Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Lessons from the US Advanced Practice Registered Nurse system
- Eun-Ok Im, Dongmi Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(4):492-505. Published online November 27, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25120
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
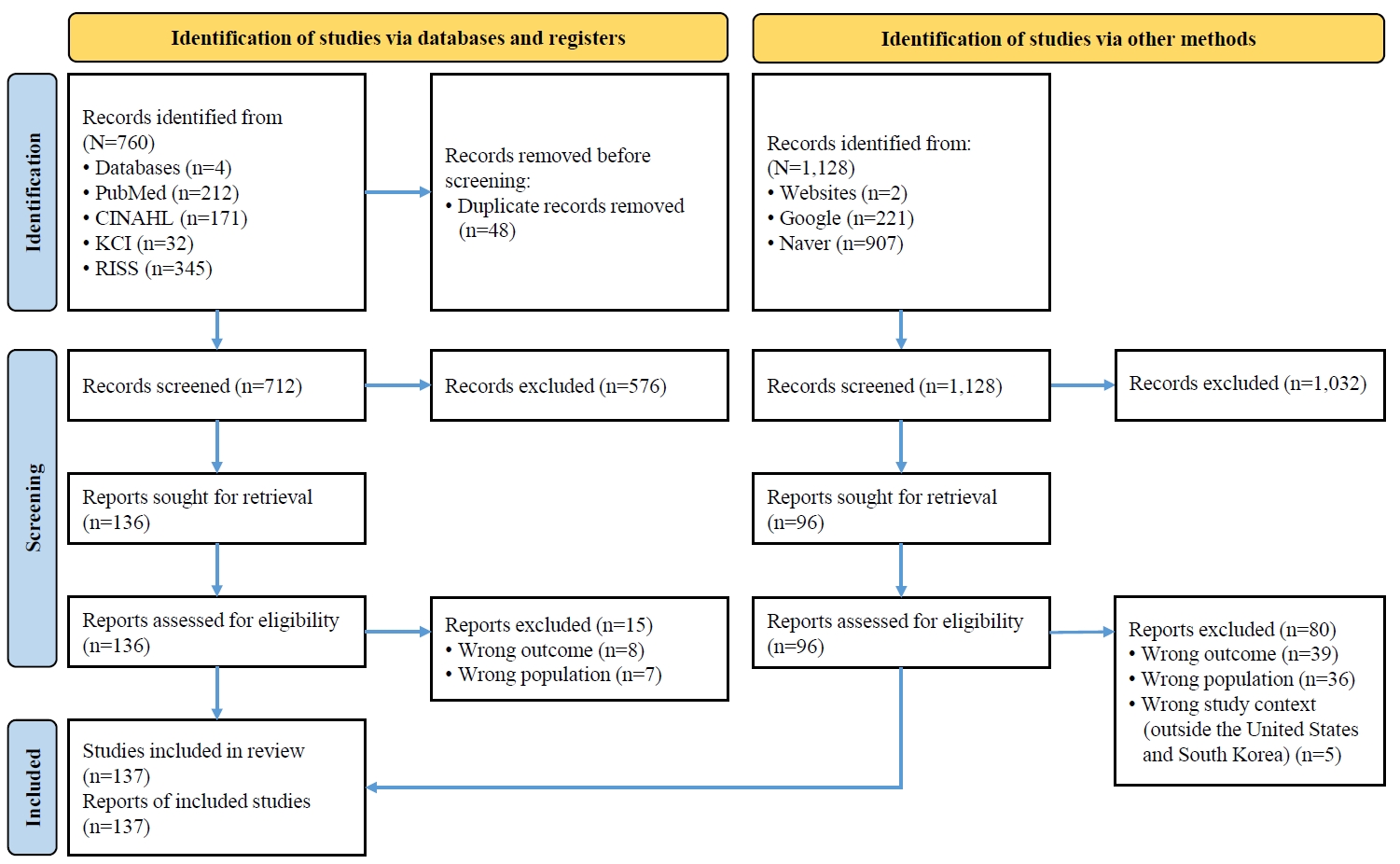
This review compares the development of South Korea’s Advanced Practice Registered Nurse (APRN) system the well-established APRN system in the United States and provides recommendations for future improvements to the APRN system in South Korea.
