Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Nurs > Volume 43(5); 2013 > Article
-
Original Article
- A Guide on the Use of Factor Analysis in the Assessment of Construct Validity
- Hyuncheol Kang
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2013;43(5):587-594.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2013.43.5.587
Published online: October 31, 2013
Department of Informational Statistics, Hoseo University, Asan, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Kang, Hyuncheol. Department of Informational Statistics, Hoseo University, 20 Hoseo-ro 79 beon-gil, Asan 336-795, Korea. Tel: +82-41-540-5902, Fax: +82-41-540-5908, hychkang@hoseo.edu
• Received: August 16, 2013 • Accepted: September 17, 2013
© 2013 Korean Society of Nursing Science
Abstract
-
Purpose
- The purpose of this study is to provide researchers with a simplified approach to undertaking exploratory factor analysis for the assessment of construct validity.
-
Methods
- All articles published in 2010, 2011, and 2012 in Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing were reviewed and other relevant books and articles were chosen for the review.
-
Results
- In this paper, the following were discussed: preliminary analysis process of exploratory factor analysis to examine the sample size, distribution of measured variables, correlation coefficient, and results of KMO measure and Bartlett's test of sphericity. In addition, other areas to be considered in using factor analysis are discussed, including determination of the number of factors, the choice of rotation method or extraction method of the factor structure, and the interpretation of the factor loadings and explained variance.
-
Conclusion
- Content validity is the degree to which elements of an assessment instrument are relevant to and representative of the targeted construct for a particular assessment purpose. This measurement is difficult and challenging and takes a lot of time. Factor analysis is considered one of the strongest approaches to establishing construct validity and is the most commonly used method for establishing construct validity measured by an instrument.
- 1. Arrindel WA, van der Ende J. An empirical test of the utility of the observations-to-variables ratio in factor and components analysis. Appl Psychol Meas. 1985;9(2):165–178. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/014662168500900205ArticlePDF
- 2. Barrett PT, Kline P. The observation to variable ratio in factor analysis. Personal Study Group Behav. 1981;1:23–33.
- 3. Bollen K, Lennox R. Conventional wisdom on measurement:A structural equation perspective. Psychol Bull. 1991;110(2):305–314.Article
- 4. Cartell L, Harman A. The scree test for the number of factors. Multivar Behav Res. 1966;1:245–276.Article
- 5. Chin WW. Issue and opinion on structural equation modeling. MIS Q. 1998;22(1):1–10.
- 6. Cho HD. A study on issues of using structure equation modeling in education study. Seoul, Korea University. 2011;Unpublished master's thesis.
- 7. Comrey AL, Lee HB. A first course in factor analysis. 2nd ed. Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum; 1992.
- 8. Guilford JP. Psychometric methods. 2nd ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 1956.
- 9. Hair JF, Anderson RE, Tatham RL, Black WC. Multivariate data analysis. 4th ed. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall; 1995.
- 10. Hogarty KY, Hines CV, Kromrey JD, Ferron JM, Mumford KR. The quality of factor solutions in exploratory factor analysis: The influence of sample size, communality, and overdetermination. Educ Psychol Meas. 2005;65(2):202–226. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/0013164404267287ArticlePDF
- 11. Jarvis CB, MacKenzie SB, Podsakoff PM. A critical review of construct indicators and measurement model misspecification in marketing and consumer research. J Consum Res. 2003;30(2):199–218. http://dx.doi.org/10.1086/376806Article
- 12. Kaiser HF. An index of factorial simplicity. Psychometrika. 1974;39(1):31–36.ArticlePDF
- 13. Kang H. Discussions on the suitable interpretation of model fit indices and the strategies to fit model in structural equation modeling. J Korean Data Anal Soc. 2013;15(2):653–668.
- 14. Kang H, Han ST, Kim K, Jhun M. Multivariate data analysis using SAS by examples. Paju: Freedom Academy; 2005.
- 15. Lawley DN, Maxwell AE. Factor analysis as a statistical method. 2nd ed. New York, NY: American Elsevier Pub. Co.; 1971.
- 16. Lee H, Kim JH. Structural equation modeling and AMOS 20.0. Seoul: JypHyunJae Publishing Co.; 2013.
- 17. MacCallum RC, Browne MW, Sugawara HM. Power analysis and determination of sample size for covariance structure modeling. Psychol Methods. 1996;1(2):130–149.Article
- 18. MacCallum RC, Widaman KF, Zhang S, Hong S. Sample size in factor analysis. Psychol Methods. 1999;4(1):84–99.Article
- 19. Munro BH. Statistical methods for health care research. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2005.
- 20. Nunnally JC. Psychometric theory. 2nd ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 1978.
- 21. Seong TJ. Validity and reliability. 2nd ed. Seoul: Hakjisa Publisher; 2002.
- 22. Shin HS, Hyun MS, Ku MO, Cho MO, Kim SY, Jeong JS, et al. Analysis of research papers published in the Journal of the Korean Academy of Nursing-focused on research trends, intervention studies, and level of evidence in the research. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2010;40(1):139–149. http://dx.doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2010.40.1.139ArticlePubMed
- 23. Snook SC, Gorsuch RL. Component analysis versus common factor analysis: A Monte Carlo study. Psychol Bull. 1989;106(1):148–154. http://dx.doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.106.1.148Article
- 24. Tabachnick BG, Fidell LS. Using multivariate statistics. 5th ed. Boston, MA: Pearson/Allyn & Bacon; 2007.
- 25. Tafreshi MZ, Yaghmaei F. Factor analysis of construct validity: A review of nursing articles. J Med Educ. 2006;10(1):19–26.
- 26. Tak JK. Psychological testing: An understanding of development and evaluation method. 2nd ed. Seoul: Hakjisa Publisher; 2007.
