-
Formative versus reflective measurement models in nursing research: a secondary data analysis of a cross-sectional study in Korea
-
Eun Seo Park, Young Il Cho, Hyo Jin Kim, YeoJin Im, Dong Hee Kim
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(1):107-118. Published online February 19, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24095
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF ePub ePub
- Purpose
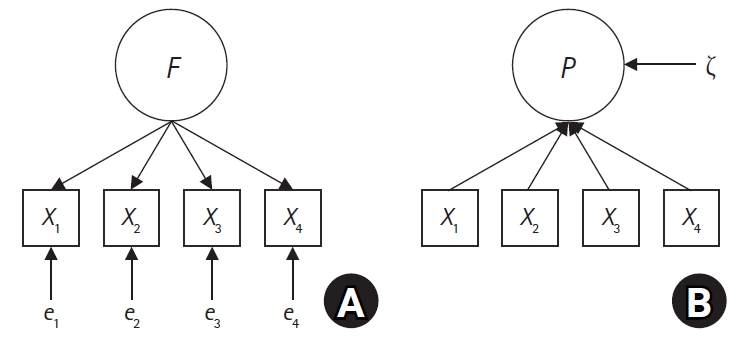
This study aimed to empirically verify the impact of measurement model selection on research outcomes and their interpretation through an analysis of children’s emotional and social problems measured by the Pediatric Symptom Checklist (PSC) using both reflective and formative measurement models. These models were represented by covariance-based structural equation modeling (CB-SEM) and partial least squares SEM (PLS-SEM), respectively.
Methods
This secondary data analysis evaluated children’s emotional and social problems as both reflective and formative constructs. Reflective models were analyzed using CB-SEM, while formative models were assessed using PLS-SEM. Comparisons between these two approaches were based on model fit and parameter estimates.
Results
In the CB-SEM analysis, which assumed a reflective measurement model, a model was not identified due to inadequate fit indices and a Heywood case, indicating improper model specification. In contrast, the PLS-SEM analysis, assuming a formative measurement model, demonstrated adequate reliability and validity with significant path coefficients, supporting the appropriateness of the formative model for the PSC.
Conclusion
The findings indicate that the PSC is more appropriately analyzed as a formative measurement model using PLS-SEM, rather than as a reflective model using CB-SEM. This study highlights the necessity of selecting an appropriate measurement model based on the theoretical and empirical characteristics of constructs in nursing research. Future research should ensure that the nature of measurement variables is accurately reflected in the choice of statistical models to improve the validity of research outcomes.
-
Untact Visit Service Development Based on an Application Reflecting the Circumstances during COVID-19: Focusing on Utilization in the Pediatric Intensive Care Units
-
Dahae Woo, Hanui Yu, Hyo Jin Kim, Minyoung Choi, Dong Hee Kim
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(5):573-584. Published online October 31, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21143
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Purpose
This study aimed to develop an untact visit service based on an application that can be utilized in the pediatric intensive care unit (PICU) during COVID-19.
Methods
This study adopted the double diamond process of service design comprising the discovery, defining, and development stages.
Results
We developed an untact visit service based on an application that considered the child’s status, schedule, photo, and video messages, and so on. Moreover, we derived a service flow regarding the required roles and the type of flow shown between each stakeholder.
