Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Nurs > Volume 39(3); 2009 > Article
-
Original Article
- The Effects of Aromatherapy on Stress and Stress Responses in Adolescents
- Ji-Yeong Seo
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2009;39(3):357-365.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2009.39.3.357
Published online: June 29, 2009
Full-time Lecturer, Department of Nursing, Youngnam Foreign Language College, Gyeongsan, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Seo, Ji-Yeong. Department of Nursing, Youngnam Foreign Language College, 220-1 Hyeopseok-ri, Namcheon-myeon, Gyeongsan 712-717, Korea. Tel: 82-53-810-7763, Fax: 82-53-810-0199, marseo@hanmail.net
Copyright © 2009 Korean Society of Nursing Science
Abstract
-
Purpose
- This study was done to examine the effects of aromatherapy on stress and stress responses in adolescents.
-
Methods
- A two-group cross-over design was used for this study. The experimental treatment was aroma essential oil inhalation and the placebo treatment was carrier oil inhalation using a necklace. The sample included 36 female high school students. Fisher's exact test, t-test, and paired t-test using SPSS/WIN program were used to analyze the data.
-
Results
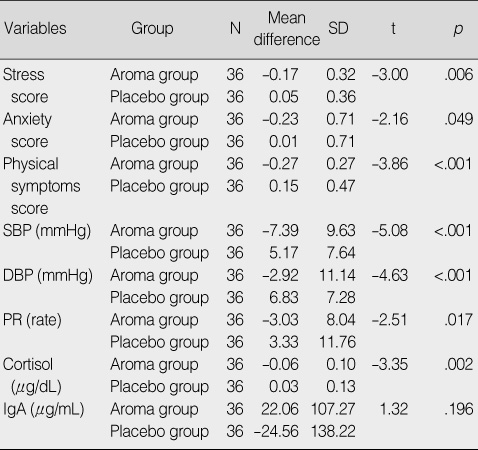
- Stress levels were significantly lower when the students received the aroma treatment compared to when they received the placebo treatment. The stress responses except salivary IgA levels were significantly lower when the students received the aroma treatment.
-
Conclusion
- Aroma inhalation could be a very effective stress management method for high school students. Therefore, it is recommended that this program be used in clinical practice as an effective nursing intervention for high school students.
- 1. Byeon YJ. A study of the relations between parents' rearing attitude, irrational beliefs and stress of adolescents. 1995;Seoul, Yonsei University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 2. Deinzer R, Schuller N. Dynamics of stress-related decrease of salivary immunoglobulin A (sIgA): Relationship to symptoms of the common cold and studying behavior. Behavioral Medicine. 1998;23:161–169.ArticlePubMed
- 3. Han SH. Effects of aromatherapy on headache, stress and immune response of students with tension-type headache. 2002;Seoul, The Catholic University of Korea. Unpublished doctoral dissertation.
- 4. Han SS, Lee SC. SPSS Nursing · Health Statistical Analysis. 2006;Seoul, Hyunmoonsa.
- 5. Hwang JH. The effect of the inhalation method using essential oils on blood pressure and stress responses of clients with essential hypertension. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2006;36:1123–1134.PubMed
- 6. Ju KY. The effect of aromatherapy on psychological stress and stress hormones in blood after maximal exercise. 2002;Seoul, Kookmin University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 7. Kim JS. A Study on stress, anxiety, mental health in high school students. 2001;Daejeon, Chungnam National University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 8. Kim JT, Shin DK. A study based on the standardization of the STAI for Korea. The New Medicine Journal. 1979;21(11):69–75.
- 9. Kim KS. Effects of aromatherapy on psychological and physiological responses in the middle aged women. 2003;Seoul, Yonsei University. Unpublished doctoral dissertation.
- 10. Kirschbaum C. Salivary cortisol technical issues. 2008;Retrieved September 17, 2008. from http://www.macses.ucsf.edu/Research/Allostatic/notebook/FAQs-salivcort.pdf.
- 11. Ko HM. Relation of anxiety, stress perception and academic achievement. 1998;Gwangju, Chonnam National University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 12. Ko MJ, Yu SJ, Kim YG. The effects of solutionfocused group counseling on the stress response and coping strategies in the delinquent juveniles. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2003;33:440–450.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 13. Lee CR. The effect of aroma inhalation method on stress, anxiety, and self-efficacy in high school seniors. 2005;Iksan, Wonkwang University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 14. Lee IS. Effects of Lavender fragrance on depression and anxiety of nursing students intending to take the National Licensing Examination. Journal of Korean Academy of Public Health Nursing. 2006;20:87–94.
