-
Development and evaluation of the Trauma-nursing Education and Skill Support program to enhance trauma nursing competencies: a quasi-experimental study
-
Tae Yeong Yang, Myung Jin Jang, Ki Ung Kim, Min So, Mi Na Choi, Eun Jung Lee, Jin Su Jo, Ji Yun Lee, Kwang Kyun Lim, Kyoung Mi Kim, Hae Jun Baek, Sun Ho Wang, Jin Oh Choi
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2026;56(1):67-80. Published online February 24, 2026
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25134
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF ePub ePub
- Purpose
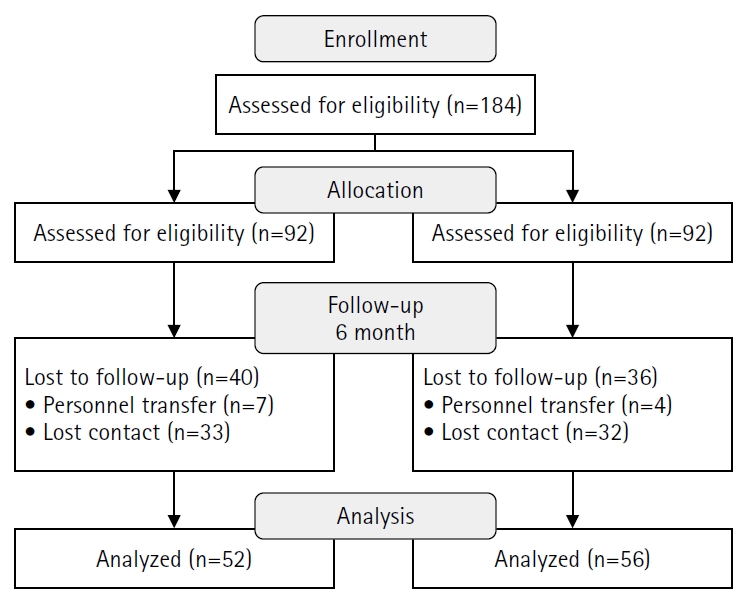
This study aimed to develop and evaluate the effectiveness of the Trauma-nursing Education and Skill Support (TESS) program based on the ADDIE model (Analysis, Design, Development, Implementation, Evaluation model). The program was designed to enhance trauma nurses’ clinical competencies, including trauma-related knowledge, self-efficacy, and problem-solving ability, through the integration of theoretical education and simulation-based practice.
Methods
A quasi-experimental study using a non-equivalent control group pretest–posttest design was conducted. Participants included 108 trauma nurses from regional trauma centers, military trauma centers, and emergency care facilities, who were assigned to an experimental group (n=52) or a control group (n=56). The TESS program consisted of a 2-day, 14-hour blended-learning course that included eight lecture sessions and four simulation-based practice stations. Data were collected at baseline, immediately after the intervention, and at 6 months using validated instruments measuring trauma-related knowledge, self-efficacy, and problem-solving ability. Two-way repeated-measures analysis of variance was used for data analysis.
Results
The experimental group demonstrated significant improvements in trauma-related knowledge, self-efficacy, and problem-solving ability compared with baseline (all p<.001). These improvements were sustained at 6 months, although trauma-related knowledge scores showed a slight decline compared with immediate posttest levels. Between-group analyses confirmed significant group-by-time interaction effects for all outcomes: trauma-related knowledge (η2=0.12, p<.001), self-efficacy (η2=0.09, p=.002), and problem-solving ability (η2=0.08, p=.003).
Conclusion
The TESS program effectively enhanced trauma nurses’ trauma-related knowledge, self-efficacy, and problem-solving ability, with effects sustained for up to 6 months. Incorporating blended learning and simulation-based training into standardized trauma nursing education may strengthen clinical competencies and ultimately contribute to improved patient outcomes.
