Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Lessons from the US Advanced Practice Registered Nurse system
- Eun-Ok Im, Dongmi Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(4):492-505. Published online November 27, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25120
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This review compares the development of South Korea’s Advanced Practice Registered Nurse (APRN) system the well-established APRN system in the United States and provides recommendations for future improvements to the APRN system in South Korea.
Methods
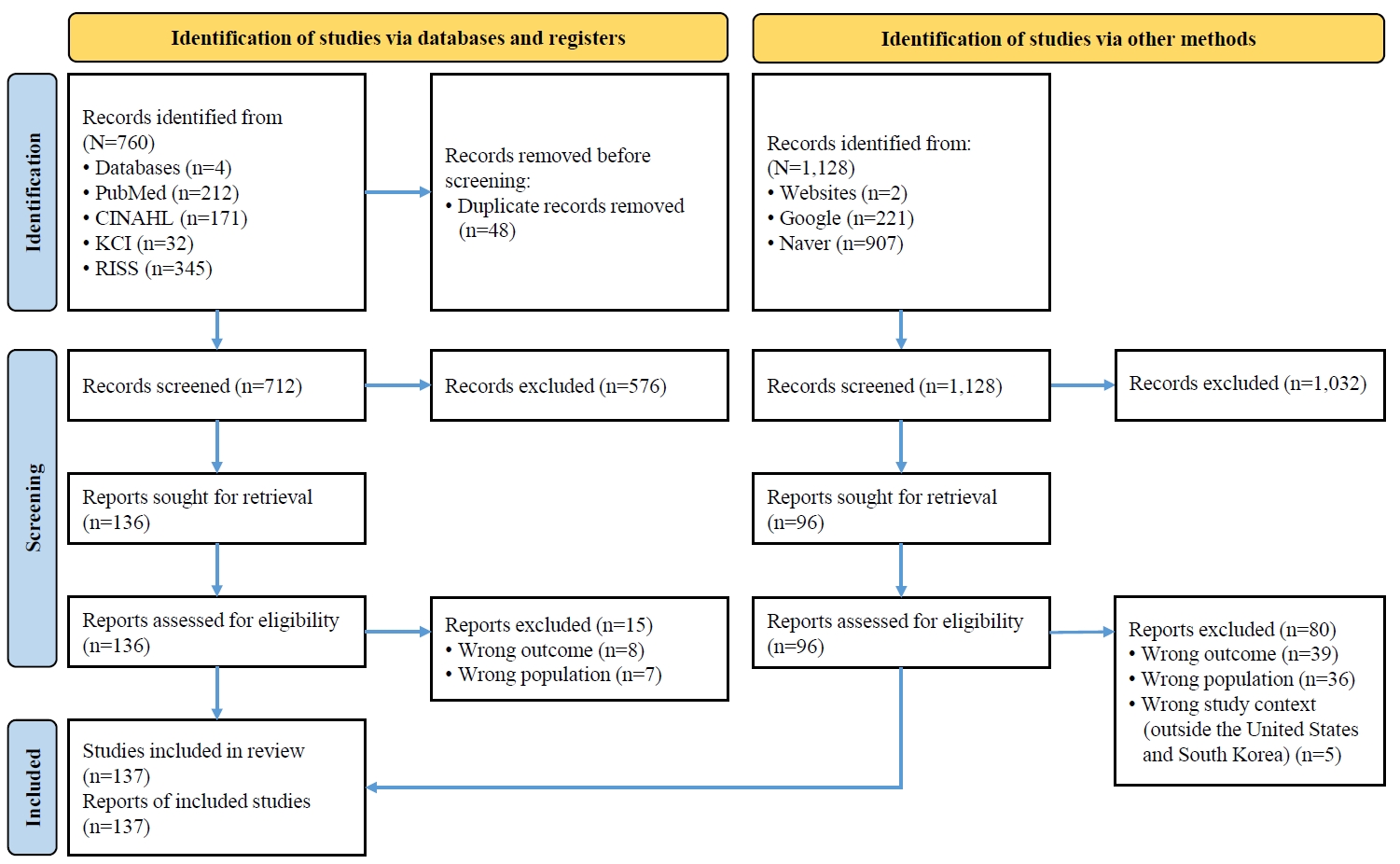
To compare the APRN systems between the two countries, an integrative literature review was conducted using multiple databases and professional nursing organization documents and reports from both the United States and South Korea.
Results
Issues were identified in five major domains: (1) research evidence, (2) education and training, (3) the scope of practice, (4) financial mechanisms, and (5) public awareness and acceptance.
