Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Nurs > Volume 45(6); 2015 > Article
-
Original Article
- Effects of Lifestyle Intervention on Fatigue, Nutritional Status and Quality of Life in Patients with Gynecologic Cancer
- Hyunjin An1, Ju-Hee Nho2, Sunyoung Yoo1, Hyunmin Kim1, Minji Nho1, Hojeong Yoo1
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2015;45(6):812-822.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2015.45.6.812
Published online: December 15, 2015
1Department of Nursing, Asan Medical Center, Seoul
2College of Nursing, Chonnam National University, Gwangju, Korea
1Department of Nursing, Asan Medical Center, Seoul
2College of Nursing, Chonnam National University, Gwangju, Korea
- Address reprint requests to : Nho, Ju-Hee College of Nursing, Chonnam National University, 160 Baekseo-ro, Dong-gu, Gwangju 61469, Korea Tel: +82-62-530-4949 Fax: +82-62-227-4009 E-mail: jhnho@jnu.ac.kr
Copyright © 2015 Korean Society of Nursing Science
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NoDerivs License. (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nd/4.0) If the original work is properly cited and retained without any modification or reproduction, it can be used and re-distributed in any format and medium.
Abstract
-
Purpose
- The purpose of this study was to examine the effect of lifestyle intervention on the development of fatigue, nutritional status and quality of life of patients with gynecologic cancer.
-
Methods
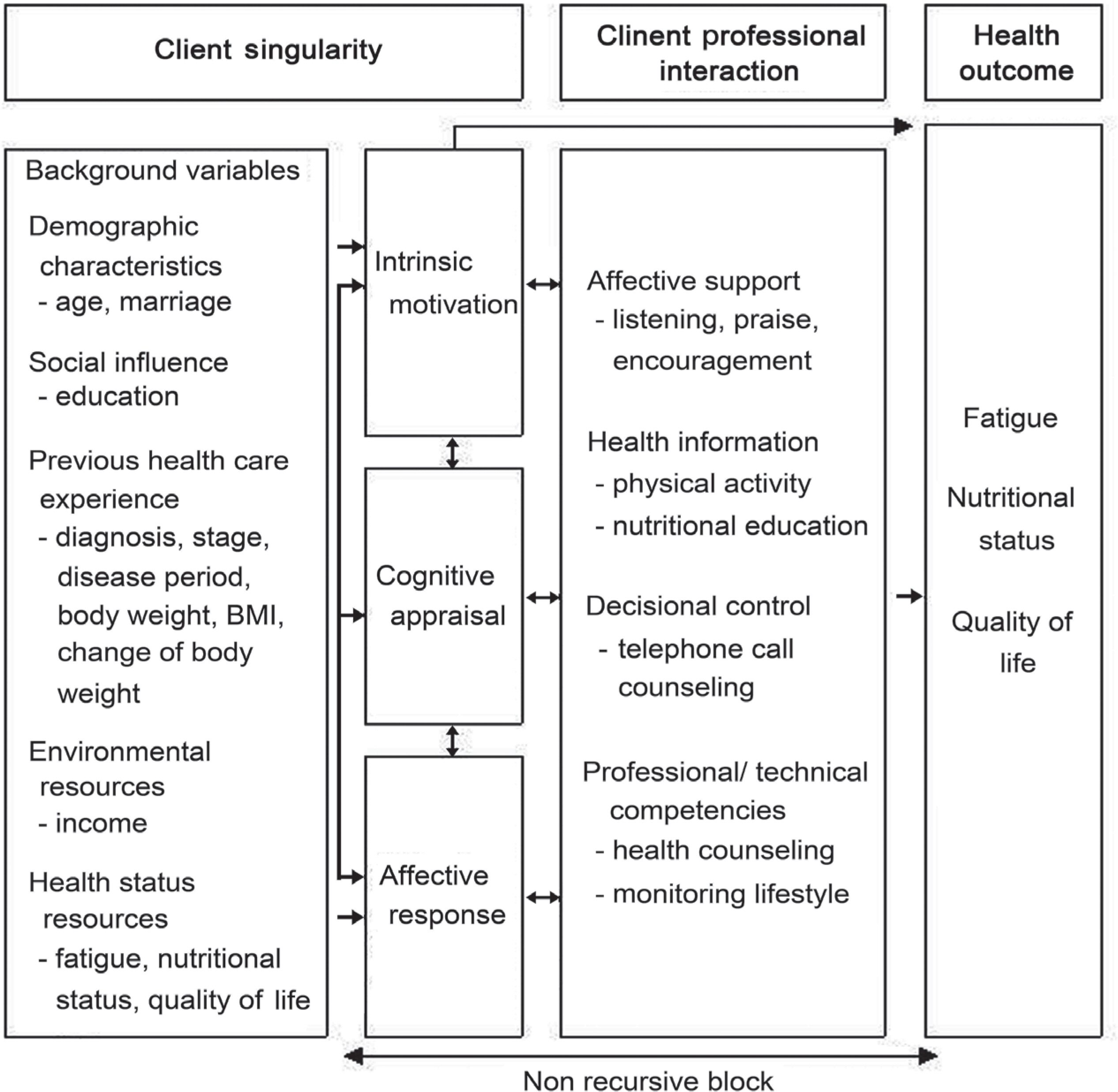
- A nonequivalent control group quasi-experimental design was used. Participants were 49 patients with gynecologic cancer. They were assigned to the experiment group (n=24) or the control group (n=25). The lifestyle intervention for this study consisted of physical activity, nutritional education, telephone call counseling, health counseling, monitoring for lifestyle, and affective support based on Cox's Interaction Model of Client Health Behavior and was implemented for six weeks.