Methods
To compare the APRN systems between the two countries, an integrative literature review was conducted using multiple databases and professional nursing organization documents and reports from both the United States and South Korea.
Results
Issues were identified in five major domains: (1) research evidence, (2) education and training, (3) the scope of practice, (4) financial mechanisms, and (5) public awareness and acceptance.
Conclusion
Recommendations are made in four areas: (1) building evidence to support APRN programs; (2) strengthening APRN education; (3) establishing legal support and reimbursement mechanisms; and (4) improving public awareness and acceptance of APRNs.
- 1,060 View
- 154 Download

- Strategies for expanding the role of advanced practice providers in the Korean nursing workforce: a mixed-methods approach
- Jeong Hye Kim, Mi-Kyeong Jeon, Suyoung Choi, Mimi Lee, Su Jung Choi
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(4):568-583. Published online November 21, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25106
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
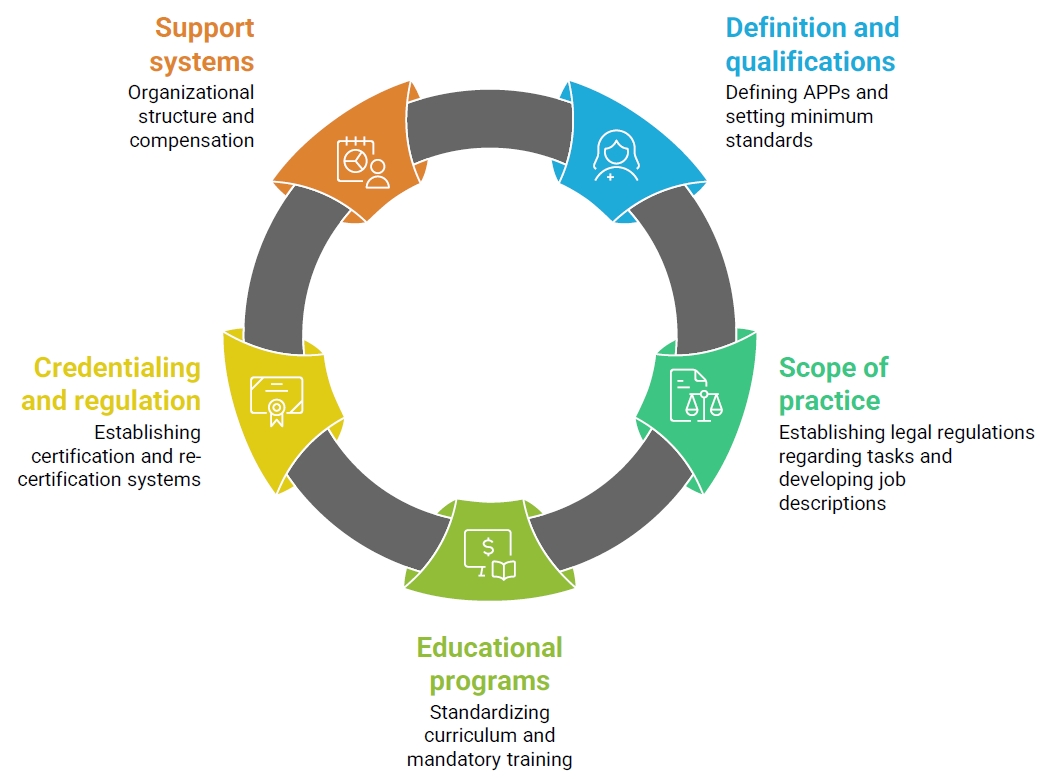
This study aimed to propose strategies for strengthening the nursing workforce by expanding their roles as advanced practice providers (APPs).
Methods
A mixed-methods approach was employed, consisting of five focus group interviews (FGIs) with 30 healthcare professionals (including 10 physicians) and a two-round Delphi survey with 49 experts. The FGIs explored practical insights from clinical settings, while the Delphi process validated and prioritized strategic recommendations through expert consensus.