Conclusion
Recommendations are made in four areas: (1) building evidence to support APRN programs; (2) strengthening APRN education; (3) establishing legal support and reimbursement mechanisms; and (4) improving public awareness and acceptance of APRNs.
- 1,059 View
- 154 Download

- Comparison of educational needs and priorities for work-related laws between hospital and community-based nurses
- Jeonghyun Kim, Min Kyoung Han, Minjae Lee, Sujin Shin
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(3):400-412. Published online August 21, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25049
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to examine the practical utilization of work-related laws in nursing practice and to prioritize educational needs to provide foundational data for improving nurses’ legal competencies.
Methods
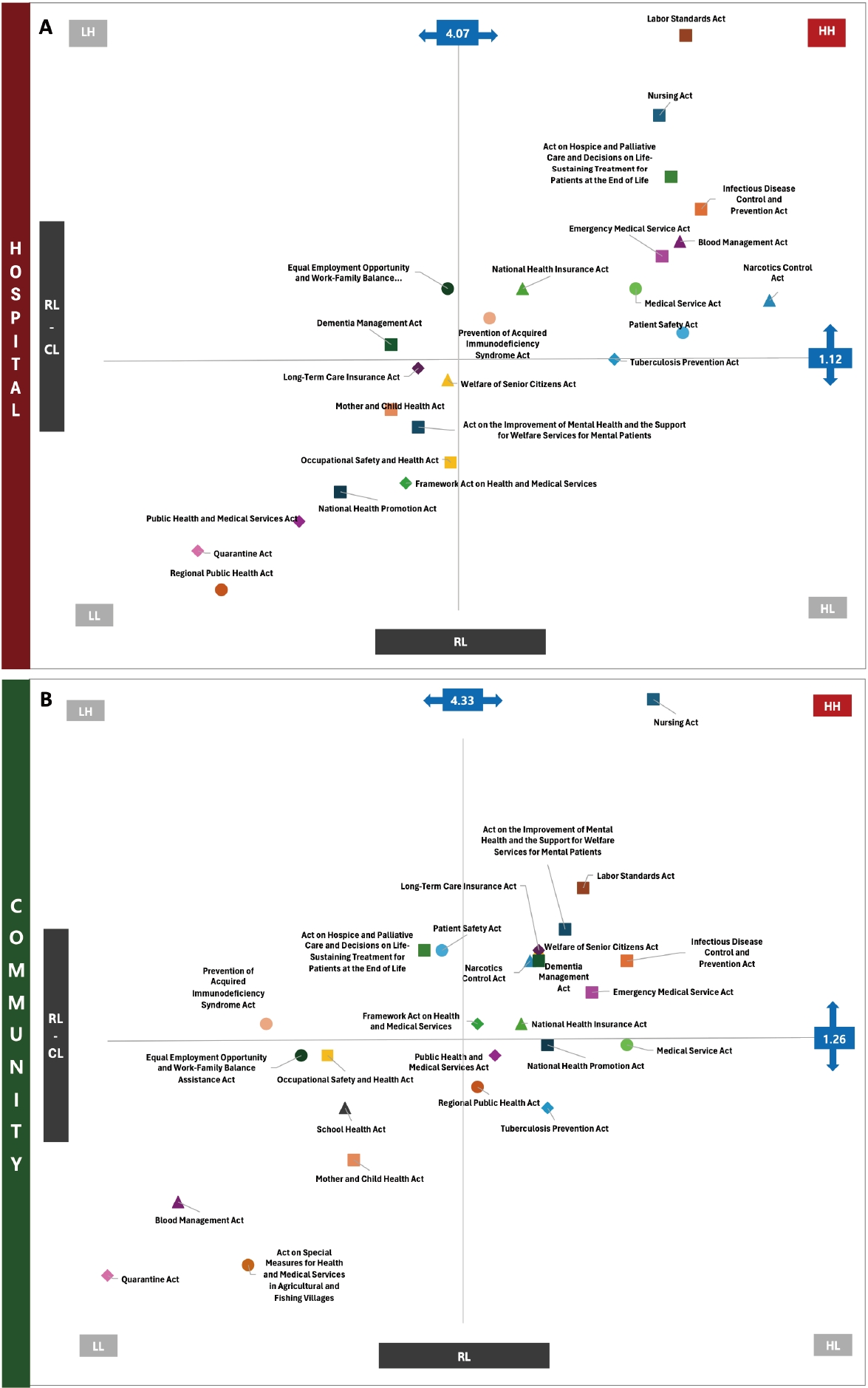
A descriptive survey was employed using an online self-reported questionnaire. Participants included 275 nurses with over 3 years of clinical experience, categorized into hospital and community-based. Convenience sampling was used, and data were collected between January 9 and February 3, 2025. Descriptive statistics and the paired t-test were conducted using IBM SPSS 26.0. Educational needs were analyzed using the Borich Needs Assessment and the Locus for Focus model.
