Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Research Papers
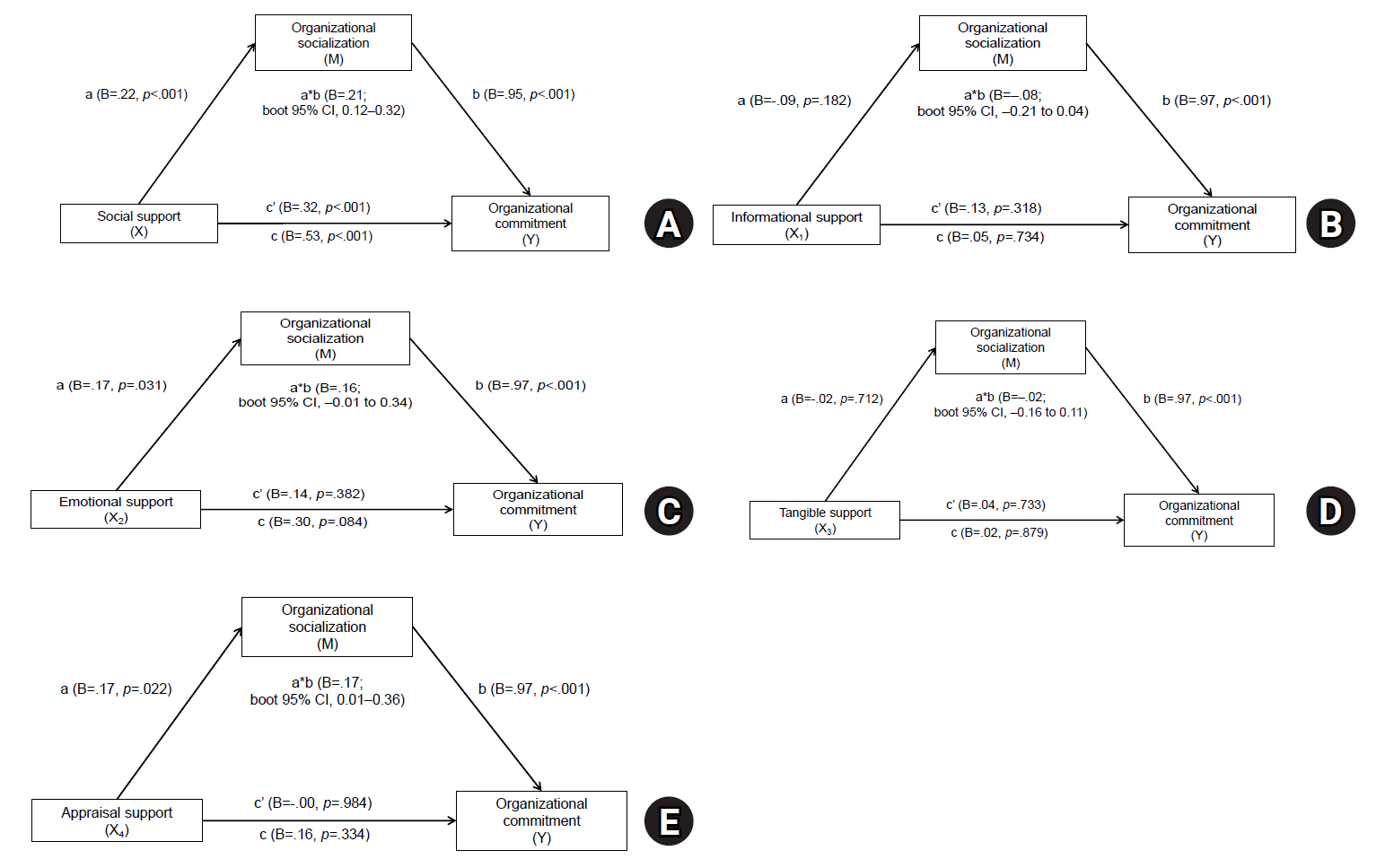
- Effects of social support on organizational commitment among experienced nurses experiencing department rotation: the mediating effect of organizational socialization
- Young Jun Jang, Jeong A Jeong, Yu Seung Ban, Seon Hwa Park, Eun Jee Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(3):364-376. Published online August 18, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25042
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study explored the mediating role of organizational socialization in the relationship between social support and organizational commitment among nurses in hospitals who had experienced department rotation.
