Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Research Paper
- The experiences of infertile women discontinuing in vitro fertilization treatment: a grounded theory approach
- Eunmi Park, Yeoungsuk Song
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(3):440-453. Published online August 11, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25048
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to develop a situation-specific theory by gaining an in-depth understanding of the deterrent processes experienced by infertile women who have discontinued in vitro fertilization (IVF) procedures, within the socio-cultural context of South Korea.
Methods
The participants were 16 infertile women who discontinued IVF procedures. Data were collected through individual in-depth interviews from February to December 2023. Theoretical sampling was conducted, and the transcribed interview contents were analyzed using Strauss and Corbin’s grounded theory method.
Results
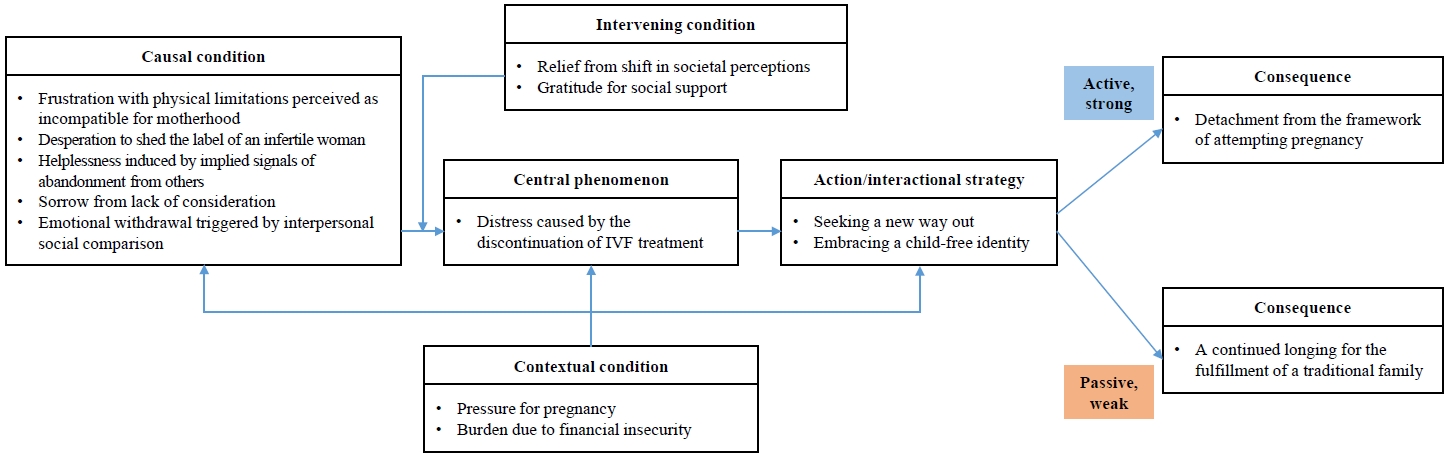
In total, 37 concepts and 14 categories were extracted through the open coding process. The central phenomenon in axial coding was “Distress caused by the discontinuation of IVF treatment.” The core category was “A journey to break free from the identity of infertility toward self-determined womanhood.” The results were categorized into two types: “Detachment from the framework of attempting pregnancy” and “A continued longing for the fulfillment of a traditional family.” The situation-specific theory was the “Theory of reconstructing subjective identity through the acceptance of childfree life,” which illustrates how infertile women actively redefine their life trajectories after discontinuing IVF treatment.
Conclusion
This study highlights the importance of public perceptions about infertile women who discontinue IVF procedures, which are seen as the last resort of assisted reproductive technology, because positive perceptions assists women in living a self-governing life. It may be necessary to develop educational and promotional programs to change negative social perceptions and to establish a psycho-social support system for infertile women who have been deterred from IVF procedures.
- 1,413 View
- 111 Download

Review Article
- Effects of First Assisted Reproductive Technologies on Anxiety and Depression among InfertileWomen: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Ju-Young Ha, Seon-Hwa Ban, Hae-Jung Lee, Misoon Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(3):369-384. Published online June 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.19187
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to analyze anxiety and depression among infertile women at different time points during the firstIn Vitro Fertilization (IVF) or Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI) treatment through a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Methods
Seven out of 3,011 studies were included for meta-analysis. To estimate the effect size, a meta-analysis of the studies was performedusing the RevMan 5.3 program. We compared the measurement outcomes at three time points: before the start of treatment (T0), cancellationof treatment after pregnancy detection (T2), one to six months after treatment (T3). The effect size used was the standardizedmean difference (SMD).
Results
In comparing the different time points of the pregnant women from their cycle, significantly lower levelsof depression were found at T2 than at T0. In non-pregnant women, anxiety at T2 and depression at T2 and T3 were significantly higherthan those at T0. At T2 and T3, the non-pregnant women reported higher levels of anxiety and depression compared with the pregnantwomen.
Conclusion
Anxiety and depression in infertile women undergoing the first IVF or ICSI are associated with the time points andpregnancy status after treatment. These findings suggest that attention should be paid to helping infertile women prepare for and copewith treatment and treatment failure. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Stress on Each of the Stages of the IVF Procedure: A Systematic Review
Anastasia Tsambika Zanettoullis, George Mastorakos, Panagiotis Vakas, Nikolaos Vlahos, Georgios Valsamakis
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(2): 726. CrossRef - An Integrative Review of Psychosocial Intervention Programs for Infertile Females
Youjin Shin, Soo-Hyun Nam
STRESS.2023; 31(4): 158. CrossRef - The dynamics of mental health measures of pre- and postpartum women undergoing assisted reproductive technology
Maria E. Blokh, Varvara O. Anikina, Svetlana S. Savenysheva, Maria I. Levintsova
Journal of obstetrics and women's diseases.2023; 72(1): 17. CrossRef
- Effect of Stress on Each of the Stages of the IVF Procedure: A Systematic Review
- 1,386 View
- 36 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 First
First Prev
Prev