Results
Four major themes emerged from the FGI analysis: (1) utilization of diverse APPs to ensure quality care, (2) expanding the scope of practice of APPs, (3) requirements to ensure the quality of APPs, and (4) strategies for sustainable management of the APP workforce. Building on these findings, the Delphi survey identified five strategic domains: “definition and qualifications,” “scope of practice,” “educational programs,” “credentialing and regulation,” and “support systems.” Key areas of consensus included the need for mandatory clinical experience and specialty training, legal clarification of role boundaries, standardized curricula with certification mechanisms, and institution-led support systems such as task-specific job descriptions and recredentialing processes.
Conclusion
To effectively strengthen APP roles, it is essential to build on the existing advanced practice nurse (APN) framework, which already includes structured curricula and national certification. Furthermore, integrative strategies should be developed to incorporate experienced clinical nurses without APN licenses into the APN system.
- 1,610 View
- 164 Download

- Intention to Delegate Clinical Practice of Medical Specialists in Accordance with the Enactment of the Scope of Practice for Advanced Practice Nurses
- Min Young Kim, Su Jung Choi, Jeong Hye Kim, Cho Sun Leem, Young-ah Kang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(1):39-54. Published online February 28, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22098
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to investigate the nationwide intention to delegate clinical practice of medical specialists in accordance with the enactment of the scope of practice for advanced practice nurses (APNs).
Methods
Data were collected from October to December 2021 using Google Surveys. In total, 147 medical specialists from 12 provinces responded to the survey. The survey questionnaire was categorized into four legislative draft duties, according to the scope of practice (a total of 41 tasks): Twenty-nine tasks on treatments, injects, etc., performed under the guidance of a physician and other activities necessary for medical treatment (treatment domain); two tasks on collaboration and coordination; six tasks on education, counseling, and quality improvement; four regarding other necessary tasks. Participants were asked whether they were willing to delegate the tasks to APN.
Results
The intention to delegate tasks to APN was higher for non-invasive tasks such as blood sampling (97.3%) or simple dressing (96.6%). Invasive tasks such as endotracheal tube insertion (10.2%), sampling: bone marrow biopsy & aspiration (23.8%) showed low intention to delegate in the treatment domain. Participants who were older, male, and had more work careers with APN, showed a higher intention to delegate tasks.
Conclusion
To prevent confusion in the clinical setting, a clear agreement on the scope of APN practice as APN delegated by physicians should be established. Based on this study, legal practices that APN can perform legally should be established. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Strategies for expanding the role of advanced practice providers in the Korean nursing workforce: a mixed-methods approach
Jeong Hye Kim, Mi-Kyeong Jeon, Suyoung Choi, Mimi Lee, Su Jung Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2025; 55(4): 568. CrossRef - Results of Applying a Ventilator Weaning Protocol Led by an Advanced Practice Nurse for Cardiac Surgery Patients
YoungJu Eim, Su Jung Choi
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2024; 17(2): 42. CrossRef - Legal and Practical Solutions for the Expanding the Roles of Medical Support Staff Nurses
Su Jung Choi, Min Young Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2024; 54(3): 300. CrossRef
- Strategies for expanding the role of advanced practice providers in the Korean nursing workforce: a mixed-methods approach
- 2,208 View
- 86 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Task Analysis of Korean Transplantation Nurse Practitioner
- Soo Ja Byun, Hee Kyung Kim, Ae Ri Kim, Hee Sun Ha, Kyung Ok Joen
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2003;33(2):179-188. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2003.33.2.179
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was designed to create the job description of Korean transplantation nurse practitioner and examine performance frequencies, criticality, and difficulties of task elements.
Method The sample consisted of 63 nurses and coordinators who performed duties related to transplantation at medical center in Korea. A survey method was used, and the questionnaire included frequencies, criticality, and difficulties of task elements in job description by the DACUM method. Using SPSS WIN 10.0, descriptive statistics such as frequency distribution, means, and standard deviations were conducted to examine the subject's general characteristics, the frequencies, criticality, and difficulties of task performance.
Result The job description of transplantation nurse practitioners revealed 5 duties, 22 tasks, and 85 task elements. On the all five duties, the averages of the performance frequency, criticality, and difficulty were 2.41, 3.38, and 2.78, meaning that the respondents rarely perform the 5 duties, but consider them critical and easy to perform.
