-
Development and evaluation of a question-answering chatbot to provide information for patients with coronary artery disease after percutaneous coronary intervention
-
Geunhee Lee, Yun Hee Shin
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(2):153-164. Published online May 13, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24128
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF ePub ePub
- Purpose
This study aimed to develop a question-answering chatbot that provides accurate and consistent answers to questions that may arise during the recovery process of patients with coronary artery disease after percutaneous coronary intervention, and to evaluate the chatbot.
Methods
The chatbot was developed through the stages of analysis, design, implementation, and evaluation. It was evaluated by five experts, and the user experience was evaluated by 27 patients who underwent percutaneous coronary intervention. Furthermore, chatbot utilization was analyzed based on user experience logs.
Results
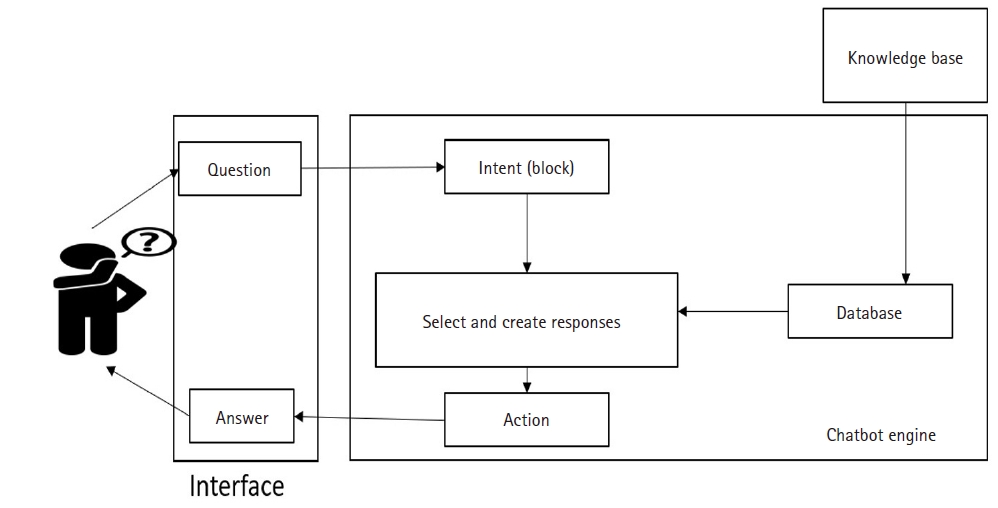
The chatbot was constructed as a question-answering database that included three categories: coronary artery disease, percutaneous coronary intervention, and post-intervention management. The question-answering chatbot, referred to as the “Cardiovascular Strong” channel, has been launched and implemented. An expert evaluation of the chatbot revealed no usability issues or necessary modifications. The overall result of the user experience evaluation was 4.26 points. Based on the user experience log, the question-answer accuracy was 84.6%, and medications during post-intervention management were the most frequently searched topic, accounting for 110 cases (20.8%) out of a total of 528.
Conclusion
The chatbot that was developed to provide information via real-time answers to questions after the intervention can be easily accessed in clinical settings with no time or space constraints. It also will contribute to providing accurate disease-related information via the familiar KakaoTalk platform.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Generative AI at the Bedside: An Integrative Review of Applications and Implications in Clinical Nursing Practice
Adrianna L. Watson, Carmel Bond, Helen Aveyard, Graeme D. Smith, Debra Jackson
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
-
2,373
View
-
249
Download
-
1
Web of Science
-
1
Crossref
-
Effects of Self-directed Feedback Practice using Smartphone Videos on Basic Nursing Skills, Confidence in Performance and Learning Satisfaction
-
Seul Gi Lee, Yun Hee Shin
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2016;46(2):283-292. Published online April 29, 2016
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2016.46.2.283
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
-
Purpose
This study was done to verify effects of a self-directed feedback practice using smartphone videos on nursing students' basic nursing skills, confidence in performance and learning satisfaction.
Methods
In this study an experimental study with a post-test only control group design was used. Twenty-nine students were assigned to the experimental group and 29 to the control group. Experimental treatment was exchanging feedback on deficiencies through smartphone recorded videos of nursing practice process taken by peers during self-directed practice.
Results
Basic nursing skills scores were higher for all items in the experimental group compared to the control group, and differences were statistically significant ["Measuring vital signs" (t=-2.10, p=.039); "Wearing protective equipment when entering and exiting the quarantine room and the management of waste materials" (t=-4.74, p<.001) "Gavage tube feeding" (t=-2.70, p=.009)]. Confidence in performance was higher in the experimental group compared to the control group, but the differences were not statistically significant. However, after the complete practice, there was a statistically significant difference in overall performance confidence (t=-3.07. p=.003). Learning satisfaction was higher in the experimental group compared to the control group, but the difference was not statistically significant (t=-1.67, p=.100).
