Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Nurs > Volume 43(6); 2013 > Article
-
Original Article
- Mothers' Parenting Experience of Premature Infants: Q Methodological Approach
- Mi-Young Chon, Eun Sun Ji, Shin-Hwa Lee
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2013;43(6):704-713.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2013.43.6.704
Published online: December 31, 2013
Department of Nursing, Konkuk University, Chungju, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Lee, Shin-Hwa. Department of Nursing, Konkuk University, 268 Chungwon-daero, Chungju 380-701, Korea. Tel: +82-2-450-3033, Fax: +82-2-450-4063, ssinna99@kku.ac.kr
• Received: July 26, 2013 • Accepted: October 18, 2013
© 2013 Korean Society of Nursing Science
Abstract
-
Purpose
- This study was done to identify the parenting experience of mothers of premature infants in order to provide basic data for educational solutions and desirable directions.
-
Methods
- Q-methodology was used as it provides a method of analyzing the subjectivity of each item. The participants were 33 mothers of premature infants who sorted 34 selected Q-statements which were then classified into the shape of a normal distribution using a 9-point scale. Subjectivity on parenting experience among the mothers was analyzed using the pc-QUANAL program.
-
Results
- Four types of parenting experience were identified. Type I was named 'struggling', type II, 'self blame', type III, 'information collecting', and type IV, 'self-introspection'.
-
Conclusion
- The results of this study indicate that different approaches to educational programs are needed for mothers of premature infants based on the four types of parenting experience.
- 1. Ahn YM. The effects of the systemic follow up health care program on the health promotion and the risk reduction in premature infants and their mothers. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2004;34(6):1129–1142.ArticlePDF
- 2. Chae YS. Adaptation of maternal roles and postpartum depression of primiparas during early postpartum period. Seoul, Ewha Womans University. 2005;Unpublished master's thesis.
- 3. Choi EJ, Lee WJ. A phenomenological study on mothers' experience of premature infants. Korean Jungang Med J. 1999;64(1):87–91.
- 4. de Kleine MJ, den Ouden AL, Kollee LA, Nijhuis-van der Sanden MW, Sondaar M, van Kessel-Feddema BJ, et al. Development and evaluation of a follow up assessment of preterm infants at 5 years of age. Arch Dis Child. 2003;88(10):870–875.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 5. Hopper A. Sources of stress for parents of a sick neonate: A literature review. Pediatr Nurs. 2000;12(4):29–32.Article
- 6. Hwang HS, Kim HS, Yoo IY, Shin HS. Parenting stress in mothers of premature infants. Child Health Nurs Res. 2013;19(1):39–48. http://dx.doi.org/10.4094/chnr.2013.19.1.39ArticlePDF
- 7. Jang YS. Effects of a maternal role promotion program for mothers of premature infants on maternal role strain, maternal role confidence and maternal identity. Korean J Child Health Nurs. 2005;11(4):472–480.
- 8. Kelly MM. The basics of prematurity. J Pediatr Health Care. 2006;20(4):238–244.ArticlePubMed
- 9. Kim ES, Kim EY, Lee JY, Kim JK, Lee HJ, Lee SH, et al. The effects of supportive nursing management on postpartum depression of mothers with premature infants. J Korean Clin Nurs Res. 2009;15(3):157–170.
- 10. Kim ES, Kim JU, Lee OK, Kim WS. Growth and neurodevelopmental outcome on very low birth weight infants during 2 years. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 1996;39(5):641–651.
- 11. Kim HK. Agreement between the Q-block and the Q-tool. J Korean Soc Sci Study Subj. 2008;16:5–16.
- 12. Kim HS, Won YM. Q methodology. Paju: Kyoyookbook; 2000.
- 13. Kim MY, Park DY. Parenting Stress, Depression and Verbal Abuse of Infant's Mothers. J Korean Acad Child Health Nurs. 2009;15(4):375–382.Article
- 14. Kim SY, Kwon M. A comparative study on infant's temperament & parenting stress by premature & full-term infant's mother. Korean Parent Child Health J. 2005;8(2):123–136.
- 15. Kwon EK, Choi MH, Kim SK. Parenting stress and guilty feeling for mothers having children with rare genetic metabolic diseases. J Korean Clin Nurs Res. 2008;14(3):153–163.
- 16. Kwon H, Kwon M. Effect of discharge education program for mothers of premature infants on maternal role confidence and parenting stress. J Korean Acad Child Health Nurs. 2007;13(1):58–65.
- 17. Lederman RP, Weingarten CG, Lederman E. Postpartum self-evaluation questionnaire: Measures of maternal adaptation. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1981;17(6):201–231.
- 18. Lee EJ. Experiences of mothers with cardiac disease children. Seoul, Kyung Hee University. 2002;Unpublished doctoral dissertation.
