Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Nurs > Volume 44(5); 2014 > Article
-
Original Article
- Effectiveness of a Self-management Program using Goal Setting based on a G-AP for Patients after a Stroke
- Min Gyeong Park, Yeongmi Ha
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2014;44(5):581-591.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2014.44.5.581
Published online: October 31, 2014
1Yeson Rehabilitation Medicine Hospital, Jinju, Korea.
2College of Nursing·Institute of Health Sciences, Gyeongsang National University, Jinju, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Ha, Yeongmi. College of Nursing & Institute of Health Sciences, Gyeongsang National University, 816-15 beon-gil Jinju-daero, Jinju 660-987, Korea. Tel: +82-55-772-8253, Fax: +82-55-772-8222, yha@gnu.ac.kr
© 2014 Korean Society of Nursing Science
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NoDerivs License. (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nd/4.0/) If the original work is properly cited and retained without any modification or reproduction, it can be used and re-distributed in any format and medium.
Abstract
-
Purpose
- This study was conducted to develop a self-management program using goal setting for patients after a stroke. The program was based on a theory-based Goal setting and Action Planning framework (G-AP), and the effectiveness of the program was examined.
-
Methods
- A non-equivalent control group pretest-posttest design was used. The experimental group (n=30) received the self-management program using goal setting based on the G-AP over 7 weeks. The education was delivered individually with a specifically designed stroke workbook. The control group (n=30) received only patient information leaflets about stroke.
-
Results
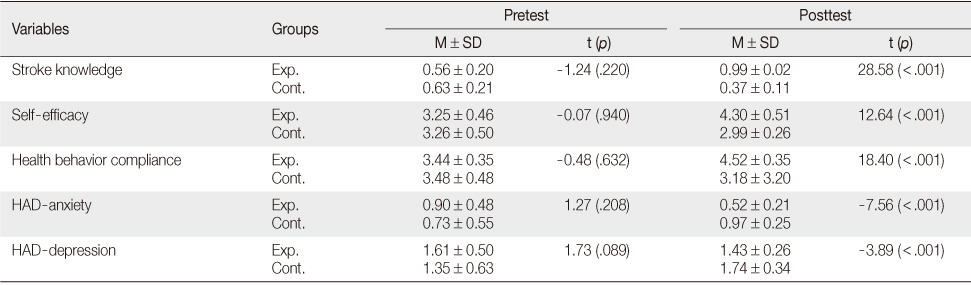
- There were significant differences between the two groups. Stroke knowledge, self-efficacy, and health behavior compliance were significantly higher (all p<.001), and hospital anxiety (p<.001) and depression (p<.001) were significantly lower in the experimental group compared to the control group.
-
Conclusion
- This self-management program using goal setting based on a G-AP was found to be useful and beneficial for patients in stroke rehabilitation settings.
This manuscript is based on a part of the first author's master's thesis from Gyeongsang National University.
- 1. Statistics Korea. Annual report on the cause of death statistics [Internet]. Daejeon, Author. 2013;cited 2013 July 20. Available from:http://kostat.go.kr/portal/korea/kor_nw/2/6/2/index.board?bmode=read&aSeq=260046
- 2. Korean Stroke Society. Stroke story [Internet]. Seoul, Author. 2011;cited 2013 August 15. Available from: http://www.stroke.or.kr/stroke/stroke_con.php
- 3. Jones F, Riazi A. Self-efficacy and self-management after stroke: A systematic review. Disabil Rehabil. 2011;33(10):797–810. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/09638288.2010.511415ArticlePubMed
- 4. Lorig KR, Holman H. Self-management education: History, definition, outcomes, and mechanisms. Ann Behav Med. 2003;26(1):1–7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1207/S15324796ABM2601_01ArticlePubMed
- 5. Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network. Management of patients with stroke: Rehabilitation, prevention and management of complications, and discharge planning. A national clinical guideline. Edinburgh, UK: NHS Quality Improvement Scotland; 2010.
- 6. Intercollegiate Stroke Working Party. National clinical guideline for stroke. 4th ed. London, UK: Royal College of Physicians; 2012.
- 7. Ajou University Industry Academic Cooperation Foundation. Development of clinical practice guideline for stroke rehabilitation in Korea. Cheongju: Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; 2012.
- 8. National Stroke Foundation. Clinical guidelines for stroke management 2010. Melbourne, AU: Author; 2010.
