Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Development and evaluation of the Trauma-nursing Education and Skill Support program to enhance trauma nursing competencies: a quasi-experimental study
- Tae Yeong Yang, Myung Jin Jang, Ki Ung Kim, Min So, Mi Na Choi, Eun Jung Lee, Jin Su Jo, Ji Yun Lee, Kwang Kyun Lim, Kyoung Mi Kim, Hae Jun Baek, Sun Ho Wang, Jin Oh Choi
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2026;56(1):67-80. Published online February 24, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25134
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
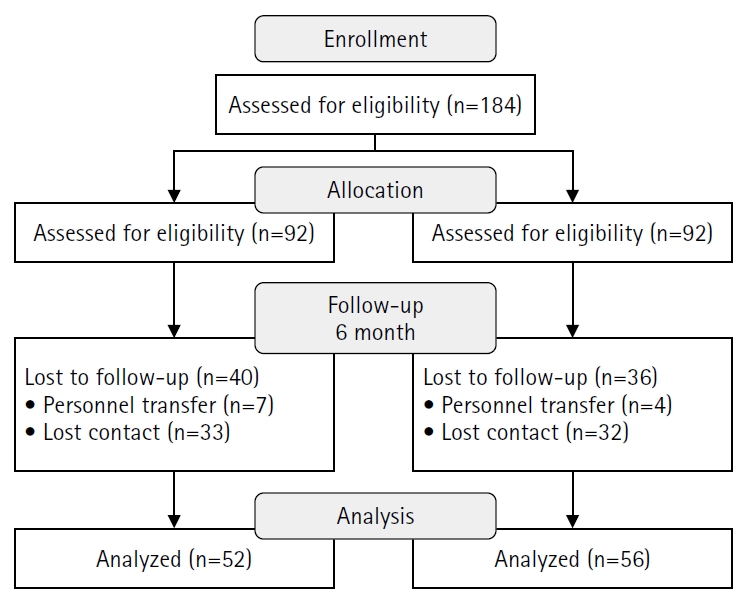
This study aimed to develop and evaluate the effectiveness of the Trauma-nursing Education and Skill Support (TESS) program based on the ADDIE model (Analysis, Design, Development, Implementation, Evaluation model). The program was designed to enhance trauma nurses’ clinical competencies, including trauma-related knowledge, self-efficacy, and problem-solving ability, through the integration of theoretical education and simulation-based practice.
Methods
A quasi-experimental study using a non-equivalent control group pretest–posttest design was conducted. Participants included 108 trauma nurses from regional trauma centers, military trauma centers, and emergency care facilities, who were assigned to an experimental group (n=52) or a control group (n=56). The TESS program consisted of a 2-day, 14-hour blended-learning course that included eight lecture sessions and four simulation-based practice stations. Data were collected at baseline, immediately after the intervention, and at 6 months using validated instruments measuring trauma-related knowledge, self-efficacy, and problem-solving ability. Two-way repeated-measures analysis of variance was used for data analysis.
Results
The experimental group demonstrated significant improvements in trauma-related knowledge, self-efficacy, and problem-solving ability compared with baseline (all p<.001). These improvements were sustained at 6 months, although trauma-related knowledge scores showed a slight decline compared with immediate posttest levels. Between-group analyses confirmed significant group-by-time interaction effects for all outcomes: trauma-related knowledge (η2=0.12, p<.001), self-efficacy (η2=0.09, p=.002), and problem-solving ability (η2=0.08, p=.003).
Conclusion
The TESS program effectively enhanced trauma nurses’ trauma-related knowledge, self-efficacy, and problem-solving ability, with effects sustained for up to 6 months. Incorporating blended learning and simulation-based training into standardized trauma nursing education may strengthen clinical competencies and ultimately contribute to improved patient outcomes.
