Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
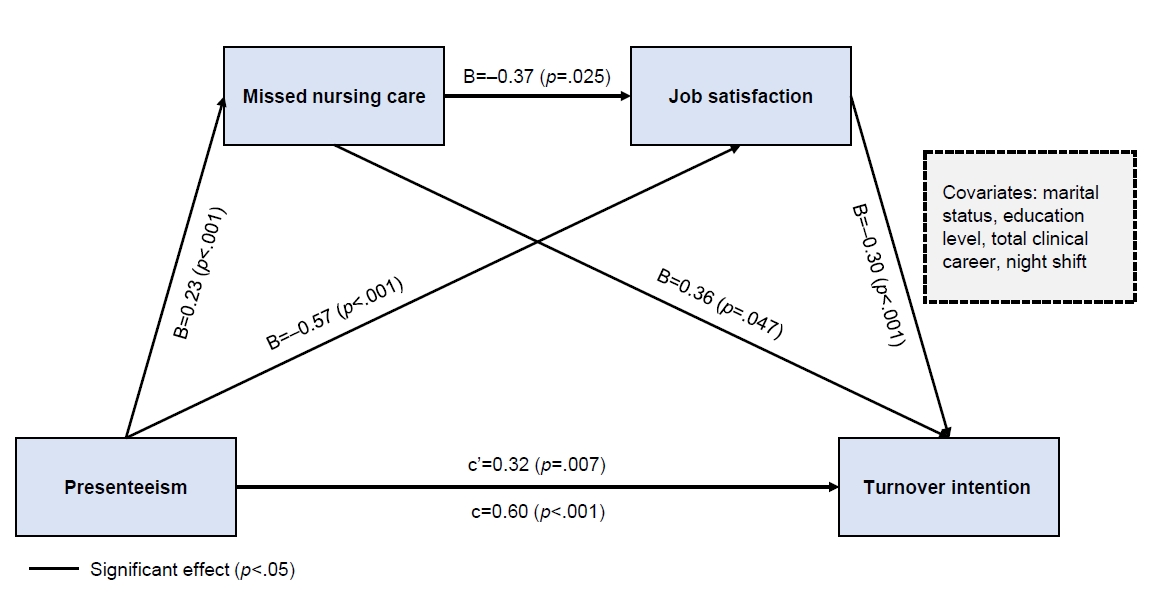
- Effects of presenteeism on turnover intention in clinical nurses through the serial mediating roles of missed nursing care and job satisfaction: a cross-sectional predictive correlational study
- Hyeonseon Cheon, Seok Hee Jeong, Hyun Kyung Kim, Hyoung Eun Chang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(4):584-597. Published online November 10, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25015
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to investigate the two-mediator serial mediation effect of missed nursing care and job satisfaction on the relationship between presenteeism and turnover intention in clinical nurses.
Methods
A cross-sectional predictive correlational study was conducted, and the participants were 208 clinical nurses working in advanced general hospitals in South Korea. Data were collected from October 6 to November 7, 2023 using self-reported questionnaires, including general characteristics, presenteeism, missed nursing care, job satisfaction, and turnover intention. Data were analyzed using IBM SPSS/WIN ver. 29.0 and PROCESS macro ver. 4.2.
Results
Missed nursing care and job satisfaction exhibited a double mediating effect on the relationship between presenteeism and clinical nurses’ turnover intention. In addition, missed nursing care showed a mediating effect on the relationship between presenteeism and clinical nurses’ turnover intention. Job satisfaction had a mediating effect on the relationship between presenteeism and clinical nurses’ turnover intention. Presenteeism had a direct effect on missed nursing care, job satisfaction, and turnover intention. Missed nursing care exerted a direct effect on job satisfaction and turnover intention among clinical nurses. Job satisfaction had a direct effect on turnover intention.
Conclusion
To reduce nurses’ turnover intention, it is essential to develop and implement programs focused on preventing presenteeism. Additionally, organizational initiatives should prioritize active support for nurses’ health management, alleviating the shortage of nursing staff, augmenting job satisfaction, and improving the overall working environment.