-
Factors Influencing Clinical Nurses’ Perception of Structural and Content Career Plateau
-
Ji Hye Kim, Ji Yun Lee
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(4):534-546. Published online October 23, 2024
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24002
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF ePub ePub
- Purpose
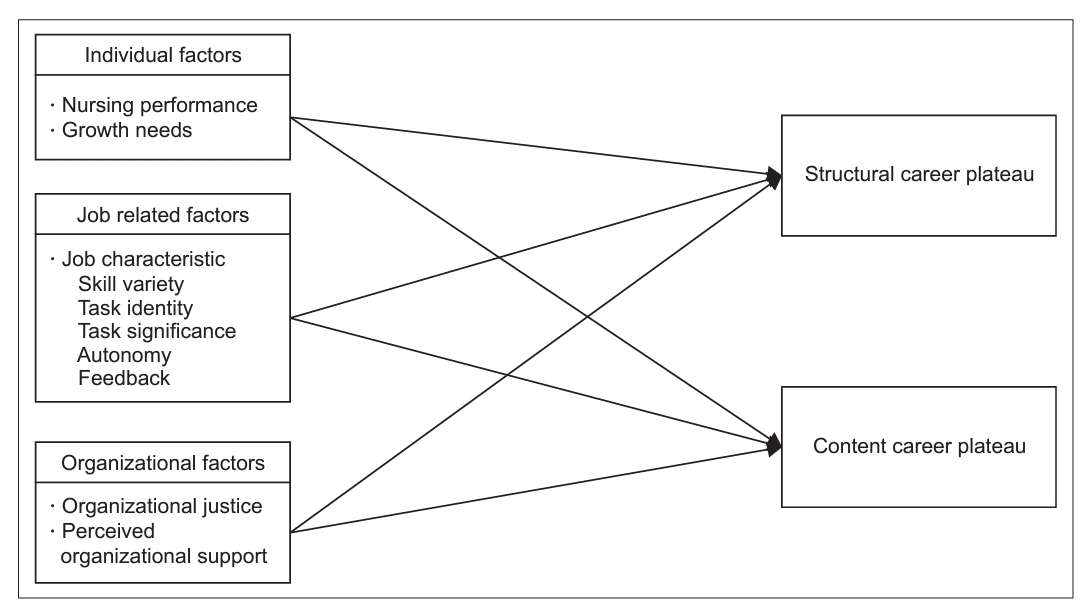
This study was intended to provide basic data for reducing the career plateaus of clinical nurses.
Methods
The participants were 288 clinical nurses who worked at five hospitals, general hospitals, and tertiary hospitals in Seoul, Gyeonggi, and Chungcheong provinces and had more than one year of clinical experience. The research data were collected from December 26, 2022, to April 7, 2023, using structured questionnaires and analyzed using SPSS software. The study conducted mean, standard deviation, percentage, t-test, ANOVA, Pearson‘s correlation coefficient, and hierarchical regression analysis.
Results
Perceived organizational support was identified as the factor influencing structural career plateaus. Factors influencing content career plateaus included growth needs, skill variety, organizational justice, and perceived organizational support.
Conclusion
The above research results suggest that to increase the motivation of clinical nurses and reduce career plateaus, it is necessary to improve awareness and systems of human resource management at the organizational level.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Nursing managers’ perceptions of clinical nurses’ self-management in professional title promotion: a qualitative user persona study
Xiang Gao, Xuemei Wang
BMC Nursing.2026;[Epub] CrossRef
-
2,424
View
-
171
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
Impact of Nurse, Nurses' Aid Staffing and Turnover Rate on Inpatient Health Outcomes in Long Term Care Hospitals
-
Yunmi Kim, Ji Yun Lee, Hyuncheol Kang
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2014;44(1):21-30. Published online February 28, 2014
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2014.44.1.21
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
-
Purpose
This study was conducted to explore the impact of registered nurse/nurses' aid (RN/NA) staffing and turnover rate on inpatient health outcomes in long term care hospitals.