Conclusion
Considering the ongoing pandemic, the untact visit service is designed to increase rapport and participation of parents, share the child’s information in real-time, and provide one-stop service without increasing healthcare providers’ work. It will be a useful visit service that can be applied and evaluated in various hospital settings and the PICU.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Factors affecting pediatric nurses’ development of partnerships with parents of hospitalized children: An evaluation based on the stress-coping adaptation model
In Young Cho, So Hyoung Hong, Ji Yeong Yun
Journal of Child Health Care.2025; 29(1): 53. CrossRef - Correlation between oral health knowledge, demand for remote education tools, and self-efficacy among parents of children and adolescents
Min-Ji Park, Herry Novrinda, Jae-Young Lee
Journal of Korean Society of Dental Hygiene.2025; 25(1): 69. CrossRef - Development and Effects of a Family-centered Care Application for Intensive Care Unit Families Based on the Facilitated Sensemaking Model : Focusing on Family Satisfaction, Family Stress, and Self-Efficacy
Yun Ha Oak, Eun Ha Kim
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2025; 18(2): 1. CrossRef - Experiences of Family Members With Visitation Prohibition for Critically Ill Patients
Sunjung Kim, Sunghee H. Tak
Western Journal of Nursing Research.2024; 46(11): 854. CrossRef - Factors influencing neonatal intensive care unit nurses' parent partnership development
Eun Kyoung Kim, In Young Cho, Ji Yeong Yun, Bobae Park
Journal of Pediatric Nursing.2023; 68: e27. CrossRef - National Petition Analysis Related to Nursing: Text Network Analysis and Topic Modeling
HyunJung Ko, Seok Hee Jeong, Eun Jee Lee, Hee Sun Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2023; 53(6): 635. CrossRef - Relationship between parental stress and post‐traumatic stress disorder: The moderating effect of visitation restrictions in paediatric intensive care units during COVID‐19
Young Il Cho, Hyo Jin Kim, Dong Hee Kim
Nursing in Critical Care.2023; 28(5): 808. CrossRef - Need for Information and Communication Technology during COVID-19: An Exploratory Study Using Nurses’ Activity Diaries
Hyeongsuk Lee, Dongmin Lee, Seungmin Lee
Healthcare Informatics Research.2023; 29(3): 256. CrossRef - Effects of a Noncontact Visit Program in the NICU for the Prevention of COVID-19
Hye Young Ahn, Hee Jee Jo, Hyun Jeong Ko
Healthcare.2023; 11(15): 2152. CrossRef - The Development of Automated Personalized Self-Care (APSC) Program for Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Gaeun Park, Haejung Lee, Ah Reum Khang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2022; 52(5): 535. CrossRef
-
1,631
View
-
28
Download
-
8
Web of Science
-
10
Crossref
-
Validity and Reliability of Korean Version of the Family Management Measure (Korean FaMM) for Families with Children having Chronic Illness
-
Dong Hee Kim, Yeo Jin Im
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2013;43(1):123-132. Published online February 28, 2013
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2013.43.1.123
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
-
Purpose
To develop and test the validity and reliability of the Korean version of the Family Management Measure (Korean FaMM) to assess applicability for families with children having chronic illnesses.
Methods
The Korean FaMM was articulated through forward-backward translation methods. Internal consistency reliability, construct and criterion validity were calculated using PASW WIN (19.0) and AMOS (20.0). Survey data were collected from 341 mothers of children suffering from chronic disease enrolled in a university hospital in Seoul, South Korea.
Results
The Korean version of FaMM showed reliable internal consistency with Cronbach's alpha for the total scale of .69-.91. Factor loadings of the 53 items on the six sub-scales ranged from 0.28-0.84. The model of six subscales for the Korean FaMM was validated by expiratory and confirmatory factor analysis (χ2<.001, RMR<.05, GFI, AGFI, NFI, NNFI>.08). Criterion validity compared to the Parental Stress Index (PSI) showed significant correlation.