- 68 View
- 6 Download

- A Comparative Study on Learning Outcomes according to the Integration Sequences of S-PBL in Nursing Students: Randomized Crossover Design
- So Young Yun, Ja Yun Choi
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(1):92-103. Published online February 28, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.1.92
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study aimed to compare the effects of simulation integrated with problem based learning (S-PBL) according to the sequences of problem-based learning (PBL) and high fidelity simulation training (HFS) on knowledge, clinical performance, clinical judgment, self-confidence, and satisfaction in fourth-grade nursing students.
Methods In this randomized crossover design study, four S-PBLs on medical-surgical nursing were applied alternatively to two randomly-assigned groups of 26 senior nursing students for 8 weeks. The collected data were analyzed using an independent t-test.
Results The method of administering PBL prior to HFS led to significantly higher scores on knowledge (t=2.28,
p =.025) as compared to the method of administering HFS prior to PBL. However, the latter method led to significantly higher scores on clinical performance (t=−6.49,p <.001) and clinical judgment (t=−4.71,p <.001) as compared to the method of administering PBL prior to HFS. There were no differences in the effect of the two methods on self-confidence (t=1.53,p =.128) and satisfaction (t=1.28,p =.202).Conclusion The integration sequences of S-PBL was associated with different learning outcomes. Therefore, when implementing S-PBL, it is necessary to consider the educational goal to executes an appropriate sequence of integration.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effectiveness of the Patient’s Severity Classification Competency Promotion Virtual Reality Program of Nursing Students during the COVID-19 Pandemic Period
Eunju Lee, Gyuli Baek, Yeonhui Hwang
Healthcare.2023; 11(8): 1122. CrossRef - The Effect of Mixed Reality-based HoloPatient in Problem-based Learning Contexts
Yun Kang, Insook Lee
Clinical Simulation in Nursing.2023; 82: 101438. CrossRef - A Literature Review of Simulation-Based Nursing Education in Korea
Sumee Oh, Jungmin Park
Nursing Reports.2023; 13(1): 506. CrossRef - The Effects of Sequencing Strategies in Teaching Methods on Nursing Students’ Knowledge Acquisition and Knowledge Retention
Wei-Ting Lin, Ching-Yun Yu, Fan-Hao Chou, Shu-Yuan Lin, Bih-O. Lee
Healthcare.2022; 10(3): 430. CrossRef - Learning effects of virtual versus high-fidelity simulations in nursing students: a crossover comparison
SoMi Park, Hea Kung Hur, ChaeWeon Chung
BMC Nursing.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The intervention effect of a nursing-media studies convergence problem-based learning (PBL) program to improve nurses’ public image: Changed perceptions of program participants and students attended a PBL presentation
Seungchul Yoo, Seungmi Kang, Jooyeon Ryu
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2021; 27(1): 59. CrossRef - Comparison of Learning Transfer Using Simulation Problem-Based Learning and Demonstration: An Application of Papanicolaou Smear Nursing Education
Jeongim Lee, Hae Kyoung Son
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(4): 1765. CrossRef - Effects of S-PBL in Maternity Nursing Clinical Practicum on Learning Attitude, Metacognition, and Critical Thinking in Nursing Students: A Quasi-Experimental Design
Hae Kyoung Son
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(21): 7866. CrossRef - Comparison of Neck Pain, Shoulder Pain, and Comfort between Buckwheat and Latex Pillows
Ji-Soo Lee, Soo-Kyoung Lee
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2019; 19(2): 107. CrossRef
- Effectiveness of the Patient’s Severity Classification Competency Promotion Virtual Reality Program of Nursing Students during the COVID-19 Pandemic Period
- 1,753 View
- 43 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref

- Development and Evaluation of a PBL-based Continuing Education for Clinical Nurses: A Pilot Study
- Hee Soon Kim, Seon Young Hwang, Eui Geum Oh, Jae Eun Lee
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2006;36(8):1308-1314. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2006.36.8.1308
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purposes of this study were to develop a PBL program for continuing nurse education and to evaluate the program after its implementation.
Methods The PBL program was developed in the core cardio-pulmonary nursing concepts through a collaborative approach with a nursing school and a hospital. The PBL packages with simulation on ACLS were implemented to 40 clinical nurses. The entire PBL program consisted of six 3-hour weekly classes and was evaluated by the participants' subjective responses.