Results
Among participants, 75.6% had received education on work-related laws, and 79.3% of those participants received related education during their undergraduate studies. However, 32.4% of nurses reported experiencing practice related difficulties due to insufficient legal knowledge, particularly related to unclear legal responsibilities and ambiguity in the scope of practice. High educational needs were identified for the Nursing Act and the Labor Standards Act across all workplaces. Hospital nurses emphasized the Hospice and Palliative Care Act and Emergency Medical Services Act, while community-based nurses prioritized the Mental Health Welfare Act, Elderly Welfare Act, and Dementia Management Act.
Conclusion
Nurses’ legal education needs are related to practical applications and their capability to respond appropriately to legal requirements, and these needs vary depending on their work environment and social changes. These findings underscore the necessity of restructuring legal education curricula to improve practical relevance and support nurses’ rights, providing a basis for developing workplace-specific legal education programs.
- 2,043 View
- 148 Download

- An Exploratory Study on the Policy for Facilitating of Health Behaviors Related to Particulate Matter: Using Topic and Semantic Network Analysis of Media Text
- Hye Min Byun, You Jin Park, Eun Kyoung Yun
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(1):68-79. Published online February 28, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20213
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to analyze the mass and social media contents and structures related to particulate matter before and after the policy enforcement of the comprehensive countermeasures for particulate matter, derive nursing implications, and provide a basis for designing health policies.
Methods
After crawling online news articles and posts on social networking sites before and after policy enforcement with particulate matter as keywords, we conducted topic and semantic network analysis using TEXTOM, R, and UCINET 6.
Results
In topic analysis, behavior tips was the common main topic in both media before and after the policy enforcement. After the policy enforcement, influence on health disappeared from the main topics due to increased reports about reduction measures and government in mass media, whereas influence on health appeared as the main topic in social media. However semantic network analysis confirmed that social media had much number of nodes and links and lower centrality than mass media, leaving substantial information that was not organically connected and unstructured.
Conclusion
Understanding of particulate matter policy and implications influence health, as well as gaps in the needs and use of health information, should be integrated with leadership and supports in the nurses’ care of vulnerable patients and public health promotion. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Online community users’ perceptions of particulate matter in South Korea through topic modeling and semantic network analysis
Hansol Choi, Yong Pyo Kim, Yungwook Kim, Ji Yi Lee, Hyemi Lee
Environmental Advances.2025; 20: 100641. CrossRef - Changes in Public Sentiment under the Background of Major Emergencies—Taking the Shanghai Epidemic as an Example
Bowen Zhang, Jinping Lin, Man Luo, Changxian Zeng, Jiajia Feng, Meiqi Zhou, Fuying Deng
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(19): 12594. CrossRef
- Online community users’ perceptions of particulate matter in South Korea through topic modeling and semantic network analysis
- 1,450 View
- 17 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- The Scope of Practice for Registered Nurses in 64 South Korean Laws
- Sungkyoung Choi, Seung Gyeong Jang, Won Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(6):760-770. Published online December 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.6.760
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The role of registered nurses is expanding in scope as the healthcare paradigm shifts from acute, hospital-based care to community and population-based care. Given this paradigm shift, this study explores the legal aspects of the role of a registered nurse.
Methods We used document analysis for extracting laws and legal orders related to nursing from the entirety of Korean law. Using textualism approach, we examined the contents utilizing a framework that was developed based on the role classification of community nurses by Clark in this study.
Results A total of 119 items related to nursing were derived from 64 laws. Of these, 71.4 % can be performed by people in multiple types of occupations including nurses. As a result of analyzing required qualifications, 45.4% of 119 items required additional qualifications besides registered nurse license. Analysis of workplace and activity type demonstrated that 26.1% of the 119 items were related to medical institutions, with nurses performing mostly “Client-oriented role.” More than half (68.9%) were non-medical institutions, with nurses performing mostly “Delivery-oriented role.” Some, however, did not stipulate the nurse's roles clearly.
