Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Nurs > Volume 40(2); 2010 > Article
-
Original Article
- Factors Affecting Mother's Adaptation to Breastfeeding
- Sun Hee Kim
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2010;40(2):225-235.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2010.40.2.225
Published online: April 30, 2010
Full-time Lecturer, College of Nursing, Catholic University of Daegu, Daegu, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Kim, Sun Hee. College of Nursing, Catholic University of Daegu, 3056-6 Daemyeong 4-dong, Nam-gu, Daegu 705-718, Korea. Tel: 82-53-650-4831, Fax: 82-53-650-4392, sunhee421@cu.ac.kr
Copyright © 2010 Korean Society of Nursing Science
Abstract
-
Purpose
- The aim of this study was to identify factors which influence breastfeeding adaptation from among the following: parity and feeding behavior, social support, psychological, and demographic factors.
-
Methods
- The respondents were 179 breastfeeding mothers. Data were collected from June 2 to 19, 2009 at two community health centers and one pediatric outpatient department. Data were analyzed using the SPSS program and included descriptive statistics, t-test, ANOVA, correlation, and multiple regression.
-
Results
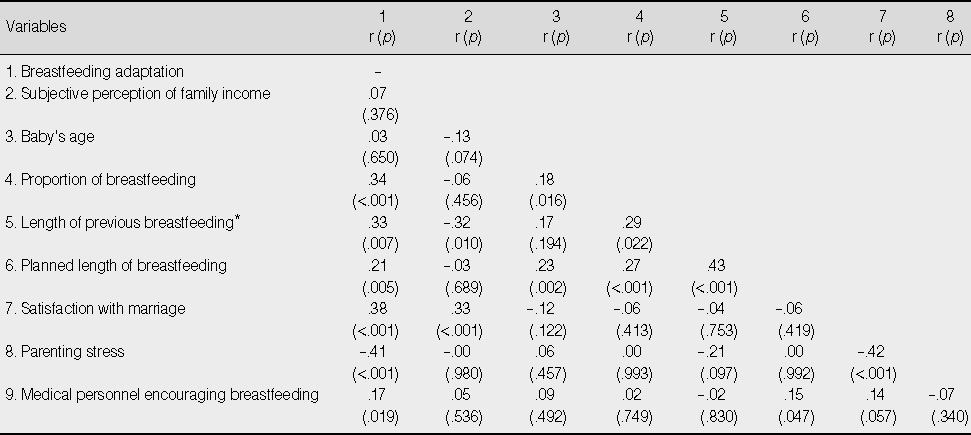
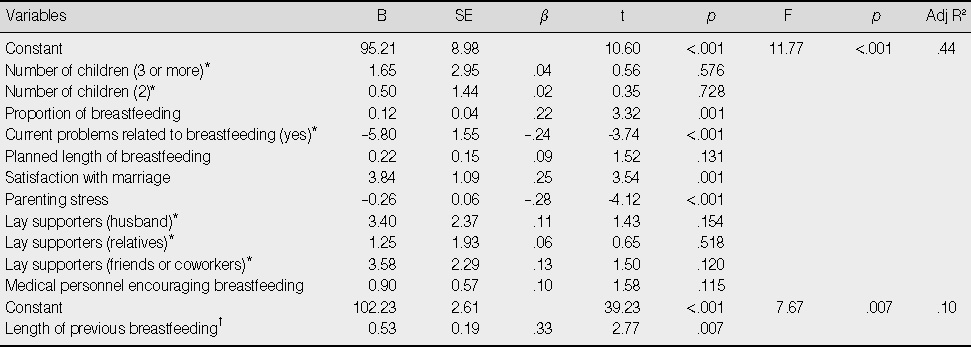
- The major findings of this study were: 1) Significant differences in the level of breastfeeding adaptation were related to number of children, current problems related to breastfeeding, and lay supporters. 2) Level of breastfeeding adaptation was significantly related to marriage satisfaction, proportion of breastfeeding, length of previous breastfeeding, planned length of breastfeeding, parenting stress, and encouragement to breastfeed given by medical personnel. 3) Regression analysis showed that parenting stress, marriage satisfaction, current problems related to breastfeeding, and proportion of breastfeeding explained 44.3% of variance for breastfeeding adaptation. Length of previous breastfeeding also explained 9.7% of breastfeeding adaptation among mothers who had breastfed an elder child.