Methods
A descriptive survey design was used with 202 nurses from a tertiary hospital who had experienced department rotation within the past 12 months. Data were collected via an online questionnaire from August 1 to August 30, 2024. Analyses included frequency analysis, descriptive statistics, Pearson correlation, and multiple regression. The mediating effect was tested using IBM SPSS WIN ver. 23.0 and the PROCESS macro (model 4) with 10,000 bootstrap resamples.
Results
Organizational socialization partially mediated the relationship between social support and organizational commitment (B=.21; bootstrapped 95% confidence interval, 0.12–0.32).
Conclusion
The findings suggest that both social support and organizational socialization play essential roles in improving nurses’ organizational commitment following department rotation. Thus, practical programs, such as mentoring systems, should be implemented that both enhance social support and actively promote organizational socialization. These efforts have the potential to help nurses adjust more effectively to new units and ultimately improve retention and performance within healthcare organizations. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effects of Nurses’ Dispatch Work Characteristics on Job Embeddedness, Organizational Commitment, and Turnover Intention
Eejee Jung, Gunjeong Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(5): 560. CrossRef - Nurses' Experience Working with Substitute Nurses
Hye Mi Kim, Yeon Hee Kim, Jeong Hye Kim
Journal of Korean Association for Qualitative Research.2025; 10(3): 208. CrossRef
- The Effects of Nurses’ Dispatch Work Characteristics on Job Embeddedness, Organizational Commitment, and Turnover Intention
- 2,008 View
- 233 Download
- 2 Crossref

- The Influence of Diversity Management of Nursing Organization on Organizational Commitment: Double Mediating Effect of Diversity Sensitivity Orientation and Positive Nursing Organizational Culture
- Hwi Gon Jeon, Keum Seong Jang, Eun A Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(3):403-417. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23120
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The aim of this study was to identify the double mediating effect of effect of diversity sensitivity orientation and positive nursing organizational culture between diversity management and organizational commitment.
Methods
Participants were 245 nurses working in six tertiary hospitals located in 3 different regions. Data collection was conducted from February 13, 2023 to March 6, 2023 through online self-reported questionnaire. The data were analyzed by IBM SPSS Statistics 27 and SPSS PROCESS Macro 4.2 program.
Results
The direct effect of diversity management on organizational commitment was significant (β = .21, p < .001). The indirect effect of diversity management on organization commitment was .34 (95% confidence interval [CI] = .23~.47). The double mediating effect of diversity sensitivity orientation and positive nursing organizational culture in the relationship between diversity management and organizational commitment was .02 (95% CI = .00~.05).
Conclusion
Diversity sensitivity orientation and positive nursing organizational culture show double mediating effect on the relationship between diversity management and organizational commitment. Education program and human resource management strategy for enhancing diversity management, diversity sensitivity orientation and positive nursing organizational culture should be provided to improve organizational commitment, and which are needed active support of the association and nursing organization. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of Resilience, Emotional Exhaustion, and Communication Competency on Organizational Commitment Among Nurses in a Tertiary Hospital Setting in South Korea: A Cross-Sectional Study
Ho Young Kim, Hee Jeong Kim, Eun Ja Yeun
Sage Open.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Organizational commitment of nursing staff: Definition of the concept and specifics of measurement (review of foreign publications)
K. V. Kuzmin, L. E. Petrova, V. S. Kharchenko
Kuban Scientific Medical Bulletin.2025; 32(5): 96. CrossRef
- Impact of Resilience, Emotional Exhaustion, and Communication Competency on Organizational Commitment Among Nurses in a Tertiary Hospital Setting in South Korea: A Cross-Sectional Study
- 1,986 View
- 160 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Pathway Analysis on the Effects of Nursing Informatics Competency, Nursing Care Left Undone, and Nurse Reported Quality of Care on Nursing Productivity among Clinical Nurses
- Mi Yu, Se Young Kim, Ji Min Ryu
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(2):236-248. Published online April 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22110
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
Nursing informatics competency is used to manage and improve the delivery of safe, high-quality, and efficient healthcare services in accordance with best practices and professional and regulatory standards. This study examined the relationship between nursing informatics competency (NIC), nursing care left undone, and nurse reported quality of care (NQoC) and nursing productivity. A path model for their effects on nursing productivity among clinical nurses was also established.
Methods
Data were collected using structured questionnaires answered by 192 nurses working in a tertiary hospital located in J city, Korea, and analyzed using SPSS/WIN 23.0 and AMOS 21.0 program.
