-
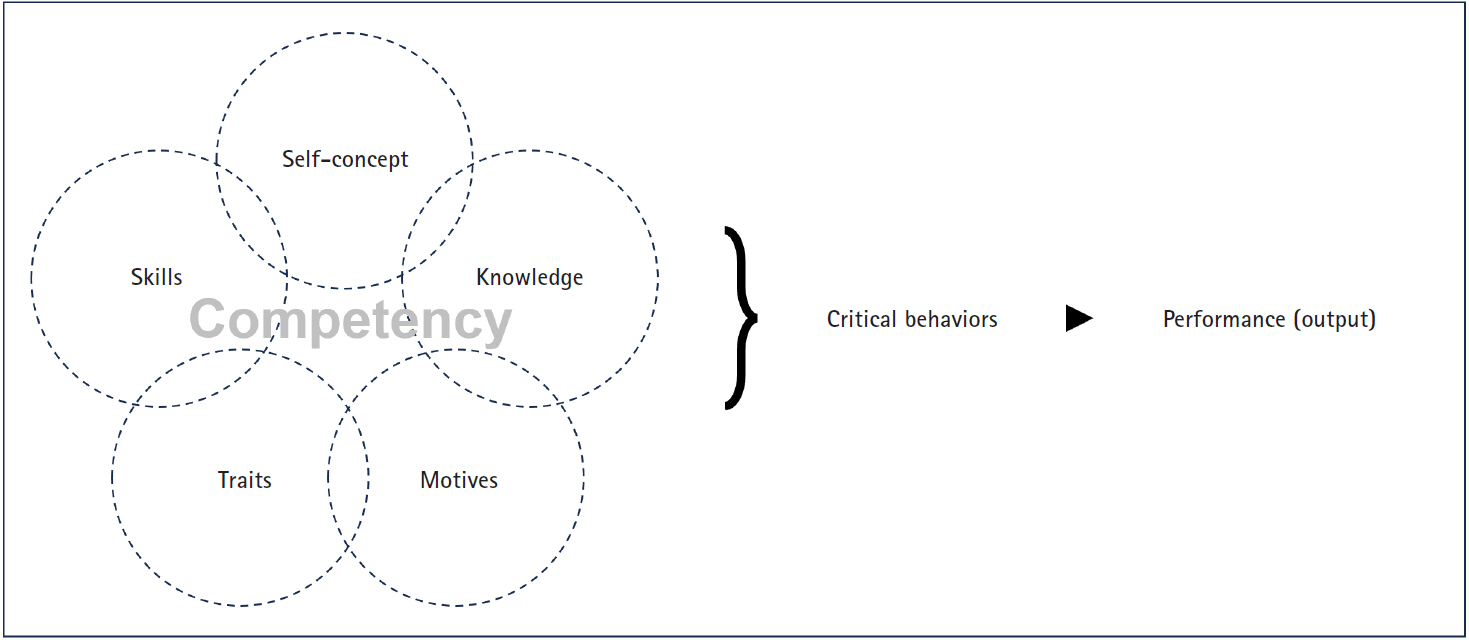
Core domains for pre-registered nurses based on program outcomes and licensing competencies
-
Soyoung Yu, Hye Young Kim, Jeung-Im Kim, JuHee Lee, Ju-Eun Song, Hyang Yuol Lee
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(2):249-268. Published online May 27, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25017
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF ePub ePub
- Purpose
This study aimed to identify core domains for pre-registered nurses by comparing licensing competencies with program outcomes (POs) in undergraduate nursing education. This was accomplished in preparation for the transition of the Korean Nurse Licensing Examination (KNLE) from a tradition seven-subject format to a newly integrated, competency-based single-subject format that reflects current trends in nursing assessment.
Methods
A literature review and survey were conducted. From 828 studies retrieved via PubMed, CINAHL, and Google Scholar using keywords such as “newly graduated registered nurses” and “competency OR competence,” 18 were selected according to pre-established inclusion and exclusion criteria. Documents from national and international nursing organizations were included to extract relevant licensing competencies. We also reviewed POs from all undergraduate nursing schools in South Korea to align educational outcomes with the identified core domains.
