Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Nurs > Volume 39(2); 2009 > Article
-
Original Article
- Prevalence and Risk Factors of Postprandial Hypotension in Korean Elderly People
- Jung Tae Son, Eunjoo Lee
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2009;39(2):198-206.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2009.39.2.198
Published online: April 28, 2009
1Associate Professor, Department of Nursing, Catholic University of Daegu, Daegu, Korea.
2Associate Professor, College of Nursing, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Lee, Eunjoo. College of Nursing, Kyungpook National University, 101 Dongin-dong, Jung-gu, Daegu 700-422, Korea. Tel: 82-53-420-4934, Fax: 82-53-421-2758, jewelee@knu.ac.kr
Copyright © 2009 Korean Society of Nursing Science
Abstract
-
Purpose
- The purposes of this study were to identify the prevalence of postprandial hypotension (PPH) and risk factors for PPH in Korean elderly people.
-
Methods
- A cross-sectional descriptive study was conducted with community dwelling and nursing home residents. The blood pressure of 162 adults aged 65 yr or older was measured before meal as a baseline and then at 15 min intervals from immediately after the meal through 90 min after the meal. Descriptive statistics and logistic regression with the SPSS WIN 14.0 program were used to analyze the data.
-
Results
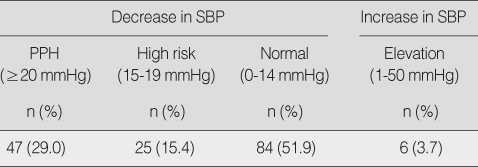
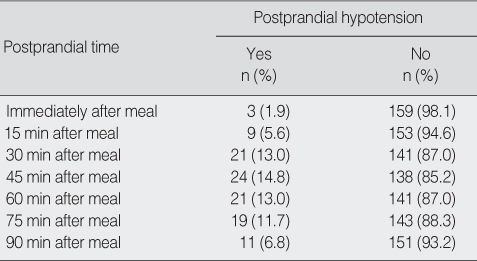
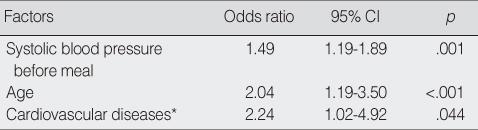
- The prevalence of PPH was 29% and the PPH occurred immediately after the meal continuously through 90 min after the meal. The biggest drop in systolic blood pressure occurred at 45 min after the meal. Risk factors for PPH were age, base line systolic blood pressure, and presence of cardiovascular disease.
-
Conclusion
- To prevent side effects of PPH such as falls and syncope, nurses should provide careful management of PPH and prohibit activities until at least 90 min after a meal. We also recommend that risk of PPH should be included in fall prevention guidelines for elderly people.
This work was supported by the Korean Research Foundation Grant by the Korean Government (MOEHRD) (KRF-2007-531-E00090).
- 1. Aronow WS, Ahn C. Association of postprandial hypotension with incidence of falls, syncope, coronary events, stoke, and total mortality at 29-month follow-up in 499 older nursing home residents. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society. 1997;45:1051–1053.PubMed
- 2. Fisher AA, Davis MW, Srikusalanukul W, Budge MM. Postprandial hypotension predicts all-cause mortality in older, low-level care residents. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society. 2005;53:1313–1320.ArticlePubMed
- 3. Gladstone SA. Cardiac output and related function under basal and postprandial condition. Archives of Internal Medicine. 1935;5:533–546.