- 27. Williams B, Brown T, Onsman A. Exploratory factor analysis: A five-step guide for novices. J Emerg Prim Health Care. 2012;8(3):Article 1. ArticlePDF
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- Integrated EFA–AHP decision-making framework for fixed offshore wind energy substructures
Sunjae Lee, Yeonjoo Kang, Youngsun Kim, Seungjun Kim, Goangseup Zi
Ocean Engineering.2026; 349: 124094. CrossRef - Development and Validation of the Korean Version of the Cochlear Implant Quality of Life Questionnaire
Jeong Seon Yun, Wha Weon Jung, Jae Hee Lee
Korean Journal of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery.2026; 69(1): 19. CrossRef - Development and validation of the psychological safety in nursing simulation (PSSANS) tool
Sook Jung Kang, Hye Young Min, Chong Min Hong
Nurse Education Today.2026; 160: 106993. CrossRef - Development and Validation of the Professional Self‐Concept Scale for Hospital Nurses (PSCS‐HN)
Eun‐Ha Kim, Hye‐Ah Yeom
Research in Nursing & Health.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Balancing priorities: An importance-performance analysis of architectural heritage protection in China's historical cities
Zihao Cao, Muhizam Mustafa, Mohd Hafizal Mohd Isa
Frontiers of Architectural Research.2025; 14(4): 928. CrossRef - Development and Psychometric Validation of a Comprehensive Questionnaire to Assess Oncologists' Knowledge of Chemotherapy-Drug Interaction
Bassam Abdul Rasool Hassan
Journal of Cancer Education.2025; 40(5): 741. CrossRef - Development of a Korean clinical decision-making ability scale for hospital nurses
Sunyoung Oh, Minkyung Gu, Sohyune Sok
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Reliability and validity of the Korean version of the Nurses Professional Values Scale-3 for nursing students: a methodological study
Eun Hee Yang, Mi Yu
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2025; 55(1): 93. CrossRef - Examining the role of ClassPoint tool in shaping EFL students' perceived E-learning experiences: A social cognitive theory perspective
Huma Akram, Abbas Hussein Abdelrady
Acta Psychologica.2025; 254: 104775. CrossRef - Mere moral beliefs aren't sufficient to determine pro-social behaviors! A moderated mediation framework tested in healthcare settings based on Belief in Self-Determinism (BSD) Theory
Muhammad Ali Asadullah, Tabassum Iqbal, Ali Haj Khalifa, Sajid Haider
Acta Psychologica.2025; 253: 104763. CrossRef - Maternal identity measurement based on the experiences of mothers with infants: a methodological study
Sun jung Park, Eun young Choi
Women's Health Nursing.2025; 31(1): 46. CrossRef - A Validation Study on the Translated Korean Version of Attitudes towards Men in Nursing Questionnaire for Nurses
Jin Ho Lee, Moon Jeong Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(2): 190. CrossRef - Assessing the Development and Validity of Educational Videos in Educating Dental Infection Control Coordinators
Na‐Young Lee, Han‐Na Kim
International Journal of Dental Hygiene.2025; 23(4): 643. CrossRef - Development and psychometric assessment of a care competency scale for family caregivers in home palliative care
Tingting Wang, Jun Kong, Xin Chen, Yiyun Yang, Dan Liu, Ting Liu, Li Li
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2025; 12: 100719. CrossRef - Self-assessment of infection prevention competency for early childhood teachers: a developed and validated scale
Won-Oak Oh, Myung Jin Jung, Yoojin Heo, Jihee Han, Eunji Lee
Journal of Early Childhood Teacher Education.2025; : 1. CrossRef - Validity and reliability of the Approaches to Dementia Questionnaire (ADQ) in Indonesian health students
Sri Mulyani, Gary Mitchell, Gillian Carter, Bob Woods, Sri Warsini, Azam David Saifullah, Aisyah Iffah Ulayya, Christine Brown Wilson
BMC Medical Education.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - 프로스포츠 메타버스 플랫폼의 지각된 가치와 이용의도 간 관계에서 혁신성과 혁신저항의 다중가산조절효과 분석
태연 구, 형일 권
The Korean Journal of Physical Education.2025; 64(2): 189. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of a Korean Diabetes Eating Problem Survey–Revised
Hye-Ryeon Park, So Yeon Park, Jaeyoung Lee, Hyeon Ok Ju
Asian Nursing Research.2025; 19(3): 220. CrossRef - Development and Validation of the Clinical Nurses' Job Crafting Scale
Eunha Jeong, Sujeong Han
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(3): 333. CrossRef - Exploration of the Application Rules and Clinical Significance of Acupoints in Acupuncture Treatment of Migraine Based on Data Mining [Response to Letter]
Yujun He, Yachao Wu, Xiaojun Li
Journal of Pain Research.2025; Volume 18: 3541. CrossRef - Evaluating the Klontz Money Script Inventory-Revised (KMSI-R): Factorial Validity, Internal Consistency, and Measurement Invariance with a Diverse Sample
Miranda Reiter, Jesse B. Jurgenson, Megan McCoy, Kimberly Watkins, Kenneth White, Dee Warmath
Journal of Family and Economic Issues.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Psychometric properties of a Korean version of the pre-sleep arousal scale
Namhee Kim, Bo Gyeong Lee, Sanja Batić Očovaj
PLOS One.2025; 20(9): e0333390. CrossRef - Development of the Dietary Practices and Food Safety Literacy Scale for Older Adults
Ye-Rin Lee, Gi-Moon Nam, Young-Sun Kim, Hye-Ri Shin, Yoo-Kyung Park, Ji-Hye Mun, Su-Hyeun Cho, Hee-Sook Lim
Nutrients.2025; 17(21): 3354. CrossRef - Acceptance Scale for Traditional Chinese Medicine Techniques in Cancer Patients: Development and Validation
Liu Yang, Xia Sheng, Jiayi Lin, Weina Wang, Xinlei Wu, Rujia Lin, Aiqin Liu, Limin Liu
Patient Preference and Adherence.2025; Volume 19: 3509. CrossRef - Impacts of Internal and External Uncertainties on Logistics Service Flexibility in Cross-Border E-Commerce Logistics: Evidence from South Korea
Seiwook Chung, Hyunho Kim, Donghyun Choi
Systems.2025; 13(12): 1082. CrossRef - Developing and validating the nurse-patient relationship scale (NPRS) in China
Yajie Feng, Chaojie Liu, Siyi Tao, Chen Wang, Huanyu Zhang, Xinru Liu, Zhaoyue Liu, Wei Liu, Juan Zhao, Dandan Zou, Zhixin Liu, Junping Liu, Nan Wang, Lin Wu, Qunhong Wu, Yanhua Hao, Weilan Xu, Libo Liang
BMC Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Perseverative cognition and health behaviours: exploring the role of intentions and perceived behavioural control
Dane McCarrick, Andrew Prestwich, Daryl B. O’Connor
Psychology & Health.2024; 39(9): 1183. CrossRef - The Influence of Behavioral and ESG Drivers on Consumer Intentions for Online Fashion Renting: A Pathway Toward Sustainable Consumption in China’s Fashion Industry
Bilal Ahmed, Hatem El-Gohary, Rukaiza Khan, Muhammad Asif Gul, Arif Hussain, Syed Mohsin Ali Shah
Sustainability.2024; 16(22): 9723. CrossRef - Cross-cultural adaptation and validation of the short nutritional literacy scale for young adults (18-35years) and analysis of the influencing factors
Yaoyao Liu, Lei Zhang, Kaiyan Xu, Yiqian Ding, Fangyan Li, Tinglin Zhang
