Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Nurs > Volume 38(5); 2008 > Article
-
Original Article
- Falls Risk Factors of Inpatients
- Eun-Kyung Kim, Jae Chang Lee, Mi-Ran Eom
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2008;38(5):676-684.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2008.38.5.676
Published online: October 30, 2008
1Professor, College of Nursing, Eulji University, Daejeon, Korea.
2Professor, Department of Industrial & Advertising Psychology, Daejeon University, Daejeon, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Eom, Mi-Ran. College of Nursing, Eulji University, 143-5 Youngdu 2-dong, Jung-gu, Daejeon 301-746, Korea. Tel: 82-42-259-1712, Fax: 82-42-259-1709, miran@eulji.ac.kr
Copyright © 2008 Korean Society of Nursing Science
Abstract
-
Purpose
- The purpose of this study was to identify the risk factors for falls and to suggest data for developing a program for preventing falls.
-
Methods
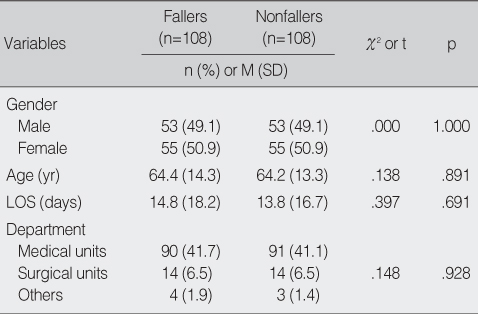
- This was a case-control study in five university hospitals and a general hospital. In total, 216 patients over the age of 18 yr admitted from January 1 to December 31, 2007 participated. One hundred eight patients with experience of falling were matched by gender, age level, diagnosis, and length of stay with 108 patents with no experience of falling admitted on the same unit. A quality assurance coordinator nurse in each hospital examined 35 fall risk factors developed by researchers.
-
Results
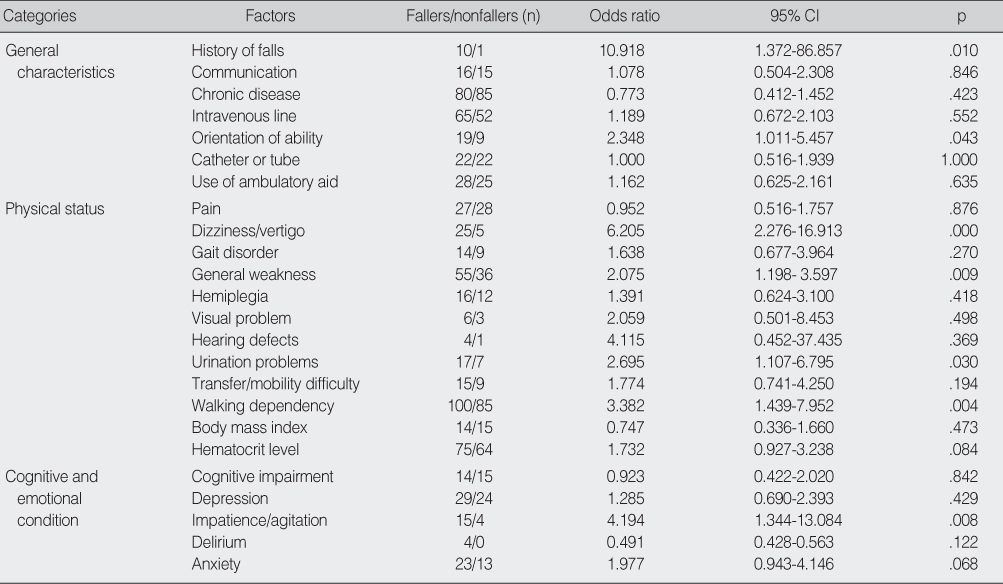
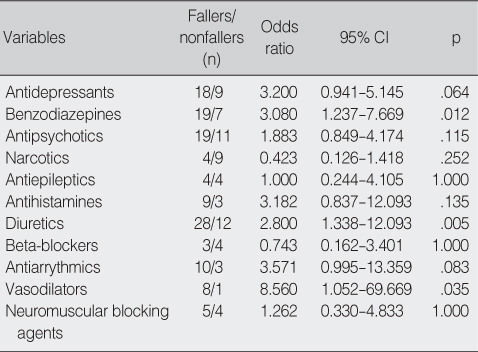
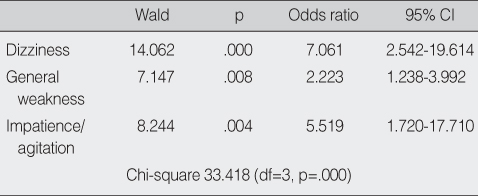
- In acute hospitals, history of falls, orientation ability, dizziness or vertigo, general weakness, urination problems, transfer/mobility difficulty, walking dependency, impatience, benzodiazepines, diuretics, and vasodilators showed significance on adjusted-odds ratios for fall. Logistic regression analysis was performed to elucidate the factors that influence falls. The probability of falls was increased by dizziness/vertigo, general weakness, and impatience/agitation.