-
Results
- Significant group differences were found for fatigue (p=.037), nutritional status (p=.034) and social/family well-being (p=.035) in these patients with gynecologic cancer.
-
Conclusion
- Results indicate that this lifestyle intervention is effective in lessening fatigue, and improving nutritional status and social/family well-being. Therefore, nurses in hospitals should develop strategies to expand and provide lifestyle interventions for patients with cancer.
| Variables |
Cont. (n=25) |
Exp. (n=24) |
χ2 or F* | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Pretest |
Posttest |
Pretest |
Posttest |
|||
| n (%) or M±SD | n (%) or M±SD | n (%) or M±SD | n (%) or M±SD | |||
| Fatigue score | 33.12±7.99 | 33.92±8.62 | 34.58± 10.68 | 39.46± 9.47 | 4.64 | .037 |
| Prevalence of fatigue | 12 (48.0) | 12 (48.0) | 9 (37.5) | 3 (12.5) | 7.27 | .007† |
| Nutritional status | 13.28±4.78 | 10.36±4.99 | 12.83± 5.69 | 7.79± 3.62 | 4.77 | .034 |
| Prevalence of malnutrition | 20 (80.0) | 17 (68.0) | 18 (75.0) | 8 (33.3) | 5.89 | .023† |
| Quality of life | 74.60±10.46 | 71.68±15.71 | 71.36± 14.95 | 75.32± 17.93 | 3.58 | .065 |
| Physical well-being | 20.28±5.68 | 19.84±6.22 | 21.25± 5.26 | 22.67± 4.60 | 2.83 | .099 |
| Social/family well-being | 20.60±4.09 | 18.80±5.02 | 19.03± 5.98 | 20.19± 4.95 | 4.73 | .035 |
| Emotional well-being | 17.80±3.99 | 18.28±3.80 | 17.04± 4.45 | 16.83± 4.76 | 0.98 | .328 |
| Functional well-being | 15.92±5.23 | 14.76±4.84 | 14.04±6.94 | 15.63±7.17 | 2.19 | .146 |
- 1. Ministry of Health & Welfare, Korea Central Cancer Registry, Na- tional Cancer Center. Annual report of cancer statistics in Korea in 2009. Seoul: Ministry of Health & Welfare; 2010.