Conclusion
The findings of this study demonstrate that the Korean FaMM showed satisfactory construct and criterion validity and reliability. It is useful to measure Korean family's management style with their children who have a chronic illness.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Family management styles of families of children and adolescents with developmental disabilities during the COVID-19 pandemic: a cross-sectional study
Anna Lee, Eun Ju Park, Yeeun Kim
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Mediating Effects of Parental Family Adaptation on the Quality of Life of Children With Down Syndrome: A Study of Father–Mother Dyads
Seung Hyeon Yang, Chang Gi Park, Eun Kyoung Choi
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Family responses and influencing factors in raising children with developmental disabilities: A cross-sectional study in South Korea
Anna Lee, Won-Oak Oh, Eun Ju Park
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Family management structural model for children with atopic dermatitis
Sunyeob Choi, Hyewon Shin
Journal of Pediatric Nursing.2024; 77: e401. CrossRef - Perception of precocious puberty among school-aged children in South Korea with the experience of treatment for precocious puberty: a Q methodological approach
Sun Jung Park, Hye Ri Nam, Eun Ju Choi
Child Health Nursing Research.2023; 29(3): 195. CrossRef - Nursing Interventions for Children with Atopic Dermatitis and Their Families
Bomi Kim, Sunyeob Choi
MCN: The American Journal of Maternal/Child Nursing.2023; 48(6): 312. CrossRef - Developing a culturally appropriate version of family management measure in Taiwan: a cognitive interviewing study
Chia-Hsuan Lin, Fan-Hao Chou
Journal of Family Studies.2023; 29(1): 28. CrossRef - Family Management Style and Psychosocial Health of Children with Chronic Conditions
YeoJin Im, Dong Hee Kim
Journal of Child and Family Studies.2021; 30(2): 483. CrossRef - Actor and partner effects of parenting stress and co-parenting on marital conflict among parents of children with atopic dermatitis
Jeong Won Han, Hanna Lee
BMC Pediatrics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Family functioning according to clusters of family management styles in Korean families of children with chronic atopic disease: A cross-sectional study
YeoJin Im, Sunyoung Jung
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2020; 109: 103674. CrossRef - Mothers' Experiences of Caring for Children with Precocious Puberty: A Q-Methodological Approach
Hye Jin Lee, Mi-Ae You
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2020; 50(2): 255. CrossRef - mHealth Family Adaptation Intervention for Families of Young Children with Down Syndrome: A Feasibility Study
Hyunkyung Choi, Marcia Van Riper
Journal of Pediatric Nursing.2020; 50: e69. CrossRef - The Family Management of Childhood Chronic Conditions: Measurement in a Turkish Sample
Ayse Ergun, Fatma Nevin Sisman, Saime Erol, Kamer Gur, Nurcan Kolac, Hasibe Kadioglu
Journal of Pediatric Nursing.2019; 47: e16. CrossRef - Family Management Style as a Mediator between Parenting Stress and Quality of Life of Children with Epilepsy
YeoJin Im, YoungIl Cho, DongHee Kim
Journal of Pediatric Nursing.2019; 45: e73. CrossRef - Adapting the Family Management Styles Framework to Include Children
Barbara L. Beacham, Janet A. Deatrick
Journal of Pediatric Nursing.2019; 45: 26. CrossRef - Effects of the Mother-Medical Staff Partnership on Mothers’ Condition Management Ability for Children with Chronic Allergic Diseases
Hae Kyoung Son, Hyo Bin Song, Dong Hee Kim
Child Health Nursing Research.2018; 24(1): 101. CrossRef - Family management of childhood atopic dermatitis
Hae Kyoung Son, Dong Hee Kim, Hyejung Lee, Heejung Kim, Kyongmee Chung, Hee‐Soon Kim
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2018; 74(6): 1371. CrossRef - Self-Management Experiences of the Adolescents with Chronic Kidney Disease
Sug Young Lee, Heesun Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2018; 48(3): 266. CrossRef - Validation of Family Management Measure for the Brazilian culture
Regina Szylit Bousso, Carolliny Rossi de Faria Ichikawa, Maira Deguer Misko, Maiara Rodrigues dos Santos, Michelle Freire Baliza, Ana Márcia Chiaradia Mendes-Castillo, Estela Regina Ferraz Bianchi
Revista Brasileira de Enfermagem.2017; 70(6): 1151. CrossRef - A Comparative Study of Family Management Style According to Severity of Childhood Atopic Dermatitis
Hae Kyoung Son, Hee-Soon Kim
Child Health Nursing Research.2016; 22(4): 309. CrossRef - Educational Programs for the Management of Childhood Atopic Dermatitis: An Integrative Review
Yunmi Lee, Jina Oh
Asian Nursing Research.2015; 9(3): 185. CrossRef - The influence of family management style on psychosocial problems of childhood cancer survivors in Korea
Dong Hee Kim, Yeo Jin Im
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2015; 19(2): 107. CrossRef
-
1,267
View
-
20
Download
-
22
Crossref
-
Development of a Questionnaire to Measure Resilience in Children with Chronic Diseases
-
Dong Hee Kim, Il Young Yoo
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2010;40(2):236-246. Published online April 30, 2010
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2010.40.2.236
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
-
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to develop and evaluate a Korean questionnaire to measure resilience in children with chronic illness.