-
Conclusion
- This finding can be used as a useful resource in developing nursing intervention programs to predict and prevent the falls of inpatients.
- 1. Aizen E, Shugaev I, Lenger R. Risk factors and characteristics of falls during inpatient rehabilitation of elderly patients. Archives of Gerontology and Geriatrics. 2006;44:1–12.ArticlePubMed
- 2. American Nurses Association. Nursing-sensitive indicators. 2008;Retrieved July 21, 2008. from http://www.nursingworld.org/MainMenuCategories/ThePracticeofProfessionalNursing/PatientSafetyQuality/NDNQI/NDNQI_/NursingSensitiveIndicators.aspx .
- 3. Bergland A, Wyller TB. Risk factors for serious fall related injury in elderly women living at home. Injury Prevention. 2004;10:308–313.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 4. Chaimowicz F, Ferreira Tde.J, Miguel DF. Use of psychoactive drugs and related falls among older people living in a community in Brazil. Revista de Saúde Pública. 2000;34:631–635.Article
- 5. Chen JS, March LM, Schwarz J, Zochling J, Makaroff J, Sitoh YY, et al. A multivariate regression model predicted falls in residents living in intermediate hostel care. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology. 2005;58:503–508.ArticlePubMed
- 6. Cho JP, Paek KW, Song HJ, Jung YS, Moon HW. Prevalence and associated factors of falls in the elderly community. Korean Journal of Preventive Medicine. 2001;34:47–54.
- 7. Daal JO, van Lieshout JJ. Falls and medications in the elderly. The Netherlands Journal of Medicine. 2005;63:91–96.PubMed
- 8. Evans D, Hodgkinson B, Lambert L, Wood J. Falls risk factors in the hospital setting: A systematic review. International Journal of Nursing Practice. 2001;7:38–45.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 9. Fehring RJ. Methods to validate nursing diagnosis. Heart & Lung. 1987;16:625–629.
- 10. Gu MO, Jeon MY, Kim HJ, Eun Y. A review of exercise interventions for fall prevention in the elderly. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2005;35:1101–1112.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 11. Gyldenvand T. Falls: the construction and validation of the risk assessment for fall scale II (RAFS II). 1984;Iowa, USA, University of Iowa. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 12. Harwood RH. Visual problems and falls. Age and Ageing. 2001;30:S13–S18.
- 13. Hendrich A, Nyhuis A, Kippenbrock T, Soja ME. Hospital falls: Development of a predictive model for clinical practice. Applied Nursing Research. 1995;8:129–139.ArticlePubMed
- 14. Hendrich AL, Bender PS, Nyhuis A. Validation of the Hendrich II fall risk model: A large concurrent case/control study of hospitalized patients. Applied Nursing Research. 2003;16:9–21.ArticlePubMed
- 15. Houghton S, Birks V, Whitehead CH, Crotty M. Experience of a falls and injuries risk assessment clinic. Australian Health Review. 2004;28:374–381.PubMed
- 16. Kim CG. An analysis of fall incidence rate and the related factors of fall in hospitalized patients. 2003;Seoul, Seoul National University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 17. Kim EA, Mordiffi SZ, Bee WH, Devi K, Evans D. Evaluation of three fall-risk assessment tools in an acute care setting. Journal of Advanced Nursing. 2007;60:427–435.ArticlePubMed
- 18. Kwon IG, Kim KH. A study on the variables forecasting elderly inpatients' fall experience. Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing. 2007;16:59–68.
- 19. Lee HS. A study on fall accident. 1997;Seoul, Seoul National University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 20. Morse JM. Preventing patient falls. 1997;Thousand Oaks, CA, Sage.
- 21. Neyens JC, Dijcks BP, van Haastregt JC, de Witte LP, van den Heuvel WJ, Crebolder HF, et al. The development of a multidisciplinary fall risk evaluation tool for demented nursing home patients in the Netherlands. BMC Public Health. 2006;6:74. PubMedPMC
- 22. Oliver D, Britton M, Seed P, Martin FC, Hopper AH. Development and evaluation of evidence based assessment tool (STRATIFY) to predict which elderly inpatients will fall: Case-control and cohort studies. British Medical Journal. 1997;315:1049–1053.PubMedPMC
- 23. Oliver D, Daly F, Martin FC, McMurdo ME. Risk factors and risk assessment tools for falls in hospital inpatients: A systematic review. Age and Ageing. 2004;33:122–130.ArticlePubMed
- 24. Ruthazer R, Lipsitz LA. Antidepressants and falls among elderly people in long term care. American Journal of Public Health. 1993;83:746–749.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 25. Shin KR, Shin SJ, Kim JS, Kim JY. The effects of fall prevention program on knowledge, self-efficacy, and preventive activity related to fall, and depression of low-income elderly women. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2005;35:104–112.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 26. Sohng KY, Moon JS, Lee KS. Prevalence and associated factors of falls among people with Parkinson's disease. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2004;34:1081–1091.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 27. Song KA, Moon JS, Kang SS, Choi JH. Activities and fear of falling in the community dwelling elderly. Korean Journal of Public Health Nursing. 2001;15:324–333.