Results Two PBL packages in cardio-pulmonary system including clinical cases and tutorial guidelines were developed. The 57.5% of the participants responded positively about the use of PBL as continuing nurse education in terms of self-motivated and cooperative learning, whereas 20.0% of the participants answered that the PBL method was not suitable for clinical nurses. Some modifications were suggested in grouping participants and program contents for PBL.
Conclusion The PBL method could be utilized to promote nurses' clinical competencies as well as self-learning abilities. Further research is needed in the implementation strategies of PBL-based continuing education in order to improve its effectiveness.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cultural and Ethical Barriers to Cancer Treatment in Nursing Homes and Educational Strategies: A Scoping Review
Cynthia Filteau, Arnaud Simeone, Christine Ravot, David Dayde, Claire Falandry
Cancers.2021; 13(14): 3514. CrossRef
- Cultural and Ethical Barriers to Cancer Treatment in Nursing Homes and Educational Strategies: A Scoping Review
- 873 View
- 7 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Perception about Problem-based Learning in Reflective Journals among Undergraduate Nursing Students
- Seon Young Hwang, Keum Seong Jang
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2005;35(1):65-76. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2005.35.1.65
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objective The aim of this study is to explore the variation in perceptions about problem-based learning(PBL) according to the level of academic achievement and learning attitude in the nursing students of a junior college (3-year program).
Method Students (n=39) learned the respiratory and cardiac system with seven PBL packages and group-based learning for a semester in 2002. Students were asked to write reflective journals that focused on their learning perception after an experience with each learning package. A total of 208 journals were used for analysis.
Result Students positively perceived that PBL making them increase their sense of responsibility for learning and felt satisfaction with the learning process, and had a confidence in the use of clinical nursing interventions. On the other hand, they negatively perceived that PBL was a burden because it took more time than traditional learning tasks, and they experienced an anxiety about regular tests and felt conflicts and diffidences in the learning process. The negative perceptions were expressed more often from students with a low academic achievement and low learning attitude compared to others.
Conclusion Students perceived the PBL as effective in understanding the learning concepts in the clinical practice environment. PBL need to be supplemented by feedback-based lecture and facilitative strategies for academically low-achieved students.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The relationship between intrinsic motivation and learning outcomes in problem-based learning
Hye-Ryoung Kim
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2020; 26(3): 238. CrossRef - An analysis of medical students’ reflective essays in problem-based learning
Jihyun Si
Korean Journal of Medical Education.2018; 30(1): 57. CrossRef - Effect of Team-based Learning using Reflection Journal on Pregnancy Nursing Course for Nursing Students
Jin Young Kim, Mi-Kyoung Lee
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2018; 24(4): 404. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of the Self-Reflection and Insight Scale for Korean Nursing Students
Mi Ok Song, Heeyoung Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2018; 25(1): 11. CrossRef - Analysis of Students’ Reflective Journals on Medical Communication Role Plays
Young Jon Kim, Seung Hyun Lee, Hyo Hyun Yoo
Korean Medical Education Review.2017; 19(3): 169. CrossRef - Effects of Writing Reflective Journal on Meta-cognition and Problem Solving Ability in Nursing Students taking a Fundamental Nursing Skills Course Applying Blended Learning
Mi Young Jho
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2016; 23(4): 430. CrossRef - Class Experience of the Students on 『Pregnancy, Delivery and Puerperium』 Nursing Course through Flipped Learning: Mixed Method Research
Byeongju Lee, Seon Young Hwang
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2016; 22(4): 221. CrossRef - Effects of a Multicultural Education Program on the Cultural Competence, Empathy and Self-efficacy of Nursing Students
Eun-Hee Peek, Chai-Soon Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2013; 43(5): 690. CrossRef - Effect of reflective journaling in team learning on the learning motivation of learners
In-Suk Park, Mi-Jeong Kim
Journal of Korean society of Dental Hygiene.2012; 12(5): 849. CrossRef - An evaluation on the implementation of problem-based learning in medical education
박민정
The Journal of Curriculum Studies.2010; 28(2): 225. CrossRef - A comparison of problem-based learning and lecture-based learning in an adult health nursing course
Seon Young Hwang, Mi Ja Kim
Nurse Education Today.2006; 26(4): 315. CrossRef
- The relationship between intrinsic motivation and learning outcomes in problem-based learning
- 775 View
- 2 Download
- 11 Crossref

- The Effects of PBL(Problem-Based Learning) on the Metacognition, Critical Thinking, and Problem Solving Process of Nursing Students
- Heejung Choi
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2004;34(5):712-721. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2004.34.5.712
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This investigation examined the effect of PBL on the meta-cognition, critical thinking, and problem solving process.