Conclusion
Results of this study indicate that self-directed feedback practice using smartphone videos can improve basic nursing skills. The significance is that it can help nursing students gain confidence in their nursing skills for the future through improvement of basic nursing skills and performance of quality care, thus providing patients with safer care.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Challenges in educating nursing students on mechanical ventilation: the case for interactive mobile learning tools – a randomized controlled trial
Alireza Samimi Sarangi, Kolsoum Deldar, Ahmad Bagheri Moghaddam, Razieh Froutan
BMC Nursing.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Expanding virtual reality simulation with reflective learning to improve mental health nursing skills of undergraduate nursing students
Sun Kyung Kim, Mihyun Lee, Youngho Lee, Younghye Go, Mi Hyeon Park
Education and Information Technologies.2025; 30(7): 8541. CrossRef - The impact of training using six thinking hats versus video training on nursing students’ insulin administration skills: a mixed-methods study
Ayşe Soylu, Ahmet Seven, Dilek Soylu
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The effects of flipped learning and mobile learning methods on nursing students’ knowledge, skills and self-efficacy in urinary catheterization: A randomized controlled trial
Ozan Konateke, Hakime Aslan
Nurse Education in Practice.2025; 89: 104593. CrossRef - Effect of a Hybrid Simulation-based Patient Safety Education Program on Patient Safety Knowledge, Attitudes, Performance Confidence and Decision-Making Abilities in Undergraduate Nursing Students
Hyun-Sook Jeong, Mi Yang Jeon
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2025; 32(4): 432. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of Nursing Clinical Practice Education Using M-Learning
Sungeun Kim, Mihae Im
Healthcare.2024; 12(2): 206. CrossRef - Development and Effects of Metaverse-Based Intradermal Injection Content for Nursing Students
Min-Kweon Ahn
Journal of Digital Contents Society.2024; 25(9): 2543. CrossRef - Dental hygienists' knowledge, performance confidence and awareness of importance of assessing oral cancer risk factors
Boguen Lee, Sojung Mun
International Journal of Dental Hygiene.2024; 22(4): 998. CrossRef - The Development and Effects of Metaverse-based Core Nursing Skill Contents (CNSC) for Nursing Students: Drainage Management
Min Kweon Ahn, Min Jeong Chae
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2024; 31(4): 447. CrossRef - Akıllı Telefon Bağımlılığı ve Ruh Hali Düzenlemenin Akış Deneyimi Aracılığı ile Çevrimiçi Anlık Satın Alma Davranışındaki Rolü
Özsev Berk, Remzi Altunışık, Nilgün Sarıkaya
Abant Sosyal Bilimler Dergisi.2024; 24(2): 780. CrossRef - Effectiveness of a virtual reality application‐based education programme on patient safety management for nursing students: A pre‐test–post‐test study
Jae Woo Oh, Ji Eun Kim
Nursing Open.2023; 10(12): 7622. CrossRef - Clinical Practice Experience of Nursing Students in the Context of the COVID-19 Pandemic
Hyeon-Young Kim, Eun-Hye Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2022; 29(1): 45. CrossRef - The development and effects of metaverse-based core nursing skill contents of vital signs measurements and subcutaneous injections for nursing students
Min Kweon Ahn
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2022; 28(4): 378. CrossRef - Development and application of a mobile-based multimedia nursing competency evaluation system for nursing students: A mixed-method randomized controlled study
Soyoung Jang, Eunyoung E. Suh
Nurse Education in Practice.2022; 64: 103458. CrossRef - Effects of a Self-Directed Clinical Practicum on Self-Confidence and Satisfaction with Clinical Practicum among South Korean Nursing Students: A Mixed-Methods Study
Hyangjin Park, Haeryun Cho
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(9): 5231. CrossRef - Effects of mobile learning for nursing students in clinical education: A meta-analysis
Bin Chen, Yan Wang, Lei Xiao, Changxia Xu, Yuan Shen, Qin Qin, Cheng Li, Fengqin Chen, Yufei Leng, Ting Yang, Zhiling Sun
Nurse Education Today.2021; 97: 104706. CrossRef - Interactive and non-interactive e-learning in prenatal care
Mehrnaz Geranmayeh, Zinat Keshtkar Bareghany, Mitra Zolfghari, Farahnaz Azizi
British Journal of Midwifery.2021; 29(10): 564. CrossRef - The Effects of Video Instruction on Neuroscience Intensive Care Unit Nursing Skills in Case Presentations and Neurological Examinations
K. H. Vincent Lau, Emily Hamlyn, Thomas James Williams, M. Mustafa Qureshi, Kimberly Mak, Asim Mian, Anna Cervantes-Arslanian, Shuhan Zhu, Courtney Takahashi
Journal of Neuroscience Nursing.2021; 53(3): 129. CrossRef - Development, Application, and Effectiveness of a Smart Device-based Nursing Competency Evaluation Test
Soyoung Jang, Eunyoung E. Suh
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2021; 39(11): 634. CrossRef - Effects of Education on the Use of Personal Protective Equipment for Reduction of Contamination: A Randomized Trial
Jeong Hwa Yeon, Yong Soon Shin
SAGE Open Nursing.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of video feedback system on medical students’ perception of their clinical performance assessment
Bee Sung Kam, So Jung Yune, Sang Yeoup Lee, Sun Ju Im, Sun Yong Baek
BMC Medical Education.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Nursing Students' Peer Feedback Types and Emotional Response, Quality of Feedback, and Self-efficacy for Learning from Peer Feedback in Skill Training
Young A Park, Eun Jung Kim
Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2019; 25(2): 186. CrossRef - Effects of Smartphone-Based Mobile Learning in Nursing Education: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Ju Hee Kim, Hanjong Park
Asian Nursing Research.2019; 13(1): 20. CrossRef - Nursing students' experiences of using a smart phone application for a physical assessment course: A qualitative study
Li‐Ling Hsu, Hsiu‐Chuan Hsiang, Yi‐Hua Tseng, Siang‐Yun Huang, Suh‐Ing Hsieh
Japan Journal of Nursing Science.2019; 16(2): 115. CrossRef - Effect of Learning Core Fundamental Nursing Skill with Social Network Service (SNS) for Nursing Students in South Korea
HyeSun Jeong, Hyuksoo Kwon, Jeonghwa Kum
EURASIA Journal of Mathematics, Science and Technology Education.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effects of an Interactive Nursing Skills Mobile Application on Nursing Students' Knowledge, Self-efficacy, and Skills Performance: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Hyunsun Kim, Eunyoung E. Suh