- 28. Song KJ, Han MY, Cheong MY, Lim KS, Kim DK. Clinical research design and biostatistical methods. Korean Journal of Urology. 2005;46:835–841.
- 29. Tinett ME, Speechley M, Ginter SF. Risk factors for falls among elderly persons living in the community. New England Journal of Medicine. 1988;319:1701–1707.ArticlePubMed
- 30. Vassallo M, Stockdale R, Sharma JC, Briggs R, Allen S. A comparative study of the use of four fall risk assessment tools on acute medical wards. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society. 2005;53:1034–1038.ArticlePubMed
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Evaluation of intrinsic and extrinsic fall risk factors in hospitals, long-term facilities, and homes: A narrative review
A.C. Dondi, K.G. Davis
Human Factors in Healthcare.2026; 9: 100125. CrossRef - The Impact of Physical Performance and Fear of Falling on Fall Risk in Hemodialysis Patients: A Cross-Sectional Study
Jiwon Choi, Sun-Kyung Hwang
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2024; 36(1): 63. CrossRef - A Clinical Data Warehouse Analysis of Risk Factors for Inpatient Falls in a Tertiary Hospital: A Case-Control Study
Eunok Kwon, Sun Ju Chang, Mikyung Kwon
Journal of Patient Safety.2023; 19(8): 501. CrossRef - Association of medication use with increased fall risk in inpatients: a single-center matched study
Hae-Jin Jeon, Eun-Joo Choi, Min-Jung Kim, Ae-Hee Jung, Sun-Hoi Jung, Hyo-Nam Woo, Kyu-Nam Heo, Ju-Yeun Lee, Hyung-Min Kwon
Journal of Geriatric Neurology.2023; 2(2): 64. CrossRef - Prediction of Falls Risk Using Toe Strength and Force Steadiness based on Deep Learning: A Preliminary Study
Jin Seon Kim, Seong Un Choi, Chang Yeop Keum, Jaehee Lee, Woong Ki Jang, Kwang Suk Lim, Hyungseok Lee, Byeong Hee Kim, Tejin Yoon
Journal of the Korean Society for Precision Engineering.2023; 40(7): 519. CrossRef - The Perceived Knowledge of Fall Prevention in Nurses Working in Acute Care Hospitals in China and the United States
Lin Wang, Li Zhang, Elizabeth Roe, Sally Decker, Gwen Howard, Angela Luth, Kristine Marks, Brenda Whitman
Journal of Patient Safety.2022; 18(2): e580. CrossRef - Development and Effect of a Fall Prevention Program Based on King’s Theory of Goal Attainment in Long-Term Care Hospitals: An Experimental Study
Bom-Mi Park
Healthcare.2021; 9(6): 715. CrossRef - Comparison of the predictive validity of three fall risk assessment tools and analysis of fall‐risk factors at a tertiary teaching hospital
Eun Hee Cho, Yun Jung Woo, Arum Han, Yoon Chung Chung, Yeon Hee Kim, Hyeoun‐Ae Park
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2020; 29(17-18): 3482. CrossRef - Improving Prediction of Fall Risk Using Electronic Health Record Data With Various Types and Sources at Multiple Times
Hyesil Jung, Hyeoun-Ae Park, Hee Hwang
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2020; 38(3): 157. CrossRef - Triggers and Outcomes of Falls in Hematology Patients: Analysis of Electronic Health Records
Min Kyung Jung, Sun-Mi Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2019; 26(1): 1. CrossRef - A risk-factor analysis of medical litigation judgments related to fall injuries in Korea
Insook Kim, Seonae Won, Mijin Lee, Won Lee
Medicine, Science and the Law.2018; 58(1): 16. CrossRef - Root Cause Analysis of Falls Occurred and Presenting Fall Prevention Strategies Using Nominal Group Technique
Zhila Najafpour, Ali Movafegh, Arash Rashidian, Mohamadreza Jafari, Ali Akbari Sari, Mohammad Arab
Health Scope.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Structural Analysis of Variables related to Fall Prevention Behavior of Registered Nurses in Small-to-Medium Sized Hospitals
Ji Hyun Park, Jung Tae Son
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2018; 25(4): 269. CrossRef - Risk factors of falls among inpatients with cancer
M.D. Jun, K.M. Lee, S.A. Park
International Nursing Review.2018; 65(2): 254. CrossRef - Characteristics and Risk Factors for Falls in Tertiary Hospital Inpatients