-
Conclusion
- Mothers with lower marriage satisfaction, breastfeeding problems, and higher parenting stress require more help from their family and nurses for breastfeeding adaptation. Future research should include variables, such as mother's and baby's behavior related to breastfeeding, knowledge about breastfeeding, and attitude toward breastfeeding.
- 1. Abidin RR. Parenting stress index (PSI). 1990;Charlottesville, VA, Pediatric Psychology Press.
- 2. Academy of Breastfeeding Medicine Korea. New mother's guide to breastfeeding. 2006;Seoul, E*PUBLIC.
- 3. Ahluwalia IB, Morrow B, Hsia J. Why do women stop breastfeeding? Findings from the pregnancy risk assessment and monitoring system. Pediatrics. 2005;116:1408–1412.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 4. Ahn OS. The influence of parenting stress and social support on postpartum depression among mothers during puerperium. 2005;Gyeongju, Dongguk University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 5. Altemus M, Deuster PA, Galliven E, Carter CS, Gold PW. Suppression of hypothalmic-pituitary-adrenal axis responses to stress in lactating women. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. 1995;80:2954–2959.ArticlePubMed
- 6. Bandura A. Self-efficacy in changing societies. 2008;Cambridge:, Cambridge University Press.
- 7. Borenstein M, Rothstein H, Cohen J. Power and precision. 1997;Englewood, NJ, Lawewnce Erlbaum.
- 8. Choi GR. Family relations. 2007;Goyang, Gongdongche.
- 9. Dennis CL. Breastfeeding initiation and duration: A 1990-2000 literature review. Journal of Obstetric, Gynecologic, and Neonatal Nursing. 2002;31:12–32.Article
- 10. Fawcett J. Contemporary nursing knowledge: Analysis and evaluation of nursing models and theories. 2005;2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA, F. A. Davis Company.
- 11. Foster DA, McLachlan HL. Breastfeeding initiation and birth setting practices: A review of the literature. Journal of Midwifery & Women's Health. 2007;52:273–280.ArticlePDF
- 12. Hannula L, Kaunonen M, Tarkka MT. A systematic review of professional support interventions for breastfeeding. Journal of Clinical Nursing. 2008;17:1132–1143.ArticlePubMed
- 13. Hedberg-Nyqvist KH, Ewald U. Infant and maternal factors in the development of breastfeeding behavior and breastfeedingoutcome in preterm infants. Acta Paediatrica. 1999;88:1194–1203.ArticlePubMed
- 14. Huggins K, Ziedrich L. The nursing mother's guide to weaning. 2007;Boston, MA, The Harvard Common Press.
- 15. Isabella PH, Isabella RA. Correlates of successful breastfeeding: A study of social personal factor. Journal of Human Lactation. 1994;10:257–264.PubMed
- 16. Jang GJ, Kim SH, Jeong KS. Effect of postpartum breast-feeding support by nurse on the breast-feeding prevalence. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2008;38:172–179.ArticlePubMed
- 17. Kalnins D, Stone D, Touw J. Better breastfeeding: A mother's guide to feeding and nutrition. 2007;Toronto, Robert Rose Inc.
- 18. Kim SH. Development of an instrument to evaluate adaptation to breastfeeding. 2008;Seoul, Ewha Womans University. Unpublished doctoral dissertation.
- 19. Kim SH. Development of a breast feeding adaptationscale (BFAS). Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2009a;39:259–269.ArticlePubMed
- 20. Kim SH. Factors explaining mothersoasis breastfeeding satisfaction. Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing. 2009b;15:270–279.
- 21. Kronborg H, Vaeth M. The influence of psychosocial factors on the duration of breastfeeding. Scandinavian Journal of Public Health. 2004;32:210–216.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 22. Lee SO. A study about breastfeeding knowledge, attitude and problem of breastfeeding in early postpartum period and breastfeeding practice. Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing. 2003;9:179–188.ArticlePDF
- 23. Lewallen LP, Dick MJ, Flowers J, Powell W, Zickefoose KT, Wall YG, et al. Breastfeeding support and early cessation. Journal of Obstetric, Gynecologic, and Neonatal Nursi. g. 2006;35:166–172.