- 15. Lee SH. Psychoneuroimmunologic effect of aromatherapy massage. Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing. 2000;6:305–315.ArticlePDF
- 16. Lemon K. An assessment of treating depression and anxiety with aromatherapy. International Journal of Aromatherapy. 2004;14:63–69.Article
- 17. Moon KS. Correlational study between stress and physical symptoms of middle school students. 2002;Seoul, Ewha Womans University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 18. Nam JS. The relationship between participation in leisure sports activities of middle and high school students and pro-social behavior. 2004;Seoul, Kyung Hee University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 19. Naughton FO. Stress and coping. 1997;Retrieved November 2, 2004. from http://www.csun.edu/~vcpsy00h/students/coping.htm.
- 20. Oh HK, Choi JY, Chun KK, Lee JS, Park DK, Choi SD, et al. A study for antistress effects of two aromatic synergic blending oils. Journal of the Korean Society of Jungshin Science. 2001;14:33–49.
- 21. Page GG, Lindsey AM. Carrieri-Kohlman V, Lindsey AM, West CM. Stress response. In: Pathophysiological phenomena in nursing : Human responses to illness. 2003;St. Louis, MO, Saunders. 275–295.
- 22. Park MK, Lee ES. The effect of aroma inhalation method on stress responses of nursing students. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2004;34:344–351.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 23. Park SO. The reduced effects of aromatherapy on stress and sleep disturbance. 2001;Daegu, Youngnam University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 24. Romine IJ, Bush AM, Charles RG. Lavender aromatherapy in recovery from exercises. Perceptual and Motor Skills. 1999;88:756–758.PubMed
- 25. Seo JY, Kim MY. Stress, physical symptoms, and coping styles of high school students. The Korean Journal of Child Health Nursing. 2006;12:470–477.
- 26. Sharrer VW, Ryan-Wenger NA. School-age children's self-reported stress symptoms. Pediatric Nursing. 2002;28:21–27.
- 27. Son KC, Song JE, Um SJ, Paek KY, Oh HK, Lee JS, et al. Effect of absorption of essential oils on the changes of arousal and antistress. Journal of Korean Society of Horticultural Science. 2001;42:614–620.
- 28. Spielberger CD. Anxiety: Current trends in theory and research. 1972;1st ed. New York, NY, Academic Press.
- 29. Tweed SA. Affective and biological reaction to the inhalation of the essential oil lavender. 1999;Texas, USA, Christopher Newport University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 30. Yoon IS. The effects of the stress-coping training on stress reaction of high school students. 2004;Seoul, Korea University. Unpublished master's thesis.
REFERENCES
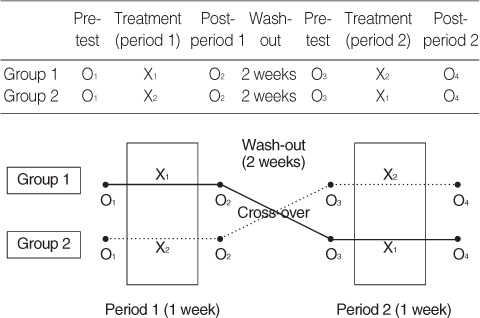
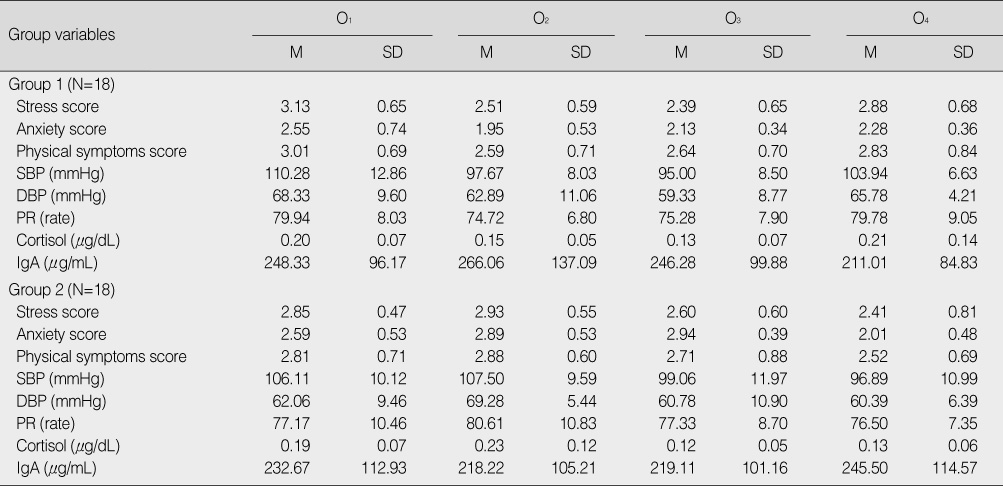
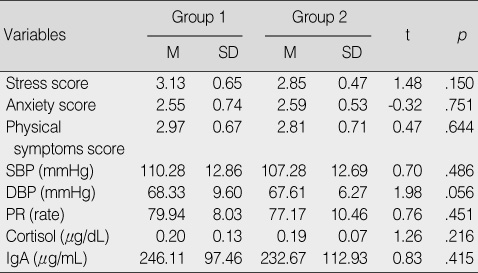
O1 & O3 was pre-test in both group 1 and group 2; O2 was after aroma inhalation in group 1, and after placebo inhalation in group 2; O4 was after placebo inhalation in group 1, and after aroma inhalation in group 2.