- 2. von Gruenigen VE, Frasure HE, Kavanagh MB, Lerner E, Wag- goner SE, Courneya KS. Feasibility of a lifestyle intervention for ovarian cancer patients receiving adjuvant chemotherapy. Gyneco- logic Oncology. 2011;122(2):328–333. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ygyno.2011.04.043Article
- 3. Lawrence DP, Kupelnick B, Miller K, Devine D, Lau J. Evidence report on the occurrence, assessment, and treatment of fatigue in cancer patients. Journal of the National Cancer Institute Mono- graphs. 2004;32:40–50. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/jncimonographs/lgh027Article
- 4. Mock V, Pickett M, Ropka ME, Muscari Lin E, Stewart KJ, Rho-des VA, et al. Fatigue and quality of life outcomes of exercise dur-ing cancer treatment. Cancer Practice. 2001;9(3):119–127.ArticlePubMed
- 5. Cramp F, Daniel J. Exercise for the management of cancer-related fatigue in adults. The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2008;2:CD006145. Article
- 6. Albrecht TA, Taylor AG. Physical activity in patients with ad- vanced-stage cancer: A systematic review of the literature. Clini- cal Journal of Oncology Nursing. 2012;16(3):293–300. http://dx.doi.org/10.1188/12.cjon.293-300Article
- 7. Sternfeld B, Weltzien E, Quesenberry CP, Castillo AL, Kwan M, Slattery ML, et al. Physical activity and risk of recurrence and mortality in breast cancer survivors: Findings from the LACE study. Cancer Epidemiology Biomarkers and Prevention. 2009;18(1):87–95. http://dx.doi.org/10.1158/1055-9965.epi-08-0595ArticlePDF
- 8. Nho JH. Effect of PLISSIT model sexual health enhancement pro- gram for women with gynecologic cancer and their husbands. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2013;43(5):681–689.ArticlePubMed
- 9. Nho JH, Kim SR, Kang GS, Kwon YS. Relationships among mal- nutrition, depression and quality of life in patients with gynecologic cancer receiving chemotherapy. Korean Journal of Women Health. http://dx.doi.org/10.4069/kjwhn.2014.20.2.117Article
- 10. Morey MC, Snyder DC, Sloane R, Cohen HJ, Peterson B, Hart- man TJ, et al. Effects of home-based diet and exercise on func- tional outcomes among older, overweight long-term cancer survi- vors: RENEW: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA: Journal of the American Medical Association. 2009;301(18):1883–1891. http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/jama.2009.643
- 11. Egger G, Binns A, Rossner S. Lifestyle medicine: Managing dis- eases of lifestyle in the 21st century. 2nd ed.Research of Lifestyle Medicine, translator. North Ryde, NSW: McGraw-Hill; 2011.
- 12. Doyle C, Kushi LH, Byers T, Courneya KS, Demark-Wahnefried W, Grant B, et al. Nutrition and physical activity during and after cancer treatment: An American Cancer Society guide for informed choices. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians. 2006;56(6):323–353.ArticlePubMed
- 13. The Royal Australian College of General Practitioners. Smoking, nu- trition, alcohol, physical activity (SNAP): A population health guide to behavioural risk factors in general practice [Internet]. Melbourne, AU: Author; 2015.[cited 2015 July 10]. Available from:. http://www.racgp.org.au/download/Documents/Guidelines/snap.pdf
- 14. Hudon C, Fortin M, Soubhi H. Single risk factor interventions to promote physical activity among patients with chronic diseases: Sys- tematic review. Canadian Family Physician. 2008;54(8):1130–1137.PubMedPMC
- 15. von Gruenigen VE, Courneya KS, Gibbons HE, Kavanagh MB, Waggoner SE, Lerner E. Feasibility and effectiveness of a lifestyle intervention program in obese endometrial cancer patients: A ran- domized trial. Gynecologic Oncology. 2008;109(1):19–26. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ygyno.2007.12.026ArticlePubMed
- 16. Cox CL. An interaction model of client health behavior: Theoreti- cal prescription for nursing. ANS Advances in Nursing Science. 1982;5(1):41–56.PubMed
- 17. Park MN, Choi SY. Development of reproductive health program and identification of effect for married women immigrants. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2014;44(3):248–258. http://dx.doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2014.44.3.248ArticlePubMed
- 18. Van Belle S, Paridaens R, Evers G, Kerger J, Bron D, Foubert J, et al. Comparison of proposed diagnostic criteria with FACT-F and VAS for cancer-related fatigue: Proposal for use as a screening tool. Supportive Care in Cancer. 2005;13(4):246–254. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00520-004-0734-yArticlePubMedPDF
- 19. Ottery FD. Definition of standardized nutritional assessment and interventional pathways in oncology. Nutrition. 1996;12(1 Suppl):S15–S19.ArticlePubMed
- 20. Bauer J, Capra S, Ferguson M. Use of the scored Patient-Gener- ated Subjective Global Assessment (PG-SGA) as a nutrition as- sessment tool in patients with cancer. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 2002;56(8):779–785. http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1601412ArticlePubMedPDF
- 21. Cella DF. FACIT manual: Manual of the functional assessment of chronic illness therapy (FACIT) measurement system. 4th ed. Ev- anston, IL: Center on Outcomes, Research and Education; 1997.
