Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Nurs > Volume 38(1); 2008 > Article
-
Original Article
- The Relationship of Perceived Health Status, Activities of Daily Living and Nutrition Status in the Community-Dwelling Korean Elderly
- Younhee Kang, Miyoung Kim, Eliza Lee
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2008;38(1):122-130.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2008.38.1.122
Published online: February 28, 2008
1Assistant Professor, College of Nursing Science, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea.
2Assistant Director, Department of Nursing, Ewha Womans University Dongdaemun Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
3Doctoral Student, College of Nursing Science, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Kim, Mi Young. Department of Nursing, Ewha Womans University Dongdaemun Hospital, 70 Jongno 6-ga-dong, Jongno-gu, Seoul 110-183, Korea. Tel: 82-2-760-5252, Fax: 82-2-760-5005, mykim0808@hanmail.net
Copyright © 2008 Korean Society of Nursing Science
Abstract
-
Purpose
- This study aimed to identify the associated factors of the perceived health status of the elderly in Korea and to provide basic data for developing nursing interventions for the elderly's health management.
-
Methods
- This study used a descriptive correlational research design. The subjects of this study were 335 elderly people over 60 yr living in an urban city. Data were collected through personal interviews using questionnaires from September 2006 to March 2007. Empirical indicators of perceived health status were measured by SF-36, nutritional screening initiative (NSI), activities of daily living (ADL) Index, and instrumental activities of daily living (IADL) scale. The collected data were analyzed by descriptive statistics, Pearson's correlation, and hierarchical regression.
-
Results
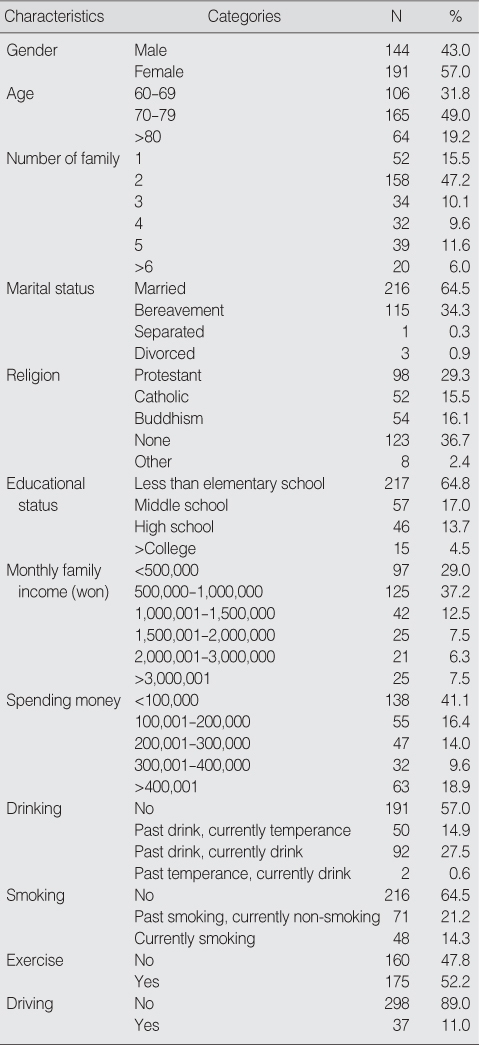
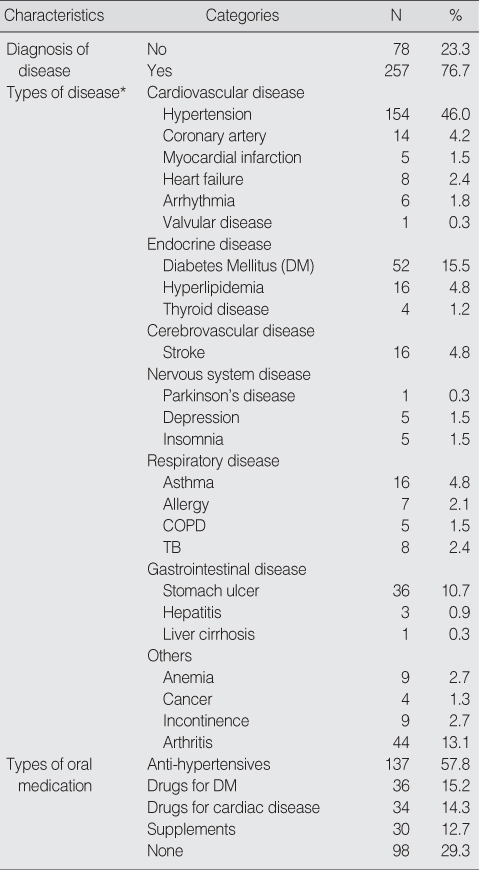
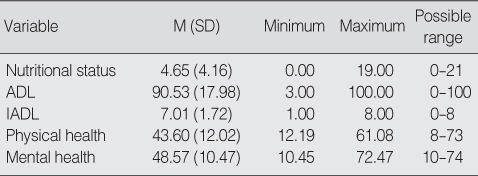
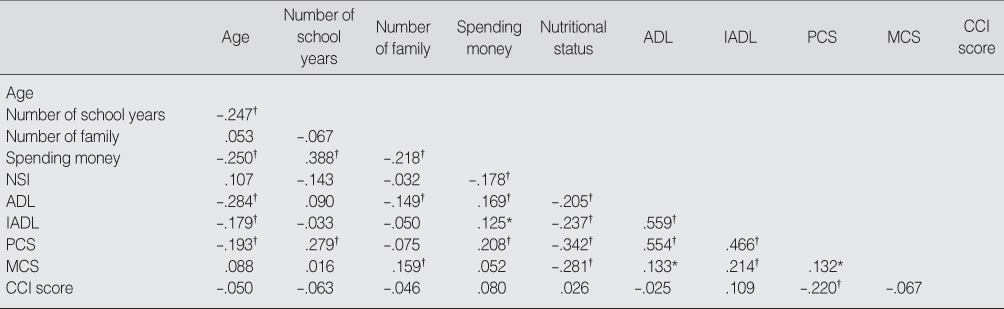
- The mean age of the subjects was 72.8 and 57.0% of subjects were female. 41.5% of variance in physical health was explained by nutrition, ADL, IADL, and the number of years attending school. Among them the most important factor was ADL. 13.2% of variance in mental health was explained by the number of family, nutrition, and IADL. Among them the most important factor was nutrition.