Asian Nursing Research.2018; 12(1): 17. CrossRef - Trends and research issues of mobile learning studies in nursing education: A review of academic publications from 1971 to 2016
Ching-Yi Chang, Chiu-Lin Lai, Gwo-Jen Hwang
Computers & Education.2018; 116: 28. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Education Program Using Video Recording and Feedback on Skill Competency for Students of Majors in Health Care: A Meta-Analysis
Yun Hee Shin, Sun Kyung Kim, Hyunjoo Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2018; 25(2): 120. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Self-directed Learning on Competency in Physical Assessment, Academic Self-confidence and Learning Satisfaction of Nursing Students
Yun Hee Shin, Jihea Choi, Margaret J. Storey, Seul Gi Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2017; 24(3): 181. CrossRef - The Effect of Smartphone Video Educational Program on Educational Satisfaction of Patients in Rehabilitation Units at a University Hospital
Kyeong- Man Jung, Min-Cheol Joo, Yu-Jin Jung, Hee-Han Kim, Kyeong-Hwa Lee, Dong-Sun Lee, Jun-Wan Choi
Quality Improvement in Health Care.2017; 23(1): 43. CrossRef - A Study on Nursing Students’ Knowledge, Attitude, Confidence in Performance and Behavior of Patient Safety
Suk-Hyun SON, Jeong Sook PARK
JOURNAL OF FISHRIES AND MARINE SCIENCES EDUCATION.2017; 29(4): 1043. CrossRef
-
1,610
View
-
28
Download
-
31
Crossref
-
Impact of Bowel Function, Anxiety and Depression on Quality of Life in Patients with Sphincter-preserving Resection for Rectal Cancer
-
Hyun Jun Kwoun, Yun Hee Shin
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2015;45(5):733-741. Published online October 30, 2015
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2015.45.5.733
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
-
Purpose
This study was a descriptive survey research to identify the impact of bowel function, anxiety and depression on quality of life in patients with rectal cancer who had a sphincter-preserving resection.
Methods
articipants were 100 patients who had rectal cancer surgery at W hospital in Korea. Bowel function, anxiety & depression, and quality of life were measured using the BFI (Bowel Function Instrument), HADS (Hospital Anxiety-Depression Scale) and the FACT-C (Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy-Colorectal).
Results
The mean scores were 39.81±5.16 for bowel function, 6.15±3.25 for anxiety, 7.24±3.13 for depression, and 72.50±13.27 for quality of life. There were significant negative correlations between quality of life and anxiety (r= -.59, p <.001) and between quality of life and depression (r= -.53, p <.001). But the correlation between quality of life and bowel function was significantly positive (r=.22, p =.025). The influence of the independent variables on the total quality of life was examined using multiple regression analysis. Anxiety (β= -.38, p =.002), bowel function (β= -.25, p =.028) and occupation (β=.16, p =.048) were identified as factors affecting quality of life. The explanation power of this regression model was 44% and it was statistically significant (F=16.53, p <.001).
Conclusion
The results of this study indicate that in order to improve the bowel function of patients after sphincter-preserving resection for rectal cancer, effective nursing interventions should be developed. As psychological problem such as anxiety and depression can relate to quality of life for these patients, nurses should work on improving the situation by providing continuous emotional nursing.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Lack of Regular Access to Primary Care Physician Associated With Increased Emergency Department Visits Related to Survivorship Needs Among Rectal Cancer Survivors
Jeongyoon Moon, Ebram M. Salama, Anna Y. Wang, Mylène Arsenault, Nathalie Leon, Carmen G. Loiselle, Fateme Rajabiyazdi, Marylise Boutros
Diseases of the Colon & Rectum.2024; 67(12): 1536. CrossRef - Major Low Anterior Resection Syndrome (LARS) and Quality of Life in Patients With Low Rectal Cancer: A Preoperative Survey Using LARS Score and European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer’s 30-Item Core Quality of Life Questionnaire
Ly Huu Phu, Ho Tat Bang, Nguyen Viet Binh, Hoang Danh Tan, Ung Van Viet, Nguyen Trung Tin
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Low Anterior Resection Syndrome in a Reference North American Sample: Prevalence and Associated Factors
Jeongyoon Moon, Alexa Ehlebracht, Michelle Cwintal, Julio Faria, Gabriela Ghitulescu, Nancy Morin, Allison Pang, Carol-Ann Vasilevsky, Marylise Boutros
Journal of the American College of Surgeons.2023; 237(5): 679. CrossRef - The Relationships among Social Support, Bowel Function Symptoms and Uncertainty in Rectal Cancer Patients
Kyungmi Lee, Semi Lim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2021; 28(4): 421. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Supportive Care Needs of Colorectal Cancer Survivors
Hyekyung Kim, Yang-Sook Yoo
Asian Nursing Research.2021; 15(1): 60. CrossRef - Effectiveness and safety of acupuncture and moxibustion for defecation dysfunction after sphincter-preserving surgery for rectal cancer: protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis
Guixing Xu, Qiwei Xiao, Hanzhou Lei, Yanan Fu, Jing Kong, Qianhua Zheng, Ling Zhao, Fanrong Liang
BMJ Open.2020; 10(5): e034152. CrossRef - Psychosocial behaviour reactions, psychosocial needs, anxiety and depression among patients with rectal cancer before and after colostomy surgery: A longitudinal study
Ying Jin, Jing Zhang, Mei‐Chun Zheng, Xiu‐Qing Bu, Jun‐E Zhang
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2019; 28(19-20): 3547. CrossRef - Predictors of Quality of Life and Social Support as a Mediator between Defecation Function and Quality of Life among Rectal Cancer Patients
Jung Rang Kim, Seon Young Hwang
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2019; 31(5): 487. CrossRef
-
1,070
View
-
7
Download
-
8
Crossref
-
Development and Psychometric Evaluation of a Scale to Measure Health Behaviors of Adolescents
-
Yun Hee Shin
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2010;40(6):820-830. Published online December 31, 2010
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2010.40.6.820
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
-
Purpose
The purpose was to develop a preliminary scale to measure Korean adolescents' health behaviors through a qualitative approach, to evaluate the scale psychometrically, and to develop a final scale.