- 9. Forster A, Brown L, Smith J, House A, Knapp P, Wright JJ, et al. Information provision for stroke patients and their caregivers. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012;11:CD001919. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD001919.pub3ArticlePubMed
- 10. Jones F, Riazi A, Norris M. Self-management after stroke: Time for some more questions. Disabil Rehabil. 2013;35(3):257–264. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/09638288.2012.691938ArticlePubMed
- 11. Department of Health. The national stroke strategy. London, UK: DH; 2007.
- 12. Hoffmann T, McKenna K, Worrall L, Read SJ. Randomised trial of a computer-generated tailored written education package for patients following stroke. Age Ageing. 2007;36(3):280–286. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/ageing/afm003ArticlePubMed
- 13. Hackett ML, Anderson CS, House A, Halteh C. Interventions for preventing depression after stroke. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008;3:CD003689. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD003689.pub3Article
- 14. Shin ES, Hwang SY, Jeong MH, Lee ES. Relationships of factors affecting self-care compliance in acute coronary syndrome patients following percutaneous coronary intervention. Asian Nurs Res. 2013;7(4):205–211. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.anr.2013.10.003Article
- 15. Lennon S, McKenna S, Jones F. Self-management programmes for people post stroke: A systematic review. Clin Rehabil. 2013;27(10):867–878. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/0269215513481045ArticlePubMedPDF
- 16. Levack WM, Taylor K, Siegert RJ, Dean SG, McPherson KM, Weatherall M. Is goal planning in rehabilitation effective? A systematic review. Clin Rehabil. 2006;20(9):739–755. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/0269215506070791ArticlePubMedPDF
- 17. Siegert RJ, Taylor WJ. Theoretical aspects of goal-setting and motivation in rehabilitation. Disabil Rehabil. 2004;26(1):1–8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/09638280410001644932ArticlePubMed
- 18. Scobbie L, Dixon D, Wyke S. Goal setting and action planning in the rehabilitation setting: Development of a theoretically informed practice framework. Clin Rehabil. 2011;25(5):468–482. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/0269215510389198ArticlePubMedPDF
- 19. Allen K, Hazelett S, Jarjoura D, Hua K, Wright K, Weinhardt J, et al. A randomized trial testing the superiority of a postdischarge care management model for stroke survivors. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2009;18(6):443–452. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2009.02.002ArticlePubMedPMC
- 20. Kang SM. An effect of the secondary stroke prevention education program on self-care of acute ischemic stroke patients [master's thesis]. Seoul, Konkuk University. 2005.
- 21. Zigmond AS, Snaith RP. The hospital anxiety and depression scale. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1983;67(6):361–370. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0447.1983.tb09716.xArticlePubMed
- 22. Oh SM, Min KJ, Park DB. A study on the standardization of the hospital anxiety and depression scale for Koreans: A comparison of normal, depressed and anxious groups. J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc. 1999;38(2):289–296.
- 23. Kim CG, Park HA. Development and evaluation of a web-based education program to prevent secondary stroke. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2011;41(1):47–60. http://dx.doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2011.41.1.47ArticlePubMed
- 24. Lowe DB, Sharma AK, Leathley MJ. The carefile project: A feasibility study to examine the effects of an individualised information booklet on patients after stroke. Age Ageing. 2007;36(1):83–89. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/ageing/afl145ArticlePubMed
- 25. Hafsteinsdóttir TB, Vergunst M, Lindeman E, Schuurmans M. Educational needs of patients with a stroke and their caregivers: A systematic review of the literature. Patient Educ Couns. 2011;85(1):14–25. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.pec.2010.07.046ArticlePubMed
- 26. Jones F, Mandy A, Partridge C. Changing self-efficacy in individuals following a first time stroke: Preliminary study of a novel self-management intervention. Clin Rehabil. 2009;23(6):522–533. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/0269215508101749ArticlePubMedPDF
- 27. Johnston M, Bonetti D, Joice S, Pollard B, Morrison V, Francis JJ, et al. Recovery from disability after stroke as a target for a behavioural intervention: Results of a randomized controlled trial. Disabil Rehabil. 2007;29(14):1117–1127. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/03323310600950411ArticlePubMed
- 28. Bandura A. Self-efficacy: The exercise of control. New York, NY: Worth Publishers; 1997.