-
Conclusion
- It is necessary to develop supportive interventions for improving the perceived health status of elderly people by considering the most important factors shown in this study.
- 1. Bobak M, Pikhart H, Hertzman C, Rose R, Marmot M. Socioeconomic factors perceived control and self-reported health in Russia. A cross-sectional survey. Soc Sci Med. 1998;47:269–279.ArticlePubMed
- 2. Choi EJ. Social relationship, social support and mental and physical health for old adults. Society Culture. 2000;11:185–203.
- 3. Choi YJ, Park YS, Kim C, Chang YK. Evaluation of functional ability and nutritional risk according to Self-Rated Health (SRH) of the elderly in Seoul and Kyunggi-do. Korean Nutr Soc. 2004;37:223–235.
- 4. Gong SJ, Kim HS, Ha MO. The predictors of subjective well-being among older adults. J Korean Acad Adult Nurs. 2005;17:368–378.
- 5. Han AK. A study on physiological parameter, physical health status, and health perception in the elderly. J Korean Acad Adult Nurs. 2004;16:460–469.
- 6. Han KH. Nutritional and health status of the elderly male and female in chong-ju area. J Appl Sci Technol. 2000;6(1):307–329.
- 7. Jang EH, Kim HJ, Kwon KN, Chung KA, Kim YH, Lee IH. A survey on physical health status and health behavior of the elderly who live alone and who live with family. Yeungnam College Science Technology. 2003;33:91–104.
- 8. Jung YM, Kim JH. Comparison of cognitive levels nutritional status, depression in the elderly according to living situations. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2004;34:495–503.ArticlePDF
- 9. Kanagae M, Abe Y, Honda S, Takamura N, Kusano Y, Takemoto T, et al. Determinants of self-rated health among community-dwelling women aged 40 years and over in Japan. Tohuku J Exp Med. 2006;210(1):11–19.Article
- 10. Keller HH. Nutrition and health-related quality of life in frail older adults. J Nutr Health Aging. 2004;8:245–252.PubMed
- 11. Kennedy-Malone L, Fletcher KR, Plank LM. Management guidelines for nurse practitioners working with older adults. 2004;2nd ed. Philadelphia, F.A. Davis Company.