Method The research design was pre-posttest with a nonequivalent control group design. Scenarios for PBL sessions were developed on the basis of textbooks and patients' charts and tested for content validity. Seventy six nursing students who took a ‘Nursing Process’ course from two nursing schools participated in the experimental group and control group. The experimental group performed PBL during the semester. Meta-cognition and problem solving processes were assessed by questionnaires which were developed using pedagogics. Critical thinking was measured by the CCTST(California Critical Thinking Skill Test) Form 2000. The data was analyzed by repeated measure (pretest-posttest) MANOVA, and correlation analysis.
Result PBL improved the participants' meta-cognition and problem solving process but not critical thinking. The relationship between meta-cognition and the problem solving process was supported but the relationship between critical thinking and problem solving was not supported.
Conclusion These results suggest that PBL has a positive effect on nursing students' educational outcomes. To improve the problem solving ability of nursing students, PBL should be applied to more subjects in the nursing curriculum.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluating the impact of a digital mapping assignment on student learning, engagement, and transferable skills
Rami Zeedan, Samantha Bishop Simmons, Michael Peper
Frontiers in Education.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - The effects of case-based, problem-based, and team-based learning on nursing students’ problem-solving, self-directed learning, and communication skills: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Ya Zou, Wenzhao Xie, Hui Huang, Dan Liu, Qing Zhou, Qifeng Yi, Xiaoliang Tong, Ping Mao
BMC Medical Education.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - The effectiveness of problem-based learning (PBL) in enhancing critical thinking skills in medical education: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Ting Su, Jing Liu, Lele Meng, Yijing Luo, Qiaoling Ke, Lingzhu Xie
Frontiers in Education.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Critical thinking disposition as a mediator in creativity and problem-solving: A MASEM study
Ayhan Koçoğlu, Sedat Kanadlı
Intelligence.2025; 113: 101951. CrossRef - Outcomes of problem-based learning in nurse education: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Sapna Sharma, Ita Daryanti Saragih, Dame Elysabeth Tuty Arna Uly Tarihoran, Fan-Hao Chou
Nurse Education Today.2023; 120: 105631. CrossRef - Metacognition in Nursing Students: A Concept Analysis
Ji-Sung Park, Hee-Joo Oh, Ji-Hyun Choi, Jin-Hui Han, Ji-Yoon Song
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2023; 30(4): 499. CrossRef - HEMŞİRELİK ÖĞRENCİLERİNİN PROBLEM ÇÖZME BECERİLERİ VE BİLİMSEL ARAŞTIRMAYA YÖNELİK KAYGI DÜZEYLERİ
Esin Ateş, Şafak Dağhan, Damla Ünal, Damla Ünsal, Ece Üzrek, Gülben Özyavuz
İnönü Üniversitesi Sağlık Hizmetleri Meslek Yüksek Okulu Dergisi.2023; 11(2): 1631. CrossRef - What are the Factors that Enhance Metacognitive Skills in Nursing Students? A Systematic Review
Shadi Asadzandi, Rita Mojtahedzadeh, Aeen Mohammadi
Iranian Journal of Nursing and Midwifery Research.2022; 27(6): 475. CrossRef - Effects of Problem-Based Learning on the Problem-Solving Ability and Self-Efficacy of Students Majoring in Dental Hygiene
Jin-Sun Choi, Soo-Myoung Bae, Sun-Jung Shin, Bo-Mi Shin, Hyo-Jin Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(12): 7491. CrossRef - Mediating effects of self-directed learning on the relationship between critical thinking and problem-solving in student nurses attending online classes: A cross-sectional descriptive study
Yeoungsuk Song, Yoonmi Lee, Junghoon Lee
Nurse Education Today.2022; 109: 105227. CrossRef - Comparing the Effects of Pure Problem-Based Learning and Hybrid Problem-Based Learning on Metacognitive Awareness in Nursing Students