Methods
A secondary analysis was done of national data from the Health Insurance Review and Assessment Services including evaluation of long term care hospitals in October-December 2010 and hospital general characteristics in July-September 2010. Final analysis of data from 610 hospitals included RN/NA staffing, turnover rate of nursing staff and 5 patient health outcome indicators.
Results
Finding showed that, when variables of organization and community level were controlled, patients per RN was a significant indicator of decline in ADL for patients with dementia, and new pressure ulcer development in the high risk group and worsening of pressure ulcers. Patients per NA was a significant indicator for new pressure ulcer development in the low risk group. Turnover rate was not significant for any variable.
Conclusion
To maintain and improve patient health outcomes of ADL and pressure ulcers, policies should be developed to increase the staffing level of RN. Studies are also needed to examine causal relation of NA staffing level, RN staffing level and patient health outcomes with consideration of the details of nursing practice.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - The Experience of turnover to long-term care hospital nurse: A phenomenological qualitative research
Inhee Choo, Milim Cho, Eunha Kim
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2024; 26(4): 392. CrossRef - Physical Therapy Provider Continuity Predicts Functional Improvements in Inpatient Rehabilitation
Mitchell D. Adam, Debra K. Ness, John H. Hollman
Journal of Neurologic Physical Therapy.2023; 47(2): 91. CrossRef - The effect of the reformed nurse staffing policy on employment of nurses in Korea
Jinhyun Kim, Sungjae Kim, Eunhee Lee, Hyunjeong Kwon, Jayon Lee, Hyunji Bae
Nursing Open.2021; 8(5): 2850. CrossRef - Nurses’ Clinical Work Experience during Pregnancy
Hyunjung Lee, Hyoung Eun Chang, Jiyeon Ha
Healthcare.2020; 9(1): 16. CrossRef - Exploring Nurses' Perceptions of Nursing Home Care in South Korea: A Qualitative Study
Eunhee Cho, Hyejin Kim, Soo Jung Chang, Hyang Kim, Jeongah Kim
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2020; 22(2): 85. CrossRef - The Effects of Long-term Care Hospitals' Nurse Staffing Level on Patient Outcomes: Differences according to Region
Kyung Jin Hong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2020; 26(4): 354. CrossRef - A Comparative Study on the Job Stress, Burnout and Nursing Performance of Nurses in Comprehensive Nursing Care Service Wards and Nurses in General Wards
Youn Sil Kim, Jung Ae Park, Eun Koung Seo
Stress.2019; 27(1): 46. CrossRef - Experiences of Long-term Care Hospital Nurses Caring for Elders with Dementia
Eun Kyoung Suh, Hye Ryoung Kim
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2019; 21(2): 99. CrossRef - Longitudinal associations of nursing staff turnover with patient outcomes in long-term care hospitals in Korea
Yoonseo Kim, Kihye Han
Journal of Nursing Management.2018; 26(5): 518. CrossRef - Influence of Nurses' Work Environment, Organizational Commitment, and Nursing Professionalism on Turnover Intention of Nurses in Long Term Care Hospitals
Hyun Suk Joo, Won Hee Jun
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2018; 24(4): 265. CrossRef - Importance, Performance and Rates of Nurse Performance of Nursing Interventions in Long-term Care Hospitals
Sunmi Kim, Seok Hee Jeong, Myung Ha Lee, Hyun Kyung Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2017; 23(4): 359. CrossRef - Comparative Analysis Research of Inpatient Satisfaction with Nursing on Comprehensive Nursing Service Units & General Units and Nurses' Work Stress
Su Mi Jung, Sook Hee Yoon
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2017; 23(3): 229. CrossRef - Delegation of Nursing Activities in Long-term Care Hospitals
Eun Ju Jang, Su Hyun Kim