Eun-Ju Choi, Young-Shin Lee, Eun-Jung Yang, Ji-Hui Kim, Yeon-Hee Kim, Hyeoun-Ae Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2017; 47(3): 420. CrossRef - Identifying Characteristics of Fall Episodes and Fall-related Risks of Hospitalized Patients
Young Ok Kang, Rhayun Song
Journal of muscle and joint health.2015; 22(3): 149. CrossRef - Fall Risk Factors and Characteristics of an Acute Hospital Setting across Clinical Departments
In-Sil Jang, Sun-Gyo Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2014; 21(3): 264. CrossRef - Evaluation of falls by inpatients in an acute care hospital in Korea using the Morse Fall Scale
Yung Hee Sung, Myung Sook Cho, In Gak Kwon, Yoen Yi Jung, Mi Ra Song, Kyunghee Kim, Sungho Won
International Journal of Nursing Practice.2014; 20(5): 510. CrossRef - Fall Risk related Factors in Postmenopausal Women
Jung-Han Lee, Hee Seung Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2014; 26(5): 533. CrossRef - Effects of Health Belief on Fall Prevention Activities of Emergency Room Nurses
Min Kyoung Park, Hyun-Young Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2014; 20(2): 176. CrossRef - Validation of the Short Form Bobath Memorial Hospital Fall Risk Assessment Scale at a Specialized Geriatric Hospital in Korea
Kyeong-Yae Sohng, Mi Hwa Park, Seung Kyo Chaung, Hye Ja Park
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2014; 28(3): 495. CrossRef - Fall Risk Factors and Fall Risk Assessment of Inpatients
Yoon Sook Kim, Smi Choi-Kwon
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2013; 25(1): 74. CrossRef - Risk Factors for Pediatric Inpatient Falls
Myung Sook Cho, Mi Ra Song, Sun Kyung Cha
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2013; 43(5): 595. CrossRef - Safety Consciousness of the Elderly Living Alone
Youngsil Kang, Sun Jae Jung
Journal of muscle and joint health.2013; 20(3): 180. CrossRef - The Effects of Fall Prevention Education on the Fall-related Knowledge and Prevention activity of the Elderly Hospitalized in Internal Medicine Department
Myung Sill Chung
Journal of muscle and joint health.2013; 20(2): 102. CrossRef - Predictive Effects of Previous Fall History on Accuracy of Fall Risk Assessment Tool in Acute Care Settings
Ihn Sook Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2012; 19(4): 444. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of Patient Safety Reporting Promoting Education Program
Myoung-Soo Kim, Yun-Hee Kim
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2012; 13(1): 284. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Fear of Falling in Stroke Patients
Hee-Sook Jeong, Eun-Nam Lee, Sam-Sook Kim
Journal of muscle and joint health.2011; 18(2): 215. CrossRef - Current Approaches to Fall Risk Assessment in Nursing Homes
Laura M. Wagner, Vicky Scott, Mara Silver
Geriatric Nursing.2011; 32(4): 238. CrossRef - A Comparative Study on the Validity of Fall Risk Assessment Scales in Korean Hospitals
Keum Soon Kim, Jin A Kim, Yun-Kyoung Choi, Yu Jeong Kim, Mi Hwa Park, Hyun-Young Kim, Mal Soon Song
Asian Nursing Research.2011; 5(1): 28. CrossRef - Evaluation of a Fall Risk Assessment Tool to Establish Continuous Quality Improvement Process for Inpatients' Falls
Ihn Sook Park, InSook Cho, Eun Man Kim, Min Kyung Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2011; 17(4): 484. CrossRef - Defining Reported Errors on Web-based Reporting System Using ICPS From Nine Units in a Korean University Hospital
Chul-Hoon Kim, Myoungsoo Kim
Asian Nursing Research.2009; 3(4): 167. CrossRef
Homogeneity Test between Fallers and Nonfallers (N=216)
LOS=length of stay.
Odds Ratios between Fallers and Nonfallers by General Characteristics, Physical Status, and Cognitive and Emotional Condition of Subjects (N=216)
CI=confidence interval.
Odds Ratios between Fallers and Nonfallers by Medication (N=216)
CI=confidence interval.
Logistic Regression Analysis of Risk Factors Related to Falls (N=216)
CI=confidence interval.
LOS=length of stay.
CI=confidence interval.
CI=confidence interval.
CI=confidence interval.
 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION
 Cite
Cite