BMC Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Cross-Cultural Adaptation and Validation of the Korean Version of the Body Image After Mastectomy Scale
Sook Jung Kang, Goh Eun Choi
Seminars in Oncology Nursing.2024; 40(1): 151576. CrossRef - Longitudinal Evaluation of the Influence of WORTH Yetu on Household Economic Status Based on the Count of Non-asset Resources for Orphaned and Vulnerable Children’s Well-being in Tanzania
Amon Exavery, Peter Josephat Kirigiti, Ramkumar T. Balan, John Charles
Child Indicators Research.2024; 17(4): 1661. CrossRef - How to Design and Evaluate mHealth Apps? A Case Study of a Mobile Personal Health Record App
Guyeop Kim, Dongwook Hwang, Jaehyun Park, Hyun K. Kim, Eui-Seok Hwang
Electronics.2024; 13(1): 213. CrossRef - Development of an infection control competency scale for clinical nurses: an instrument design study
Yong Hwan Hyeon, Kyoung Ja Moon
BMC Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Development of Maternal Adaptation Scale for the Primipara Women
Jungmi Ko, Ju-Eun Song
Journal of Korean Maternal and Child Health.2024; 28(2): 51. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of the Korean Version of the Occupational Coping Self-Efficacy Scale for Nurses
Youngrye Park, Sunah Park, Hee Ran Kang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2024; 54(4): 633. CrossRef - Psychometric Testing of the Korean Version of the Self-Care of Coronary Heart Disease Inventory Version 3
Jin-Hee Park, Seok Hyun Gwon, Myeong-Ho Yoon, A-Young Lee, Sun Hyoung Bae
Asian Nursing Research.2024; 18(3): 238. CrossRef - Development of Colleague Solidarity Scale for Nurses
Moon Yeon Kong, Nah-Mee Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(5): 504. CrossRef - Engineering undergraduates’ knowledge: insights into skills’ awareness, difference and interdependence
Rajni Singh, Kuldip Singh Sangwan, Devika Sangwan
Journal of Applied Research in Higher Education.2024; 16(5): 2245. CrossRef - Translation and Cross‐Cultural Adaptation of the Osteoarthritis Knowledge Scale Into Turkish
Hilal Ata Tay, Gönül Acar, Mert Gündoğdu, Murat Kaya, Hasan Hilmi Muratli, Ben Darlow
Musculoskeletal Care.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Translation and psychometric evaluation of the Chinese version of the Nursing Time Management Scale
Zhaoquan Fu, Yaping Wang, Limei Zhang, Mingyang Tan
Frontiers in Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Development of a Physical Literacy Instrument for Rural Elderly
Jin-Yeong Park, Ji-Youn Kim, Ae-Rim Seo, Ki-Soo Park
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2024; 49(3): 270. CrossRef - Development and psychometric assessment of a health action process approach (HAPA) inventory for home nutritional behavior among postoperative gastric cancer patients
Xiaohan Jiang, Jiamin Chen, Xiuhong Yuan, Yonghe Chen, Qian Sun, Hui Zhao, Peirong Xu, Ting Luo, Junsheng Peng
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2024; 11(10): 100569. CrossRef - The effect of country image, brand image, and warranty knowledge on car purchase intentions: a comparison of use situations
Albert Kriestian Novi Adhi Nugraha, Cara Edo Krista, Andrian Dolfriandra Huruta
Cogent Business & Management.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Non-suicidal self-injury motivation scale in a community sample of adolescents: a methodological study
Jungok Yu, Myo-Sung Kim, Miyoung Kim
BMC Psychology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and validation of suicide crisis scale for international students in South Korea
Ki-Hyun Choi, Jung Hee Ha, Juliet Jue
Frontiers in Psychology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Psychometric evaluation of the Chinese version of the stressors in breast cancer scale: a translation and validation study
Wenqi Hu, Jiahui Bao, Xiaolin Yang, Mao Ye
BMC Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and psychometric analysis of the smombie scale for adolescents
Sunhee Park, Sumi Oh
Journal of Pediatric Nursing.2024; 75: 89. CrossRef - Classification of Rural Areas Based on the Related Population Concept
Chae-Wan Lee, Chang-Su Lim
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2024; 35(4): 701. CrossRef - Development and validation of a quality of healthy work environment instrument for shift nurses
Sun-Hwa Shin, Eun-Hye Lee
BMC Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - On the Factors that Affect People's Involvement in Reducing Marine Waste
Sunsil HUR, Jungwoon KANG, Mincheol KIM
THE JOURNAL OF FISHERIES AND MARINE SCIENCES EDUCATION.2024; 36(5): 982. CrossRef - Cultural translation of the ethical dimension: a study on the reliability and validity of the Chinese nurses’ professional ethical dilemma scale
Wei Hu, Ke Shang, Xin Wang, Xia Li
BMC Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of orderliness of underground workplace system based on occupational ergonomics: A case study in Guangzhou and Chengdu metro depots
Jianna Li, Bin Guo, Zhoubo Du
Work.2024; 78(3): 687. CrossRef - The Translation, Culture-Adaptation and Psychometric Evaluation of the Cardiac Rehabilitation Barriers Scale Among Chinese Older Population
Sisi Zhang, Miao Yu, Yu Zhang, Conying Liang, Dayi Hu, Dao Wen Wang, Xiaoping Meng
Journal of Multidisciplinary Healthcare.2024; Volume 17: 723. CrossRef - Development, validation and reliability testing of the hospice care environment scale
Junping Zhong, Wei Zhang, Rong Xu, Huifen Wang, Jing Zhao, Yingjuan Huang, Yanlin Chen, Xiaoli Chen, Jianfei Chen, Qing Zhang, Zhijie Zou, Yingzi Zhang
BMC Palliative Care.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Development of a Standard Tool of Pattern Identification for Functional Dyspepsia: A Cross-Sectional Study from Korea
Na-Yeon Ha, Seok-Jae Ko, Jae-Woo Park, Jinsung Kim
Healthcare.2024; 12(23): 2331. CrossRef - Development and psychometric evaluation of nutrigenomics and personalized nutrition-related knowledge, attitude, and behavior questionnaire in dietetic students and professionals
Panchali Moitra, Janvi Nemani, Saba Madre, Jagmeet Madan
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Gender disparities in defining factors of pedestrian level of service of sidewalks
G. R. Bivina, Manoranjan Parida
Environment, Development and Sustainability.2024; 27(11): 26637. CrossRef - Development and validation of a knowledge, attitude, and practice questionnaire regarding exercise and exergames for obese patients with gout
Manting Cao, Hazwani Ahmad Yusof, Jianer Chen, Liping Zhou
BMC Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Developing and validating an instrument for assessing E-entrepreneurial idea feasibility
Guan-Yu Lin, Wen-Hsuan Li, Yi-Shun Wang
The International Journal of Management Education.2024; 22(3): 101060. CrossRef - Impacts of Just Culture on Perioperative Nurses' Attitudes and Behaviors With Regard to Patient Safety Incident Reporting: Cross-Sectional Nationwide Survey