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2017; 19(2): 101. CrossRef - Effects of Empathy and Attitude in Caring for Elders by Nurses in Geriatric Nursing Practice in Long-term Care Hospitals
Young Kyoung Kim, Suhye Kwon
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2017; 19(3): 203. CrossRef - Predictors of Turnover among New Nurses using Multilevel Survival Analysis
Suhee Kim, Kyongeun Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2016; 46(5): 733. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Nurse Turnover Intention of Senior Convalescence Hospitals in the Metropolitan Area
Youn Sun Hwang, Eunyoung Cho
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2016; 25(3): 156. CrossRef - Nursing outcomes of inpatient on level of nursing staffing in long term care hospitals
Eun Hee Kim, Eunjoo Lee
Journal of the Korean Data and Information Science Society.2015; 26(3): 715. CrossRef - The Effects of Emotional Labor and Job Involvement on Turnover Intention of Nurses in Long-term Care Hospitals
Su-Jeong Kang, Suhye Kwon
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2015; 24(4): 290. CrossRef
-
1,587
View
-
20
Download
-
18
Crossref
-
Geographical Imbalances: Migration Patterns of New Graduate Nurses and Factors Related to Working in Non-Metropolitan Hospitals
-
Sung-Hyun Cho, Ji Yun Lee, Barbara A. Mark, Han Yi Lee
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2012;42(7):1019-1026. Published online December 31, 2012
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2012.42.7.1019
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
-
Purpose
To examine geographical imbalances by analyzing new graduate nurses' migration patterns among regions where they grew up, attended nursing school, and had their first employment and to identify factors related to working in non-metropolitan areas.
Methods
The sample consisted of 507 new graduates working in hospitals as full-time registered nurses in South Korea. Migration patterns were categorized into 5 patterns based on sequential transitions of "geographic origin-nursing school-hospital." Multiple logistic regression analysis was conducted to identify factors associated with working in non-metropolitan hospitals.
Results
Nurses who grew up, graduated, and worked in the same region accounted for the greatest proportion (54%). Sixty-five percent had their first employment in the region where they graduated. Nurses tended to move from poor to rich regions and from non-metropolitan to metropolitan areas. Working in non-metropolitan hospitals was related to older age, the father having completed less than 4 years of college education, non-metropolitan origin, non-capital city school graduation, and a diploma (vs. baccalaureate) degree.
Conclusion
Admitting students with rural backgrounds, increasing rural nursing school admission capacities, and providing service-requiring scholarships, particularly for students from low-income families, are recommended to address geographical imbalances.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Factors influencing nursing students’ preferences for hospitals by geographic location and bed capacity
Hae Na Nam, Hyun Ji Bae
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2025; 31(4): 387. CrossRef - Empirical Analysis of Geographic Inequalities in the Distribution of Nurses
Euntae Park, Jinhyun Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(3): 271. CrossRef - Job change among early career nurses and related factors: A postgraduation 4‐year follow‐up study
Eun‐Young Kim, Sun‐Hee Kim
Journal of Nursing Management.2022; 30(7): 3083. CrossRef - Turnover Rates and Factors Influencing Turnover of Korean Acute Care Hospital Nurses: A Retrospective Study Based on Survival Analysis
Bohyun Park, Yukyung Ko
Asian Nursing Research.2020; 14(5): 293. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Nursing Students' Choices of a Place of Employment
Sun Ju You, Jong Kyung Kim, Myun Sook Jung, Se Young Kim, Eun Kyung Kim