- 1,544 View
- 217 Download

- Reliability and Validity of the Korean Version of the Coping and Adaptation Processing Scale–Short-Form in Cancer Patients
- Chi Eun Song, Hye Young Kim, Hyang Sook So, Hyun Kyung Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(3):375-388. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.3.375
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study was conducted to assess the reliability and validity of the Korean version of the Coping and Adaptation Processing Scale-Short-Form in patients with cancer.
Methods The original scale was translated into Korean using Brislin's translation model. The Korean Short-Form and the Functional Assessment Cancer Therapy-General were administered to 164 Korean patients with cancer using convenience sampling method. The collected data were analyzed using SPSS 23.0 and AMOS 23.0. Construct validity, criterion validity, test-retest reliability, and internal consistency reliability of the Korean Coping and Adaptation Processing Scale-Short-Form were evaluated.
Results Exploratory factor analysis supported the construct validity with a four-factor solution that explained 60.6% of the total variance. Factor loadings of the 15 items on the four subscales ranged .52~.86. The four-subscale model was validated by confirmatory factor analysis (Normed χ 2=1.38 (
p =.013), GFI=.92, SRMR=.02, RMSEA=.05, TLI=.94, and CFI=.95), and criterion validity was demonstrated with the Functional Assessment Cancer Therapy-General. Cronbach's alpha for internal consistency of the total scale was .83 and ranged .68~.81 for all subscales, demonstrating sufficient test-retest reliability.Conclusion The Korean version showed satisfactory construct and criterion validity, as well as internal consistency and test-retest reliability.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Colombian validation of the short-form coping and adaptation processing scale in caregivers
Carolina Gutiérrez-López, Gustavo Ordoñez-Sierra, Ricardo Borda Hernández, Marcia Andrea Quiñonez-Mora
International Journal of Nursing Studies Advances.2026; 10: 100497. CrossRef - Disease Activity and Psychosocial Factors Associated with Heath-Related Quality of Life in Patients with Crohn’s Disease: A Cross-Sectional Study
YoonJi Roh, Hye-Ah Yeom
Healthcare.2026; 14(4): 432. CrossRef - Risk factors for inadequate and excessive gestational weight gain during pregnancy among women
Ju Sun Cho, Sook Jung Kang
Midwifery.2025; 144: 104345. CrossRef - A cross-sectional study of Malaysian low-income drug addict wives: Relationship between family impact, coping and mental wellbeing
Haikal Anuar Adnan, Zarinah Arshat, Nurul Saidatus Shaja’ah Ahmad Shahril
F1000Research.2025; 11: 683. CrossRef - Mental health in female breast cancer survivors post-mastectomy: A structural model based on Roy's adaptation model
Hyeng Sook Yoon, Eunjung Ryu
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2025; 12: 100820. CrossRef - North Korean defectors with PTSD and complex PTSD show alterations in default mode network resting-state functional connectivity
Byung-Hoon Kim, Jiwon Baek, Ocksim Kim, Hokon Kim, Minjeong Ko, Sang Hui Chu, Young-Chul Jung
BJPsych Open.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Coping and adaptation of adults with cancer: the art of nursing care
Lina Marcela Cepeda-Trujillo, Jesús Miguel Mosquera-Aguirre, Daniela Yurani Rojas-Atehortua, Alix Yaneth Perdomo-Romero
Aquichan.2022; 22(1): 1. CrossRef - A cross-sectional study of Malaysian low-income drug addict wives: Relationship between family impact, coping and mental wellbeing
Haikal Anuar Adnan, Zarinah Arshat, Nurul Saidatus Shaja’ah Ahmad Shahril
F1000Research.2022; 11: 683. CrossRef - Relationship between cancer stigma, social support, coping strategies and psychosocial adjustment among breast cancer survivors
No Eul Kang, Hye Young Kim, Ji Young Kim, Sung Reul Kim
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2020; 29(21-22): 4368. CrossRef - Psychometric Testing of the Chinese Version of the Coping and Adaptation Processing Scale-Short Form in Adults With Chronic Illness
Xiyi Wang, Leiwen Tang, Doris Howell, Jing Shao, Ruolin Qiu, Qi Zhang, Zhihong Ye