- 24. Mezzacappa ES, Katlin ES. Breast-feeding is associated with reduced perceived stress and negative mood in mothers. Health Psychology: Official Journal of the Division of Health Psychology. American Psychological Association. 2002;21:187–193.
- 25. 2005 Korean national health and nutrition survey: Nutrition survey. Ministry of Health, Welfare, and Family Affairs. 2006;07 05 Retrieved October 12, 2007. from http://www.mw.go.kr/front/al/sal0301ls.jsp?PAR_MENU_ID=04&MENU_ID=0403.
- 26. Park HM. A study on parental stress based on the parenting of young children. 1994;Seoul, Ewha Womans University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 27. Rempel LA, Fong GT. Why breastfeed? A longitudinal test of the reasons model among first-time mothers. Psychology & Health. 2005;20:443–466.Article
- 28. Riordan J, Wambach K. Breastfeeding and human lactation. 2009;4th ed. Sudbury, MA, Jones and Bartlett Publishers.
- 29. Roy SC, Andrews HA. The Roy adaptation model. 1999;2nd ed. Stamford, CT, Appleton & Lange.
- 30. Yeo JH. Influencing factors in breast feeding duration. Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing. 2005;11:142–147.ArticlePDF
- 31. Yoon JW. The development and evaluation of the breastfeeding self-efficacy program for working mothers. 2006;Seoul, Korea University. Unpublished doctoral dissertation.
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Women's quality of life and mental health in the first year after birth: Associated factors and effects of antenatal preventive measures among mothers in the ELFE cohort
S. Barandon, L. Castel, C. Galera, J. van der Waerden, A.-L. Sutter-Dallay
Journal of Affective Disorders.2023; 321: 16. CrossRef - Social policies and breastfeeding duration in South Korea: A survival analysis of the national data
Jung Hee Yeo, Eun-Young Kim
Midwifery.2022; 107: 103282. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Quality of Life in Early Postpartum Women
Yu-Jeong Jeong, Ju-Hee Nho, Hye Young Kim, Ji Young Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(6): 2988. CrossRef - Breastfeeding Adaptation Scale-Short Form for mothers at 2 weeks postpartum: construct validity, reliability, and measurement invariance
Sun-Hee Kim
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2020; 26(4): 326. CrossRef - Effects of Breast-Feeding Adaptation and Quality of Sleep on Postpartum Depression in Puerperal Women
Chae Yeon Lee, Hun Ha Cho
Journal of The Korean Society of Maternal and Child Health.2019; 23(3): 162. CrossRef - Influencing Factors on Breastfeeding Nursing Activities of Nursing Students
Ya Ki Yang
Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2019; 25(1): 83. CrossRef - Impact of Parenting Stress and Husband's Support on Breastfeeding Adaptation among Breastfeeding Mothers