- 12. Kim CG. The relationship of family support, health perception, nutritional status and depression in elders. J Korean Gerontol Nurs. 2007;9(1):14–21.
- 13. Kim YS. Health state variation and health management of old men. 2003;Pusan, Kosin University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 14. Kim CG, Jang HJ, Kim SS. The correlation between ability of activity in daily living and self-care agency among elderly in chunchon province. J Korean Acad Adult Nurs. 2001;13(1):40–52.
- 15. Korean standard industrial classification. Korea National Statistical Office. 2006;Retrieved from http://www.nso.go.kr.
- 16. Lawton MP, Brody EM. Assessment of older people: Self-maintaining and instrumental activities of daily living. Gerontologist. 1969;9:179–186.ArticlePubMed
- 17. Lee SY, Choi SJ, Na YH. A study on the healthrelated quality of life. Korean J Gastrointestinal Mortality. 2001;7(1):6–17.
- 18. Lee KJ, Park HS. A study on the perceived health status, depression, and activities of daily living for elderly in urban areas. Korean J Women Health Nurs. 2006;12:221–230.ArticlePDF
- 19. Mahoney FJ, Barthel DW. Functional evaluation: The barthel index. Md State Med J. 1965;14(1):1–3.Article
- 20. The World Health Report. Ministry of Health & Welfare. 2007;Retrieved Nov. 6, 2007. from http://www.nso.go.kr.
- 21. Society at a glance-OECD social indicators. Ministry of Health & Welfare. 2006;Retrieved Aug. 31, 2007. from http://www.nso.go.kr.
- 22. Phillips LJ, Hammock RL, Blanton JM. Predictors of self-rated health status among Texas residents. Prev Chronic Dis. 2005;2(4):1–10.
- 23. Ro YJ, Kim CG. Comparisons of physical fitness, self efficacy, instrumental activities of daily living, and quality of life between institutionalized and noninstitutionalized elderly. J Korean Acad Nurs. 1995;25:259–278.ArticlePDF
- 24. Shah S, Vanclay F, Cooper B. Improving the sensitivity of the barthel Index for stroke rehabilitation. J Clin Epidemiol. 1989;42:703–709.ArticlePubMed
- 25. Smith AM, Shelley JM, Dennerstein L. Self-rated health: biological continuum or social discontinuity? Soc Sci Med. 1994;39(1):77–83.ArticlePubMed
- 26. Song KC, Kim DK. Activities of daily living of elderly in a rural area and study for related factors. J Korean Geriatr Soc. 2002;6(1):29–40.
- 27. Sung JA. A study on the cognitive function and quality of life in the elderly people living at home. 2007;Seoul, Ewha Womans University. Unpublished doctoral dissertation.
- 28. Ware JE. Scales for measuring general health perceptions. Health Serv Res. 1976;11:396–415.PubMedPMC
- 29. Ware JE, Sherbourne CD. The MOS 36-item short-form health survey (SF-36). I. Conceptual framework and item selection. Med Care. 1992;30:473–483.PubMed
- 30. Woo EK, Han CS, Jo SA, Park MK, Kim SS, Kim EK, et al. Morbidity and related factors among elderly people in South Korea: results from the Ansan Geriatrics (AGE) cohort study. BMC Public Health. 2007;7(10):1–9.PubMedPMC
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- A Causal Model of Health-related Quality of Life Among Pakistani Older Persons with Multimorbidity (HRQL-OPM)
Razia Sultana, Dr. Sirirat Panuthai, Dr. Jindarat Chaiard, Dr. Rojanee Chintanawat
Geriatric Nursing.2025; 61: 210. CrossRef - Associations Between Physical Features and Behavioral Patterns in Macau Outdoor Community Public Spaces and Older Adults’ Performance of Instrumental Activities of Daily Living
Hong-Zhan Lai, Stephen Siu-Yu Lau, Chen-Yi Sun
Land.2025; 14(5): 955. CrossRef - Effects of Nutritionally Balanced Soymilk Intake on Eating Habits, Diet Quality, and Blood Protein Factors in Elderly Patients with Alcoholic Liver Disease
Hyo-Jeong Hwang, Jae-Il Chung, Kwang-Jin Chon, Chung-Hwa Song, Dae-Gyun Moon, Kyung-Ok Shin
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2024; 34(5): 341. CrossRef - Effects of Subjective Health Perception on Health Behavior and Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors in Patients with Prediabetes and Diabetes