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2018; 18(4): 184. CrossRef - Factors Associated with the Choices of Local Hospitals among New Graduate Nurses
Eun-Young Kim, Hun Ha Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2018; 24(3): 202. CrossRef - Impact of Increased Supply of Newly Licensed Nurses on Hospital Nurse Staffing and Policy Implications
Yunmi Kim, Sunju You, Jinhyun Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2017; 47(6): 828. CrossRef - Geographic Mobility and Related Factors among Newly Graduated Nurses
Hyo Jeong Yoon, Sung Hyun Cho
Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2017; 23(3): 353. CrossRef - Patterns and Influential Factors of Inter-Regional Migration of New and Experienced Nurses in 2011~2015
Bohyun Park, Se Young Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2017; 47(5): 676. CrossRef - A final-year nursing student survey: rural attitudes, perceived competencies and intention to work across five Asian countries
Nareerut Pudpong, Rapeepong Suphanchaimat, Bipin Batra, Jianlin Hou, Lan T. H. Vu, Paul Dipika
BMC Nursing.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Predictors of Turnover among New Nurses using Multilevel Survival Analysis
Suhee Kim, Kyongeun Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2016; 46(5): 733. CrossRef - Factors influencing the intent to return to practice (work) of inactive RNs
Nami Hwang, Insun Jang, Eunjun Park
Journal of the Korean Data and Information Science Society.2016; 27(3): 791. CrossRef - Qualitative Research on Nurses Experiencing Taeoom
SunHwa Choeng, InSook Lee
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2016; 25(3): 238. CrossRef - Impact of a financial incentive policy on Korean nurse staffing
Y. Kim, J. Kim
International Nursing Review.2015; 62(2): 171. CrossRef - Geographic mobility of Korean new graduate nurses from their first to subsequent jobs and metropolitan-nonmetropolitan differences in their job satisfaction
Sung-Hyun Cho, Ji Yun Lee, Barbara A. Mark, Cheryl B. Jones
Nursing Outlook.2014; 62(1): 22. CrossRef - Issues and Challenges of Nurse Workforce Policy: A Critical Review and Implication
Taewha Lee, Kyeong Hwa Kang, Yu Kyung Ko, Sung-Hyun Cho, Eun-Young Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2014; 20(1): 106. CrossRef - Interventions for supporting nurse retention in rural and remote areas: an umbrella review
Gisèle Mbemba, Marie-Pierre Gagnon, Guy Paré, José Côté
Human Resources for Health.2013;[Epub] CrossRef
-
1,635
View
-
7
Download
-
17
Crossref
-
Development of Outcome Indicators of Urinary Incontinence for Quality Evaluation in Long Term Care Hospitals
-
Ju Young Yoon, Ji Yun Lee
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2010;40(1):110-118. Published online February 28, 2010
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2010.40.1.110
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
-
Purpose
To develop outcome indicators of urinary incontinence to measure quality of care in long term care hospitals in Korea.
Methods
The draft indicators of urinary incontinence were developed from a literature review and clinical expert panel. A survey of medical records of 280 patients in 20 hospitals was conducted to test inter-rater reliability. Statistical analysis was done to test risk adjustment criteria, variation between hospitals, and stability of indicators, using assessment data from 77,918 patients in 623 hospitals.
Results
The inter-rater reliability of items was high (Kappa range: 0.66-0.92). Severe cognitive impairment (odds ratio [OR]: 3.15, confidence interval [CI]: 3.03-3.26) and total mobility activities of daily living (ADLs) dependency (OR: 4.85, CI: 4.72-4.98) increased the prevalence of urinary incontinence, thus they proved to be significant criteria to stratify high and low risk groups. The prevalence for low risk showed more substantial variation than the high risk group. The indicators were stable over one month.