Methods
Item construction was drawn from an extensive review of the literature, existing questionnaires and interviews with parents. Content validity was tested by experts. To further refine the questionnaire and test its reliability and validity, data were collected from the 202 children with asthma, diabetes mellitus or nephrotic syndrome. Corrected items were used to total correlation coefficient and test-retest reliability. Questionnaire testing was conducted using factor analysis, Cronbach's α, and correlation coefficients. Validity of the questionnaire was tested using internal consistency, construct validity, and criterion-related validity.
Results
Components of the questionnaire were in three domains; interpersonal characteristics, characteristics of coping, and intrapersonal characteristics. Factor analysis is showed five factors; positive self-understanding, self-reliance, resourcefulness, perception of positive family relationships, and intimacy. The questionnaire showed a high internal consistency. A significant positive correlation with the Numerical Rating Score and negative correlation with the Child Depression Inventory support the validity of the questionnaire.
Conclusion
This instrument demonstrated high reliability and validity. Therefore, this instrument can contribute to the evaluation of resilience of chronically ill children and to any subsequent intervention as well as to develop a theory for resilience.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Development and evaluation of an educational picture book targeted at perioperative psycho-behaviors among children undergoing tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy: A mixed-method study
Yao Tang, Ka Yan Ho, Jinlin Ye, Lei Yang, Yunfan Li, Xianhong Li
Journal of Pediatric Nursing.2026; 87: 1. CrossRef - Qualitative Content Analysis of the Resilience Scale for Patients With Kidney Transplantation
Mi Ha Chung
Journal of Renal Care.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and Validation of the Resilience Scale for Kidney Transplantation (RS-KTPL)
Mi Ha Chung, Hyojung Park
Asian Nursing Research.2024; 18(2): 167. CrossRef - A disease‐targeted picture book for children with Henoch‐Schonlein purpura nephritis: A quasi‐experimental study
Yao Tang, Weiti Chen, Jingping Li, Yuqian Deng, Shibo Liu, Xia Zhou, Jianhui Xie, Chaohong Zhan, Xianhong Li
Journal of Renal Care.2023; 49(4): 243. CrossRef - Defining and Measuring Resilience in Children with a Chronic Disease: a Scoping Review
Sabine E. I. van der Laan, Emma E. Berkelbach van der Sprenkel, Virissa C. Lenters, Catrin Finkenauer, Cornelis K. van der Ent, Sanne L. Nijhof
Adversity and Resilience Science.2023; 4(2): 105. CrossRef - Development of Resilience Scale for Adolescent Allergic Children
Yoshie Shimizu, Takanori Imai, Tsutomu Matsumoto, Kazuo Nonomura, Taro Kamiya, Yuki Okada, Aiko Honda
Nihon Shoni Arerugi Gakkaishi. The Japanese Journal of Pediatric Allergy and Clinical Immunology.2022; 36(5): 499. CrossRef - Less is more. Discovering the latent factors of trait resilience
John Maltby, Sophie S. Hall
Journal of Research in Personality.2022; 97: 104193. CrossRef - Effects of the Mother-Medical Staff Partnership on Mothers’ Condition Management Ability for Children with Chronic Allergic Diseases
Hae Kyoung Son, Hyo Bin Song, Dong Hee Kim
Child Health Nursing Research.2018; 24(1): 101. CrossRef - Association of Resilience and Depression with Self-care Competence in Adult Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Youngrye Park, Eun Hee Jang, Ji Ok Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2018; 30(5): 555. CrossRef - Development of Resilience Scale for Nurses
Mi Mi Park, Jee-Won Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2016; 23(1): 32. CrossRef - Health Impaired Children's Participation Experience of Hospital School Programs as Perceived by Mothers
Hyun Jung Yun
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2015; 29(3): 515. CrossRef - Predictors of Resilience in Adolescents with Leukemia
Sung Sil Hong, Ho Ran Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2015; 45(4): 595. CrossRef - Resilience as a protective factor for the behavioral problems in school-aged children with atopic dermatitis
Dong Hee Kim, Yeo Jin Im
Journal of Child Health Care.2014; 18(1): 47. CrossRef - Predictors of Resilience in Adolescents with Cancer.