Sungjung Kwak, Yoonmi Lee, Seunghui Baek, Jieun Shin
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(13): 7900. CrossRef - Nutritional Status according to the Frailty Status of the Elderly at Home in Seo-gu, Gwangju, Korea
Ye Eun Kim, Young-Ran Heo
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(5): 382. CrossRef - Effects of Calcium Fortified Beverage Intake on Insulin Sensitivity and Antioxidant Metabolism in Healthy Elderly
Seonjeong Kim, Eunju Park, Jae-Hee Park
Clinical Nutrition Research.2021; 10(4): 303. CrossRef - Comparison Analysis of Dietary Behavior and Nutrient Intakes of the Elderly according to Their Family Status: The Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2013–2016
Ji-Hong Oh, Bok-Mi Jung
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(4): 309. CrossRef - Nutritional Risk of the Elderly Receiving a Home-Delivered Meal Service Program and the Factors for Nutritional Risk
Na-Young Yi, Jung-Hwa Choi
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2019; 24(3): 197. CrossRef - Subjective Health Status, Mental Health, and Cancer Stigma in Long-term Cancer Survivors after Gastric Surgery
Bo Yun Jang, Jeong Yun Park
Asian Oncology Nursing.2018; 18(2): 86. CrossRef - Key Food Selection for Assessement of Oral Health Related Quality of Life among Some Korean Elderly
Soo-Jeong Hwang
Journal of dental hygiene science.2016; 16(5): 361. CrossRef - Diet and Health Status of Elderly Women According to the Family Type
Mi-Kyeong Choi, Myung-Hwa Kang, Mi-Hyun Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2016; 21(3): 256. CrossRef - Effect of Liposome-coated Hemicellulase on the Tenderization of Burdock
Kwang-Il Kim, SangYoon Lee, Jiseon Lee, JungGyu Lee, Sang-Gi Min, Mi-Jung Choi
Korean Journal of Food Science and Technology.2015; 47(6): 698. CrossRef - Influence of Frailty, Nutritional Status, Positive Thinking and Family Function on Health Conservation of the Elderly at Home
Hae Kyung Chang
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2015; 27(1): 52. CrossRef - Comparative analysis of food intake according to the family type of elderly women in Seoul area
Yeon Joo Lee, Min Kyung Kwon, Hee Joon Baek, Sang Sun Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2015; 48(3): 277. CrossRef - Correlation with subjective oral health status and food preference in elderly people
Chung-Soon Park, In-Ja Kim, So-Young Park
Journal of Korean society of Dental Hygiene.2015; 15(6): 973. CrossRef - Elderly Health and Literature Therapy: A Theoretical Review
Yeongcheol Eum, Jongeun Yim, Wonjae Choi
The Tohoku Journal of Experimental Medicine.2014; 232(2): 79. CrossRef - Nutritional Status and Risk Factors for Malnutrition in Low-income Urban Elders
Hye Sun Hyun, Insook Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2014; 44(6): 708. CrossRef - The Effect of a Community-Based Nutrition Intervention Program on Dietary Behavior and Nutritional Status of Low-Income Elderly Women in Gwangju City
Bok Hee Kim, Ji-Suk Yang, Seung-Hee Kye, Yoonna Lee
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2014; 27(3): 495. CrossRef - Investigation on Influencing Environmental Factors on Health Status of Korean Septuagenarians Dwelling in Longevity Region in Jeonla Province
Chung Shil Kwak, Miyong Yon, Mee Sook Lee, Se In Oh, Sang Chul Park
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2014; 19(2): 142. CrossRef - A Study on the Blood Health Status and Nutrient Intake in Elderly Women Dwelling in Longevity Region in Jeonla Province according to Family Arrangement
Se In Oh, Chung Shil Kwak, Miyong Yon, Mee Sook Lee
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2014; 27(5): 940. CrossRef - Appetite and Related Factors among Community Elders in Korea
Soojin Park
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2014; 43(9): 1431. CrossRef - Factors Related to Perceived Health Status in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Ang Li Won, Seung Hyun Yoo, Myoung Soon You