- 22. Cho MY, Park JY, Lee CE, Song SK, Lee SH, Byun ES, et al. The effect of a video exercise program on cancer-related fatigue, physical function and emotional status in patients with cancer dur- ing chemotherapy. Journal of Korean Clinical Nursing Research. 2012;18(3):368–380.
- 23. Vickers AJ, Altman DG. Statistics notes: Analysing controlled tri- als with baseline and follow up measurements. BMJ: British Medi- cal Journal. 2001;323(7321):1123–1124.Article
- 24. Demark-Wahnefried W, Peterson B, McBride C, Lipkus I, Clipp E. Current health behaviors and readiness to pursue life-style changes among men and women diagnosed with early stage prostate and breast carcinomas. Cancer. 2000;88(3):674–684.ArticlePubMed
- 25. Speck RM, Courneya KS, Masse LC, Duval S, Schmitz KH. An update of controlled physical activity trials in cancer survivors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Cancer Survivor- ship. 2010;4(2):87–100. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11764-009-0110-5ArticlePDF
- 26. Oldervoll LM, Loge JH, Paltiel H, Asp MB, Vidvei U, Wiken AN, et al. The effect of a physical exercise program in palliative care: A phase II study. Journal of Pain and Symptom Management. 2006;31(5):421–430. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2005.10.004ArticlePubMed
- 27. Alshadwi A, Nadershah M, Carlson ER, Young LS, Burke PA, Daley BJ. Nutritional considerations for head and neck cancer pa- tients: A review of the literature. Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery. 2013;71(11):1853–1860. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.joms.2013.04.028ArticlePubMed
- 28. Byun MS, Kim NH. Energy intake and fatigue in patients receiving chemotherapy. The Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science. 2012;14(4):258–267. http://dx.doi.org/10.7586/jkbns.2012.14.4.258Article
- 29. Dhillon HM, van der Ploeg HP, Bell ML, Boyer M, Clarke S, Vardy J. The impact of physical activity on fatigue and quality of life in lung cancer patients: A randomised controlled trial protocol. BMC Cancer. 2012;12:572http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-12-572ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 30. Pierce JP, Faerber S, Wright FA, Rock CL, Newman V, Flatt SW, et al. A randomized trial of the effect of a plant-based dietary pat- tern on additional breast cancer events and survival: The Women’s Healthy Eating and Living (WHEL) study. Controlled Clinical Tri- als. 2002;23(6):728–756.
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Effectiveness of Postoperative Dietary Intervention in Patients with Gastric Cancer who Underwent Gastrectomy: Quasi-Experimental Study Design
Dahye KIM, Myung Kyung LEE
