS, Kim JH, Oh BM, Han TR. Clinical validity of the functional dysphagia scale based on videofluoroscopic swallowing study. Journal of Korean Academy of Rehabilitation Medicine. 2005;29:43–49.
- 12. Park CI, Moon JH, Kang SW, Park ES, Shin JC, Kim DY, et al. Rehabilitation Medicine. 2008;2nd ed. Seoul, Hanmibook.
- 13. Ramsey DJ, Smithard DG, Kalra L. Early assessments of dysphagia and aspiration risk in acute stoke patients. Stroke. 2003;34:1252–1257.ArticlePubMed
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Screening for aspiration risk associated with dysphagia in acute stroke
Elizabeth Boaden, Jane Burnell, Lucy Hives, Paola Dey, Andrew Clegg, Mary W Lyons, C Elizabeth Lightbody, Margaret A Hurley, Hazel Roddam, Elizabeth McInnes, Anne Alexandrov, Caroline L Watkins
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and Utilization of Assessment and Intervention Checklist for Post-stroke Dysphagia
Eun Ha Lee, Ja Yun Choi
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2013; 25(2): 113. CrossRef
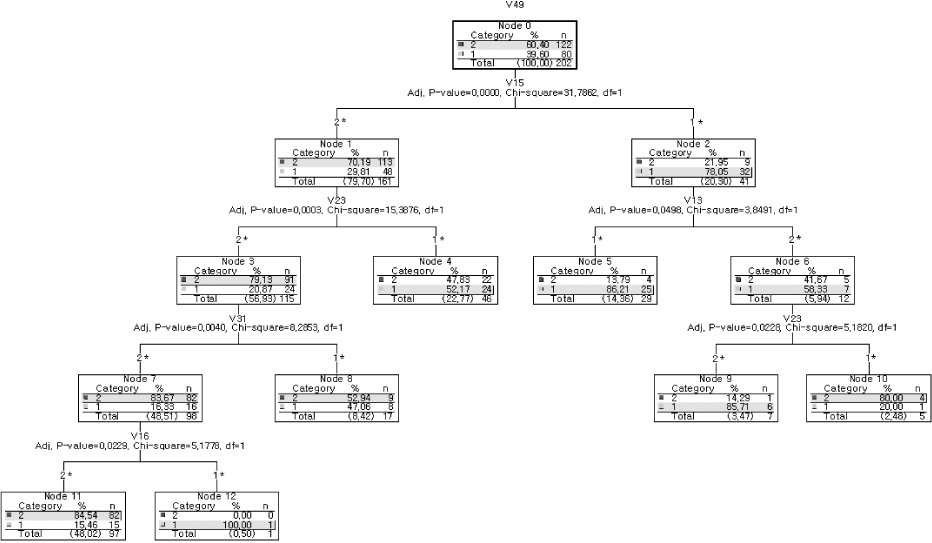
Figure 1
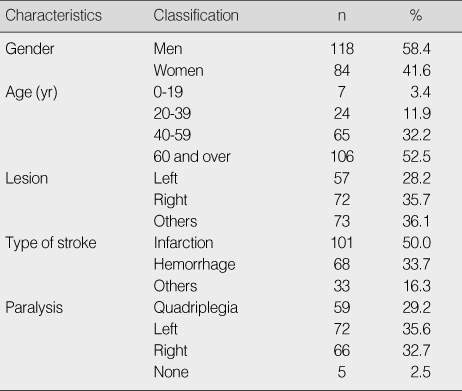
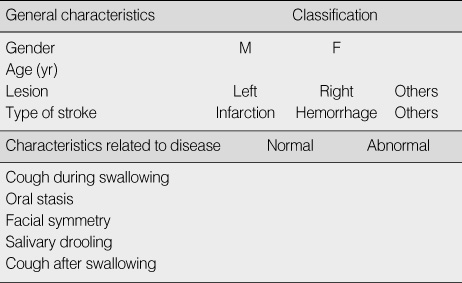
General Characteristics of Patients (N=202)
Diseases Related Characteristics of Patients (N=202)
*Missing responses excluded.
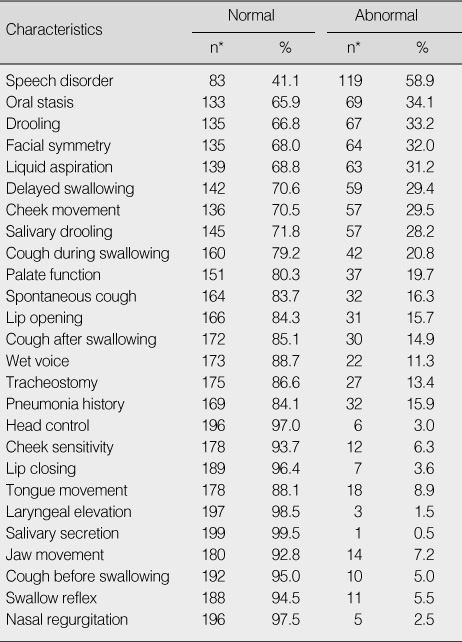
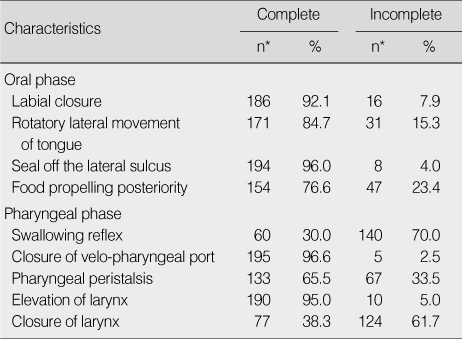
Characteristics Related to Videofluoroscopy (N=202)
*Missing responses excluded.
Revised Dysphagia Assessment Tool
Comparison of Risk Estimate Error of Aspiration in Revised Dysphagia Assessment Tool and Videofluoroscopy (N=202)
*Missing responses excluded.
*Missing responses excluded.
 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION
 Cite
Cite