SBP=systolic blood pressure; DBP=diastolic blood pressure; PR=pulse rate; IgA=immunoglobulin A.
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Aromatherapy and Its Impact on Taekwondo Athletes' Performance: A Bibliographic Review
Bahouq Madiha, Bahouq Hanane, Soulaymani Abdelmajid, Amassnaou Ali, Elhilali Driss
International Journal of Sports Science and Physical Education.2025; 10(1): 1. CrossRef - A Toolkit of Biophilic Interventions for Existing Schools to Enhance Student and Faculty Health and Performance
Kari Leif, Vivian Loftness
Architecture.2024; 4(2): 445. CrossRef - The association of air pollution with blood pressure, heart rate and stress among office workers using essential oils
Chien-Yu Lee, I-Jung Liu, Chih-Hong Pan, Lian-Yu Lin, Hsiao-Chi Chuang, Kin-Fai Ho, Chia-Huang Chang, Kai-Jen Chuang
Atmospheric Environment.2024; 338: 120808. CrossRef - The effect of musk incense stick aroma inhalation on different features of electroencephalogram signals and working memory for use in neurofeedback training
Siminsadat Hasheminia, Nasrin Sho’ouri
Biomedical Signal Processing and Control.2023; 83: 104658. CrossRef - Evaluating the effectiveness of applying aroma seals to masks in reducing stress caused by wearing masks: A randomized controlled trial
Nobuyuki Wakui, Kotoha Ichikawa, Aika Okami, Hinako Kagi, Shoko Kawakubo, Chikako Togawa, Raini Matsuoka, Mai Watanabe, Miho Yamamura, Shunsuke Shirozu, Yuika Tsubota, Yukiko Yoshizawa, Yoshiaki Machida, Kamal Sharma
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(11): e0294357. CrossRef - Effectiveness of lemon essential oil in reducing test anxiety in nursing students
Zülfinaz Özer, Neslihan Teke, Gülcan Bahcecioglu Turan, Ayşe Nefise Bahçecik
EXPLORE.2022; 18(5): 526. CrossRef - Long-Term Exposure to Essential Oils and Cardiopulmonary Health from a Population-Based Study
Chien-Yu Lee, Lian-Yu Lin, Hsiao-Chi Chuang, Kin-Fai Ho, Kai-Jen Chuang
Atmosphere.2022; 13(4): 631. CrossRef - Effect of aromatherapy on autonomic nervous system regulation with treadmill exercise-induced stress among adolescents
Pin-Hsuan Lin, Yuan-Ping Lin, Kai-Li Chen, Shang-Yu Yang, Yin-Hwa Shih, Po-Yu Wang, Nejka Potocnik
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(4): e0249795. CrossRef - Intranasal use of lavender and fennel decreases salivary cortisol levels and improves quality of sleep: A double-blind randomized clinical trial
Hudson Polonini, Dominique Mesquita, Julia Lanine, Eli Dijkers, Spiros Gkinis, Nádia Rezende Barbosa Raposo, Marcos Antônio Fernandes Brandão, Anderson de Oliveira Ferreira
European Journal of Integrative Medicine.2020; 34: 101015. CrossRef - Evaluation of aromatherapy with lavender oil on academic stress: A randomized placebo controlled clinical trial
Rizwan Ahmad, Atta Abbas Naqvi, Hamdan Moayed Al-Bukhaytan, Ahmed Habib Al-Nasser, Ali Hassan Baqer Al-Ebrahim
Contemporary Clinical Trials Communications.2019; 14: 100346. CrossRef - Quality Assurance in Interventional Radiology: Intra-procedural Care
Roberto Forcella, Tarek Jazmati, Abhishek Kumar, Hani Abujudeh
Current Radiology Reports.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Can aromatherapy be used to reduce anxiety in hospitalised felines
Samantha Goodwin, Helen Reynolds
The Veterinary Nurse.2018; 9(3): 167. CrossRef - A novel approach of substitution therapy with inhalation of essential oil for the reduction of inhalant craving: A double-blinded randomized controlled trial
Rasmon Kalayasiri, Wanjaree Maneesang, Michael Maes