Seminars in Oncology Nursing.2025; 41(1): 151797. CrossRef - Health-Related Behaviors of Middle-Aged Cancer Survivors: A Comparative Study with Matched Non-Cancer Controls Using the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey VI–VII (2013–2018) Data
Mi Lee KIM, Ju Ri JEONG, Yu Ri CHOE
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2025; 25(1): 20. CrossRef - Analysis of Educational Needs Related to Chemotherapy among Patients with Solid Tumors
Se-Na Lee
Asian Oncology Nursing.2025; 25(2): 89. CrossRef - A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Interventions for Lower Limb Lymphedema in Patients with Gynecologic Cancer
Soon Yang Jang, Ji Hyeon Kim
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2025; 28(1): 40. CrossRef - Effects of a Customized Diet Education Program Using a Mobile Instant Messenger for People Undergoing Peritoneal Dialysis: A Feasibility Test
Hyun-Jung Lee, Hee-Young Kang
Asian Nursing Research.2024; 18(4): 367. CrossRef - Effects of an integrated lifestyle intervention for overweight and obese breast cancer survivors: A quasi-experimental study
Su Jin Seo, Ju-Hee Nho
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2024; 73: 102714. CrossRef - Literature Review on Lifestyle Intervention Program for Adults in Korea
Keun-Young Yang
Journal of Digital Contents Society.2023; 24(8): 1815. CrossRef - Effect of a Hospital-To-Home Transitional Intervention Based on an Interaction Model of Client Health Behavior for Adult Patients with Stroke
Su-Jin Cho, Sung Reul Kim, Kyung-Hee Cho, Nah-Mee Shin, Won-Oak Oh
Journal of Community Health Nursing.2023; 40(4): 273. CrossRef - Development and Effect of the Integrated Health Promotion Program for Cancer Survivors Living at Home
Hee Sang Yoon, Eun A Hwang
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2021; 32(1): 51. CrossRef - Attitudes About Coping With Fatigue in Patients With Gastric Cancer
Eun Ja Yeun, Misoon Jeon
Gastroenterology Nursing.2020; 43(1): 97. CrossRef - Health-related Quality of Life and Its Related Factors among Cancer Survivors and General Adults: Focusing on Lifestyle Behaviors and Mental Health
Eun A Song, Youngran Kweon, Yoon Young Hwang, Minjeong An
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2020; 32(4): 385. CrossRef - Deriving the Components of Lifestyle-Related Occupational Therapy Intervention Program for the Elderly: Through the Delphi Technique
Yun-Chan Shin, Da-Sol Park, Eun-Hye Cho, Kyung-A Won, Dae-Sung Han, Jung-Ran Kim
Journal of Korean Society of Occupational Therapy.2020; 28(1): 45. CrossRef - Theoretical evaluation of Cox’s interaction model of client health behavior for health promotion in adult
women
Youlim Kim, Hyeonkyeong Lee, Gi Wook Ryu
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2020; 26(2): 120. CrossRef - A Comparative Study on the Characteristics of Cancer Patients and Cancer Survivors