Nara Han, Seok Hee Jeong, Myung Ha Lee, Hee Sun Kim
Asian Nursing Research.2024; 18(4): 323. CrossRef - A study on the habitat characteristics and key environmental factors of an endangered species, Viola websteri
Minhan Kim, Sunryoung Kim, Jea-hwa Tho, Yeongjun Lee, Rae-Ha Jang, Do-Hun Lee
Environmental Biology Research.2024; 42(4): 411. CrossRef - Functional Classification and Analysis of Key Factor in National Fishing Ports
Ji-Yeong Ko
Journal of the Korean Society of Marine Environment and Safety.2024; 30(7): 744. CrossRef - Development and psychometric properties of the social adjustment scale for youth cancer survivors in South Korea
Sumi Oh, Hyejung Lee, Sue Kim, Sanghee Kim, Chuhl Joo Lyu, Chang Gi Park, Hyoung Jin Kang
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2023; 10(7): 100241. CrossRef - The psychometric properties of the Chinese version of the stressor scale for emergency nurses
Yuxin Wang, Qi Zhang, Saiwen Li, Yi Jin
Australasian Emergency Care.2023; 26(2): 179. CrossRef - Transcultural adaptation and validity of the nurse professional competence scale Korean version for graduating nursing students: An explanatory factor analysis
Su Jung Lee, Hyun‐Ju Seo, Kye Ha Kim, Jinhee Kim, Hyunlye Kim, Jeong‐Min Park
Nursing Open.2023; 10(2): 579. CrossRef - Psychometric evaluation of nursing interns’ consciousness of rights scale in clinical practice
Yuting Zeng, Hongyu Li
BMC Nursing.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Reliability and Validity Analysis of the Korean Version of the Affinity for Technology Interaction Scale
Taehui Kim, Seyeon Park, Miri Jeong
Healthcare.2023; 11(13): 1951. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of the Korean Version of Nurses' Ethical Behaviors for Protecting Patient's Rights Scale: A Methodological Study
Jihye Yun, Heeyoung Oh
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2023; 35(2): 138. CrossRef - The Reliability and Validity of a Korean version of the Quality of Life in Life Threatening Illness - Family Carer Version 3: Focused on the families of patients with terminal cancers
Kyung-Ah Kang, Hyun Sook Kim, Myung-Nam Lee
Asian Oncology Nursing.2023; 23(3): 102. CrossRef - Investigation of the Validity and Reliability of the Turkish Adaptation of Allen Cognitive Level Screen-5 (ACLS-5) with Individuals with Schizophrenia
Leyla Kaya Ozturk, Gonca Bumin, Ebru Ozturk, Gokcen Akyurek
Occupational Therapy in Mental Health.2023; 39(4): 419. CrossRef - Everyday Digital Literacy Questionnaire for Older Adults: Instrument Development and Validation Study
JiYeon Choi, Seongmi Choi, Kijun Song, Jiwon Baek, Heejung Kim, Mona Choi, Yesol Kim, Sang Hui Chu, Jiyoung Shin
Journal of Medical Internet Research.2023; 25: e51616. CrossRef - Development and validation of the 23-item preterm birth risk assessment scale-Korean version
Jeung-Im Kim
BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and validation of a Decision‐Making Ability Scale for postpartum urinary incontinence women engaging in pelvic floor physical therapy
Jie Li, Tiantian Li, Xiaoling Zhao, Juanhua Li, Lanlan Yu, Wenjun Tang, Yuanwen Liu, Xiaoli Huang, Ling Chen, Wenzhi Cai
Neurourology and Urodynamics.2023; 42(8): 1756. CrossRef - Psychometric properties of the Chinese version of the knowledge, attitudes and practices of the incontinence‐associated dermatitis questionnaire (C‐KAP‐IAD‐Q) used with Chinese nurses
Qi Zhang, Xintong Li, Ke Zhang, Lijun Lv, Yi Jin
International Journal of Nursing Practice.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and Validation of a Clinical Practicum Transition Shock Scale (CPT-Shock) for Korean Nursing Students
Soo-Yeon Kim, Yeong-Ju Ko
Healthcare.2023; 11(20): 2789. CrossRef - Consumer Preference of Traditional Korean Soy Sauce (Ganjang) and Its Relationship with Sensory Attributes and Physicochemical Properties
Yang Soo Byeon, JeongAe Heo, Kwon Park, Young-Wook Chin, Sang-pil Hong, Sang-Dong Lim, Sang Sook Kim
Foods.2023; 12(12): 2361. CrossRef - Assessing psychometric properties of the Turkish version of the Fear of COVID‐19 Scale for Nurses
Sadık Hançerlioğlu, İsmail Toygar
International Journal of Nursing Practice.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Psychometric Validation of the Korean Version of the Family-Centered Care Questionnaire—Revised
Jihee Han, Won-Oak Oh, YooJin Heo, Sunho Kim
Journal of Nursing Measurement.2023; 31(3): 347. CrossRef - Association between COVID-19-related stress and self-directed learning ability among Korean nursing students
Jeong Min Park, Hyun-Ju Seo, Seong Min Kim, Hyuncheol Kang, Su Jung Lee
Nurse Education in Practice.2023; 69: 103613. CrossRef - Validation of a Questionnaire to Analyze Teacher Training in Inclusive Education in the Area of Physical Education: The CEFI-R Questionnaire
Jorge Rojo-Ramos, María Mendoza-Muñoz, Santiago Gómez-Paniagua, Miguel Ángel García-Gordillo, Ángel Denche-Zamorano, Jorge Pérez-Gómez
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2023; 20(3): 2306. CrossRef - 혼합현실 사이클링 플랫폼 참여자의 참여동기, 운동재미, 운동지속의도의 관계
관희 남, 범영 박
The Korean Journal of Physical Education.2023; 62(6): 597. CrossRef - The Chinese version of the self-efficacy scale for daily life activities among older adults: translation, validity and reliability
Yuecong Wang, Tianxiang Jiang, Fang Zhou
Geriatric Nursing.2023; 54: 46. CrossRef - Translation and validation of the Persian version of diabetic foot ulcer scaleshort form (DFS‐SF)
Sedigheh Sadat Tavassolmand, Ali Montazeri, Farzan Madadizadeh, Hamid Reza Dehghan, Mohammad Ranjbar, Hosein Ameri
International Wound Journal.2023; 20(3): 822. CrossRef - Psychometric properties of the Korean version of the oncofertility barriers scales among nurses: A methodological study
Hae Jeong An, Yoonjung Kim
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2023; 10(9): 100275. CrossRef - Integration of patient experience factors improves readmission prediction
Harry M. Burke, Jocelyn Carter
Medicine.2023; 102(3): e32632. CrossRef - Testing the validity and reliability of an assessment tool for dental hygienists’ consideration of patients with mild disabilities
Journal of Korean Society of Dental Hygiene.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The transcultural adaptation and validation of the Chinese version of the Attitudes Toward Recognizing Early and Noticeable Deterioration scale
Wenbo Li, Hongyu Yu, Bing Li, Yanli Zhang, Mingshu Fu
Frontiers in Psychology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Development of mealtime difficulty scale for older adults with dementia in long-term care facilities
Dukyoo Jung, Eunju Choi, Leeho Yoo, Hyesoon Lee
BMC Geriatrics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Psychometric Properties of the Korean Version of the Environmental Health Literacy Scale