Frontiers in Psychology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - A Simple Framework of Smart Geriatric Nursing considering Health Big Data and User Profile
Shijie Li, Yongchuan Tang, Mirian C. D. Pinheiro
Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Psychosocial Adjustment in Hemodialysis Patients
Kang Sun Lee, Hye Young Kim, Myung Ha Lee
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2019; 31(1): 38. CrossRef
- Colombian validation of the short-form coping and adaptation processing scale in caregivers
- 2,084 View
- 46 Download
- 12 Crossref

- Transmission Aspect of Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in the Neurosurgical Intensive Care Unit by Analysing Genotype
- Yun Kyung Kim, Hae Sook Hong
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2007;37(6):976-985. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2007.37.6.976
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: The aim of this study was to identify the present situation of hospital infection and route of infection by clarifying the transmission aspect of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus(MRSA) in a Neurosurgical Intensive Care Unit by analysing genotype. METHODS: MRSA was cultured from twenty five patients with a tracheostomy, twenty five health care workers, and environments in the Neurosurgical Intensive Care Unit of one hospital in D city. Data was collected from December 21, 2004 to November 5, 2005. MRSA isolates representing each genotype were analyzed by spaA typing and a multiplex PCR method capable of identifying the structural type of the staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec(SCCmec) carried by the bacteria. RESULTS: As the same genotype and gene sequence were found among health care workers, patients, and environments, it was assumed that there was cross transmission among them. CONCLUSION: This study suggests that first, as the hospital infection by MRSA between health care workers and patients in the Neurosurgical Intensive Care Unit was due to result of cross transmission and the relevance of transmission between them was verified, it is necessary to take preventive measures and conduct education. Secondly, development of nursing interventions and study of infection are needed. Thirdly, consistent investment in prevention against hospital infections and environmental renovation is needed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Comparison between the Contamination Level of Uniforms and the Nasal Staphylococcus aureus Colonization before and after the Clinical Practice of Nursing Students
Jin Hee Park, Gisoo Shin, Jiyoung Kim
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2014; 16(2): 90. CrossRef - The Effect of the Hand Hygiene Education Program on Hand Hygiene Knowledge, Hand Hygiene Perception, Nasal Staphylococcus aureus Colonization and Hand Hygiene Adherence in Nursing Students
Jin Hee Park, Hee Sun Kim
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2012; 14(3): 156. CrossRef
- A Comparison between the Contamination Level of Uniforms and the Nasal Staphylococcus aureus Colonization before and after the Clinical Practice of Nursing Students
- 763 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Life Experience following Suicide Attempt among Middle-aged Men
- Eun-Young Chin, Hyun Kyung Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2016;46(2):215-225. Published online April 29, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2016.46.2.215
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was performed to identify the meaning of life experience following suicide attempt among middle-aged men.
Methods A qualitative research design was adopted using van Manen's hermeneutic phenomenological approach. The participants were six middle-aged men who had attempted suicide at least one time. Data were collected in 2013 through in-depth interviews. Individual interviews were recorded; and literary, art works and phenomenological literature were searched to identify the meaning of the experience.
Results The five essential themes of the life experience of middle-aged men who attempted suicide were 'Bitter reality confronted again', 'Anger buried deep inside', 'Broken family, inescapable fetters', 'Blocked relationships, closed world' and 'A step towards a new life'.