Conclusion Therefore, to match the enhanced scope and responsibilities of registered nurses and to appropriately recognize, guide, and hold these nurses accountable, laws and policy must reflect these changes. In doing so, these updated laws and policies will ultimately serve as a basis for improving the quality and safety of nursing services.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Role of community health officers: opportunities and challenges
Namita Batra, Kamlesh K. Sharma
International Journal Of Community Medicine And Public Health.2025; 12(3): 1557. CrossRef - Priorities and barriers of dementia policy response and action in South Korea and China: SWOT-PESTLE-AHP model
Bo Zhao, Fanlei Kong, Hyoung-Sun Jeong, Young-Joo Won, Myung-Bae Park, Eun Woo Nam
Geriatric Nursing.2025; 65: 103512. CrossRef - Comparison of educational needs and priorities for work-related laws between hospital and community-based nurses
Jeonghyun Kim, Min Kyoung Han, Minjae Lee, Sujin Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2025; 55(3): 400. CrossRef - Telecare legislation priorities: A Delphi study grounded in ethical challenges
Seongyu Han, Eun Kyoung Yun
Nursing Ethics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of issues related to nursing law: Examination of news articles using topic modeling
JooHyun Lee, Hyoung Eun Chang, Jaehyuk Cho, Seohyun Yoo, Joonseo Hyeon, Andrea Cioffi
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(8): e0308065. CrossRef - Relationships among basic psychological needs, organizational commitment, perceived authentic leadership and turnover intention in Korean nurses: A cross‐sectional study
Jina Hwang, Eun Kyeung Song, Sangjin Ko
Journal of Nursing Management.2022; 30(7): 2176. CrossRef - The Current Status of the Administrative Dispositions of Nurses: A Nationwide Survey in South Korea
Suyoung KIM, Sanghee KIM
Journal of Nursing Research.2021; 29(5): e170. CrossRef - Association of the Magnitude of Nurses With the Use of Health Information Exchanges: Analyzing the National Health Insurance Claim Data of Hospitals and Clinics in Korea
Young-Taek Park, Yeon Sook Kim, Yun-Jung Heo, Jae-Ho Lee, Hyejung Chang
INQUIRY: The Journal of Health Care Organization, Provision, and Financing.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The conundrum of professionalising building surveying in Malaysia
Abdul-Rashid Abdul-Aziz, Subashini Suresh, Suresh Renukappa
International Journal of Building Pathology and Adaptation.2020; 38(5): 621. CrossRef
- Role of community health officers: opportunities and challenges
- 5,174 View
- 44 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref

- The Effects of Hospitals’ Family Friendly Management on Married Female Nurses’ Retention Intention: Focused on the Mediating Effects of Work-Family Interface
- Jin Hwa Lee, Jee-In Hwang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(4):386-397. Published online January 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.4.386
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study examined the effect of hospitals’ family-friendly management on married female nurses’ retention intention. The focus was the mediating effects of the work-family interface (work-family conflict, work-family enrichment and work-family balance).
Methods This study was a cross-sectional study. The participants were 307 nurses working at five public and five private hospitals with more than 200 beds in Seoul. Data were collected using structured questionnaires from September 10 to September 17, 2018 and analyzed with SPSS 24.0. Data were analyzed using an independent t-test, a one-way ANOVA, Pearson's correlation coefficients, and multiple regression following the Baron and Kenny method and Sobel test for mediation.
Results There were significant correlations among family-friendly management, the work-family interface, and retention intention. Work-family conflict showed a partial mediating effect on the relationship between family-friendly management and retention intention. Work-family enrichment showed a partial mediating effect on the relationship between family-friendly management and retention intention. Work-family balance showed a partial mediating effect on the relationship between family-friendly management and retention intention.