Jung-Min Kwak, Ju-Hee Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(7): 4079. CrossRef - A Study on the development of Defensive Verbal Scale
Jae Seok Kwak, Sun Jung Kwon, Yena Kim
The Korean Journal of Psychology: General.2022; 41(1): 63. CrossRef - Psychometric validation of the AOSL scale using confirmatory factor analysis: A nationally representative sample
Olufunmilola Abraham, Claire A. Rosenberger, Jen Birstler
Journal of the American Pharmacists Association.2022; 62(5): 1638. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of Korean Version of the Schwartz Center Compassionate Care Scale*
Seong Eun KIM, Jeong Suk KIM
Korean Journal of Medical Ethics.2022; 25(2): 137. CrossRef - Development of Nursing Informatics Competence Scale for Korean Clinical Nurses
Seon Mi Jang, Jeongeun Kim
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2022; 40(10): 725. CrossRef - Development of a Scale for Quantitative Evaluation of Exercise Instructors for Older People
Jeeyoung Hong, Haeryung Kim, Hyoun-Joong Kong
Exercise Science.2022; 31(4): 438. CrossRef - Influence of Pain Management Knowledge, Pain Management Self-Efficacy, and Empathic Capacity on Pain Management Performance of Nurses in Orthopedic Units
Ji-Eon Han, Jeonghyun Cho
STRESS.2022; 30(2): 109. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of the Korean version of Nurses' Attitudes towards the Forensic Psychiatric Patients Scale (NAFPPS-K)
Moonju Song, Yul-Mai Song, Kuem Sun Han
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2022; 31(3): 304. CrossRef - Development and psychometric testing of learning immersion scale in clinical simulation: A methodological study
Eun Jeong Ko, Kyoung A. Nam, Eun Jung Kim
Nurse Education Today.2022; 113: 105363. CrossRef - Cross-Cultural Validation of the McGill Quality of Life Questionnaire-Revised (MQOL-R), Korean Version; A Focus on People at the End of Life
Kyung-Ah Kang, Myung-Nam Lee
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2022; 25(3): 110. CrossRef - The Reliability and Validity of Korean Version of the Infertility Stigma Scale (K-ISS)
Miok Kim, Minkyung Ban
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2022; 52(6): 582. CrossRef - Structural equation model based on salutogenesis theory for evaluating factors affecting health-related quality of life in adolescents with moyamoya disease
Won-oak Oh, Insun Yeom, Sung-Hyun Lim
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of the Korean Version of the Climate, Health, and Nursing Tool
Da Woon Jeong, Gwang Suk Kim, Min Kyung Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2022; 52(2): 173. CrossRef - Reliability and Validity of the Korean Version of the High-Performance Work System Scale (HPWS-K)
Hyesun Kim, Kawoun Seo, Taejeong Jang
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(20): 13708. CrossRef - Cognitive and Emotional Assessment toward Suicidal People: Korean Suicide Stigma Scale for General Public
Soontae An, Hannah Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2022; 29(1): 115. CrossRef - Factors associated with difficulty in adapting and intent to leave among new graduate nurses in South Korea
Sun-young Park, Heejung Kim, Chenjuan Ma
Health Care Management Review.2022; 47(2): 168. CrossRef - A comparative perspective on destination competitiveness through visitors' and stakeholders' perceptions in the region of Cappadocia
Mehmet Halit Akin, Yuksel Ozturk, Kurtulus Karamustafa
Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Insights.2022; 5(5): 966. CrossRef - Development of Critical Reflection Competency Scale for Clinical Nurses
Sujin Shin, Eunmin Hong, Jiyoung Do, Mee Sun Lee, Youngsun Jung, Inyoung Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(6): 3483. CrossRef - The validity and reliability of the Korean version of the General Attitudes towards Artificial Intelligence Scale for nursing students
Yon Hee Seo, Jung-Won Ahn
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2022; 28(4): 357. CrossRef - Intention to Use Mobile Easy Payment Services: Focusing on the Risk Perception of COVID-19
JiWon Kim, Mincheol Kim
Frontiers in Psychology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Development of an endometriosis self-assessment tool for patient
Hyun-Hee Cho, Young-Sub Yoon
Obstetrics & Gynecology Science.2022; 65(3): 256. CrossRef - Psychometric Properties of the Korean Version of the Nursing Profession Self-Efficacy Scale
Seon Mi KIM, Ju Hee KIM, Jung Min KWAK
Journal of Nursing Research.2022; 30(2): e197. CrossRef - Assessing the psycholinguistic and psychometric properties of the Turkish version of the Transition Questionnaire grounded on the Hospital-to-Home Transition Model
Şerife Tutar, Yasemin Demir Avcı
Journal of Pediatric Nursing.2022; 65: 91. CrossRef - Development of the Korean Health Behavior for Dementia Prevention Scale for Older Adults
Hyukjoon Kim, Moonjoo Oh, Hyangsuk Kwon, Seohee Jeong, Hyangsoon Cho, Hye Young Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2022; 29(3): 363. CrossRef - Development of a scale for assessing meal satisfaction in older adults: Meal satisfaction assessment questionnaire (MSAQ)
Beste Alpay Jeong, Kyung Hee Lee, Huan Fan, Min Young Uhm
Geriatric Nursing.2022; 44: 30. CrossRef - Factors Facilitating and Hindering the Use of Newly Acquired Positioning Skills in Clinical Practice: A Longitudinal Survey
Vera U. Ludwig, Heidrun Pickenbrock, Daniel A. Döppner
Frontiers in Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Translation of the Chinese version of the Self‐Care for Aspiration Pneumonia Prevention Scale and its validation among Chinese community dwelling elderly with risk of dysphasia
Zhen Yang, Fengmin Chen, Yibo Zhang, Sien Pan, Yingying Lu, Huijun Zhang
Nursing Open.2022; 9(3): 1902. CrossRef - Structural validity of the Insomnia Severity Index: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Md Dilshad Manzar, Haitham A. Jahrami, Ahmed S. Bahammam
Sleep Medicine Reviews.2021; 60: 101531. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of Revised Version of the Self-Care Behaviors Scale-Korean (SCBS-K19) for Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients
Geungyeong Park, Heeyoung Oh
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2021; 33(3): 294. CrossRef - How I see is how I feel. Identification of illness perception schema and its association with adaptation outcomes in multiple sclerosis – a 5-year prospective study
Jagoda Różycka, Marcello Moccia
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(10): e0258740. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of K-MCQ to Assess Quality of Life of Older Adults with Mild Cognitive Impairment
Rhayun Song, Moonhee Gang, Myonghwa Park, Moonkyoung Park, Myoungock Jang, In Ok Hwang, Jeong Lan Kim
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2021; 23(2): 164. CrossRef - Development of a Korean version of the Bereavement Care Confidence Scale (K-BCCS)