Conclusion The job description of the transplantation nurse practitioner included duty, task, and task element and definition of job completed. Thus we recommended a data based trial to confirm and validate the information gathered.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Workforce, task performance, and analysis of organ transplant coordinators in Korea: a survey study
Suhee Kim, Sun Young Son, Man Ki Ju, Seungheui Hong, Ji Yeon Park, Hyung Sook Kim
Clinical Transplantation and Research.2024; 38(3): 222. CrossRef - Job Analysis of Visiting Nurses in the Process of Change Using FGI and DACUM
Jieun Kim, Insook Lee, Jina Choo, Songwhi Noh, Hannah Park, Sohyeon Gweon, kyunghee Lee, Kyoungok Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2022; 33(1): 13. CrossRef - Job Analysis of Nurse Care Coordinators for Chronic Illness Management in Primary Care Settings: Using Developing a Curriculum Process
Ju-Hee Hwang, Yong-Jun Choi, Mi-Sook Kim, Seng-Eun Yi, Yong-Soon Park, Ji-Hyang Kim, Ju-Young Yoon, Dong-Soo Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2021; 51(6): 758. CrossRef - Job Analysis and Curriculum Development for Gambling Addiction Prevention Counselors based on DACUM
Sungjae Kim, Soo Mi Jang
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2013; 22(1): 34. CrossRef - Job Analysis of Clinical Research Coordinators Using the DACUM Process
Hyun-Sook Kang, Haeng-Mi Son, Nan-Young Lim, Kyung-Sook Cho, Sung-Bok Kwon, Yeo-Jin Yi, Young-Sook Park, Eun-Hee Lee, Joo-Hyun Kim, Hye-Ja Han, Jung-Mi Baik, Younhee Jeong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2012; 42(7): 1027. CrossRef - Job Analysis of Medical Care Client Managers based on DACUM
Jeong-Myung Choi
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2011; 20(3): 299. CrossRef - Task Analysis of the Job Description of Gerontological Nurse Practitioners based on DACUM
Keum Soon Kim, Yeon-Hwan Park, Nan Young Lim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(6): 853. CrossRef
- Workforce, task performance, and analysis of organ transplant coordinators in Korea: a survey study
- 833 View
- 5 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Development of a Resource-based Relative Value Scale and Its Conversion Factor for Advanced Nursing Practices in the National Health Insurance
- Jin Hyun Kim, Myung Ae Kim, Mi Won Kim, Kyung Sook Kim, Cheong-Suk Yoo
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2011;41(3):302-312. Published online June 13, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2011.41.3.302
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to develop a resource-based relative value scale (RBRVS) and its conversion factor for advanced nursing practices carried out by critical care nurse practitioners (CCNP) in intensive care units.
Methods The methodology was developed by calculating CCNP's RBRVS for 32 advanced nursing services based on CCNP's workload and time spent in the context of national health insurance. A cost analysis was performed to estimate the conversion factor of CCNP's RBRVS. The share of CCNP's contribution to fee-for-service in intensive care units was also analyzed.
Results Calculation of the RBRVS of 32 advanced nursing practices showed a range of points from 100.0 to 1,181.4 and an average of 296.1 points. The relevant conversion factor for advanced nursing practices in CCNP were estimated at 37.3-48.4 won. The contribution rate of CCNP's advanced nursing practices in the relative value scale of the national health insurance was estimated at 0.1-31.3%.
Conclusion Measuring the economic value of advanced nursing services will be a basis for esta-blishing a reimbursement system for CCNP's practices and thus encourage a social demand for advanced nurse practitioners.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Measuring the Work Relative Value of Common Nursing Items for the General Departments of Tertiary Hospitals: A Descriptive Study
Yingli Wang, Cong Wang, Hongfei Ren, Ling Mao, Fenjiao Chen, Taoyun Liang, Yuqin Luo, Yan Jiang
Journal of Evaluation in Clinical Practice.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A Resource-Based Relative Value for Clinical Research Nurses’ Workload
Sangmi Lee, Ihn Sook Jeong
Therapeutic Innovation & Regulatory Science.2018; 52(3): 313. CrossRef - An Empirical Analysis of Costs related to Nursing Practice
Yu Kyung Ko, Bo-Hyun Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2017; 23(2): 139. CrossRef - Economic Analysis and Fee Development by Relative Value Scale of Nursing Practices by Emergency Nurse Practitioner
Jin Hyun Kim, Kyung Sook Kim, Mi Won Kim, Kyoung-A Lee
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2013; 25(3): 275. CrossRef
- Measuring the Work Relative Value of Common Nursing Items for the General Departments of Tertiary Hospitals: A Descriptive Study
- 1,102 View
- 9 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Task Analysis of the Job Description of Gerontological Nurse Practitioners based on DACUM
- Keum Soon Kim, Yeon-Hwan Park, Nan Young Lim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2008;38(6):853-865. Published online December 31, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2008.38.6.853
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The aim of this study was to develop and to analyze the task of gerontological nurse practitioners (GNPs) in Korea.
