Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Research Paper
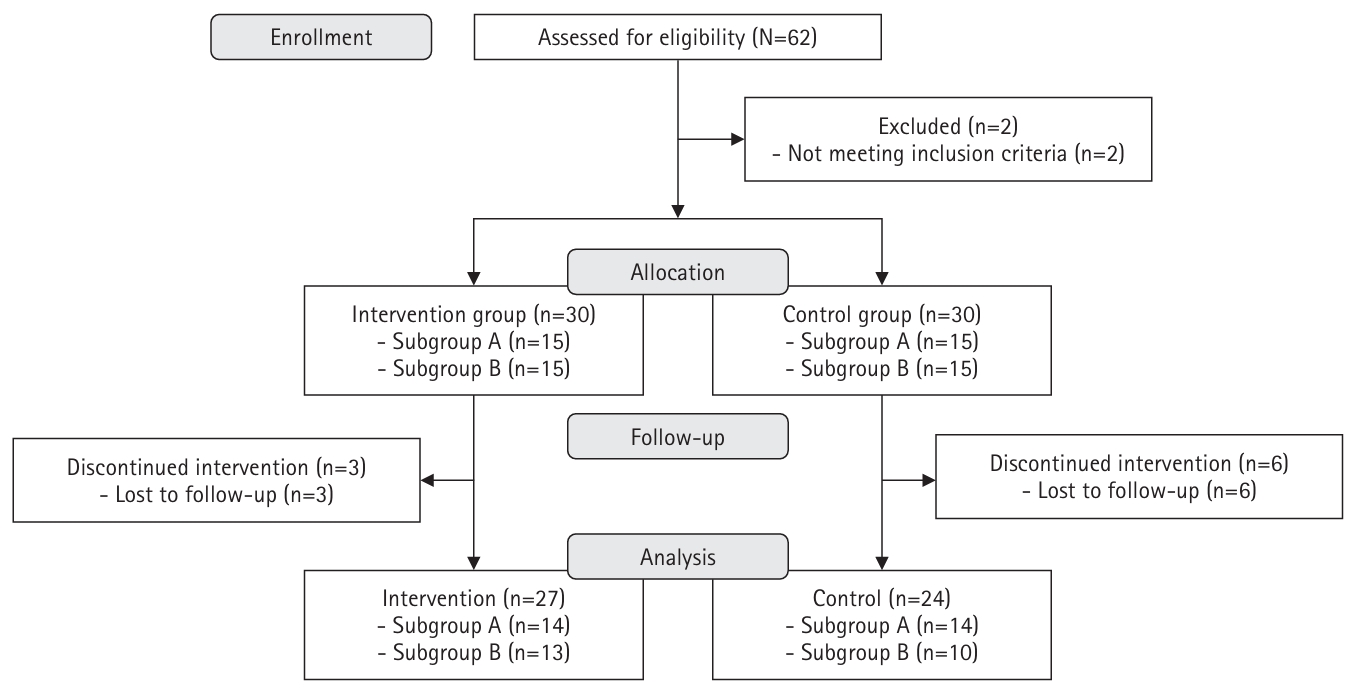
- A non-face-to-face diabetes self-management program based on self-efficacy theory and health literacy: a non-randomized controlled trial
- Jung Hee Lee, Soo Jin Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(2):165-177. Published online May 23, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25009
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to assess the impact of a non-face-to-face diabetes self-management program based on self-efficacy theory and focusing on health literacy.
Methods
A quasi-experimental, nonequivalent control group pre–post design was used. Participants from a community health promotion center were included if they (1) were 30–70 years of age, (2) had type 2 diabetes with glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) ≥6.5%, and (3) had internet access via computers or mobile devices. The 8-week program was developed based on self-efficacy theory, and it included virtual education using an online platform, telephone counseling, videos, and social networking site activities considering health literacy. Fasting blood glucose levels, HbA1c levels, diabetes self-efficacy, social support, depression, and self-management behaviors were assessed. Data were analyzed using the independent t-test, paired t-test, and others.
Results
Post-test results showed that the intervention group had significantly lower fasting blood glucose levels and improved diabetes self-efficacy, social support, and self-management behaviors compared with the control group. An analysis of the pre-to-post changes in scores indicated that the intervention group had significantly greater improvements in fasting blood glucose levels, diabetes self-efficacy, and overall diabetes self-management behaviors than those observed in the control group.
Conclusion
Non-face-to-face programs based on self-efficacy theory that consider health literacy can provide effective diabetes management support to patients when in-person diabetes management at community health centers is challenging.
- 3,341 View
- 243 Download

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION
 First
First Prev
Prev