So-Hi Kwon, Young-Joo Kim
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2021; 27(2): 197. CrossRef - Validity and reliability of new instruments for measuring patient satisfaction with removable dentures, Arabic Version
Ahmad Al Jaghsi, Musab Saeed, Salem Abu Fanas, Ahmed Yaseen Alqutaibi, Torsten Mundt
BMC Oral Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Development of a high-risk neonatal infection control competency scale
Mi Yu, Hyunju Kang, Jisun Park, Miran Yang
Journal of Child Health Care.2021; 25(3): 393. CrossRef - Validity and Development of a Social Exclusion Scale (SES) for Marriage Immigrant Women
Soon Mi Yang, Sun Hee Ahn, Minja Jung
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2021; 32(4): 611. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of the Korean Version of Assessment of Health Literacy in Breast and Cervical Cancer Screening
Hye Sook Shin, Eunlim Chi, Hae-Ra Han
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2021; 51(6): 769. CrossRef - A validation study of the Korean version of the Toronto empathy questionnaire for the measurement of medical students’ empathy
Sanghee Yeo, Kyong-Jee Kim
BMC Medical Education.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - A Validation Study of the Korean Version of the Nurses’ Patient Education Questionnaire
Myung-Jin Jung, Young-Sook Roh
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(11): 5609. CrossRef - Validity and reliability of the coronavirus anxiety scale: Turkish adaptation for nurses
Sadık HANÇERLİOĞLU, Filiz ÖZEL, Gülbin KONAKÇI
Ege Tıp Dergisi.2021; 60(2): 99. CrossRef - Supply chain management antecedents of performance in small to medium scale enterprises
Welby V. Loury-Okoumba, Chengedzai Mafini
South African Journal of Economic and Management Sciences.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Music Program Development Using the Ukulele in Community-dwelling Old Adults and Its Effect
Gyeong Hye Kang, Nam Joo Je
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2021; 32(2): 220. CrossRef - Development of emergency nursing care competency scale for school nurses
Jaehee Yoon
BMC Nursing.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and Validation of a Self-Efficacy Scale for Nursing Educators’ Role in Sri Lanka
Shyamamala S. Weerasekara, Jina Oh, Haeryun Cho, Mihae Im
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(15): 7773. CrossRef - Development of a Positive Nursing Organizational Culture Measurement Tool
Mi Jung Kim, Jong Kyung Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2021; 51(3): 305. CrossRef - The Development and Validation of a Perceived Nursing Support Scale for Mothers of Preterm Infants
Mihae Im, Jina Oh
Asian Nursing Research.2021; 15(5): 317. CrossRef - Development of the Self-Care Non-adherence Risk Assessment Scale for Patients with Chronic Illness
Mirae Jo, Heeyoung Oh
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2021; 32(4): 415. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of a Screening Scale for Indirect Trauma Caused by Media Exposure to Social Disasters
Eun Young Choi, Seung-Hye Choi, Haeyoung Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(2): 698. CrossRef - Development and validation of a novel instrument to measure pedestrians’ smartphone use: The Smombie Scale
Sunhee Park, Beomsoo Kim
Transportation Research Part F: Traffic Psychology and Behaviour.2021; 82: 440. CrossRef - A Validation Study of the Revised Caregiving Burden Instrument in Korean Family Caregivers of Stroke Survivors
So Sun Kim, Young Sook Roh
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(6): 2960. CrossRef - Development and Validation of the Happiness Scale for Middle-Aged Women Based on Existence, Relation, and Growth Theory
Hee-Jin Shin, Jeung-Im Kim
Asian Nursing Research.2021; 15(2): 96. CrossRef - The Moyamoya Health Behavior Scale for Adolescent Patients: Measurement Tool Development and Psychometric Evaluation
Won-oak Oh, Insun Yeom, Sung-Hyun Lim, Dong-Seok Kim, Kyu-won Shim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(8): 4064. CrossRef - Distance education perception scale for medical students: a validity and reliability study
Güven Özkaya, Mevlüt Okan Aydin, Züleyha Alper
BMC Medical Education.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and Validity Testing of a Morning Stiffness Assessment Scale for Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis
HyunSoo Oh, SuHyang Bang, BoAe Im, SiWon Lee, WhaSook Seo
Orthopaedic Nursing.2021; 40(1): 23. CrossRef - Development and Validation of Motivation Balance Scale and Balance Index
Myung-Jun Park, Sung-Man Shin
The Korean Journal of Psychology: General.2021; 40(4): 597. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of the Korean Version of the Fear of COVID-19 Scale
Jeong-Won Han, Junhee Park, Hanna Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(14): 7402. CrossRef - A Study of the Effectiveness Verification of Computer-Based Dementia Assessment Contents (Co-Wis): Non-Randomized Study
Seung Il Song, Hyun Seok Jeong, Jung Pil Park, Ji Yean Kim, Dai Seg Bai, Gi Hwan Kim, Dong Hoon Cho, Bon Hoon Koo, Hye Geum Kim
Applied Sciences.2020; 10(5): 1579. CrossRef - Validation of the Korean Version of Gatekeeper Behavior Scale
Jung Suk Park, Jae Hong Park
Journal of Korean Neuropsychiatric Association.2020; 59(2): 170. CrossRef - Turkish Adaptation of Diabetic Foot Ulcer Scale–Short Form
İsmail Toygar, Sadık Hançerlioğlu, Selden Gül, Tülün Utku, Ilgın Yıldırım Şimşir, Şevki Çetinkalp
The International Journal of Lower Extremity Wounds.2020; 19(3): 269. CrossRef - Reliability and Validity of the Korean version of the Pain in Older Adults Knowledge Survey (K-POAKS) among Nurses Who Have Worked in Long-term Care Hospitals
Young Seun Ryu, Jeong Sook Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2020; 31(2): 130. CrossRef - Development of the Forensic Nursing Competency Scale for Nurses
Na Young Jo, Min Hye Kim, Yun Mi Lee
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2020; 13(3): 24. CrossRef - Analysis of Equivalence and Reliability of Korean Translated Abbreviated Profile of Hearing Aid Benefits
Taehwa Kim, Jinsook Kim
Audiology and Speech Research.2020; 16(3): 175. CrossRef - Psychometric evaluation of the Turkish version of two traditional and complementary medicine scales for nurses
I. Toygar, S. Hançerlioğlu
Progress in Health Sciences.2020; 10(2): 15. CrossRef - Training needs analysis of Korean nurses' neurological assessment competency
Ki Sook Bae, Young Sook Roh
Nursing & Health Sciences.2020; 22(1): 99. CrossRef - Validation and implementation of a national survey to assess antimicrobial stewardship awareness, practices and perceptions amongst community pharmacists in Australia
Tasneem Rizvi, Angus Thompson, Mackenzie Williams, Syed Tabish R. Zaidi
Journal of Global Antimicrobial Resistance.2020; 21: 28. CrossRef - Validity and reliability of a Korean version of the breast cancer survivors resilience scale