- 4. Grodzicki T, Rajzer M, Fagard R, O'Brien ET, Thijs L, Clement D, et al. Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring and postprandial hypotension in elderly patients with isolated systolic hypertension. Journal of Human Hypertension. 1998;12:161–165.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 5. Jansen RW. Postprandial hypotension: Simple treatment but difficulties with the diagnosis. The Journal of Gerontology. 2005;60:1268–1270.Article
- 6. Jansen RW, Lipsitz LA. Postprandial hypotension: Epidemiology, pathophysiology, and clinical management. Annals of Internal Medicine. 1995;122:286–295.ArticlePubMed
- 7. Jones KL, MacIntosh C, Su YC, Wells F, Chapman IM, Tonkin A, et al. Guar gum reduces postprandial hypotension in older people. Journal of American Geriatrics Society. 2001;49:162–167.Article
- 8. Kawaguchi R, Nomura M, Miyajima H, Nakaya Y, Mouri S, Ito S. Postprandial hypotension in elderly subjects: Spectral analysis of heart rate variability and electrogastrograms. Journal of Gastroenterology. 2002;37:87–93.ArticlePDF
- 9. Kohara K, Jiang Y, Igase M, Takata Y, Fukuoka T, Okira T, et al. Postprandial hypotension is associated with asymptomatic cerebrovascular damage in essential hypertensive patients. Hypertension. 1999;33:565–568.ArticlePubMed
- 10. Kohara K, Uemura K, Takata Y, Okura T, Kitami Y, Hiwada K. Postprandial hypotension: Evaluation by ambulatory blood pressure monitoring. American Journal of Hypertension. 1998;11:1358–1363.ArticlePubMed
- 11. Causes of Death. Korea National Statistical Office. 2006;10 20 Retrieved June 30, 2008. from http://www.kosis.kr/html/InterStatic/staticCount.jsp.
- 12. Kuipers HM, Jansen RW, Peeters TL, Hoefnagels WH. The influence of food temperature on postprandial blood pressure reduction and its relation to substance P in healthy elderly subjects. Journal of American Geriatrics Society. 1991;39:181–184.Article
- 13. Le Couteur DG, Fisher AA, Davis MW, McLean AJ. Postprandial systolic blood pressure responses of older people in residential care: Association with risk of falling. Gerontology. 2003;49:260–264.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 14. Lipsitz LA, Nyquist RP Jr, Wei JY, Rowe JW. Postprandial reduction in blood pressure in the elderly. The New England Journal of Medicine. 1983;309:81–83.ArticlePubMed
- 15. Lubart E, Segal R, Baumoehl Y, Matron M, Leibovitz A. Postprandial hypotension in long-term care elderly patients on enteral feeding. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society. 2006;54:1377–1381.ArticlePubMed
- 16. Health Disease Information. National Health Insurance Corporation. 2008;05 16 Retrieved June 30, 2008. from http://www.nhic.or.kr.
- 17. Oberrman AS, Gagnon MM, Kiely DK, Nelson JC, Lipsitz LA. Autonomic and neurohumoral control of postprandial blood pressure in healthy aging. Journal of Gerontology. 2000;55:M477–M483.Article
- 18. O'Donovan D, Feinle C, Tonkin A, Horowitz M, Jones KL. Postprandial hypotension in response to duodenal glucose delivery in healthy older subjects. The Journal of Physiology. 2002;540:673–679.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 19. Puisieux F, Bulckaen H, Fauchais AL, Drumez S, Salomez-Granier F, Dewailly P. Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring and postprandial hypotension in elderly persons with falls or syncopes. Journal of Gerontology. 2000;55:M535–M540.Article
- 20. Sidery MB, Cowley AJ, MacDonald IA. Cardiovascular response to a high fat and a high carbohydrate meal in healthy elderly subjects. Clinical Science. 1993;84:263–270.PubMed
- 21. Smirk FM. Action of a new methonium compound (M & B 2050A) in arterial hypertension. Lancet. 1953;1:457. PubMed
- 22. Smith NL, Psaty BM, Rutan GH, Lumley T, Yanez D, Chaves PH, et al. The association between time since last meal and blood pressure in older adults: The cardiovascular health study. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society. 2003;51:824–828.ArticlePubMed
- 23. Vaitkevicius PV, Esserwein DM, Maynard AK, O'Connor FC, Fleg JC. Frequency and importance of postprandial blood pressure reduction in elderly nursing-home patients. Annals of Internal Medicine. 1991;115:865–870.ArticlePubMed
- 24. Vloet LC, Smits R, Jansen RW. The effect of meals at different mealtimes on blood pressure and symptoms in geriatric patients with postprandial hypotension. The Journals of Gerontology. 2003;58:1031–1035.PubMed
- 25. Yokota T, Kamata T, Mitani K. Postprandial cerebral ischemia. Stroke. 1997;28:2322–2323.PubMed
- 26. Yu SJ, Song MS, Kim HS. A study on the prevalence and risk factors of postprandial hypotension among the community-dwelling aged. Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing. 2002;9:434–444.