Methods
Participants were 61 adolescents for qualitative interviews and 1,687 adolescents for the psychometric evaluation. Procedure included content analysis of interviews to identify health behavior categories for Korean adolescents, pre-test to confirm that preliminary scale items were understandable, content validity by an expert panel, development of the web-based computer-assisted survey (CAS), and psychometric analysis to determine reliability and validity of the final scale.
Results
A final scale was developed for both paper-and-pencil and CAS. It consisted of 14 health behaviors (72 items), including stress and mental health (10), sleep habits (5), dietary habits (12), weight control (4), physical activity (4), hygiene habits (5), tobacco use (5), substance use (2), alcohol consumption (4), safety (4), sexual behavior (9), computer use (3), health screening (4), and posture (1).
Conclusion
The scale's strong points are: 1) Two thirds of the final scale items are Likert scale items, enabling calculation of a health behavior score. 2) The scale is appropriate to Korean culture. 3) The scale focuses on concrete health behaviors, not abstract concepts.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - The Moyamoya Health Behavior Scale for Adolescent Patients: Measurement Tool Development and Psychometric Evaluation
Won-oak Oh, Insun Yeom, Sung-Hyun Lim, Dong-Seok Kim, Kyu-won Shim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(8): 4064. CrossRef - Health Behaviors and Related Demographic Factors among Korean Adolescents
YunHee Shin, Sook Jung Kang
Asian Nursing Research.2014; 8(2): 150. CrossRef - Health Behaviors among Korean Adolescents: A Content Analysis
Yun Hee Shin, Jihea Choi
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2014; 14(3): 83. CrossRef - Lecturers’ Performance and Technology at Private Higher Education in South Sulawesi Indonesia
Sanusi Hamid
Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences.2013; 83: 580. CrossRef - Effects of a Mentoring Program on Stress and Self-esteem for Middle School Girls of Low Income Families
Yun Hee Shin, Jee Hae Lee, So Young Lee, Kyeung Min Lim, Sook Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2012; 21(3): 220. CrossRef - The Reliability and Validity of the Personal Competence of Health Care (PCHC) Scale
Kyung-Sook Lee, Jung-Sook Choi, Ae-Young So, Eun-Hee Lee
Journal of muscle and joint health.2012; 19(2): 197. CrossRef
-
1,143
View
-
6
Download
-
6
Crossref
-
Development of a Mentoring Program to Improve Exercise and Dietary Habits of Adolescents
-
Yun Hee Shin, Soo Hyun Ahn, Joo Rim Ahn, Go Woon Yang, Sook Kyung Oh
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2007;37(5):703-714. Published online March 28, 2017
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2007.37.5.703
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
-
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effects of a mentoring program to improve the exercise and dietary habits of adolescents.
Methods
A non-equivalent control group, pretest-posttest design was used. The independent variable was a mentoring program for improvement of exercise and dietary habits of adolescents, in which the mentors were nursing students and the mentees were female middle school students. The dependent variables were weekly exercise frequency, weekly exercise time, perception of exercise benefit, frequency of vegetable intake, and dietary habits. The intervention was conducted by various methods such as group education, individual approach through the mentor-mentee relationship, and multimedia approaches.
Results
At follow-up, the perception of the exercise benefit was significantly greater in the intervention group than in the control group. The weekly exercise frequency and frequency of vegetable intake in the intervention group were significantly greater after the intervention than those before the intervention.
Conclusion
This mentoring program is potentially of an effective health promotion program for adolescents and will enable nursing students who participate in the program as mentors to gain confidence in their professional capability.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Role of sports activities in developing the important life skill of decision making; a psychological perspective
Wasim Khan, Salahuddin Khan, Tasleem Arif, Sohail Roman Khan
Physical education of students.2018; 23(4): 179. CrossRef - Development of the Pregnancy Nutrition Knowledge Scale and Its Relationship with Eating Habits in Pregnant Women visiting Community Health Center
Hae Won Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(1): 33. CrossRef
-
773
View
-
1
Download
-
2
Crossref
-
The Effects of a Sex Education Program on Knowledge Related to Sexually Transmitted Diseases and Sexual Autonomy among University Students
-
Yun Hee Shin, Young Kyung Chun, Sung Mi Cho, Ye Ryung Cho
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2005;35(7):1304-1313. Published online March 28, 2017
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2005.35.7.1304
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
-
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effects of a sex education program, which was based on the Health Belief Model, on knowledge related to sexually transmitted diseases and sexual autonomy among university students.
Methods
A non-equivalent control group, pretest-posttest design was used. The four session program was delivered to 18 students during 4 weeks; the control group consisted of 23 students. The theme of the first session was “sex, gender, and sexuality: all our concern”, “dangerous sex” for the second session, “safe sex” for the third session, and “right sex for you and me” for the fourth session.
Results
At follow-up, the knowledge related to sexually transmitted diseases and sexual autonomy were significantly greater in the intervention group than in the control group.