Methods The definition of GNP and job description was developed based on developing a curriculum (DACUM) by 7 panels who have experienced in DACUM analysis and gerontological nursing. One hundred sixty nurses who were working at long term care facilities were participated. The questionnaire included frequency, importance, and difficulty of duties, tasks, and task elements. The data were collected in November 2006, analyzed by descriptive statistics.
Results The job description of GNPs in Korea revealed 5 duties, 23 tasks, and 86 task elements. On the all five duties, the highest duty in frequency and in importance was professional nursing care (3.25±0.35, 3.49±0.29). But the highest duty in difficulty was research (3.24±0.46). 'Prevent health problem (3.42±0.43, 3.56±0.33)', 'Teach other staffs (2.83±0.77, 3.39±0.43)', 'Develop the evidence-based standards (2.43±0.76, 3.22±0.43)', 'Develop the self (2.81±0.65, 3.26±0.42)', and 'Participate the team activities' were the highest score in frequency and in criticality of tasks. 'Provide emotional support to older adults and families (3.16±0.41)', 'Counsel older adults and their families (3.14±0.49)', 'Do clinical research (3.32±0.49)', 'Quality insurance (3.25±0.49)', and 'Build collaborative system (3.18±0.47)' were perceived the most difficult tasks.
Conclusion The political efforts for the legislation of role and task of GNPs were needed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Job analysis of vaccination health workers at public health centers and sub‐centers
No‐Yai Park, Chung‐Min Cho, Eun‐Hyun Lee, Jeong‐Mo Park, Young‐Ran Lee, Jeong‐Ik Hong, Geun‐Yong Kwon
Public Health Nursing.2024; 41(4): 723. CrossRef - Development and Analysis of the Job Description for Dementia Care Center Nurses in Korea Using Developing a Curriculum (DACUM)
Hana Ko, SuJung Jung
Journal of Gerontological Nursing.2023; 49(10): 29. CrossRef - Job Analysis of Nurse Care Coordinators for Chronic Illness Management in Primary Care Settings: Using Developing a Curriculum Process
Ju-Hee Hwang, Yong-Jun Choi, Mi-Sook Kim, Seng-Eun Yi, Yong-Soon Park, Ji-Hyang Kim, Ju-Young Yoon, Dong-Soo Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2021; 51(6): 758. CrossRef - Is there an agreement among the items of the Korean physical therapist licensing examination, learning objectives of class subjects, and physical therapists’ job descriptions?