REFERENCES
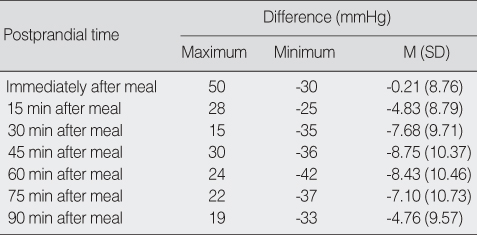
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Postprandial Hypotension as a Risk Factor for the Development of New Cardiovascular Disease: A Prospective Cohort Study with 36 Month Follow-Up in Community-Dwelling Elderly People
Aelee Jang
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2020; 9(2): 345. CrossRef - Effect of blood insulin level on postprandial hypotension in elderly people
Hui Hu, Wei Qiao, Xi Wang, Yunyun Wang, Ying Li, Kejing Wang, Shuang Liu
Blood Pressure Monitoring.2020; 25(4): 201. CrossRef - Evaluation of Cardiac Autonomic Functions in Older Parkinson’s Disease Patients: a Cross-Sectional Study
Ahmet Yalcin, Volkan Atmis, Ozlem Karaarslan Cengiz, Esat Cinar, Sevgi Aras, Murat Varli, Teslime Atli
Aging and disease.2016; 7(1): 28. CrossRef - Effects of guar gum ingestion on postprandial blood pressure in older adults
A.L. Jang, Sun-Kyung Hwang, D.U. Kim
The Journal of nutrition, health and aging.2015; 19(3): 299. CrossRef - Effects of the amount of rice in meals on postprandial blood pressure in older people with postprandial hypotension: a within‐subjects design
Jung Tae Son, Eunjoo Lee
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2015; 24(15-16): 2277. CrossRef - Effects of Tailored Water Drinking on the Orthostatic Hypotension in the Elderly
Eunjoo Lee, Eun Hee Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2014; 26(3): 341. CrossRef - Effects of Green Tea Ingestion on Postprandial Drops in Blood Pressure in Older Adults
Jung Tae Son, Eunjoo Lee
Journal of Gerontological Nursing.2012; 38(3): 30. CrossRef - Postprandial Hypotension and Heart Rate Variability in Older Adults
Ae-Lee Jang, Sun-Kyung Hwang
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2012; 24(2): 139. CrossRef - Postprandial Blood Pressure in Hypertensive and Normotensive Elderly and Young Adult Subjects
Jung Tae Son
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2012; 13(12): 5849. CrossRef - Postprandial hypotension among older residents of a nursing home in Korea
Jung Tae Son, Eunjoo Lee
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2012; 21(23-24): 3565. CrossRef - A Case of Postprandial Hypotension in the Intensive Care Unit Treated With Acarbose
Joon Hyouk Choi, Hyung Seok Lee, Tae-Yu Lee, EunHa Jang, Min Ho Kang, Dae Kyoung Cho
Korean Circulation Journal.2011; 41(10): 629. CrossRef
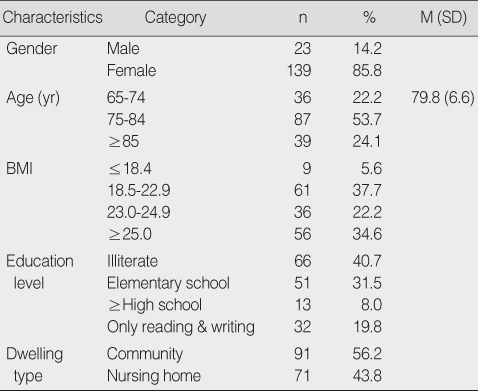
Demographics of Participants (N=162)
BMI=body mass index.