Results
The core domains identified were clinical performance and decision-making, professional attitudes and ethics, communication and interpersonal skills, leadership and teamwork, quality improvement and safety, health promotion and prevention, and information technology and digital health. These domains showed strong alignment with POs under the fourth-cycle accreditation standards.
Conclusion
It concludes the seven core domains will be appropriate for evaluating pre-registered nurses in the integrated KNLE. Based on the seven identified core domains, expert consensus should be sought in the next phase to support the development of integrated, competency-based test items grounded in these domains.
-
Public Reporting on the Quality Ratings of Nursing Homes in the Republic of Korea
-
Hyang Yuol Lee, Juh Hyun Shin
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(2):161-170. Published online April 30, 2019
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.2.161
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
-
Background
Quality ratings could provide vital information to help people in choosing a nursing home.
Purpose
This study investigated factors aligned with quality ratings of nursing homes.
Methods
We employed a cross-sectional descriptive design to assess publicly available data on 1,354 nursing homes with 30 or more beds in the Republic of Korea. After excluding 289 nursing homes with no reported quality-evaluation ratings, we analyzed the 2015 data of 1,065 nursing homes. To prevent multicollinearity among independent variables, we carefully selected the final set of variables based on clinical and theoretical meaningfulness to direct nursing care. Quality, the ordinal outcome, was scored from 1 to 5 with a higher score indicating higher quality of the organization. We constructed a multivariate ordered logistic regression model.
Results
Higher quality ratings of nursing homes was significantly related to the number of unoccupied beds (OR=0.99, p=.024), registered nurses (RNs) (OR=1.30, p=.003), qualified care workers (OR=1.03, p=.011), cognitive-improvement programs (OR=1.05, p=.024), and other programs for residents' activities (OR=1.09, p<.001).
Conclusion
The number of RNs had the strongest influence on the publicly reported quality rating, while the rating of qualified care workers demonstrated little effect and that of nursing assistants had no effect. The number of RNs could be used as a crucial indicator for high-quality homes; more resident-engaging programs also demonstrated better quality of nursing home care.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Performance indicators on long-term care for older people in 43 high- and middle-income countries: literature review, web search and expert consultation
Mircha Poldrugovac, Joost D. Wammes, Véronique L. L. C. Bos, Erica Barbazza, Damir Ivanković, Hanneke Merten, Janet L. MacNeil Vroomen, Niek S. Klazinga, Dionne S. Kringos
BMC Health Services Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficiency and equity of elderly care service resource allocation in China, 2014–2022
Min Bao, Rongji Ma, Jianqian Chao
Health Policy and Technology.2025; 14(3): 101016. CrossRef - Institutional and individual factors influencing urinary tract infections and pressure injuries in Korean nursing home residents: A multilevel analysis of National Health Insurance Service Data
Hee Seung Lee, Jung Suk Lee
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2025; 27(4): 349. CrossRef - Nurse staffing and adverse events in residential aged care: Retrospective multi-site analysis
Dorika Nhongo, Annie Holt, Tracy Flenady, Amanda Rebar, Kasia Bail
Collegian.2023; 30(2): 343. CrossRef - Nursing Management-Associated Factors Associated with Urinary Tract Infection in Residents from Nursing Home Based on LTCfocus Database
Wei Wang, Hui Wang
Urologia Internationalis.2022; 106(7): 744. CrossRef - Effects of registered nurse staffing levels, work environment, and education levels on adverse events in nursing homes
Seonhwa Choi, Eunhee Cho, Eunkyo Kim, Kyongeun Lee, Soo Jung Chang
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Increasing Registered Nurse Hours Per Resident Day for Improved Nursing Home Residents’ Outcomes Using a Longitudinal Study
Juh Hyun Shin, Rosemary Anne Renaut, Mark Reiser, Ji Yeon Lee, Ty Yi Tang
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(2): 402. CrossRef
-
2,340
View
-
11
Download
-
7
Web of Science
-
7
Crossref
|