Conclusion
A sex education program with several sessions within the theoretical frame of HBM was effective to improve knowledge related to sexually transmitted diseases and sexual autonomy. The results suggest the potential of a systematic sexual education program to teach healthy sex and to extend the program for other various populations.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - User-centered design to enhance university students’ sex and menstrual education in South Korea: randomized controlled trial
Hana Kim, Ji Woon Ko, Doyon Kim, Nagyeom Yoon, Jisan Lee
BMC Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - An Integrative Literature Review on Sex Education Programs for Korean College Students
Hyewon Shin, Jung Lee, Hye Min
Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2020; 26(1): 78. CrossRef - Gender Difference in Mediating Effects of Self-Efficacy for the Prevention of Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STD) among College Students' STD Knowledge, Susceptibility, and Sexual Autonomy
Mijeong Park
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2016; 28(4): 482. CrossRef - Affecting Factors Sexual Experience Among College Students
Ae Hwa Jaung, Yu Jin Jung, Min Young Kim
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2015; 16(1): 555. CrossRef - Effects of sexual autonomy enhancement program for university students in South Korea
Ju-Eun Song, So Mi Park, Jeongok Park, Hyun Ju Chae
Journal of Public Health.2014; 22(2): 165. CrossRef - Knowledge on Cardiovascular Prevention and Nicotine Dependency among Smoking Male College Students
Seon Young Hwang, Kyongok Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2014; 25(2): 75. CrossRef - Effect of Sexual Education Program on Female College Student's Sexual Knowledge and Sexual Autonomy
Nami Chun
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2012; 18(2): 108. CrossRef - Self-Efficacy and Sexual Autonomy among University Students
Kyung-Won Kim, Kyeong-Hwa Kang, Geum-Hee Jeong
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2012; 26(1): 51. CrossRef - A Mentoring Program for the Promotion of Sexual Health Among Korean Adolescents
YunHee Shin, Lynn Rew
Journal of Pediatric Health Care.2010; 24(5): 292. CrossRef
-
873
View
-
14
Download
-
9
Crossref
-
Content Analysis of the Experience of Preceptors in Clinical Education for Senior Student Nurses
-
Hea Kung Hur, Sang Soon Choi, Yang Heui Ahn, Young Mi Lim, Yun Hee Shin, So Mi Park, Gi Yon Kim, Hee Young Song
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2004;34(5):859-868. Published online March 28, 2017
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2004.34.5.859
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
-
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to identify experiences of nurses who served as preceptors in clinical education for senior student nurses in a college of medicine in Wonju city.
Method
Data was collected from 20 preceptors instructing senior student nurses in 2001 using a self-completion questionnaire. To analyze data, content analysis was done using an analysis scheme developed by the investigators.
Result
The analysis scheme consisted of 7 categories and 25 subcategories. 135 significant statements were analyzed and categorized. Preceptors indicated that they were role models, socialization facilitators and educators while instructing students in the clinical practicum. In performing the preceptors' role, preceptors reported that their most important change was self-enhancement,and positive experience was a constructive work atmosphere. The most important factor facilitating the preceptors' role performance was support from head nurses, and the most discouraging factor was work loads.
Conclusion
This study suggests that interventions for encouragement and socialization of preceptors should be developed to promote clinical education for senior student nurses.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Development of a field training instructor model through analysis of satisfaction and dissatisfaction factors of field training for dental technology students
Sun-Kyoung Lee
Journal of Korean Acedemy of Dental Technology.2024; 46(4): 174. CrossRef - Effect of Nurses’ Preceptorship Experience in Educating New Graduate Nurses and Preceptor Training Courses on Clinical Teaching Behavior
Kyung Jin Hong, Hyo-Jeong Yoon
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(3): 975. CrossRef - Clinical Instructors' Role Experience in College of Nursing
Hyunju Kang, Kyung-Sook Bang, Ji-Sun Park, Juyoun Yu, Inju Hwang
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2014; 20(3): 443. CrossRef - Study on Clinical Education for Nursing in Hospitals in Korea
Jiho Song, Miwon Kim
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2013; 19(2): 251. CrossRef - The Role Experience of Preceptor Nurses in Hospitals
Se Young Kim, Jong Kyung Kim, Kwang-Ok Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2012; 18(1): 33. CrossRef - Clinical Track Faculty: Merits and Issues
Won-Hee Lee, Cho Ja Kim, Young Sook Roh, Hyunsook Shin, Mi Ja Kim
Journal of Professional Nursing.2007; 23(1): 5. CrossRef
-
786
View
-
3
Download
-
6
Crossref
-
The Correlational Analysis between Perceived Heath Status, Self-Esteem, and Self-Care Agencies among Adolescents
-
Hee Jung Jang, Yun Hee Shin
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2002;32(2):186-195. Published online March 29, 2017
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2002.32.2.186
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
PURPOSE: This study was to identify and clarify the relationship between perceived health, self-esteem, and self-care agencies for promoting self care among Korean adolescents.
METHOD: Data were collected from 817 adolescents in schools located in Seoul, Kyungki-do, and Chuncheon from Sept, 16th to Sept, 28th, 1999, and from Mar 10th to Mar 25th, 2000. The instruments used for this study were the Health Self-Rating Scale, Self-Care Agency Assessment Questionnaire (Denyes, 1981), the Self-Esteem Questionnaire (Rosenberg, 1971).
RESULT: 1) The mean perceived health status among Korean adolescents was 8.75 (SD=1.72) 2) The mean self-esteem was 27.27 (SD=4.64). 3) The mean self-care agency was 99.64 (SD=21.02) and the average self-care agency score was 3.99 (SD=0.84). In the subcategories, the highest degree was feelings towards health (4.15), followed by ego strength (4.06), attending to health (3.87), general health knowledge (3.56), and the lowest degree was specific health knowledge (3.20) 4) There was statistical significant differences between demographic factors and self-care agencies, expecially, gender (t=28.65), grade (F=3.79), pocket money (t=5.72), and height (F=9.82) 5) The statistical relationship between perceived health status, self-esteem, and self-care agencies were found to have a positive correlation. 6) Self-care agencies among adolescents was the highest factor predicting self-esteem (15%).