- 29. Taylor WJ, Brown M, William L, McPherson KM, Reed K, Dean SG, et al. A pilot cluster randomized controlled trial of structured goal-setting following stroke. Clin Rehabil. 2012;26(4):327–338. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/0269215511419384ArticlePubMedPDF
- 30. Jones F, Partridge C, Reid F. The stroke self-efficacy questionnaire: Measuring individual confidence in functional performance after stroke. J Clin Nurs. 2008;17(7B):244–252. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2702.2008.02333.xArticlePubMed
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Study Protocol for a Hospital-to-Home Transitional Care for Older Adults Hospitalized with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease in South Korea: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Heui-Sug Jo, Woo-Jin Kim, Yukyung Park, Yu-Seong Hwang, Seon-Sook Han, Yeon-Jeong Heo, Dahye Moon, Su-Kyoung Kim, Chang-Youl Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2023; 20(15): 6507. CrossRef - Predictive Model of Self-management in Patients With Stroke Based on the Information-Motivation-Behavioral Skills Model
Sung Reul Kim, Sunho Kim, Hye Young Kim, Kyung-Hee Cho
Journal of Cardiovascular Nursing.2023; 38(2): 158. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Health Behavior Compliance in Adult Moyamoya Patients
Bo Eun Kim, Ju-Eun Song
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2021; 51(1): 80. CrossRef - The Effect of a Movie-Based Nursing Intervention Program on Rehabilitation Motivation and Depression in Stroke Patients
Hye Kyung Kwon, Sook Ja Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2017; 47(3): 345. CrossRef - Comparison of Motivation for Rehabilitation, Family Support and Adherence to Rehabilitation between Depressive and Non-depressive Stroke Patients
An Suk Park, Eun Ko, Hee Sun Kang
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2016; 19(2): 138. CrossRef - Influence of Uncertainty, Physiologic Risk Factors, Self-efficacy on Self-management in Stroke Patients
Sook Hee Cho, Kyung Soon Yun
Journal of muscle and joint health.2016; 23(2): 114. CrossRef - Effectiveness of a Stroke Risk Self-Management Intervention for Adults with Prehypertension
Hee-Young Song, Kyoung A Nam
Asian Nursing Research.2015; 9(4): 328. CrossRef - Factors related to Fear of Recurrence in Stroke Patients*
Ji won Chung, Jung-Hee Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2015; 22(2): 190. CrossRef
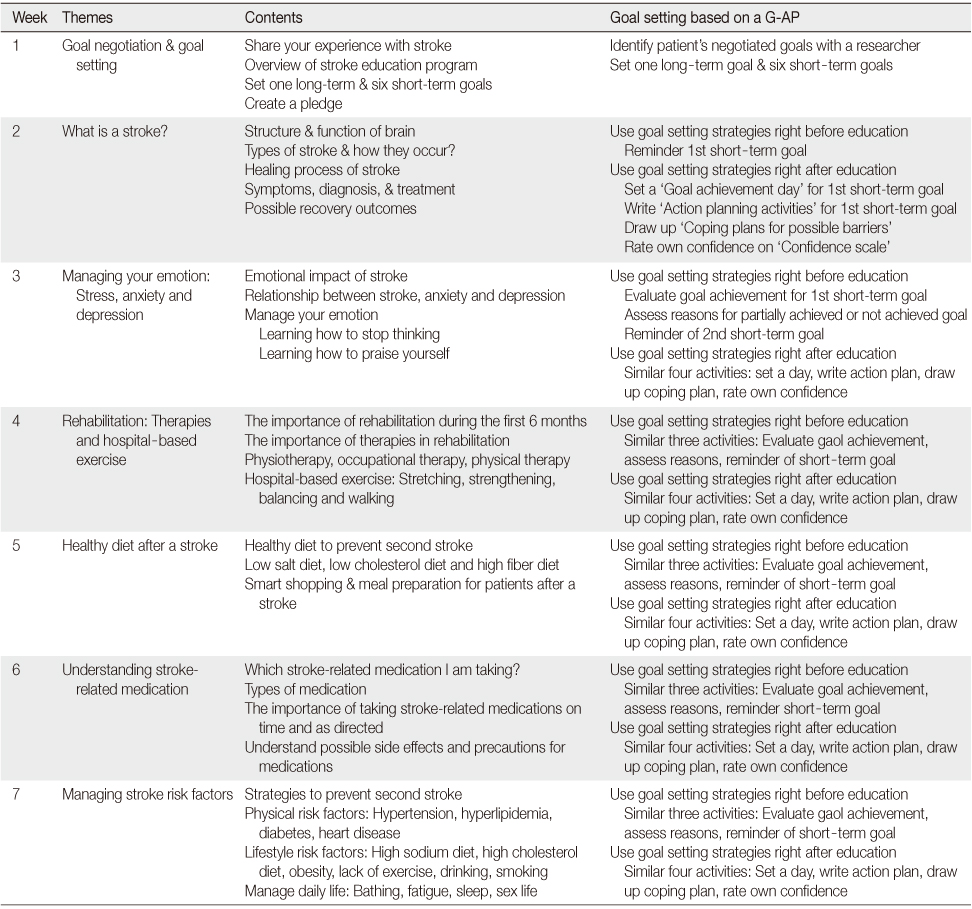
Self-management Program using Goal Setting based on a G-AP for Patients after a Stroke
G-AP=Goal setting and Action Planning framework.