Young Ok Park, Gwi Ryung Son Hong, Young Ran Tak
Child Health Nursing Research.2013; 19(3): 177. CrossRef - Factors associated with the resilience of school‐aged children with atopic dermatitis
Yeo Jin Im, Dong Hee Kim
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2012; 21(1-2): 80. CrossRef - Relationship among Perception of Parenting Attitude, Behavior Problems and Resilience of School Age Children
Hyun-Jung Yun, Il-Young Yoo, Eui-Geum Oh
Journal of Korean Academy of Child Health Nursing.2011; 17(3): 174. CrossRef
-
1,472
View
-
11
Download
-
16
Crossref
-
Relationship between Depression and Resilience among Children with Nephrotic Syndrome
-
Dong Hee Kim, Il Young Yoo
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2004;34(3):534-540. Published online March 28, 2017
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2004.34.3.534
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
-
Purpose
The purposes of this study were to describe the relationship between depression and resilience and to identify variables associated with depression among children with nephrotic syndrome.
Method
Data was collected from 45 children who were registered at one hospital in Seoul. The criteria for sample selection were 10 to 15 year-old children who were diagnosed at least 6 month prior. The instruments included a self-reported questionnaire on resilience by Kim, CDI by Beck, and MBRI by Kwak. Descriptive, Pearson correlation and multiple regression analyses were done.
Result
The mean score of depression was 11.44 (range:0-54) and resilience was 97.47 (range:32-128). There were significant positive relationships between depression and age (r=0.302, p<.005) and academic achievement (r=-0.318, p<.005). In addition, negative relationships between depression and maternal attitude (r=-0.412, p<.001) and resilience (r=-0.649, p<.001) occurred. The results of multiple regression analysis showed that maternal behavior (β=-0.421, p<.005) and resilience (β=-0.639, p<.001) were related to depression.
Conclusion
Children with higher resilience and with an affectionate mother were less depressed. Thus, it is important to identify strengths of children and help them to increase resilience and implement parenting and counseling programs for parents' of these children. Similar studies with children with other chronic illnesses are needed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Effects of Envy on Depression: The Mediating Roles of Psychological Resilience and Social Support
Yanhui Xiang, Xia Dong, Jiaxu Zhao
Psychiatry Investigation.2020; 17(6): 547. CrossRef - Variations and factors associated with psychotropic use in cognitively impaired elderly residing in long‐term care facilities in East Asia: a cross‐sectional study
Saya Terada, Miyae Yamakawa, Younhee Kang, Sayuri Kobayashi, Xiao‐yan Liao, Sirirat Panuthai, Huei‐chuan Sung, Mizue Suzuki, Kiyoko Makimoto
Psychogeriatrics.2019; 19(4): 291. CrossRef - Structural Equation Modeling With Many Variables: A Systematic Review of Issues and Developments
Lifang Deng, Miao Yang, Katerina M. Marcoulides
Frontiers in Psychology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Predictors of Behavioral and Psychological Symptoms of Dementia: Based on the Model of Multi-Dimensional Behavior
Jeong Eun Yang, Gwi-Ryung Son Hong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2018; 48(2): 143. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Health-related Quality of Life among Knee or Hip Arthroplasty Patients
Mi Kyung Kang, Geun Jin Kim, Hye Young Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2017; 24(3): 209. CrossRef - The Relationships among Resilience, Family Support, and Diabetes Adaptation in Children with Diabetes Mellitus
Yongmi Kim, Kyung-Sook Bang
Perspectives in Nursing Science.2017; 14(1): 21. CrossRef - Impact of Behavioral Symptoms in Dementia Patients on Depression in Daughter and Daughter-in-Law Caregivers