- 19. Lee H, White-Traut R, Park CG. Health problems and health services utilization of infants born prematurely in the U.S. J Korean Acad Child Health Nurs. 2008;14(2):146–154.
- 20. Lee MJ, Suh HS, Hong YH, Kim SY, Yoo EJ, Park SJ. The educational needs and perception of the mothers of high risk infant and normal neonate. Korean J Child Health Nurs. 2003;9(1):18–27.
- 21. Lee SB, Shin HS. Effects of kangaroo care on anxiety, maternal role confidence, and maternal infant attachment of mothers who delivered preterm infants. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2007;37(6):949–956.ArticlePDF
- 22. Lee SH, Chi SA. A study on experience of the mother of premature infant in NICU. Chung-Ang J Nurs. 2001;5(2):45–54.
- 23. Lopez GL, Anderson KH, Feutchinger J. Transition of premature infants from hospital to home life. Neonatal Netw. 2012;31(4):207–214.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 24. McCain GC. Parenting growing preterm infants. Pediatr Nurs. 1990;16(5):467–470.PubMed
- 25. Moon JH. Experience of mothers with very low birth weight infant. Korean J Child Health Nurs. 2002;8(1):110–120.
- 26. Shin HS. Maternal identity in mothers of premature infants admitted in NICU. Korean J Child Health Nurs. 2004;10(1):117–125.
- 27. Song AS, Park IH, Joo AR. Effects of supportive care using the telephone for mothers of premature infants on anxiety and confidence of baby care after discharge. J Korean Soc Matern Child Health. 2007;11(1):98–108.Article
- 28. Statistics Korea. Birth statistics in 2010. 2011;02 27 Retrieved August 23, 2012. from http://kostat.go.kr/portal/korea/kor_nw/2/1/index.board?bmode=read&aSeq=259511
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- Subjectivity study on health conservation of elderly hemodialysis patients