So Young Baek, Ja Yun Choi
Asian Oncology Nursing.2018; 18(1): 11. CrossRef - The Effects of Stress and Stress Coping on Life Quality in Cancer Patients and Caregivers: A Dyadic Analysis Using an Actor-Partner Interdependence Model
Eun-Jung Kim, Jeong Won Han
Asian Oncology Nursing.2018; 18(3): 135. CrossRef - The Effects of Integrated Intervention Program for Community Dwelling Cancer Patients' Quality of Life, Depression and Self Care Agency
Young Sil Kang, In Soo Kwon, Eunyoung Hong
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2016; 30(3): 445. CrossRef
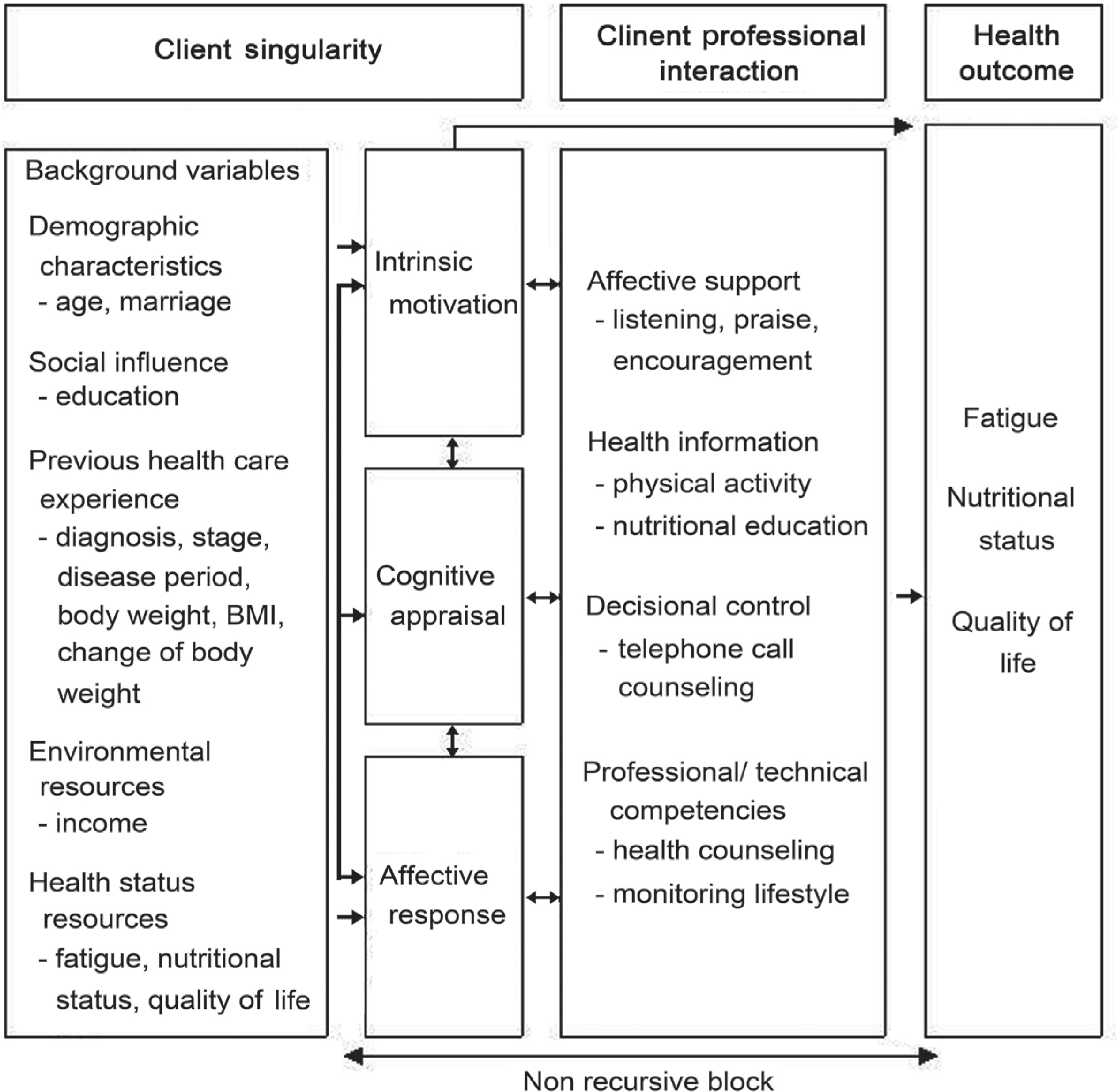
Figure 1.
Figure 2.
| Week | Contents | Methods | Time (min) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Physical activity | Education | 60 |
| Stretching | Demonstration | ||
| Muscle strength exercise | Correction of posture | ||
| Flexibility exercise | Encouragement | ||
| Nutritional management | Face-to-Face | ||
| Accurate diet, balanced diet | |||
| Ntritional supplement food | |||
| Diet according to side effect of treatment | |||
| Helpful recipe for treatment,dietary life after chemotherapy | |||
| Health counseling | |||
| Checking lifestyle | |||
| 2 | Health counseling | Telephone call | 10~20 |
| Monitoring of lifestyle | Listening | ||
| Affective support | Praise | ||
| Encouragement | |||
| 3 | Health counseling | Telephone call | 10~20 |
| Monitoring of lifestyle | Listening | ||
| Affective support | Praise | ||
| Encouragement | |||
| 4 | Physical activity | Education | 60 |
| Stretching | Demonstration | ||
| Muscle strength exercise | Correction of posture | ||
| Flexibility exercise | Encouragement | ||
| Nutritional management | Face-to-Face | ||
| Accurate diet, balanced diet | |||
| Nutritional supplement food | |||
| Diet according to side effect of treatment | |||
| Helpful recipe for treatment,dietary life after chemotherapy | |||
| Health counseling | |||
| Monitoring of lifestyle | |||
| 5 | Health counseling | Telephone call | 10~20 |
| Monitoring of lifestyle | Listening | ||
| Affective support | Praise | ||
| Encouragement | |||
| 6 | Health counseling | Telephone call | 10~20 |
| Monitoring of lifestyle | Listening | ||
| Affective support | Praise | ||
| Encouragement |
| Characteristics | Classification | Exp. (n=24) |
Cont. (n=25) |
χ2 or t | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) or M±SD | n (%) or M±SD | ||||
| Age (yr) | <40 | 4 (16.7) | 5 (20.0) | 0.66 | .883 |
| 40~49 | 4 (16.7) | 6 (24.0) | |||
| 50~59 | 13 (54.1) | 11 (44.0) | |||
| ≥60 | 3 (12.5) | 3 (12.0) | |||
| 50.75±10.50 | 49.76±10.21 | − 0.33 | .742 | ||
| Education | Middle school or lower | 2 (8.3) | 3 (12.0) | 2.41 | .492 |
| High school | 14 (58.3) | 13 (52.0) | |||
| College or higher | 8 (33.3) | 9 (36.0) | |||
| Marriage | Married | 17 (70.8) | 20 (80.0) | 1.56 | .669 |