Juwon Lee, Bo Kyung Sohn, Hyunjoo Lee, Sujeong Seong, Soowon Park, Jun-Young Lee
Journal of Women's Health.2017; 26(1): 36. CrossRef - Associations between remaining teeth and salivary flow, activity of daily living, and cognitive impairment among the elderly in a rural area: A pilot study
Eun-Kyong Kim, Sung Kook Lee, Yun Sook Jung, Hee-Kyung Lee, Keun-Bae Song, Youn-Hee Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Oral Health.2016; 40(1): 43. CrossRef - The effects of resilience on subjective stress response and salivary secretory immunoglobulin A in university students
Hisashi Mitsuishi, Shintaro Endo, Takayuki Ishiwata, Kazuo Oishi
The Journal of Physical Fitness and Sports Medicine.2016; 5(4): 319. CrossRef - Effect of Muscle Strength Training on Urinary Incontinence and Physical Function: A Randomized Controlled Trial in Long-term Care Facilities
Hyekyung Kang, Gwi-Ryung Son Hong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2015; 45(1): 35. CrossRef - Estimation of minimally important differences in the EQ-5D and SF-6D indices and their utility in stroke
Sang-Kyu Kim, Seon-Ha Kim, Min-Woo Jo, Sang-il Lee
Health and Quality of Life Outcomes.2015; 13(1): 32. CrossRef - Sleep Problems Associated with Behavioral and Psychological Symptoms as Well as Cognitive Functions in Alzheimer's Disease
Hye-Young Shin, Hyun Jung Han, Dong-Jin Shin, Hyeon-Mi Park, Yeong-Bae Lee, Kee Hyung Park
Journal of Clinical Neurology.2014; 10(3): 203. CrossRef - Factors that influence activities of daily living in the elderly with probable dementia
E. Ha, K. Kim
Journal of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2014; 21(5): 447. CrossRef - Cognitive Intervention in a Patient with Carbon Monoxide Intoxication
Ji-Hyang Oh, Go-Woon Kim, Seong H. Choi, Jee H. Jeong, Hae R. Na, Jung E. Kim, Duk L. Na, Chang Hee Hong, Eun-Joo Kim
Dementia and Neurocognitive Disorders.2014; 13(4): 139. CrossRef - Effects of Resilience on Work Engagement and Burnout of Clinical Nurses
Inn Oh Moon, Sook Kyoung Park, Jung Mi Jung
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2013; 19(4): 525. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Social Adjustment of Childhood Cancer Survivors.
Su Mi Oh, Hye Jung Lee, Gwang Suk Kim, Kyung Duk Park
Child Health Nursing Research.2013; 19(3): 238. CrossRef - Effects of Multisensory Stimulation Using Familiarity: Persons with Dementia in Long-term Care Facility in Korea
Gwi-Ryung Son Hong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2011; 41(4): 528. CrossRef - Relationship among Perception of Parenting Attitude, Behavior Problems and Resilience of School Age Children
Hyun-Jung Yun, Il-Young Yoo, Eui-Geum Oh
Journal of Korean Academy of Child Health Nursing.2011; 17(3): 174. CrossRef - Depressive Symptoms and Related Risk Factors in Old and Oldest-old Elderly People with Arthritis
Ji-Yeon An, Young-Ran Tak
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(1): 72. CrossRef - Factors influencing depression in adolescents with congenital heart disease
Ju Ryoung Moon, June Huh, I.-Seok Kang, Seung Woo Park, Tae-Gook Jun, Heung Jae Lee
Heart & Lung.2009; 38(5): 419. CrossRef - Concept Analysis of Resilience in Patients with Cardiovascular Diseases
Su-Jin Shin, Duk-Yoo Jung, Eun-Hee Hwang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(6): 788. CrossRef - Change of Cognitive Function and Associated Factors among the Rural Elderly: A 5-Year Follow-up Study
Sang-Kyu Kim, Pock-Soo Kang, Tae-Yoon Hwang, Joon Sakong, Kyeong-Soo Lee
Journal of Preventive Medicine and Public Health.2007; 40(2): 162. CrossRef - Relationship between depression and resilience in adolescents with congenital heart disease
Ju Ryoung Moon, Yoen Yi Jung, June Huh, I-Seok Kang, Seung Woo Park, Ji-Hyuk Yang, Tae-Gook Jun, Myung Ja Kim, Heung Jae Lee
Korean Journal of Pediatrics.2006; 49(5): 523. CrossRef
-
957
View
-
1
Download
-
23
Crossref
|