Conclusion These findings indicate that both hospitals’ family-friendly management and nurses’ work-family interface are important factors associated with nurses’ retention intention. Therefore, hospitals should actively implement family-friendly management for nurses and establish strategies to enhance nurses’ work-family interface for effective human resource management.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- How parenting-related characteristics influence parenting stress among nurses with young children in the Seoul metropolitan area, South Korea: a cross-sectional study
Minhwa Hwang, Nagyeong Lee, Gunjeong Lee
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Influencing the Retention Intention of Female Nurses Raising Young and School-Age Children during the COVID-19 Pandemic
Ha Neul Lee, Suyon Baek
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(5): 504. CrossRef - Psychometric Properties of Instruments Measuring Dyadic Communication and Environment in Dementia Care: A Systematic Review
Sohyun Kim, Wen Liu, Patricia Heyn
The Gerontologist.2023; 63(1): 52. CrossRef - Disaster Preparedness and Associated Factors Among Emergency Nurses in Guangdong Province, China: A Descriptive Cross-Sectional Study
Jia Wang, Xinglan Sun, Sihui Lu, Fen Wang, Meijuan Wan, Hanxi Chen, Yibing Tan
Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Causes and Effects of Burnout Experienced by Insurance Review Nurses: Focus Group Interview
Eun Sil Jeong, Seok Hee Jeong, Hyun Kyung Kim, Myoung Hee Seo
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2022; 28(5): 545. CrossRef - Nurses’ Clinical Work Experience during Pregnancy
Hyunjung Lee, Hyoung Eun Chang, Jiyeon Ha
Healthcare.2020; 9(1): 16. CrossRef
- How parenting-related characteristics influence parenting stress among nurses with young children in the Seoul metropolitan area, South Korea: a cross-sectional study
- 1,245 View
- 33 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- Approaches to Teaching Health Policy: Moving Students into the Political Process
- Young Hee Yom
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1995;25(1):156-163. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1995.25.1.156
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF No abstract available.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analysis of the health policy education needs of nursing students
HyungSeon Kim
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2024; 38(3): 410. CrossRef
- Analysis of the health policy education needs of nursing students
- 571 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Variations in Nurse Staffing in Adult and Neonatal Intensive Care Units
- Sung Hyun Cho, Jeong Hae Hwang, Yun Mi Kim, Jae Sun Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2006;36(5):691-700. Published online August 31, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2006.36.5.691
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was done to analyze variations in unit staffing and recommend policies to improve nursing staffing levels in intensive care units (ICUs).
Method A cross-sectional study design was used, employing survey data from the Health Insurance Review Agency conducted from June-July, 2003. Unitstaffing was measured using two indicators; bed-to-nurse (B/N) ratio (number of beds per nurse), and patient-to-nurse (P/N)ratio (number of average daily patients per nurse). Staffing levels were compared according to hospital and ICU characteristics.
Result A total of 414 institutions were operating 569 adult and 86 neonatal ICUs. Tertiary hospitals (n=42) had the lowest mean B/N (0.82) and P/N (0.76) ratios in adult ICUs, followed by general hospitals (B/N: 1.34, P/N: 0.97). Those ratios indicated that a nurse took care of 3 to 5 patients per shift. Neonatal ICUs had worse staffing and had greater variations in staffing ratios than adult ICUs. About 17% of adult and 26% of neonatal ICUs were staffed only by adjunct nurses who had responsibility for a general ward as well as the ICU.
Conclusion Stratification of nurse staffing levels and differentiation of ICU utilization fees based on staffing grades are recommended as a policy tool to improve nurse staffing in ICUs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development of a competency for professional oral hygiene care of endotracheally-intubated patients in the intensive care unit: development and validity evidence
Eun-Sil Choi, Hie-Jin Noh, Won-Gyun Chung, So-Jung Mun
BMC Health Services Research.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Associated Factors with Performance of Infection Control for the Prevention of Ventilator-associated Pneumonia among Some Intensive Care Unit Nurses
Hyeon Hwa Lee, Mi Ah Han, Jong Park, Seong Woo Choi
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2018; 43(1): 1. CrossRef - Influencing Factors on Nursing Practices for Healthcare-associated Infections Control in Intensive Care Unit
Soon Ok Kim, Jin Suk Ra
Korean Journal of Healthcare-Associated Infection Control and Prevention.2018; 23(2): 39. CrossRef - The Study of Preceptor Nurses’ Occupational Stress and Burden
Joohee Han, Eun Kwang Yoo
Korean Journal of Stress Research.2018; 26(1): 38. CrossRef - Financial Projection of the Nursing Fee Differentiation Policy Improvement Proposal in the National Health Insurance: Using a Break-even Analysis Model for the Optimal Nursing Fee
Sungjae Kim, Jinhyun Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2013; 19(5): 565. CrossRef - Nurse Staffing and Patient Mortality in Intensive Care Units
Sung-Hyun Cho, Jeong Hae Hwang, Jaiyong Kim
Nursing Research.2008; 57(5): 322. CrossRef
- Development of a competency for professional oral hygiene care of endotracheally-intubated patients in the intensive care unit: development and validity evidence
- 1,017 View
- 6 Download
- 6 Crossref

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 First
First Prev
Prev