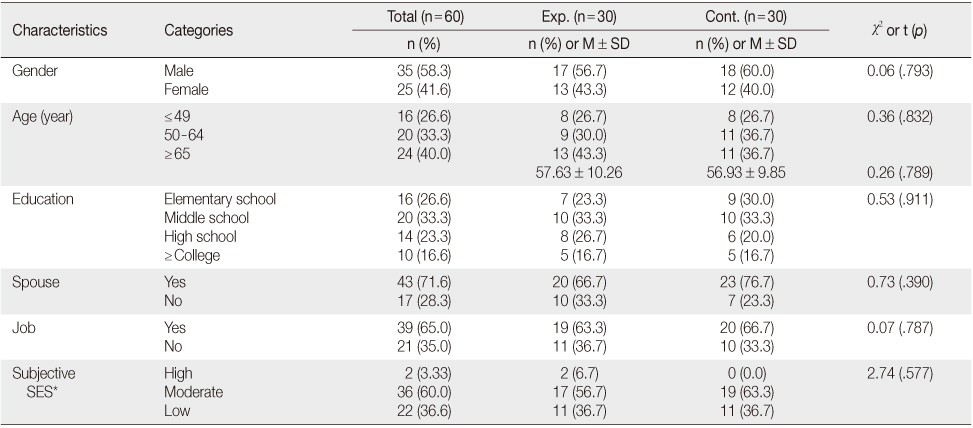
Test of General Characteristics in Patients after a Stroke (N=60)
*Fisher's exact test; Exp.=Experimental group; Cont.=Control group; SES=socioeconomic status.
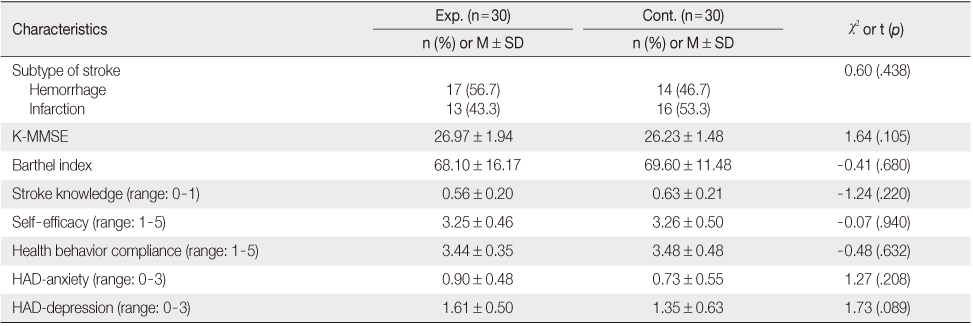
Homogeneity Test of Disease-related Characteristics in Patients after a Stroke (N=60)
Exp.=Experimental group; Cont.=Control group; K-MMSE=Korea Mini Mental State Examination; HAD=Hospital anxiety and depression.
Effectiveness of a Self-management Program Using Goal Setting based on a G-AP (N=60)
Exp.=Experimental group; Cont.=Control group; HAD=Hospital Anxiety and Depression; G-AP=Goal setting and Action Planning framework.
G-AP=Goal setting and Action Planning framework.
*Fisher's exact test; Exp.=Experimental group; Cont.=Control group; SES=socioeconomic status.
Exp.=Experimental group; Cont.=Control group; K-MMSE=Korea Mini Mental State Examination; HAD=Hospital anxiety and depression.
Exp.=Experimental group; Cont.=Control group; HAD=Hospital Anxiety and Depression; G-AP=Goal setting and Action Planning framework.
 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION
 Cite
Cite