| Single | 4 (16.7) | 2 (8.0) | |||
| Others | 3 (12.5) | 3 (12.0) | |||
| Monthly income (10,000 won) | <200 | 8 (33.3) | 3 (12.0) | 3.75 | .157 |
| 200~499 | 9 (37.5) | 15 (60.0) | |||
| ≥500 | 7 (29.2) | 7 (28.0) | |||
| Disease period (month) | 1.65±0.57 | 1.50±0.59 | − 1.00 | .323 | |
| Cancer site | Cervix | 2 (8.3) | 3 (12.0) | 0.61 | .882 |
| Ovary | 19 (79.2) | 17 (68.0) | |||
| Endometrium | 3 (12.5) | 5 (20.0) | |||
| Stage | I | 5 (20.8) | 3 (12.0)) | 0.72 | .789 |
| II | 4 (16.7) | 6 (24.0) | |||
| III | 11 (45.8) | 12 (48.0) | |||
| IV | 4 (16.7) | 4 (16.0) | |||
| Body weight | 54.07±7.98 | 53.16±8.56 | − 0.39 | .702 | |
| Body mass index | <18.5 | 3 (12.5) | 5 (20.0) | 0.68 | .804 |
| 18.5~24.9 | 18 (75.0) | 18 (72.0) | |||
| ≥25 | 3 (12.5) | 2 (8.0) | |||
| Change of body weight (1month) | 3.88±3.37 | 2.88±2.64 | − 1.16 | .250 | |
| Fatigue | Fatigue (≤34) | 9 (37.5) | 12 (48.0) | 0.55 | .567 |
| Non fatigue (> 34) | 15 (62.5) | 13 (52.0) | |||
| 34.58±10.68 | 33.12±7.99 | − 0.54 | .589 | ||
| Nutritional status | Malnutrition (≥9) | 18 (75.0) | 20 (80.0) | 0.18 | .742 |
| Non-malnutrition (<9) | 6 (25.0) | 5 (20.0) | |||
| 12.83±5.69 | 13.28±4.78 | 0.30 | .767 | ||
| Quality of life | Physical well-being | 21.25±5.26 | 20.28±5.68 | − 0.62 | .539 |
| Social/family well-being | 19.03±5.98 | 20.60±4.09 | 1.08 | .286 | |
| Emotional well-being | 17.04±4.45 | 17.80±3.99 | 0.63 | .533 | |
| Functional well-being | 14.04±6.94 | 15.92±5.23 | 1.07 | .289 | |
| 71.36±14.95 | 74.60±10.46 | 0.88 | .386 |
| Variables | Cont. (n=25) |
Exp. (n=24) |
χ2 or F |
p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pretest |
Posttest |
Pretest |
Posttest |
|||
| n (%) or M±SD | n (%) or M±SD | n (%) or M±SD | n (%) or M±SD | |||
| Fatigue score | 33.12±7.99 | 33.92±8.62 | 34.58± 10.68 | 39.46± 9.47 | 4.64 | .037 |
| Prevalence of fatigue | 12 (48.0) | 12 (48.0) | 9 (37.5) | 3 (12.5) | 7.27 | .007 |
| Nutritional status | 13.28±4.78 | 10.36±4.99 | 12.83± 5.69 | 7.79± 3.62 | 4.77 | .034 |
| Prevalence of malnutrition | 20 (80.0) | 17 (68.0) | 18 (75.0) | 8 (33.3) | 5.89 | .023 |
| Quality of life | 74.60±10.46 | 71.68±15.71 | 71.36± 14.95 | 75.32± 17.93 | 3.58 | .065 |
| Physical well-being | 20.28±5.68 | 19.84±6.22 | 21.25± 5.26 | 22.67± 4.60 | 2.83 | .099 |
| Social/family well-being | 20.60±4.09 | 18.80±5.02 | 19.03± 5.98 | 20.19± 4.95 | 4.73 | .035 |
| Emotional well-being | 17.80±3.99 | 18.28±3.80 | 17.04± 4.45 | 16.83± 4.76 | 0.98 | .328 |
| Functional well-being | 15.92±5.23 | 14.76±4.84 | 14.04±6.94 | 15.63±7.17 | 2.19 | .146 |
Cont.=Control group; Exp.=Experimental group.
Cont.=Control group; Exp.=Experimental group; ANCOVA were done after adjusting pretest value;
 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION
 Cite
Cite