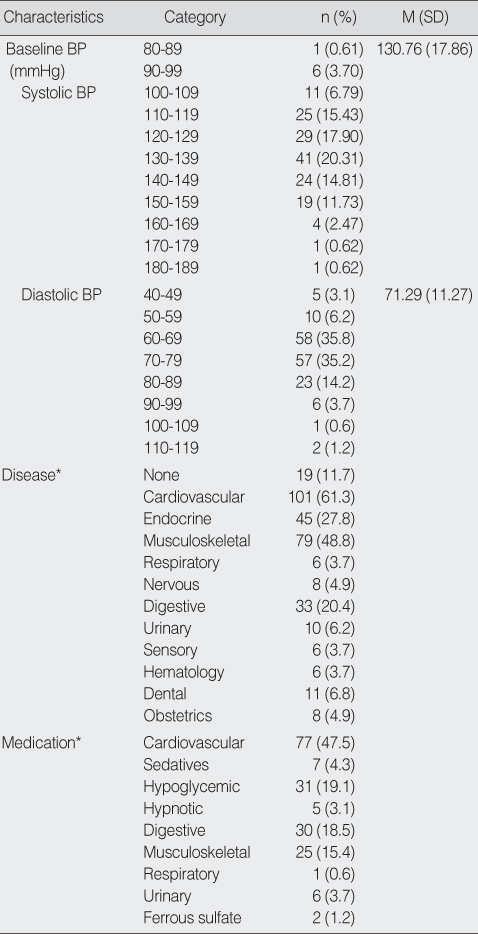
Postprandial Hypotension related Characteristics (N=162)
*Multiple response.
BP=blood pressure.
Incidence of the Postprandial Hypotension (N=162)
SBP=systolic blood pressure; PPH=postprandial hypotension.
Postprandial Hypotension Incidence by Time after Meal (N=162)
Comparison of After Meal Systolic Blood Pressure with Baseline Systolic Blood Pressure (N=162)
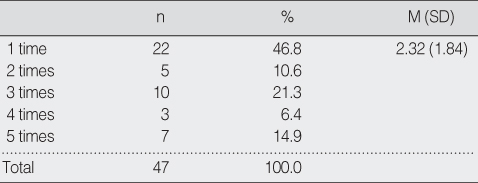
Number of Postprandial Hypotension Occurrence among Postprandial Hypotension Cases during 90 min after Meal
PPH=postprandial hypotension.
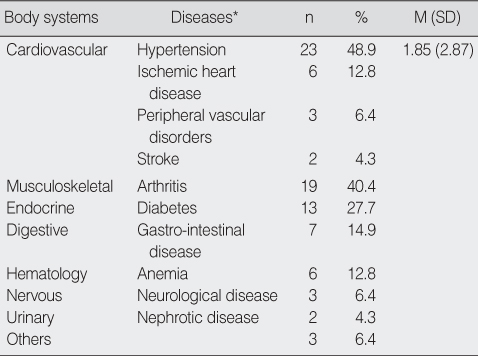
Underlying Diseases among Postprandial Hypotension Cases (N=47)
*Multiple response.
Risk Factors of the Postprandial Hypotension
*Cardiovascular diseases included congestive heart failure, hypertension, ischemic heart disease, peripheral vascular disorders, myocardial infarction, hypotension, arteriosclerosis, and stroke.
95% CI=95% confidence Interval.
BMI=body mass index.
*Multiple response. BP=blood pressure.
SBP=systolic blood pressure; PPH=postprandial hypotension.
PPH=postprandial hypotension.
*Multiple response.
*Cardiovascular diseases included congestive heart failure, hypertension, ischemic heart disease, peripheral vascular disorders, myocardial infarction, hypotension, arteriosclerosis, and stroke. 95% CI=95% confidence Interval.
 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION
 Cite
Cite