Jung Min Kim, Jin Hyuk Choi, Jeong‐Won Han
Japan Journal of Nursing Science.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Development of a Coping Scale for Infertility-Women (CSI-W)
Miok Kim, Jung-Mi Ko
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2020; 50(5): 671. CrossRef - Development and Validation of a Self-control Competency Scale for Late-school-aged Children
Bo Kyoung Jin, Hye Young Ahn
Child Health Nursing Research.2020; 26(4): 411. CrossRef Reliability and Validity of the Arabic Version of the EORTC QLQ-C30 and QLQ-BR23 Questionnaires
Ghufran Jassim, Ahmed AlAnsari
Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment.2020; Volume 16: 3045. CrossRef- Development and psychometric validation of a scale of the compliance with blood-borne pathogens prevention
Kyungmi Lee, Younhee Kang
Applied Nursing Research.2020; 52: 151244. CrossRef - Developing a Korean Version of the Scale for the Observation of Agitation in Persons with Dementia of Alzheimer-Type
Eun Young Kim, Ye-Na Lee, Eunhye Jeong, Sung Ok Chang
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2020; 22(4): 316. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of Korean Version of Post-traumatic Stress Disorder Scale (K-PTSD) Measuring Attitudes and Knowledge of PTSD
Kyung-sook Bang, Hwal Bang, Sun-Woo Hong, Jihee Lim
Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2020; 26(1): 47. CrossRef - Analysis of the moral mechanism to purchase counterfeit luxury goods: evidence from China
Yushi Jiang, Miao Miao, Tariq Jalees, Syed Imran Zaman
Asia Pacific Journal of Marketing and Logistics.2019; 31(3): 647. CrossRef - Core nursing competency assessment tool for graduates of outcome‐based nursing education in South Korea: A validation study
YuKyung Ko, Soyoung Yu
Japan Journal of Nursing Science.2019; 16(2): 155. CrossRef - Development of the Short Form Adolescent Parenting Stress Scale
Kyung Mi Sung, Seung Min Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2019; 28(4): 287. CrossRef - The rating model of corporate information for economic security activities
Onechul Na, Lee Won Park, Harang Yu, Yanghoon Kim, Hangbae Chang
Security Journal.2019; 32(4): 435. CrossRef - Reliability and Validity of Korean Version of Nursing Students' Anxiety and Self-Confidence with Clinical Decision Making Scale
Mi Yu, Young Eun, KA White, KyungJa Kang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2019; 49(4): 411. CrossRef - Development and Validation of an Instrument to Measure Nursing Information Literacy Competency
Meanjung Jo, Yeongmi Ha
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2019; 30(1): 25. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Korean version of the self-assessment of nursing informatics competencies scale
Kyoungsan Seo, Yul Ha Min, Seung-Hye Choi, Haeyoung Lee
BMC Nursing.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Development of an Aging Anxiety Scale for Middle-Aged Women
Haejin Lee, Mi-Ae You
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2019; 49(1): 14. CrossRef - Reliability and validation of the Korean Compassionate Communication Scale
Hae-Kyung Jo, Sook Kyoung Park, EunJu Song
Frontiers of Nursing.2019; 6(3): 175. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of the Korean Version of the Partners In Health Scale (PIH-K)
Mi-Kyeong Jeon, Jung-Won Ahn, Yeon-Hwan Park, Mi-Kyoung Lee
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2019; 12(2): 1. CrossRef - Development and Validation of an Ego Strength Scale for Early School-Age Children
Se Young Kim
Korean Journal of Child Studies.2018; 39(6): 175. CrossRef - Cross-cultural Adaptation and Validation of the eHealth Literacy Scale in Korea
Sun Ju Chang, Eunjin Yang, Hyunju Ryu, Hee Jung Kim, Ju Young Yoon
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2018; 30(5): 504. CrossRef - Validation of the Korean Version of the Maternal Postpartum Attachment Development Scale for Mothers of Children who were in a Neonatal Intensive Care Unit
Ah Rim Kim, Young Ran Tak
Korean Journal of Child Studies.2018; 39(1): 129. CrossRef - A Study on the Effects of IT Utilization Level and Social Capital on Knowledge Management, Management Performance: Focusing on Incheon International Airport
Yoon-Tae Sim, Sang-Beom Park
Journal of Industrial Distribution & Business.2018; 9(11): 77. CrossRef - Comparison of EQ-5D and OHIP-14 sub-dimensions for measuring oral health-related quality of life
Eunsuk Ahn, Hosung Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Oral Health.2018; 42(3): 77. CrossRef - Development of the Clinical Short-Form Positive Resources Test
Hyu Jung Huh, Sun-Young Kim, Jung-A Min, Jeong-Ho Chae
Stress.2018; 26(2): 77. CrossRef - In reply to Korean translation and validation of the WHOQOL-DIS for people with spinal cord injury and stroke: Methodological issues
Hyun Choi
Disability and Health Journal.2018; 11(1): 5. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of the Korean Version of the Families’ Importance in Nursing Care-Pediatric Nurses’ Attitudes Instrument
Jina Oh, Yae Young Kim, So Yeon Yoo, Haeryun Cho
Child Health Nursing Research.2018; 24(3): 274. CrossRef - A Chinese version of the Language Screening Test (CLAST) for early-stage stroke patients
Hongyan Yang, Shenghua Tian, Constance Flamand-Roze, Ling Gao, Wei Zhang, Yan Li, Jiajia Wang, Zhou Sun, Ying Su, Libin Zhao, Zhihou Liang, Jong-Ling Fuh
PLOS ONE.2018; 13(5): e0196646. CrossRef - Development and Psychometric Testing of the Clinical Nursing Competency Scale for Clinical Preceptor Use (CNCS-CP)
Eunmi Kwak, Heeyoung Oh
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2018; 48(4): 419. CrossRef - Metagenome Analysis as a Tool to Study Bacterial Infection Associated with Acute Surgical Abdomen
Shao-Chun Wu, Cheng-Shyuan Rau, Hang-Tsung Liu, Pao-Jen Kuo, Peng-Chen Chien, Ting-Min Hsieh, Ching-Hua Tsai, Jung-Fang Chuang, Chun-Ying Huang, Hsiao-Yun Hsieh, Ching-Hua Hsieh
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2018; 7(10): 346. CrossRef - The reliability and validity of instruments measuring pattern identification in Korean medicine: A systematic review
Mi Mi Ko, Myeong Soo Lee, Stephen Birch, Ju Ah Lee
European Journal of Integrative Medicine.2017; 15: 47. CrossRef - Development and Validation of the Cancer-Specific Posttraumatic Growth Inventory
Young-Mi Jung, Jin-Hee Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2017; 47(3): 319. CrossRef - Development of the Korean Paternal-Fetal Attachment Scale (K-PAFAS)
Nan Iee Noh, Hye-Ah Yeom
Asian Nursing Research.2017; 11(2): 98. CrossRef - Stakeholder Management in Long-Term Complex Megaconstruction Projects: The Saemangeum Project
Hyoungbae Park, Kyeongseok Kim, Yong-Woo Kim, Hyoungkwan Kim