H. Zarida, A. Zarifi, M. Zoladl, M. Salari
Journal of Clinical Care and Skills.2021; 2(3): 113. CrossRef - Literature Review and Meta-Analysis of Problem-Based Learning in Nursing Students
Yeoungsuk Song, Seurk Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2020; 27(3): 246. CrossRef - Effect of a Situational Module Learning Course on Critical Thinking Disposition and Metacognition in Nursing Students: A Quasi-experimental Study
Kwang Ok Park, Mi Yu
Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2019; 25(2): 251. CrossRef - An analysis of medical students’ reflective essays in problem-based learning
Jihyun Si
Korean Journal of Medical Education.2018; 30(1): 57. CrossRef - Utilizing Video vs Simulation Practice for Handoff Education of Nursing Students in Pediatric Nursing
Sun-Nam Park, Young Soon Im
Child Health Nursing Research.2018; 24(1): 27. CrossRef - Effects of Simulation With Problem-Based Learning Program on Metacognition, Team Efficacy, and Learning Attitude in Nursing Students
Myung-Nam Lee, Kyung-Dong Nam, Hyeon-Young Kim
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2017; 35(3): 145. CrossRef - A meta-analysis of the effects of non-traditional teaching methods on the critical thinking abilities of nursing students
JuHee Lee, Yoonju Lee, SaeLom Gong, Juyeon Bae, Moonki Choi
BMC Medical Education.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Convergence Study about Problem-based Learing and Self-directed Learning Ability, Problem Solving Skills, Academic Self-efficacy, Motivation toward Learning of Nursing Students
Seung-Ju Kang, Eun-Ju Kim, Hae-Jin Shin
Journal of the Korea Convergence Society.2016; 7(2): 33. CrossRef - THE EFFECTS OF PROBLEM-BASED LEARNING WITH THINKING MAPS ON FIFTH GRADERS’ SCIENCE CRITICAL THINKING
Nyet Moi Siew, Ruslan Mapeala
Journal of Baltic Science Education.2016; 15(5): 602. CrossRef - The Survey on the Influence of Clinical Nurse's Critical Thinking Disposition, Problem-solving Skill and Self-efficacy on Patients Safety Competencies
Hyo-Sun Kim, Suk-Jung Han
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2016; 17(6): 598. CrossRef - Effects of full problem based learning of dental students on self-directed learning, communication, and problem solving abilities
Kang-Wook Lee, Jin-Sil Hong, Kee-Wan Chang
Journal of Korean Academy of Oral Health.2016; 40(4): 277. CrossRef - Impacts of Critical Thinking Disposition and Nursing Work Environment on Nurses' Clinical Decision Making Abilities
Insook Oh, Jeong-Hee Kim
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2016; 22(3): 304. CrossRef - The effectiveness of workshop (cooperative learning) based seminars
Kevin Baird, Rahat Munir
Asian Review of Accounting.2015; 23(3): 293. CrossRef - Effects of a Simulation-based Program on Self-Directed Learning Ability, Metacognition and Clinical Competence in a Nursing Student
Myung-Ock Chae
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2015; 16(10): 6832. CrossRef - Empowerment on Clinical Nursing Skills Core Program
Hye-Suk Kim, Hae-Ryoung Park, Eun-Hee Park
Journal of Digital Convergence.2014; 12(12): 589. CrossRef - Effects of problem-based learning vs. traditional lecture on Korean nursing students' critical thinking, problem-solving, and self-directed learning
Eunyoung Choi, Ruth Lindquist, Yeoungsuk Song
Nurse Education Today.2014; 34(1): 52. CrossRef - Impact of Self-Directed Learning Ability and Metacognition on Clinical Competence among Nursing Students
Mi Young Jho, Myung-Ock Chae
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2014; 20(4): 513. CrossRef - Effects of S-PBL in Fundamental Nursing Practicum among Nursing Students : Comparision Analysis of a Ordinary Least Square and a Quantile Regression for Critical Thinking Disposition
Won Hee Jun, Eunju Lee
The Journal of the Korea Contents Association.2013; 13(11): 1036. CrossRef - Developing Students’ Critical Thinking Skills by Task-Based Learning in Chemistry Experiment Teaching