CONCLUSION: The relationship between perceived health status, self-esteem, and self-care agencies revealed a significant positive correlation among adolescents. Therefore, nursing intervention for adolescents needs to develop self-esteem programs to increase self-care agencies. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - The relationship between self-esteem and overall health behaviors in Korean adolescents
Junghyun Park, Young-Ho Kim, Seon-Joo Park, Sooyeon Suh, Hae-Jeung Lee
Health Psychology and Behavioral Medicine.2016; 4(1): 175. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Perceived Health among Korean Adolescents
JongSerl Chun, Sunghee Nam, Ick-Joong Chung, Hyunah Kang, Choong Rai Nho, Seokjin Woo
Social Work in Public Health.2014; 29(6): 528. CrossRef - Relationship between Health Status and Life Styles and Atopic Dermatitis in Adolescents
Eun-Sun So, Ji-Young Yeo
Journal of Korean Academy of Child Health Nursing.2012; 18(3): 143. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Health Risk Behavior in High School Students
Jin Choi, Mi-Ye Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Child Health Nursing.2009; 15(2): 182. CrossRef
-
724
View
-
4
Download
-
4
Crossref
-
Perceived Exercise Self-Efficacy and Exercise Benefits/Barriers of Korean Adults with Chronic Diseases
-
Yun Hee Shin, Hee Jung Jang
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(4):869-879. Published online March 29, 2017
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.4.869
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
The purpose of this study was to assess the perceived exercise self-efficacy and exercise benefits/barriers of
Korean adults with chronic diseases, and the relationship between the two variables. For the study, 249 Korean
adults with chronic diseases with ages ranging from 18 to 79 years were recruited from hospitals or health centers
in five Korean cities and surrounding rural areas. The research instruments were the scales that researchers
psychometrically verified the Exercise Self-Efficacy Scale, developed by Bandura (1997), and the Exercise Benefits/
Barriers Scale, developed by Sechrist, Walker, and Pender(1987). Results of descriptive analysis showed that Korean
adults with chronic diseases perceived relatively low exercise self-efficacy and relatively high exercise benefits/ barriers.
Exercise self-efficacy was significantly correlated with gender, education, regular exercise, and exercise
benefits/barriers was significantly correlated with gender, regular exercise. Pearson correlation coefficient showed the
significant relationship between the two variables. Further researches, which are a study to evaluate a causal
structure for Pender's Health Promotion Model and an intervention study to increase physical activity of chronic
patients, are recommended. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Factors Influencing Physical Activity after Discharge from Hospital for Total Hip Arthroplasty Patients
Ju Young Kim, Mi Yang Jeon
Physical Therapy Rehabilitation Science.2022; 11(4): 535. CrossRef - A Pilot Primary Stroke Prevention Program for Elderly Korean Americans
Minjeong An, Eun-Shim Nahm, Marianne Shaughnessy, Carla L. Storr, Hae-Ra Han, JuHee Lee
Journal of Neuroscience Nursing.2018; 50(6): 327. CrossRef - The Relationship between Health Belief and Exercise Compliance among Elderly Adults at Senior Centers
Kyung Im Lee, Young Eun
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2015; 26(2): 79. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Exercise Behavior of the Male Manual Worker and Office Worker based on Health Promotion Model
SeungKyoung Yang, Yeongmi Ha, Mi-Ra Jung
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2015; 24(3): 235. CrossRef - The Effects of Task-Oriented Training Program on Balance, Activities of Daily Living Performance and Self-Efficacy in Stroke Patients : A Pilot Study
Jinuk Choi, Soonhee Kang
Journal of The Korean Society of Integrative Medicine.2013; 1(4): 15. CrossRef - Influences of oral health behaviors according to oral health education experiences in middle school students
Mi-Sook Cho, Min-Kyung Park, Kyeung-Ae Jang
Journal of Korean society of Dental Hygiene.2013; 13(4): 639. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Fear of Falling in Stroke Patients
Hee-Sook Jeong, Eun-Nam Lee, Sam-Sook Kim
Journal of muscle and joint health.2011; 18(2): 215. CrossRef - A Predictive Model on Health Promotion Behavior in Women who Immigrate for Marriage
Namok Jeong, Myung Ha Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2010; 40(5): 695. CrossRef - Gender differences in physical activity and its determinants in rural adults in Korea
Hyun Kyung Kim, Mi Ja Kim, Chang Gi Park, Hyeon Ok Kim
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2010; 19(5-6): 876. CrossRef - Health Locus of Control, Exercise Self-efficacy, and Exercise Benefits/Barriers of Female College Students
Ju Young Ha
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2010; 16(2): 116. CrossRef - Effects of the Exercise Self-Efficacy and Exercise Benefits/Barriers on doing Regular Exercise of the Elderly
Eun-Hee Hwang, Yeo-Sook Chung
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(3): 428. CrossRef - Exercise self-efficacy, exercise benefits and barriers, and commitment to a plan for exercise among Korean women with osteoporosis and osteoarthritis
Yun Hee Shin, Hea Kung Hur, Nola J. Pender, Hee Jung Jang, Moon-Sil Kim
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2006; 43(1): 3. CrossRef - Test of the health promotion model as a causal model of commitment to a plan for exercise among Korean adults with chronic disease
YunHee Shin, SangKyun Yun, Nola J. Pender, HeeJung Jang
Research in Nursing & Health.2005; 28(2): 117. CrossRef
-
822
View
-
9
Download
-
13
Crossref
-
A Study on Verification of the Profile of Mood States(POMS) for Korean Elders
-
Yun Hee Shin
-
Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1996;26(4):743-758. Published online March 30, 2017
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1996.26.4.743
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