Seung Hui Heo, Yoon Goo Noh
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2017; 23(4): 233. CrossRef - Quality of life of mothers at the sixth week and sixth month post partum and type of infant feeding
José Matías Triviño-Juárez, Beatriz Nieto-Pereda, Dulce Romero-Ayuso, Begoña Arruti-Sevilla, Beatriz Avilés-Gámez, Maria João Forjaz, Cristina Oliver-Barrecheguren, Sonia Mellizo-Díaz, Consuelo Soto-Lucía, Rosa Plá-Mestre
Midwifery.2016; 34: 230. CrossRef - Effects of Breastfeeding Empowerment Program on Breastfeeding Self-efficacy, Adaptation and Continuation in Primiparous Women
Seon Mi Song, Mi Kyung Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2016; 46(3): 409. CrossRef - Association of Parenting Stresses, Maternal Role Adjustment, and Types of Feeding during Hospital Stays at Birth to Breastfeeding Adaptation
Sukhee Ahn, Yunmi Kim
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2015; 21(4): 262. CrossRef - Maternal Psychosocial Factors that Affect Breastfeeding Adaptation and Immune Substances in Human Milk
Eun Sook Kim, Mi Jo Jeong, Sue Kim, Hyun-A Shin, Hyang Kyu Lee, Kayoung Shin, Jee Hee Han
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2014; 20(1): 14. CrossRef - Comparison of Lactation Problems, Knowledge, and Adaptation on Breastfeeding between Users and Non-Users of Lactation Clinic
Myoung Hee Yun, Hye Sook Shin
Journal of East-West Nursing Research.2014; 20(2): 112. CrossRef - Factors affecting exclusive breast‐feeding during the first 6 months in Korea
Myo Jing Kim, Yu‐Mi Kim, Jae‐Ho Yoo
Pediatrics International.2013; 55(2): 177. CrossRef - A Structural Model for Primiparas' Breastfeeding Behavior
Hyun-Joo Yang, Ji-Min Seo
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2013; 43(3): 399. CrossRef - A Study on the Experience of Breastfeeding Education for Women with Children 24 Months of Age and Younger
Ji-Eun Kim, Dong-Yean Park
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2012; 23(4): 523. CrossRef - Types of Breastfeeding and its Predictors of Mothers in Twenty-four Months after Birth
Miyoung Kim, Sun Hee Kim, Ja Hyung Lee
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2011; 17(1): 21. CrossRef - The color stability of aesthetic restorative materials resulting from accelerated aging
Jeong-Seon Lee, Kyu-Won Suh, Jae-Jun Ryu
The Journal of Korean Academy of Prosthodontics.2008; 46(6): 577. CrossRef
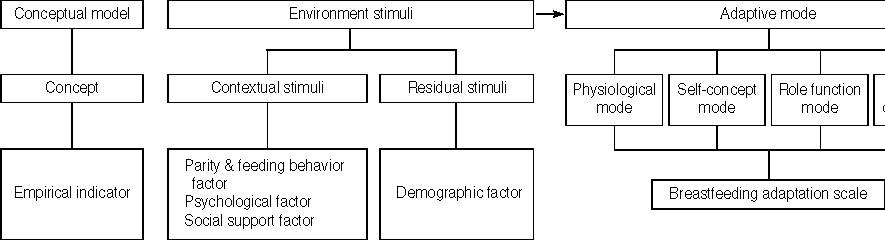
Figure 1
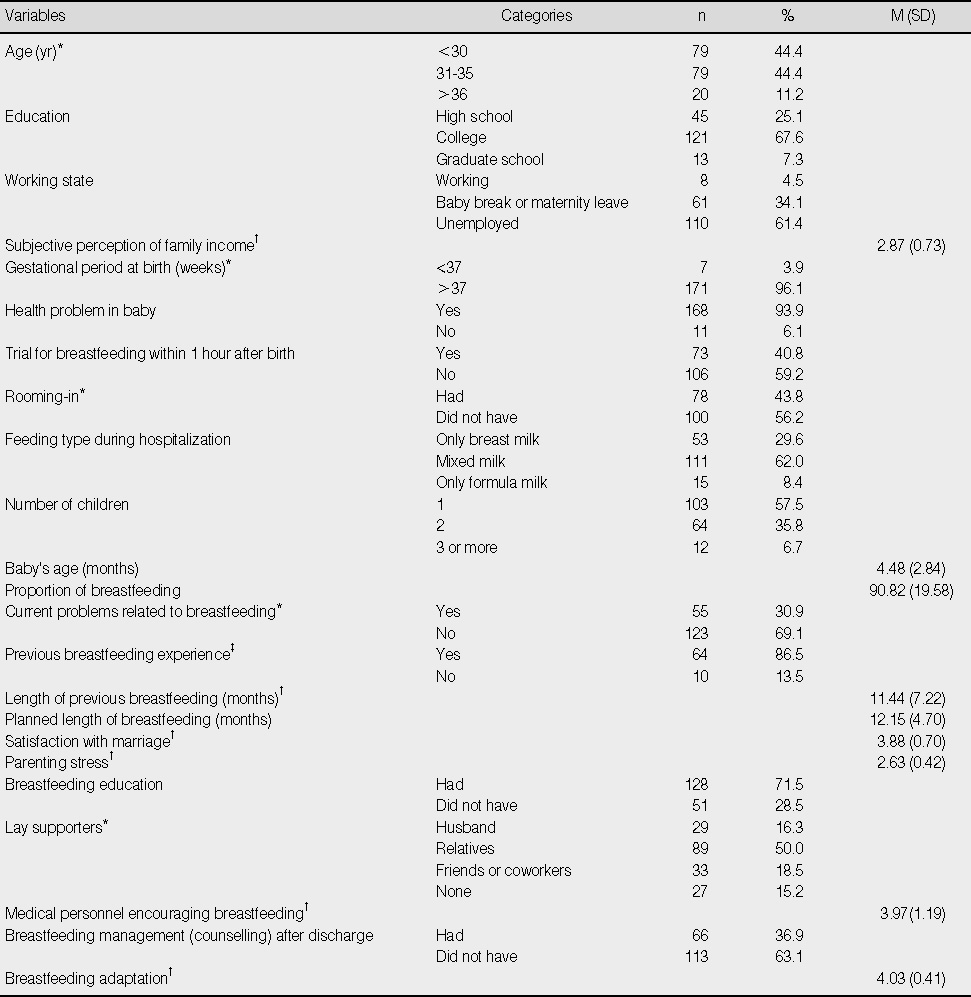
Descriptive Statistics for Study Variables of Breastfeeding Mothers (N=179)
*Missing data were excluded; †Mean of total items (range of score from 1 to 5); ‡Impertinent data were excluded.