Conclusion The meaning of lived experience found in this study provides deep insight into the experience following suicide attempt in middle-aged men and crucial information to give directions to appropriate support and nursing interventions.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Exploring the Lives of Korean College Students Who Attempted Suicide: A Qualitative Study
Min-Soo Kang, Hye-Young Jang
Asian Nursing Research.2024; 18(4): 393. CrossRef - Illness Experiences of People with Young-onset Dementia
Suyoun Ahn, Yeojin Yi
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2023; 32(1): 67. CrossRef - Latent Class Analysis for Health-Related Quality of Life in the Middle-Aged Male in South Korea
Youngsuk Cho, Dong Moon Yeum
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2019; 49(1): 104. CrossRef - A Qualitative Study of Korean Men Experiencing Stress Due to Nonprestigious Hakbeol
Yunkyoung Loh Garrison, Ji Youn Cindy Kim, William Ming Liu
The Counseling Psychologist.2018; 46(6): 786. CrossRef - A Study of Subjectivity among Nursing Students Regarding Suicide Attempters
Jeong Lim Cho, Eun Nam Lee, Eun Young Park
Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2017; 23(3): 341. CrossRef
- Exploring the Lives of Korean College Students Who Attempted Suicide: A Qualitative Study
- 1,060 View
- 11 Download
- 5 Crossref

- Identification of Subgroups with Lower Level of Stroke Knowledge Using Decision-tree Analysis
- Hyun Kyung Kim, Seok Hee Jeong, Hyun Cheol Kang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2014;44(1):97-107. Published online February 28, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2014.44.1.97
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was performed to explore levels of stroke knowledge and identify subgroups with lower levels of stroke knowledge among adults in Korea.
Methods A cross-sectional survey was used and data were collected in 2012. A national sample of 990 Koreans aged 20 to 74 years participated in this study. Knowledge of risk factors, warning signs, and first action for stroke were surveyed using face-to-face interviews. Descriptive statistics and decision tree analysis were performed using SPSS WIN 20.0 and Answer Tree 3.1.
Results Mean score for stroke risk factor knowledge was 7.7 out of 10. The least recognized risk factor was diabetes and four subgroups with lower levels of knowledge were identified. Score for knowledge of stroke warning signs was 3.6 out of 6. The least recognized warning sign was sudden severe headache and six subgroups with lower levels of knowledge were identified. The first action for stroke was recognized by 65.7 percent of participants and four subgroups with lower levels of knowledge were identified.
Conclusion Multi-faceted education should be designed to improve stroke knowledge among Korean adults, particularly focusing on subgroups with lower levels of knowledge and less recognition of items in this study.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Knowledge, practice, and awareness of stroke warning signs and potential risk factors among future rehabilitation specialists in Saudi Arabia
Alaa M. Albishi, Futun Almutairi, Waleed M. Alshehri, Muneera M. Almurdi, Sami S. Alabdulwahab
Frontiers in Medicine.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Global Awareness and Response to Early Symptoms of Acute Stroke: A Systematic Literature Review
Theodoros Vatsalis, Dimitrios Papadopoulos, Vasiliki Georgousopoulou, Prodromos Bostantzis, Jobst Rudolf
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Stroke knowledge and health-promoting behaviors: Mediating effect of patient self-esteem
GyeongChae MUN, JaeLan SHIM
Patient Education and Counseling.2024; 129: 108398. CrossRef - Comparison of Stroke Knowledge, Health Beliefs, and Stroke Prevention Behavior between Early and Middle-Aged Adults
Eun Ko
STRESS.2022; 30(2): 98. CrossRef - Variation in Knowledge of Stroke Warning Signs by Age and Presence of Conventional Risk Factors
Juyeon Oh, Hyun Young Kim, Young Seo Kim, Sun Hwa Kim
Journal of Cardiovascular Nursing.2022; 37(2): 177. CrossRef - Analysis of Subgroups with Lower Level of Patient Safety Perceptions Using Decision-Tree Analysis
Sun Hwa Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2020; 50(5): 686. CrossRef - Stroke Management Awareness and Behavior among Nursing Students in Bangladesh
Shariful Islam, Eui Geum Oh, Tae Wha Lee, Sanghee Kim
Open Journal of Nursing.2017; 07(01): 1. CrossRef - Awareness of Stroke Warning Symptoms and Related Factors among Residents in a Province
Yu-Mi Lee, Keon-Yeop Kim, Ki-Su Kim
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2014; 15(8): 5116. CrossRef
- Knowledge, practice, and awareness of stroke warning signs and potential risk factors among future rehabilitation specialists in Saudi Arabia
- 1,168 View
- 18 Download
- 8 Crossref

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 First
First Prev
Prev