Qing Zhou, Qiuyan Huang, Hong Tian
Creative Education.2013; 04(12): 40. CrossRef - The Effects of Problem-Based Learning on Self-Regulated Learning Ability in LIS Education: Based on Cognitive and Motivational Components
Jeong-Mee Lee
Journal of the Korean Society for Library and Information Science.2013; 47(4): 103. CrossRef - Nursing Students' Experiences with Facilitator in Problem-Based Learning Class
Jin Hyang Yang, BokSun Yang
Asian Nursing Research.2013; 7(4): 198. CrossRef - Influence of Nurses' Performance with Critical Thinking and Problem Solving Process
Haeran Choi, Dongsook Cho
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2011; 17(3): 265. CrossRef - Effects of Differences in Problem-Based Learning Course Length on Academic Motivation and Self-Directed Learning Readiness in Medical School Students
So Jung Yune, Sun Ju Im, Sun Hee Lee, Sun Yong Baek, Sang Yeoup Lee
Korean Journal of Medical Education.2010; 22(1): 23. CrossRef - The Effects of Case-Based Learning Using Video on Clinical Decision Making and Learning Motivation in Undergraduate Nursing Students
Moon-Sook Yoo, Jin-Hee Park, Si-Ra Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2010; 40(6): 863. CrossRef - Critical Thinking Disposition and Problem Solving Ability in Nursing Students
Seung-Ae Yang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2010; 16(4): 389. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Problem Solving Abilities of Freshmen Nursing Students
Yun Min Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2010; 16(2): 190. CrossRef - A comparison of problem-based learning and lecture-based learning in an adult health nursing course
Seon Young Hwang, Mi Ja Kim
Nurse Education Today.2006; 26(4): 315. CrossRef
- Evaluating the impact of a digital mapping assignment on student learning, engagement, and transferable skills
- 1,586 View
- 48 Download
- 37 Crossref

- Effects of a Problem-Based Learning Program on Health Education for Elders
- Young Ju Son, Eun Young Choi, Young A Song
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2009;39(2):207-216. Published online April 28, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2009.39.2.207
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purposes of this study was to analyze the effects of a health education program using problem-based learning on health related knowledge, behavior, and quality of life in elderly people.
Methods The participants included 44 elders, of whom 23 took the health education program and 21 did not. All participants were over 60 yr of age and were selected from residents of nursing homes or participants in activities of social welfare facilities in Jeju Province. Elders in both groups completed pre- and post-tests. Elders in the education group participated in 5 weekly sessions, 100-120 min/session of problem-based learning on health education. Data were analyzed using SPSS WIN 12.0.
Results Scores for health knowledge, health behavior, and quality of life for the education group were significantly higher than those of the control group.
Conclusion A problem-based learning health education program can be recommended as a method to promote the health of the elders. Indirectly, the results seem to indicate that proper assessment and support should be provided simultaneously in the management of elders' health. Finally, future study is needed to examine whether problem-based learning is more helpful compared to traditional education.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nursing Students' Experiences with Facilitator in Problem-Based Learning Class
Jin Hyang Yang, BokSun Yang
Asian Nursing Research.2013; 7(4): 198. CrossRef
- Nursing Students' Experiences with Facilitator in Problem-Based Learning Class
- 888 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Crossref

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 First
First Prev
Prev