This paper was done to verify the use of the Profile of Mood States (POMS) which was developed by McNair, Lorr, and Droppleman(1992) with modifi cations so that it is appropriate for Korean elders. Through the modified tool, it is possible to examine the mood of Korean elders and to contribute to the welfare of elders. The subjects were 370 elderly persons over 60 years old and the data for 319 persons(86%) were analyzed. The research tool was the POMS translated by Yun(1993) and corrected by the researcher. Data were collected between February 12 and April 9 in 1996 and analyzed using the SAS package. The result are as follows: 1. Items with low Cronbach coefficient alpha which means low correlation with total items were removed. The items were removed; friendly, tense, considerate, relaxed, sympathetic, resentful, good-natured, rebellious, trusting, carefree. 2. Overlapped or ambiguous items were discussed by colleagues and elders through verification of content-validity and were removed. Five items were removed in tense-anxiety, seven, in depression -dejection, three, in vigor-activity, three, in fatigue-inertia, two, in confusion-bewilderment, five, in friendliness, and six, in anger? hostility. Thirty four items remainined; angry, clear-headed, lively, confused, sorry, shaky, listless, peeved, sad, active, blue, hopeless, spiteful, uneasy, unable to concentrate, fatigued, helpful, nervous, lonely, cheerful, bitter, exhausted, anxious, ready to fight, sluggish, helpless, alert, deceived, efficient, worthless, forgetful, terrified, vigorous, and uncertain about things. 3. Factor analysis was done in order to confirm con struct validity and three factors were obtained from the result. The first factor, 'anxiety-depression' included 21 items, the second factor, 'vigor' included eight items, and the third factor, 'anger' included five items. Cronbach coefficient alpha for the 34 items was .95. Based on the result, the following is suggested: 1. a contribute to elder's welfare can be made by examining Korean elder's mood in life. 2. there is a need to develop tools appropriate to Korean culture which can be used to examine elders' mood. 3. The modified POMS tool needs to be reverified with appropriate age groups and settings.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - The structural validity and latent profile characteristics of the Abbreviated Profile of Mood States among Chinese athletes
Chenhao Tan, Jun Yin, Yan An, Jinhao Wang, Jun Qiu
BMC Psychiatry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Predictors of Emergency Room Admission in Patients With Liver Cirrhosis
Eun Kyung Kim, Heeok Park
Gastroenterology Nursing.2020; 43(1): 65. CrossRef - Music interventions for acquired brain injury
Wendy L Magee, Imogen Clark, Jeanette Tamplin, Joke Bradt
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors affecting the Fatigue of Hospitalized Women Cancer Patients Receiving Chemotherapy
Kyunghee Kim, MyoSuk Lee, Yeunhee Kwak, Ji-Su Kim
Asian Oncology Nursing.2014; 14(3): 182. CrossRef
-
875
View
-
2
Download
-
4
Crossref
-
The Effect of Walking Exercise Program on Cardiorespiratory Function and Flexibility in Elderly Women
-
Yun Hee Shin, Young Hee Choi
-
Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1996;26(2):372-386. Published online March 30, 2017
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1996.26.2.372
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
Recently, the ratio of elderly in the population are fastly growing due to socio-economical development and the better medical service. Proportionally, the health problems in elderly are increasing, too. Medical professionals must try so that the elderly have the better life through health promotion and disease prevention as well as disease treatment. This study evaluated the effect of walking exercise program on the cardiorespiratory function and the flexibility in the elderly women. The design of research was one group pretest -posttest design. The subjects were eleven elderly women over sixty years old to live in K-city, Kyonggi-do. The type of exercise was walking, which was the most popular exercise in questionnaire. The exercise intensity was 40%~60% of the target heart-rate by Karvonen's method and maintained by the heart-rate monitor. The exercise period was five weeks and the exercise frequency was three times per week. The exercise duration was forty minites at first and gradually increased up to a hour. In order to evaluate the effect of walking exercise, we measured VO2 max, resting heart-rate, systolic/diastolic blood pressure, FVC, FEV1, the flexibility before and after the five week's exercise program. The data are analyzed by the paired t-test and Wilcoxon signed rank test using SAS package. The results are as follows: 1) The hypothesis that cardiorespiratory function will be improved was partly supported. In VO2 max(p=0.0001), resting heart-rate(p=0. 0030), systolic/diastolic blood-pressure (p=0.0387/p=0.0024), there was significant difference. FVC and FEV1 were increased after the exercise, but there were no significant difference. 2) The hypothesis that the flexibility will be improved was supported. There was significant difference in the flexibility (p=0.0140). As the further study, it is necessary to reevaluate the effect with more refined design. We also need to try meta-analysis about the results of previous studies obtained in the experimental setting and compare our result obtained in the field setting with them.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - 여성 노인과 여가 스포츠
재윤 배
The Korean Journal of Physical Education.2024; 63(3): 403. CrossRef - Effect of a Home-based Exercise Program on Elderly Women’s Health
Hyo-Lyun Roh, Dae-Hee Lee
Journal of Physical Therapy Science.2012; 24(5): 449. CrossRef - The Effects of Aerobic Exercise Therapy on Physical Functions in the Elderly
Sook Hee Jung, Kyung Hee Chung
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2010; 21(2): 252. CrossRef
-
625
View
-
0
Download
-
3
Crossref
-
Review of Environment in the Korean Traditional Thought
-
Moon Sil Kim, Young Ran Han, Yun Hee Shin
-
Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1994;24(2):251-263. Published online March 31, 2017
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1994.24.2.251
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
This paper reviewed the concept of the environ merit in Korean traditional thought according to Shamamism, Buddhism, Confucianism, and Taoism. The differences in the views of the environment between Korean traditional thought and Western thought were compared according to the ontological point of view. This study attempted to investigate the concept of environment, one of the four metaparadigm(hu-man, environment, health, nursing)as it is experssed in Korean traditional thought. However, it was difficult to find the concept of environment separated out in the traditional thought pattern. Instead, environment concepts are represented in the natural views and universal views. Even though the four traditional thought patterns (Shamaism, Buddhism, Confucianism, and Taoism) represent some difference in their view of nature, the combination of natural and human, harmony, anti-dichotomy and so forth are emphasized in common in four thought patterns. Korean traditional thought includes a more comprehensive meaning than the unitary-transformative perspective discussed in modern Westen thought patterns. Environment has been dealt with in narrow view until now. Now we avoid this narrow view and must regard environment as an integrated concept with person. Through this research, it is hoped that a contribution will be made to the development of nursing knowledge suitable to Korean culture.