Conclusion
This study demonstrated the feasibility of outcome indicators of urinary incontinence. Improving the reliability of the patient assessment tool and refining the indicators through validation study is a must for future study.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Development of Health Assessment Tool for Middle-aged Adults in Long-term Care Settings
Yoon-Jin Park, Nam Cho Kim
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2017; 20(1): 1. CrossRef - Factors Associated with the Changes in Activities of Daily Living in Older Adults with Stroke: A Comparison of Home Care and Institutional Care
Woon-Sook Jung, Eun-Shil Yim
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2016; 27(4): 388. CrossRef - Mobility is the key! Trends and associations of common care problems in German long-term care facilities from 2008 to 2012
Nils A. Lahmann, Antje Tannen, Simone Kuntz, Kathrin Raeder, Gabriela Schmitz, Theo Dassen, Jan Kottner
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2015; 52(1): 167. CrossRef - Comparison of Hospital Standardized Mortality Ratio Using National Hospital Discharge Injury Data
Jong-Ho Park, Yoo-Mi Kim, Sung-Soo Kim, Won-Joong Kim, Sung-Hong Kang
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2012; 13(4): 1739. CrossRef - The impact of organizational factors on the urinary incontinence care quality in long-term care hospitals: A longitudinal correlational study
Ju Young Yoon, Ji Yun Lee, Barbara J. Bowers, David R. Zimmerman
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2012; 49(12): 1544. CrossRef
-
945
View
-
1
Download
-
5
Crossref
-
Effects of Case Management using Resident Assessment Instrument-Home Care (RAI-HC) in Home Health Services for Older People
-
Kyung Ja June, Ji Yun Lee, Jong Lull Yoon
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2009;39(3):366-375. Published online June 29, 2009
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2009.39.3.366
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
-
Purpose
To evaluate the effects of case management using Resident Assessment Instrument-Home Care (RAI-HC) in home health service for older people.
Methods
All elders were assessed at baseline and 3 months later using RAI-HC. The change of function in the intervention group was compared with that of a conventional intervention group. Function was measured with Activities of Daily Living (ADL), Instrumental Activities of Daily Living (IADL), Cognitive Performance Scale (CPS), Depression Rating Scale (DRS), Pain and the number of Clinical Assessment Protocols (CAP).
Results
Among ninety two elders participated in the program, 59 were allocated to the case management group and 33 to the conventional group. The intervention, home health service by a nurse over a 3 month period, consisted of comprehensive assessment, case conference for care plan, direct care, education and referral, and outcome evaluation. The percent of elders whose function improved in the intervention group was greater than the conventional group for depression (odds ratio [OR]: 10.941, confidence interval [CI]: 2.338-51.206), IADL (OR: 4.423, CI: 1.151-16.999) and the number of CAP (OR: 11.443, CI: 3.805-34.410).
Conclusion
Case management was effective for older people in the community. The effect might have resulted from individual, systematic intervention, however, standards of service including eligibility criteria for case management and collaboration of multi-disciplines is required for more effective home health service programs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Examining Utilization of Formal Supports and Related Impacts on Overall Well-Being Among East Asian American Family Caregivers of Persons With Dementia: A Mixed-Methods Study
Kathy Lee, Jessica Cassidy, Jihui Lee, Chang Hyun Seo, Alan Kunz Lomelin, Hye-Won Shin, Joshua D Grill, Tonya J Roberts
The Gerontologist.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Case management for integrated care of older people with frailty in community settings
Euan Sadler, Zarnie Khadjesari, Alexandra Ziemann, Katie J Sheehan, Julie Whitney, Dan Wilson, Ioannis Bakolis, Nick Sevdalis, Jane Sandall, Tayana Soukup, Teresa Corbett, Daniela C Gonçalves-Bradley, Dawn-Marie Walker
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and testing of the Geriatric Care Assessment Practices (G-CAP) survey
