Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Serial mediation effects of social support and antepartum depression on the relationship between fetal attachment and anxiety in high-risk pregnant couples of South Korea
- Mihyeon Park, Sukhee Ahn
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(1):19-33. Published online February 4, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24070
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study examined the direct effects of fetal attachment, social support, and antepartum depression on anxiety in pregnant women with high-risk pregnancy-related conditions and their husbands. Furthermore, it aimed to explore the serial mediation effects of social support and antepartum depression in the relationship between fetal attachment and anxiety.
Methods
A survey-based study was conducted among pregnant women diagnosed with high-risk pregnancy conditions at 24–32 weeks and their husbands, recruited from a pregnant women’s online community between January 20, 2021 and July 20, 2022. Data were collected from 294 individuals (147 couples) using self-report questionnaires. Correlations between variables were analyzed using the IBM SPSS software ver. 26.0 (IBM Corp.), and the mediation effects were assessed using the PROCESS macro, model 6.
Results
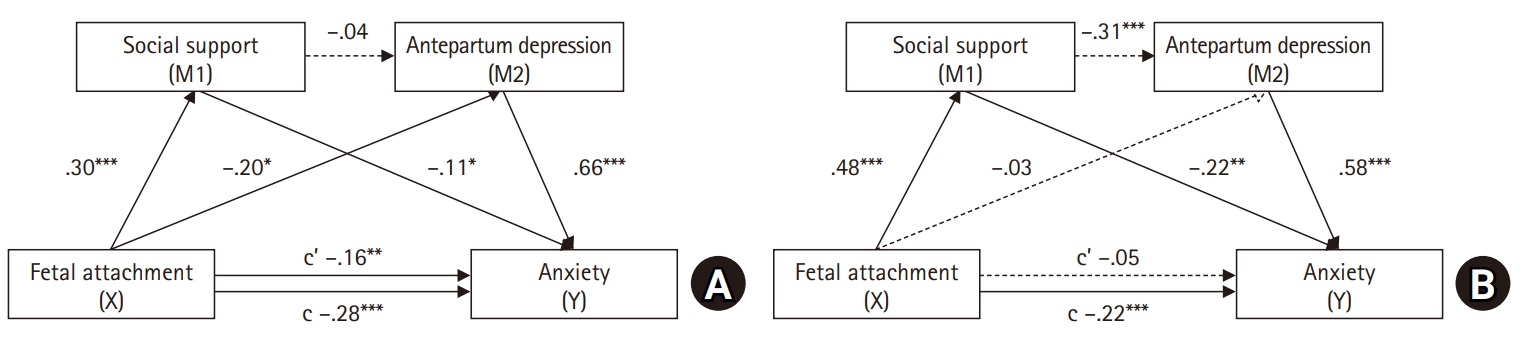
In the maternal model, maternal-fetal attachment directly affected anxiety (p=.005), with antepartum depression partially mediating this relationship (95% confidence interval [CI], –0.26 to –0.01). In the paternal model, paternal-fetal attachment had no direct effect on anxiety (p=.458). However, social support and antepartum depression fully mediated the relationship between paternal-fetal attachment and anxiety (95% CI, –0.14 to –0.03).
Conclusion
The findings indicate that social support in the relationship between fetal attachment and depression in high-risk pregnant women and their partners can have direct or indirect effects on the negative emotions of high-risk pregnant couples. It is necessary to assess the level of anxiety in couples experiencing high-risk pregnancies and provide comprehensive nursing interventions that address fetal attachment, social support, and antepartum depression in order to reduce anxiety.
- 2,583 View
- 247 Download

- Assessment of Gestational Age using New Ballard Examination in High-Risk Infants
- Young Mee Ahn, Sang Mi Lee
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2002;32(2):176-185. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2002.32.2.176
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: Knowing the accurate GA is critical in nursing care of high-risk newborns. A descriptive study was performed to examine the reliability and clinical applicability of the new Ballard examination (NBE) in high-risk infants. METHOD: A NBE was performed to measure GA by assessing the neuromuscular and physical maturity in the course of physical examination of a convenient sample of 50 high-risk infants. RESULTS: 1) There was a highly correlation between both the GA by LMP (GA-LMP) and GA by NBE (GA-NBE) (r = .894, p = .000) 2) There was a greater positive relationship in neuromuscular maturity than physical maturity in the GA-NBE of the high-risk newborn (r = .657 versus r = .915, p<. 05). 3) The high-risk infants were thoes with congenital anomalies, prematurity, and RDS(Respiratory Distress Syndrome). Male infants showed a higher neuromuscular maturity, compared to female infants. 4) There was a positive correlation between neuromuscular, physical, total maturity, GA-LMP and GA-NBE in the birth weight, 1 minute Apgar score. CONCLUSION: The study supports the reliability an clinical relevance of NBE in assessment of the accurate GA in high-risk infants.
- 507 View
- 1 Download

