Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Research Paper
- Serial mediation effects of social support and antepartum depression on the relationship between fetal attachment and anxiety in high-risk pregnant couples of South Korea
- Mihyeon Park, Sukhee Ahn
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(1):19-33. Published online February 4, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24070
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study examined the direct effects of fetal attachment, social support, and antepartum depression on anxiety in pregnant women with high-risk pregnancy-related conditions and their husbands. Furthermore, it aimed to explore the serial mediation effects of social support and antepartum depression in the relationship between fetal attachment and anxiety.
Methods
A survey-based study was conducted among pregnant women diagnosed with high-risk pregnancy conditions at 24–32 weeks and their husbands, recruited from a pregnant women’s online community between January 20, 2021 and July 20, 2022. Data were collected from 294 individuals (147 couples) using self-report questionnaires. Correlations between variables were analyzed using the IBM SPSS software ver. 26.0 (IBM Corp.), and the mediation effects were assessed using the PROCESS macro, model 6.
Results
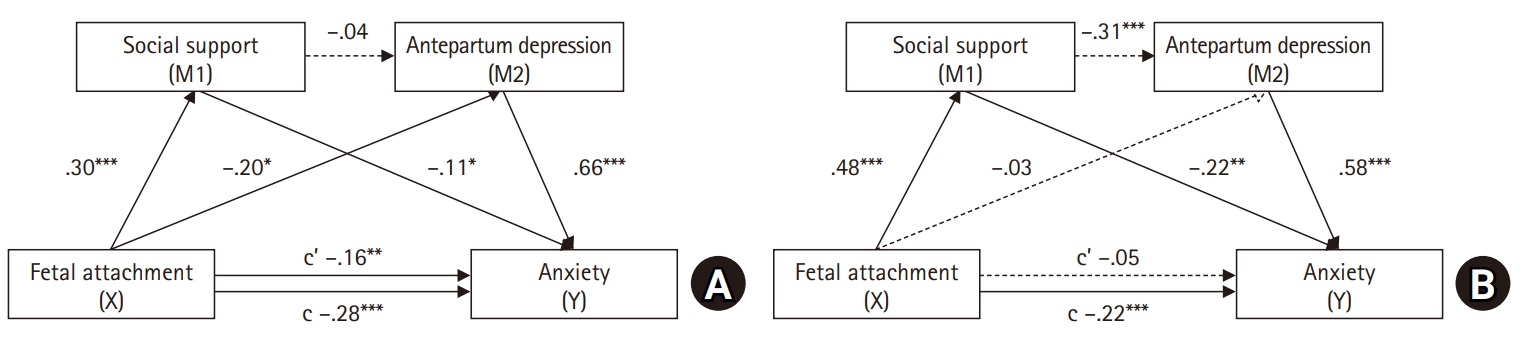
In the maternal model, maternal-fetal attachment directly affected anxiety (p=.005), with antepartum depression partially mediating this relationship (95% confidence interval [CI], –0.26 to –0.01). In the paternal model, paternal-fetal attachment had no direct effect on anxiety (p=.458). However, social support and antepartum depression fully mediated the relationship between paternal-fetal attachment and anxiety (95% CI, –0.14 to –0.03).
Conclusion
The findings indicate that social support in the relationship between fetal attachment and depression in high-risk pregnant women and their partners can have direct or indirect effects on the negative emotions of high-risk pregnant couples. It is necessary to assess the level of anxiety in couples experiencing high-risk pregnancies and provide comprehensive nursing interventions that address fetal attachment, social support, and antepartum depression in order to reduce anxiety.
- 2,583 View
- 247 Download

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION
 First
First Prev
Prev