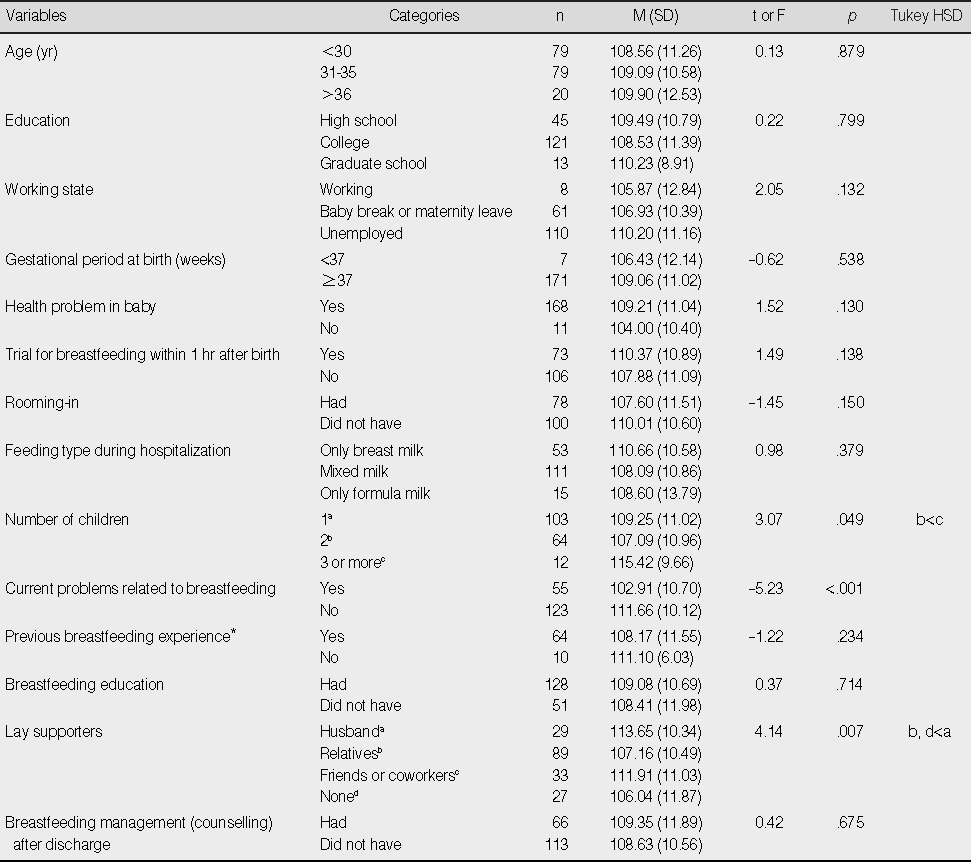
Differences in Breast Feeding Adaptation by Study Variables (N=179)
*Impertinent data were excluded (n=74).
Correlation of Study Variables (N=179)
*Impertinent data were excluded (n=63).
Factors Influencing Breastfeeding Adaptation (N=175)
*Dummy variables; †Impertinent data were excluded (n=63).
*Missing data were excluded; †Mean of total items (range of score from 1 to 5); ‡Impertinent data were excluded.
*Impertinent data were excluded (n=74).
*Impertinent data were excluded (n=63).
*Dummy variables; †Impertinent data were excluded (n=63).
 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION
 Cite
Cite