Psychiatry Research.2018; 261: 61. CrossRef - The effects of aromatherapy essential oil inhalation on stress, sleep quality and immunity in healthy adults: Randomized controlled trial
Mi-kyoung Lee, Sunog Lim, Ji-Ah Song, Mi-Eun Kim, Myung-Haeng Hur
European Journal of Integrative Medicine.2017; 12: 79. CrossRef - The Effects of Aroma Foot Massage on Blood Pressure and Anxiety in Japanese Community-Dwelling Men and Women: A Crossover Randomized Controlled Trial
Eri Eguchi, Narumi Funakubo, Kiyohide Tomooka, Tetsuya Ohira, Keiki Ogino, Takeshi Tanigawa, Yoshihiro Fukumoto
PLOS ONE.2016; 11(3): e0151712. CrossRef - Health Literacy and Health Promoting Behaviors in adolescents
Ji Young Kim, Min Hyun Suk
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2016; 30(3): 570. CrossRef - Citrus bergamia essential oil: from basic research to clinical application
Michele Navarra, Carmen Mannucci, Marisa Delbò, Gioacchino Calapai
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - The effects of aromatherapy in relieving symptoms related to job stress among nurses
Miao‐Chuan Chen, Shu‐Hui Fang, Li Fang
International Journal of Nursing Practice.2015; 21(1): 87. CrossRef - Effects of the Aroma Inhalation Method with a Roll-on on Life Stress, Salivary Cortisol and Fatigue in Nursing Student
In-Sook Kim, Seung-Ju Kang, Ja-Ok Kim
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2014; 15(12): 7214. CrossRef - Effect of lavender inhalation on the symptoms of primary dysmenorrhea and the amount of menstrual bleeding: A randomized clinical trial
Ziba Raisi Dehkordi, Fatemeh Sadat Hosseini Baharanchi, Reza Bekhradi
Complementary Therapies in Medicine.2014; 22(2): 212. CrossRef - Effects of Aroma-Necklace Application on Perceived Stress, Symptoms of Stress and Changes in Autonomic Nervous System among Nursing Students in Clinical Training
Mi Hee Kim, Jin Il Kim, Eun Ha
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2014; 16(4): 334. CrossRef - The effect of aromatherapy and massage administered in different ways to women with breast cancer on their symptoms and quality of life
Özlem Ovayolu, Ümit Seviğ, Nimet Ovayolu, Alper Sevinç
International Journal of Nursing Practice.2014; 20(4): 408. CrossRef - The effect of essential oil on heart rate and blood pressure among solus por aqua workers
Kai-Jen Chuang, Hua-Wei Chen, I-Jung Liu, Hsiao-Chi Chuang, Lian-Yu Lin
European Journal of Preventive Cardiology.2014; 21(7): 823. CrossRef - Anticancer activity of essential oils: a review
Yashika Bhalla, Vinay Kumar Gupta, Vikas Jaitak
Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture.2013; 93(15): 3643. CrossRef - Two-week aroma inhalation effects on blood pressure in young men with essential hypertension
Kayeon Seong, Jun-Hwa Hong, Myung-Haeng Hur, Myeong Soo Lee
European Journal of Integrative Medicine.2013; 5(3): 254. CrossRef - Effects of Aroma Inhalation Method on Test Anxiety, Stress Response and Serum Cortisol in Nursing Students
Ye-Jung Ko, Myoung-Soon Jung, Kyung-Sook Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2013; 20(4): 410. CrossRef - Effects of Phytoncide Aromatherapy on Stress, Symptoms of Stress and Heart Rate Variability among Nursing Students
Chul-Gyu Kim, Mi-Kyoung Cho, Jin-Il Kim
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2012; 14(4): 249. CrossRef - Boarding High School Students' Life Stress and Coping Skills
Kwisoon Choe, Sung Bok Kwon, Hye Gyeong Cha
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2011; 20(1): 25. CrossRef - Actions of essential oils on the central nervous system: An updated review.