-
Petient's Perceptions of Health Professionals' Unkind Behavior
-
Moon Sil Kim, Yun Hee Shin
-
Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1992;22(4):421-443. Published online March 31, 2017
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1992.22.4.421
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
The purpose of this study was to identify patients' perceptions of health professionals' unkind behavior and the effects of this unkind behavior using a phenomenological research methodology. Understanding of this phenomena should enlighten nurses to interaction and relationship problems between patient and health professionals and thus lead to further research toward enhancing these interaction and relationships. The subjects were 40 adult patients hospitalized in a university hospital in Seoul. They were form 20 to 65 years old and hospitalized at IM, GS, OS, NS, OB/GY ward. Their hospital days were from 4 to 72. Data were collected from July 29 to August 9, 1991 and from January 6 to 17, 1992. The research questions were "What behavior on the part of health of health professionals you perceive as unkind and what effect does such behavior have in you?". Responses to the non-structured open-ended questions were audio-recorded during the interviews done by two nurses researchers. Data were analyzed using the phenomenological method of Colazzi. The validity was enhanced by confirmation of the analysis by two nursing clinical researchers, and professor of psychology, and philosophy, all knowledgable of phenomenological research.
From the protocols, 146 significant statements about unkind behavior were organized into 38 formulating meanings which then grouped into six clusters of themes. Perceived health professional' unkind behavior as being cold, insincere, unconcerned, disregardful, lacking in technical skill, and failing to provide a therapeutic environment.
From the protocols, 65 significant statements about the influence of such behavior on patient care were organized into 18 formulating meanings which were then grouped into four clusters of themes. Patients perceived these unkind behavior influencing then emotionally, physically and having negative effects on their compliance with medical and nursing care.
The study points to the need for health professionals to understand how their may be perceived by their patients as unkind behavior. Patients perceptions of health professionals' unkind behavior may suggest the opposite desire, that professionals have excellent medical knowledge and skill and that they be sincere, concerned, respectful and warm emotionally toward their patients.
-
A Study of the Health Status of Elderly Residing in Large city, Medium and Small city, Rural areas in Korea
-
Young Hee Choi, Yun Hee Shin
-
Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1991;21(3):365-382. Published online March 31, 2017
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1991.21.3.365
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
This study was designed to measure the physical, mental-emotional and social health status of elderlies according to rural areas, medium-small cities, and large city environment.
Data collection was done from July 18 to August 17, 1990. The subjects were a convenience sample after their place of residence was stratified into large, medium-small cities and rural areas. Those who attended elderly centers in Seodaemun, Mapo, and Kangnam districts in Seoul were considered to be residents of a large city and interviewed by trained research assistants and student nurses. Elderlies living in Chungju, Jinju, Chuncheon, and Jeonju cities were coded as resident of medium-small cities and were interviewed by professors of nursing college. Rural residents were interviewed by the community health practioners working in community health practioners working in community health clinics in North and South Kyongsang, North and South Jeolla, and Kyonggi provinces.
The tool used in this study was the health assessment tool developed by Choi, Young Hee in 1990. This tool was organized into 20 physical health status, 17 mental-emotional health status, and 37 social health status items. Physical health status items consisted of six factors-personal hygiene activity ability, external activity utilizing traffic, mass media, and spare time ability, sexual ability, digestive system related ability, sexual ability, sensory ability, and elimination ability. Mental-emotional health status items consisted of two factors-mental health factor and emotional health factor. Social health status items consisted of seven factors-grandparental role ability, parental role ability, spoused role ability, friendship role ability, kinship role ability.
Data Analysis included frequencies, percentage mean, standard deviation, ANOVA, and chi-square test.
The results of the analysis are as follows :
1. The mean physical health status score for large city residents was 4.1132, for rural residents 4.0787, and for medium and small city residents 3.9565. There were significant differences according to residential area for personal hygiene activity ability, external activity ability, sexual ability, and digestive system related ability items
2. The mean mental-emotional health status score for rural residents was 3.8291, for medium and small city residents 3.7967, and for large city residents 3.7807. There was a significant difference according to residential area in the mental health ability item.
3. The mean social health status score for medium and small city residents was 3.0000, for rural residents 2.9362, and for large city residents 2.8960. There were significant differences according to residential area for kinship role ability and religious believer role ability items.
The following conclusion was derived from the above results :
1. The physical health status of elderlies residing in medium-small cities and in rural areas was lower than that of those residing in Seoul, a large urban area. Therefore, more medical facilities are needed in rural area so as to monitor their health, prevent disease, and promote their health.
2. The mental-emotional status and social health status of elderlies residing in the large city were lower than the of those residing in medium-small cities and rural areas. This may reflect weakening of the strong traditional family bond that may happen with urbanization. Continued support for elderly parents is essential and education should emphasize the traditional cultural norm and value of filial piety.
3. Facilities and programs for elderly are needed so that they may spend their time more valuably in their urban environment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Analysis of Importance of and Satisfaction with the Values and Major Achievements of Urban Agriculture
Yumin Park, Yong-Wook Shin
Journal of People, Plants, and Environment.2023; 26(6): 637. CrossRef - Trends in Dietary Behavior Changes by Region using 2008 ~ 2019 Community Health Survey Data
Yun-Hui Jeong, Hye-Young Kim, Hae-Young Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(2): 132. CrossRef
-
683
View
-
1
Download
-
2
Crossref
|