Results
The fit indices of the alternative path model satisfied recommended levels χ2 = .11 (p= .741), normed χ2 (χ2/df) = .11, SRMR = .01, RMSEA = .00, GFI = 1.00, NFI = 1.00, AIC = 18.11. Among the variables, NIC (β = .44, p < .001), NQoC (β = .35, p < .001) had a direct effect on nursing productivity. Due to the mediating effect of NQoC on the relationship between NIC and nursing productivity, the effect size was .14 (95% CI .08~.24). Meanwhile, nursing care left undone through NQoC in the relationship between NIC and nursing productivity, has a significant mediation effect (estimate .01, 95% CI .00~.03). The explanatory power of variables was 44.0%.
Conclusion
Education and training for enhancing NIC should be provided to improve nursing productivity, quality of care and to reduce missed nursing care. Furthermore, monitoring the quality of nursing care and using it as a productivity index is essential. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Information Literacy Competencies and Associated Variables among Korean Nursing Students
Shin Hyang Kim, Jong Mi Lim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(4): 358. CrossRef - The impact of nursing informatics competency, social influence, and medical information culture on nurses’ intention to use new medical technology in general hospitals
Jeong Ho Ji, Kyungja Kang
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2025; 31(4): 484. CrossRef - Effects of digital literacy and nursing informatics competency as job resources on nurses’ burnout and work engagement: a cross-sectional study
Jeehae Chung, Hyesil Jung, Sang Mi Park, Kyeongmin Lee
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Influencing Nursing Care Left Undone by Cancer Ward Nurses
Chung Hee Woo, Yeon Joo Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(5): 594. CrossRef
- A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Information Literacy Competencies and Associated Variables among Korean Nursing Students
- 2,880 View
- 124 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Influence of Learning Presence of Non-Face-to-Face Class Experience in Nursing Students on Academic Achievement: Mediating Effect of Learning Flow and Moderated Mediation of Digital Literacy
- Eui Jeong Ryu, Keum Seong Jang, Eun A Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(3):278-290. Published online June 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21241
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to identify the mediating effect of learning flow and the moderated mediation effect of digital literacy on the effect of the learning presence of non-face-to-face class experience in nursing students on academic achievement.
Methods
Participants were 272 nursing students from six universities in two different cities. A self-report questionnaire was used to measure learning presence, learning flow, digital literacy, and academic achievement. Analysis was performed using SPSS 26.0 and SPSS PROCESS Macro (4.0).
Results
The mediating effect of learning flow on the effect of learning presence on academic achievement was 0.42, and the moderated mediation index of digital literacy was 0.17. Learning flow showed a mediating effect on the relationship between learning presence and academic achievement. Digital literacy had a moderated mediation effect on the relationship between learning presence and academic achievement that was mediated by learning flow.
Conclusion
The intensity of the mediating effect of nursing students’ learning presence on academic achievement through learning flow increases as the level of digital literacy increases. These results suggest that educational programs considering the level of learning presence, learning flow, and digital literacy are required to promote the academic achievement of nursing college students. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Information Literacy Competencies and Associated Variables among Korean Nursing Students
Shin Hyang Kim, Jong Mi Lim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(4): 358. CrossRef - The influence of nursing students’ digital literacy on academic achievement in a blended learning environment: Parallel multiple mediation effects of learning presence
Ja Hyeon Ha, Eun Ju Choi
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2025; 31(4): 452. CrossRef - Study on the Attitudes toward Artificial Intelligence and Digital Literacy of Dental Hygiene Students
Seon-Ju Sim, Ji-Hye Kim, Min-Hee Hong, Su-Min Hong, Myung-Jin Lee
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2024; 24(3): 171. CrossRef - The influence of e-learning digital literacy on cognitive flexibility and learning flow in nursing students
Jeongim Lee, Su Ol Kim
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2023; 25(2): 87. CrossRef - The Impact of Self-Efficacy on Nurses’ Well-Being: Does Digital Competence Matter?
Yali Li, Qi Jing, Taiwen Feng, Xiaoling Yang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2023; 53(4): 385. CrossRef - Relationship between learning flow and academic performance among students: a systematic evaluation and meta-analysis
Zhang Jinmin, Fang Qi
Frontiers in Psychology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Information Literacy Competencies and Associated Variables among Korean Nursing Students
- 2,604 View
- 184 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 First
First Prev
Prev