Clara Dobetsberger, Gerhard Buchbauer
Flavour and Fragrance Journal.2011; 26(5): 300. CrossRef - Aromatherapy Benefits Autonomic Nervous System Regulation for Elementary School Faculty in Taiwan
Kang-Ming Chang, Chuh-Wei Shen
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine.2011;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Inhaling Essential Oils from Lavender, Silver Fir, Grapefruit on the Restraint Stress in Mice
Seun-Ah Yang, Sang-Kyung Jeon, Eun-Jung Lee, Nam-Kyung Im, Chang-Hyun Shim, In-Seon Lee
Journal of Life Science.2010; 20(8): 1230. CrossRef
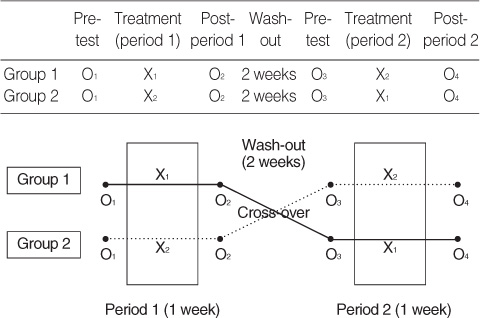
Figure 1
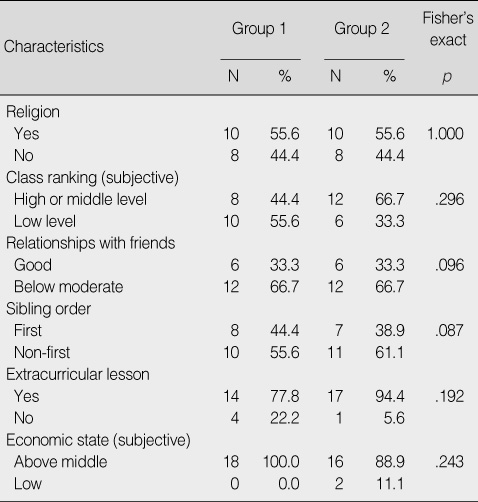
Homogeneity Test for General Characteristics between the Group 1 and Group 2 at Pre-test (O1) (N=36)
Group 1=aroma inhalation-1st & placebo inhalation-2nd; Group 2=placebo inhalation-1st & aroma inhalation-2nd.
Homogeneity Test for Dependent Variables at Pre-test (O1) (N=36)
Group 1=aroma inhalation-1st & placebo inhalation-2nd; Group 2=placebo inhalation-1st & aroma inhalation-2nd; SBP=systolic blood pressure; DBP=diastolic blood pressure; PR=pulse rate; IgA=immunoglobulin A.
Stress Score and Stress Response per Every Period in Group 1 and Group 2
O1 & O3 was pre-test in both group 1 and group 2; O2 was after aroma inhalation in group 1, and after placebo inhalation in group 2; O4 was after placebo inhalation in group 1, and after aroma inhalation in group 2.
SBP=systolic blood pressure; DBP=diastolic blood pressure; PR=pulse rate; IgA=immunoglobulin A.
Changes in Stress Score and Stress Response between the Post-Aroma and Post-Placebo
Mean difference of aroma group=O2-O1 of Group 1 and O4-O3 of Group 2; Mean difference of placebo group=O4-O3 of Group 1 and O2-O1 of Group 2; SBP=systolic blood pressure; DBP=diastolic blood pressure; PR=pulse rate; IgA=immunoglobulin A.
Group 1=aroma inhalation-1st & placebo inhalation-2nd; Group 2=placebo inhalation-1st & aroma inhalation-2nd.
Group 1=aroma inhalation-1st & placebo inhalation-2nd; Group 2=placebo inhalation-1st & aroma inhalation-2nd; SBP=systolic blood pressure; DBP=diastolic blood pressure; PR=pulse rate; IgA=immunoglobulin A.
O1 & O3 was pre-test in both group 1 and group 2; O2 was after aroma inhalation in group 1, and after placebo inhalation in group 2; O4 was after placebo inhalation in group 1, and after aroma inhalation in group 2. SBP=systolic blood pressure; DBP=diastolic blood pressure; PR=pulse rate; IgA=immunoglobulin A.
Mean difference of aroma group=O2-O1 of Group 1 and O4-O3 of Group 2; Mean difference of placebo group=O4-O3 of Group 1 and O2-O1 of Group 2; SBP=systolic blood pressure; DBP=diastolic blood pressure; PR=pulse rate; IgA=immunoglobulin A.
 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION
 Cite
Cite