- Maternal Transition in Mothers with High Risk Newborns
- Hyun Jeong Shin
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2004;34(2):243-251. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2004.34.2.243
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was a comprehensive understanding about maternal transition in mothers with high risk newborns according to the degree of situational meaning.
Method A methodological triangulation that combines qualitative and quantitative methods was used. The situational meaning of a high risk newborn mother was identified using a Family Meaning Attribution Scale. According to the degree of situational meaning, in-depth interviews were conducted at 3 time periods postpartum : between 3-10 days after childbirth, around the time of the newborn's discharge, and between 10-12 weeks after childbirth. Quantitative data was analyzed using descriptive statistics and t-test. Qualitative data was analyzed using Tutty, Rothery, & Grinnell's methodology.
Result The average score of the situational meaning in high the risk newborn mother was 53.57(possible score is between 0-96) and the average score of each item was 1.67. A Maternal transition process in the mother that has a positive situational meaning was conceptualized in three distinctive phases : confusion, accepting, and shaping phases. The Maternal transition process in the mother that has a negative situational meaning was also conceptualized in three distinctive phases : avoiding, conflicting, and accepting phases.
Conclusion It is necessary that the nurses provide high risk newborn mothers with individualized care considering both the situational meaning that is attributed to them and the maternal transition phase that they are faced with.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Concept analysis of transition to motherhood: a methodological study
Woon Young Hwang, Sun Yeob Choi, Hae Jeong An
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2022; 28(1): 8. CrossRef - Effects on Maternal Attachment, Parenting Stress, and Maternal Confidence of Systematic Information for Mothers of Premature Infants.
Hyo Sin Choi, Yeong Hee Shin
Child Health Nursing Research.2013; 19(3): 207. CrossRef - Effects of a Home-based Discharge Program for Mothers of Premature Infants on Oxygen Therapy at Home
Ji Min Lee, Soon Ja Oh, Kyung A Kim, Eun Jung Lee, Ji Yoon Lee, Moon Sook Hwang, Jung Sook Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Child Health Nursing.2010; 16(2): 144. CrossRef - Life Transition of Mothers of Children with Autism
Ae Ran Lee, Sun Woo Hong, Ji Soo Kim, Se Jin Ju
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2010; 40(6): 808. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of a Transitional Care Program for Patients Discharged from Military Hospitals
Seun Young Joe
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2010; 40(4): 599. CrossRef - Predictors of maternal sensitivity during the early postpartum period
Hyunjeong Shin, Young‐Joo Park, Mi Ja Kim
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2006; 55(4): 425. CrossRef
- Concept analysis of transition to motherhood: a methodological study
- 711 View
- 2 Download
- 6 Crossref

- Situational Meaning and Maternal Self-esteem in Mothers with High Risk Newborn
- Hyun Jeong Shin
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2004;34(1):93-101. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2004.34.1.93
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was designed to explore the relationship of situational meaning with maternal self-esteem in mothers with high risk newborn.
Method The subjects of this study were 82 mothers with high risk newborn. Data were collected using a translated Family Meaning Attribution Scale and Maternal Self-Report Inventory. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, t-test, Pearson Correlation Coefficients and Stepwise Multiple Regression.
Result The average score of the situational meaning in high risk newborn mothers was 64.01(possible score is between 0-96) and the average score of each item was 1.98. The average score of the maternal self-esteem in high risk newborn mothers was 81.96(possible score is between 26-104) and the average score of each item was 3.15. No significant differences were found in situational meaning according to general characteristics except whether it was a planned pregnancy or not. No significant differences were found in maternal self-esteem according to general characteristics except disease or admission experience during pregnancy. There was significant positive correlation between situational meaning and maternal self-esteem.
Conclusion It is necessary for nurses to provide high risk newborn mothers with care for improving situational meaning that is attributed to the mothers. It can be helpful to improve maternal self-esteem and in the end it will facilitate the maternal transition in mothers with high risk newborn.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Exploration of the process of maternal role attainment in Iranian mothers with preterm neonate: A grounded theory
Mona Alinejad-Naeini, Mahnaz Shoghi, Hamid Peyrovi
Journal of Human Behavior in the Social Environment.2023; 33(1): 44. CrossRef - Stress, postpartum depression, and anxiety in mothers of neonates admitted in the NICU: A cross-sectional hospital-based study
Dikshita Garg, Suprakash Chaudhury, Daniel Saldanha, Santosh Kumar
Industrial Psychiatry Journal.2023; 32(1): 48. CrossRef - Childbearing culture: a prominent context in the process of maternal role attainment in Iranian mothers with preterm neonates
Mona Alinejad-Naeini, Hamid Peyrovi, Mahnaz Shoghi
Journal of Biosocial Science.2022; 54(6): 1035. CrossRef - The Relationship between Parental Stress and Nurses' Communication as Perceived by Parents of High-risk Newborns
Chang Hee Lee, Mi Heui Jang, Yong Sung Choi, Hyunsook Shin
Child Health Nursing Research.2019; 25(2): 184. CrossRef - Impact of a health education tool on enhancing communication between health providers and parents of neonates in intensive care in Egypt
Mohamed S. Hesham, Yasmin Mansi, Tamer A. Abdelhamid, Rehan M. Saleh
Journal of the Chinese Medical Association.2016; 79(7): 394. CrossRef - Nursing Needs of the Parents of Infants in Neonatal Intensive Care Unit
Ji-Sun Park, Kyung-Sook Bang
Journal of East-West Nursing Research.2014; 20(2): 136. CrossRef - The conceptual structure of transition to motherhood in the neonatal intensive care unit
Hyunjeong Shin, Rosemary White‐Traut
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2007; 58(1): 90. CrossRef
- Exploration of the process of maternal role attainment in Iranian mothers with preterm neonate: A grounded theory
- 780 View
- 1 Download
- 7 Crossref

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 First
First Prev
Prev