Eunji Yim, Mijin Yun, Sohyune Sok
BMC Geriatrics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Experiences of Mothers of Premature Infants Receiving Rehabilitation Therapy
Hyun-Ju Kang
Child Health Nursing Research.2018; 24(3): 298. CrossRef - Predictors of Quality of Life in Mothers of Premature Infant
Hyosin Choi, Yeonghee Shin
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2017; 23(3): 191. CrossRef - Experience of Becoming a Father of a High Risk Premature Infant
Jeong Eon Park, Byoung Sook Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2017; 47(2): 277. CrossRef - Effects of a Hospital Based Follow-Up Program for Mothers with Very Low Birth Weight Infants
Min Hee Kim, Eun Sun Ji
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2016; 46(1): 79. CrossRef - Maternal Role Development in Neonatal Intensive Care Unit Graduate Mothers of Premature Infant
Ah Rim Kim, Young Ran Tak
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2015; 21(4): 308. CrossRef
Mothers' Parenting Experience of Premature Infants: Q Methodological Approach
Mothers' Parenting Experience of Premature Infants: Q Methodological Approach
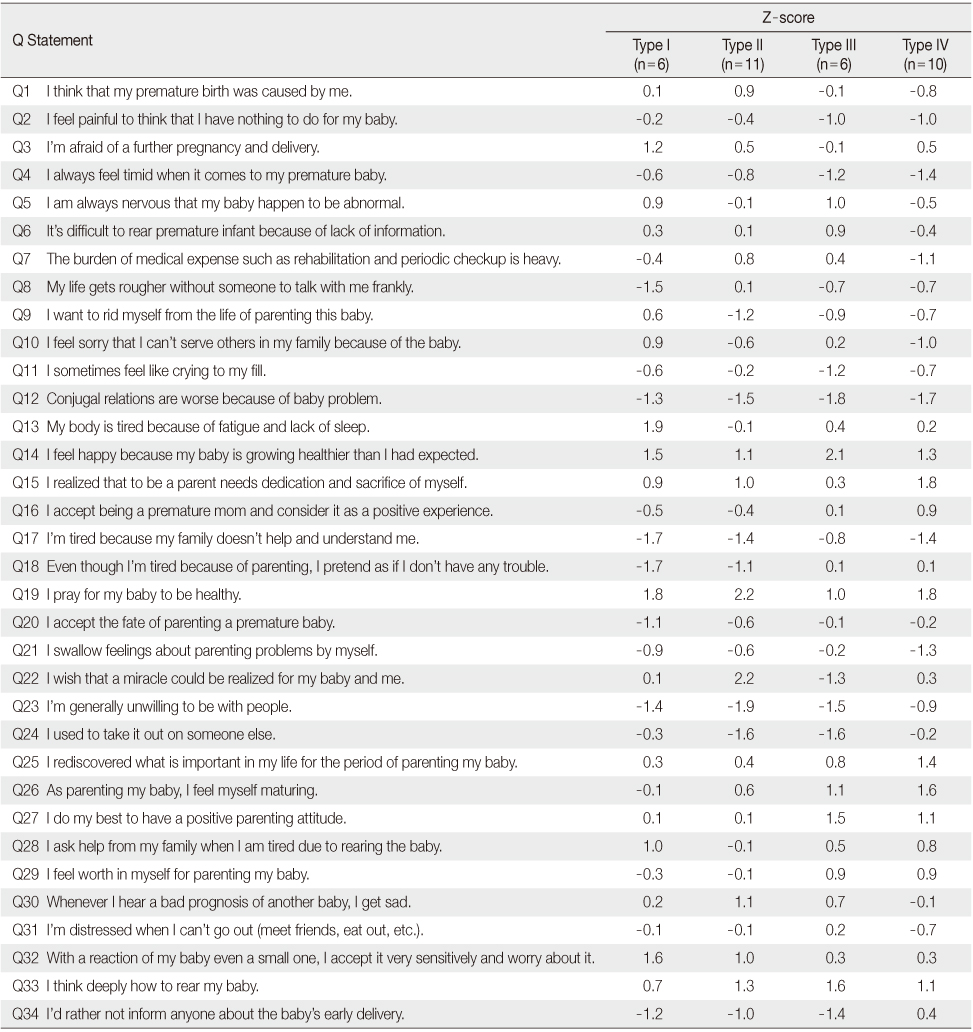
Q statements on Parenting Experience and Z Scores (N=33)
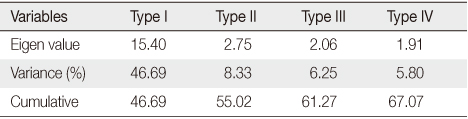
Eigen Value, Variance, and Cumulative Percentage
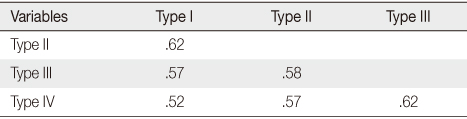
Correlation Matrix between Types
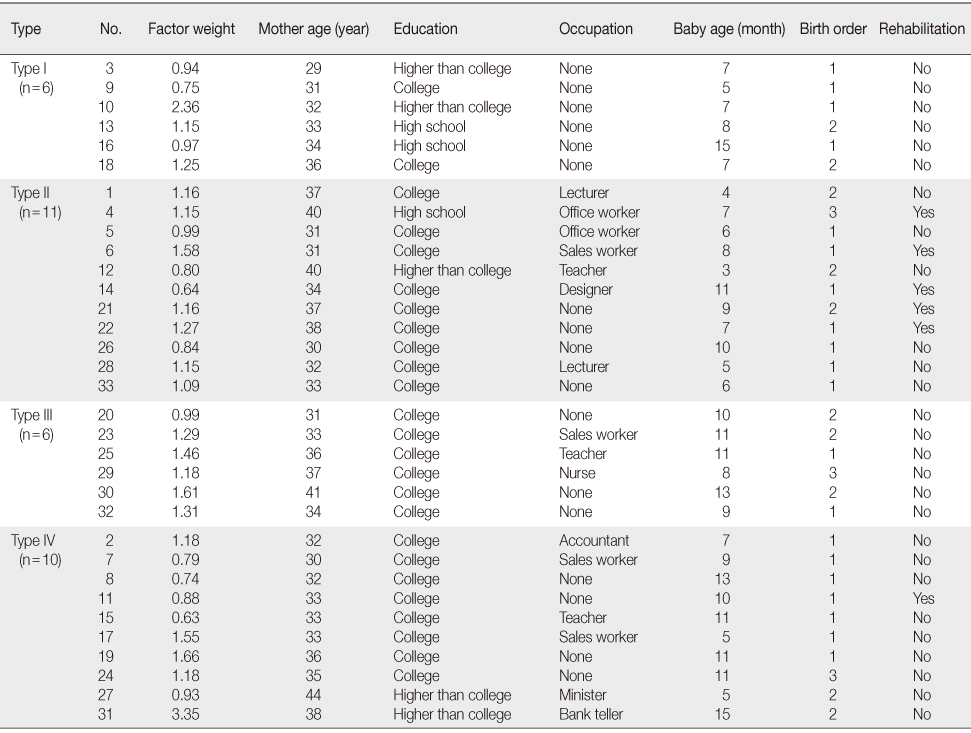
Demographic Characteristics and Factor Weight for P-sample (N=33)
Table 1
Q statements on Parenting Experience and Z Scores (N=33)
Table 2
Eigen Value, Variance, and Cumulative Percentage
Table 3
Correlation Matrix between Types
Table 4
Demographic Characteristics and Factor Weight for P-sample (N=33)
 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION
 Cite
Cite