Min-Hyeok Kang, Oh-Yun Kwon, Yong-Wook Kim, Ji-Won Kim, Tae-Ho Kim, Tae-Young Oh, Jong-Hyuk Weon, Tae-Sik Lee, Jae-Seop Oh
Journal of Educational Evaluation for Health Professions.2016; 13: 3. CrossRef - The Role-expectations of Gerontological Nurse Practitioners and Performance of Gerontological Nursing by Nurses in Long Term Care Hospitals and General Hospitals
Hye Jin Lee, Kye Ha Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2014; 26(6): 642. CrossRef - Job Analysis and Curriculum Development for Gambling Addiction Prevention Counselors based on DACUM
Sungjae Kim, Soo Mi Jang
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2013; 22(1): 34. CrossRef - Comparison of Job Tasks and Task Elements of Korean Nurse Anesthetists by Type of Medical Institution: Hospital, General Hospital and Higher General Hospital
Chungsim Bai, Haesang Yoon
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2013; 19(2): 239. CrossRef - Development of Job Description of Clinical Dietitians in Hospitals by the DACUM Method
Jin-A Cha, Kang-Eun Kim, Eun-Mi Kim, Mi-Sun Park, Yoo-Kyoung Park, Hee-Joon Baek, Song-Mi Lee, Soo-Kyong Choi, Jung-Sook Seo
Journal of the Korean Dietetic Association.2013; 19(3): 265. CrossRef - Job Analysis of Clinical Research Coordinators Using the DACUM Process
Hyun-Sook Kang, Haeng-Mi Son, Nan-Young Lim, Kyung-Sook Cho, Sung-Bok Kwon, Yeo-Jin Yi, Young-Sook Park, Eun-Hee Lee, Joo-Hyun Kim, Hye-Ja Han, Jung-Mi Baik, Younhee Jeong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2012; 42(7): 1027. CrossRef - Task Analysis of Managers in the Customized Visiting Health Services
Young Ran Han, Young Rye Park, Young Hee Kim, Hee Chung Choi, Mi Ja Chung
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2012; 23(2): 165. CrossRef
- Job analysis of vaccination health workers at public health centers and sub‐centers
- 1,158 View
- 5 Download
- 10 Crossref

- Role-Identity of Home Care Nurse Practitioners
- Sung Jae Kim, Myung Sun Yi, Young Eun, Moon Hee Ko, Joo Hyun Kim, Dong Ok Kim, Haeng Mi Son, Kyung Sook Choi
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2006;36(1):103-113. Published online February 28, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2006.36.1.103
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Introduction It is important to understand the nature of the identity through the live experiences of Home Care Nurse Practitioner(HCNP) because the role identity of a professional is constructed by continuous social interactions, This study aims to understand the construction of the role identity of HCNP.
Method Data was collected from 12 hospital based HCNPs. This study involved two focus group discussion sand four in-depth individual interviews. The main question was “what is the role of HCNP?” The debriefing notes and field notes were analyzed using consistent comparative data analysis method.
Result First, Home care (HC) is a small clinic. HCNP brings it to home to provide various services. Second, HC is the real nursing and HCNP is the ‘genuine’ nurse who actualizes the essence of nursing in practice. Third, HC is empowering activity to promote self-care ability of the patients and their caregivers. Forth, HC is like the dish-spinning required high-level mastery and HCNP is an expert who provides the most appropriate services to the patients.
Conclusion HCNPs have the role identity as a highly qualified professional who delivers services from hospital to home, actualizes the essence of nursing in practice, empowers the patients and their caregivers to have self-efficacy to recover, and offers the most appropriate nursing care.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Study on Youth Worker’s Occupational Identity
Hee-Jung SEO, Mi-Jeong KIM, Jin-Mi HWANG
JOURNAL OF FISHRIES AND MARINE SCIENCES EDUCATION.2021; 33(3): 783. CrossRef - Difficulties and Coping Experienced by Advanced Practice Nurses in Home Health Nursing Field
Moon-Sook Hwang, Hak Young Park, Soo Jung Chang
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2020; 31(2): 143. CrossRef - Nursing Students' Practice Experience on Community Visiting Nursing
Jae-Hyun Ha, Jeong-Hee Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2020; 31(1): 43. CrossRef - The Effects of Motivational Interviewing Training Program on Communication Skills and Self-Efficacy of Home Visiting Nurses
Sungjae Kim, Jeongwoon Yang
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2016; 30(2): 274. CrossRef - The Job Experience of Oncology Nurse Specialists
Young Sook Tae, Suhye Kwon, Young Sook Lee
Asian Oncology Nursing.2014; 14(4): 236. CrossRef - Occupational Health Nurses' Role Experiences
Kyung-Ja June, Hea-Ju Joo, Young-Mi Kim
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2011; 20(3): 250. CrossRef - A Study on Participation in Clinical Decision Making by Home Healthcare Nurses
Se Young Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2010; 40(6): 892. CrossRef - Self Role Perception of Health Teachers in Elementary Schools
Jeong Hee Lee, Byoung Sook Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2010; 21(4): 398. CrossRef - Economic Evaluation of Gemcitabine-cisplatin Chemotherapy for Non Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patient in an Outpatient Setting
Su Hyun Min, Su-kyoung Ko, Ji Young Lim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(3): 363. CrossRef
- A Study on Youth Worker’s Occupational Identity
- 826 View
- 8 Download
- 9 Crossref

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 First
First Prev
Prev