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2014; 31(3): 1. CrossRef - The Relationships among Satisfaction with Food-Related Life, Depression, Isolation, Social Support, and Overall Satisfaction of Life in Elderly South Koreans
Sunhee Seo, Misook Cho, Yuri Kim, Jiyoon Ahn
Journal of the Korean Dietetic Association.2013; 19(2): 159. CrossRef - Dietary Patterns among the Elderly in Jeollanam-do Area based on Their Physical and Mental Function State
Eunju Yoon, Soon-Sil Chun
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2013; 26(4): 783. CrossRef - Effects of Nutrition Education and Personalized Lunch Service Program for Elderly at Senior Welfare Center in Jeonju
Jeong-Sook Bae, Mi-Hyun Kim, Sook-Bae Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2013; 18(1): 65. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Successful Aging in Rural Elderly People
Okhee Ahn, Hye Gyeong Cha, Soo Jung Chang, Hee Sun Kim, Eun Hee Jang
The Journal of Digital Policy and Management.2013; 11(11): 499. CrossRef - Characteristics of Eating Behavior in Elders with Dementia residing in Long-Term Care Facilities
Kyoung Min Lee, Jun-Ah Song
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2012; 42(4): 466. CrossRef - Study on Food Culture of Koreans over 80-Years-Old Living in Goorye and Gokseong
Hae-Kyung Chung, Mi-Hye Kim
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Culture.2012; 27(2): 142. CrossRef - Stress and Coping Strategies of Breast Cancer Patients and their Spouses
Kyeong-Sook Cha, Yang-Sook Yoo, Ok-Hee Cho
Asian Oncology Nursing.2012; 12(1): 20. CrossRef - A comparison of food frequency for the elderly regarding different family types - Based on Community Health Survey for 2008 -
Song Kyoung Shin, Hyun-Ja Kim, Bo-Youl Choi, Sang Sun Lee
Korean Journal of Nutrition.2012; 45(3): 264. CrossRef - A Study on Customized Nutrition Intervention Program Design and Application for the Low-Income Elderly
Do Hyun Joo, Youngmee Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2011; 16(6): 716. CrossRef - Life Satisfaction, Activities of Daily Living, Depression and Health Behavior of Low Income Elderly Living at Home
Soon-Yi Seo
Journal of muscle and joint health.2010; 17(2): 162. CrossRef - The Association Between Frequency of Food Group Consumption and Functional Disability in Older People
Jinhee Kim, Yunhwan Lee, Joung Hwan Back
Journal of the Korean Geriatrics Society.2010; 14(1): 25. CrossRef - Oral Health, Nutrition, and Oral Health-Related Quality of Life: Among Korean Older Adults
Young-Mi Jung, Dong-soo Shin
Journal of Gerontological Nursing.2008; 34(10): 28. CrossRef
General Characteristics of Subjects (N=335)
Description of Diseases (N=335)
*multiple response.
COPD=chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; TB=tuberculosis.
Summary of Descriptive Statistics for Study Variables (N=335)
ADL=activities of daily living; IADL=instrumental activities of daily living.
Relations among Characteristics (N=335)
*p<.05; †p<.01.
NSI=nutritional screening initiative; ADL=activities of daily living; IADL=instrumental activities of daily living; PCS=physical component summary; MCS=mental component summary.
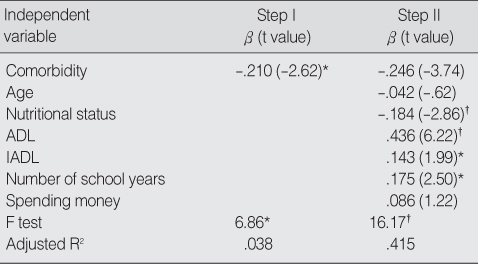
Physical Health (N=335)
*p<.05; †p<.01.
ADL=activities of daily living; IADL=instrumental activities of daily living.
Mental Health (N=335)
*p<.05; †p<.01.
ADL=activities of daily living; IADL=instrumental activities of daily living.
*multiple response. COPD=chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; TB=tuberculosis.
ADL=activities of daily living; IADL=instrumental activities of daily living.
*p<.05; †p<.01. NSI=nutritional screening initiative; ADL=activities of daily living; IADL=instrumental activities of daily living; PCS=physical component summary; MCS=mental component summary.
*p<.05; †p<.01. ADL=activities of daily living; IADL=instrumental activities of daily living.
*p<.05; †p<.01. ADL=activities of daily living; IADL=instrumental activities of daily living.
 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 Cite
Cite