Justine L. Giosa, Paul Stolee, Paul Holyoke
BMC Geriatrics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Social Support, Activities of Daily Living, and Depression among Older Japanese and Koreans Immigrants in the U.S
Bumjung Kim, Hyeyoun Jun, Jisun Lee, Yun Min Kim
Social Work in Public Health.2020; 35(4): 163. CrossRef - Care Tips for Self-Care among Older Diabetic Patients
Been Yoo
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2019; 20(3): 190. CrossRef - Identifying and prioritizing topics for evidence‐based geriatric nursing practice guidelines in Korea
S. Kim, K. Kim, S. J. Kim
International Nursing Review.2018; 65(4): 550. CrossRef - Risk and protective factors associated with intentional self‐harm among older community‐residing home care clients in Ontario, Canada
Eva Neufeld, John P. Hirdes, Christopher M. Perlman, Terry Rabinowitz
International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry.2015; 30(10): 1032. CrossRef - Current Status and Barriers to Health Care Services for Nursing Home Residents: Perspectives of Staffs in Korean Nursing Homes
Yeon-Hwan Park, Hwal Lan Bang, Ga Hye Kim, Seieun Oh, Young-Il Jung, Hongsoo Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2015; 27(4): 418. CrossRef - Improving health status and reduction of institutionalization in long‐term care—Effects of the Resident Assessment Instrument‐Home Care by degree of implementation
Claudia Stolle, Annika Wolter, Günter Roth, Heinz Rothgang
International Journal of Nursing Practice.2015; 21(5): 612. CrossRef - The Relationship Between Activities of Daily Living (ADL), Chronic Diseases, and Depression Among Older Korean Immigrants
Bum Jung Kim, Young Choi
Educational Gerontology.2015; 41(6): 417. CrossRef - Home Visits for Prevention of Impairment and Death in Older Adults: A Systematic Review
Sean Grant, Amanda Parsons, Jennifer Burton, Paul Montgomery, Kristen Underhill, Evan Mayo Wilson
Campbell Systematic Reviews.2014; 10(1): 1. CrossRef - RAI-HC as an innovative tool for future practice in home care
Helena Kisvetrová, Yukari Yamada
Journal of Nursing, Social Studies, Public Health and Rehabilitation.2014; 5(1-2): 16. CrossRef - Preventive Home Visits for Mortality, Morbidity, and Institutionalization in Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Evan Mayo-Wilson, Sean Grant, Jennifer Burton, Amanda Parsons, Kristen Underhill, Paul Montgomery, Hemachandra Reddy
PLoS ONE.2014; 9(3): e89257. CrossRef - Structural Equation Modeling on Case Management Outcomes and Factors Influencing Outcomes in the Community-dwelling Vulnerable Elders
Hyunjung Moon, In-Sook Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2013; 43(6): 791. CrossRef - Effects of the Resident Assessment Instrument in home care settings
C. Stolle, A. Wolter, G. Roth, H. Rothgang
Zeitschrift für Gerontologie und Geriatrie.2012; 45(4): 315. CrossRef - Developing a Comprehensive Geriatric Assessment Package for Successful Aging
Seon-Ho Kim, Doo-Nam Oh
The Journal of the Korea Contents Association.2012; 12(9): 257. CrossRef - The Effects of Case Management for Clients with Clonorchiasis in Riverside Areas
Chunmi Kim, Hee-Gerl Kim, Kyung-Ja June, Souk-Young Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2012; 23(4): 427. CrossRef - Effects of Tailored Case Management using a Gatekeeper for the Depressed Single-household Elderly Population -Focusing on the Mental Health Case Management-
Yun-Jung Choi, Mi-Ra Won
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2012; 23(4): 376. CrossRef - The Effects of a Case Management Program of Customized Home Visiting Health Service for Clients with Arthritis
Soon-Ok Yang, Myung Soon Kwon, Yong-Jun Choi, Seung-Hee Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2011; 22(2): 151. CrossRef - Health Needs of the Elderly in Long-term Care Facilities: Using RAI-MDS-FC
Eun-Joo Bang, Soon-Young Yun
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2010; 21(2): 263. CrossRef - The Comparison of Functional Status and the Level of Health Care Needs in Elderly Koreans in Health Care Institutions
Hyun-Sil Kim, Young-Mi Jung, Hung-Sa Lee, Yoo-Hyang Cho, In-Young Yoo
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2010; 21(4): 386. CrossRef
-
1,243
View
-
8
Download
-
21
Crossref
|