Journal of Management in Engineering.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Reliability and dimensionality of PHQ-9 in screening symptoms of depression among health science students in Cartagena, 2014
Carlos Arturo Cassiani-Miranda, María Camila Vargas-Hernández, Eduard Pérez-Anibal, Mariana Isabel Herazo-Bustos, Mauricio Hernández-Carrillo
Biomédica.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of Separation Anxiety Scale for Mothers Using Child Care Facilities
Hyo Sung Cha, Jihyun Ko, Kyoung Ju Lee, Aelee Choi, Gunjung Lee
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2016; 17(1): 409. CrossRef - Validity and reliability of a Korean version of the wellness evaluation of lifestyle (K-WEL)
Hee Sook Kim, Yeonungsuk Song, So-Hi Kwon
Journal of the Korean Data and Information Science Society.2016; 27(6): 1609. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of the Suicide Resilience Inventory-Korean Version for Korean University Students
Jun Hee Noh, Soo Jung Chang, Seong Eun Kim
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2016; 17(1): 508. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of the Korean Version of a Tool to Measure Uncivil Behavior in Clinical Nursing Education
Su Ok Jo, Jina Oh
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2016; 22(4): 537. CrossRef - Health Status Assessment Tool Development based on Dietary Patterns in Middle-Aged Women
Hye-Jin Lee, Kyung-Hea Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2016; 21(1): 37. CrossRef - Reliability and Validity of the Korean Version of the Perinatal Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Questionnaire
Yu Kyung Park, Hyeon Ok Ju, Hunjoo Na
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2016; 46(1): 29. CrossRef - Development and Validation of Nurse's Character Scale for Care in Clinical Settings
Jeong Hye Park
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2016; 22(2): 137. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability Test of the Korean Version of the Oncology Patients' Perception of the Quality of Nursing Care Scale
Jiyoung Kang, Heiyoung Kang, Nanyeon Kim, Mijung Lee, Youjine Kim, Juhyeon Kim, Sujeong Yeo, Yunye Seo, E, Eunyoung Suh
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2016; 28(2): 191. CrossRef - Development of the Damage Investigation Item to Debris Flow using the Delphi Method
Yo Seph Byun, Min Gi Kim, Kyung Han Park, Tae Keun Oh, Joo Hyun Seong
Journal of the Korean Society of Safety.2016; 31(2): 41. CrossRef - Predictors of Persistence and Adherence with Secondary Preventive Medication in Stroke Patients
Young Taek Kim, Ki Soo Park, Sang-Geun Bae
Journal of agricultural medicine and community health.2015; 40(1): 9. CrossRef - Medication Adherence and its Predictors in Community Elderly Patients with Hypertension
Sang Geun Bae, Hye Ji Jeon, Hyeon Su Yang, Bo Kyoung Kim, Ki Soo Park
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2015; 15(3): 121. CrossRef - Development and Clinical Validity of a Mild Vascular Cognitive Impairment Assessment Tool for Korean Stroke Patients
Hyun Soo Oh, Ji Sun Kim, Eun Bi Shim, Wha Sook Seo
Asian Nursing Research.2015; 9(3): 226. CrossRef - A Study on the Factor Analysis of the Encounter Data in the Maritime Traffic Environment
Kwang-Il Kim, Jung Sik Jeong, Gyei-Kark Park
Journal of Korean Institute of Intelligent Systems.2015; 25(3): 293. CrossRef - A Validation Study of the Modified Korean Version of Ethical Leadership at Work Questionnaire (K-ELW)
Jeong-Eon Kim, Eun-Jun Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2015; 45(2): 240. CrossRef - Factor Analysis of Working Memory Tasks Based on Information Processing Characteristics: Predictive Factors of Receptive Vocabulary and Quick Incidental Learning in Children with Typically Developing and Receptive Vocabulary Delay
Dongsun Yim, Shin-Young Kim, Yoonhee Yang
Communication Sciences & Disorders.2015; 20(2): 304. CrossRef - Effects of Business Environmental Factors on 4P Mix of Eco-friendly Textile in Textile Fashion Firms
Sangmoo Shin, Song H. Lee
Fashion business.2015; 19(2): 36. CrossRef - Tool Development for Cancer Patients' Sexuality Information Needs
Yeon Hee Kim, Hae Won Kim, Mikyung Kwon
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2015; 21(3): 207. CrossRef - Psychometric Properties of the Alzheimer's Disease Knowledge Scale-Korean Version
Eun Joo Kim, Ji-young Jung
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2015; 45(1): 107. CrossRef - Development of an Instrument to Measure the Quality of Care through Patients’ Eyes for Hospitalized Child
Haeryun Cho, Jina Oh, Dukyoo Jung
Child Health Nursing Research.2015; 21(2): 131. CrossRef - Escala de Estrés Percibido-10: Desempeño psicométrico en estudiantes de medicina de Bucaramanga, Colombia
Adalberto Campo-Arias, Heidi Celina Oviedo, Edwin Herazo
Revista de la Facultad de Medicina.2015; 62(3): 407. CrossRef - A Study on Selection Factors of Consulting Company for the Certification of Information Security Management System
Kyeong-Tae Park, Sehun Kim
Journal of the Korea Institute of Information Security and Cryptology.2014; 24(6): 1309. CrossRef - Construct Validity of the Life Transition Scale for Parents of Children with Autism
Ae Ran Lee, Sun Woo Hong, Se Jin Ju
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2014; 44(5): 563. CrossRef - Development and Validity of Workplace Bullying in Nursing-Type Inventory (WPBN-TI)
Younju Lee, Mihyoung Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2014; 44(2): 209. CrossRef - Comparison of Hospital Nurses' Recognition of the Team System and Effects on the Nursing Organizational Team System
Kwang-ok Park, Sung Hee Park, Mi Yu
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2014; 20(4): 414. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of a Korean version of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Questionnaire
Juhyae Oh, Ju Hee Kim
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2014; 20(4): 255. CrossRef - Development of Health Dieting Competency Scale for College Students
Jeongsoo Kim, Yumi Lee
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2014; 26(3): 300. CrossRef - Testing the Validity and Reliability of Korean Version of the Expectations Regarding Aging (ERA-12) Instrument among Middle-aged and Elderly Women
Min Hee Park, Yoorim Kweon
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2014; 28(3): 460. CrossRef - Validity of Instrument Development Research in Korean Nursing Research
Kyunghee Lee, Sujin Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2013; 43(6): 697. CrossRef
A Guide on the Use of Factor Analysis in the Assessment of Construct Validity
A Guide on the Use of Factor Analysis in the Assessment of Construct Validity
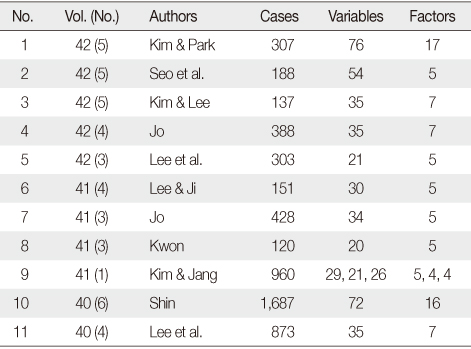
The Number of Cases, Variables, and Factors in the Papers of JKAN (2010-2012)
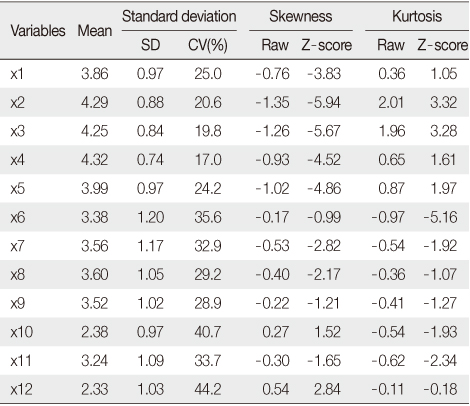
Descriptive Statistics from an Example
CV=(SD / Mean)×100(%).
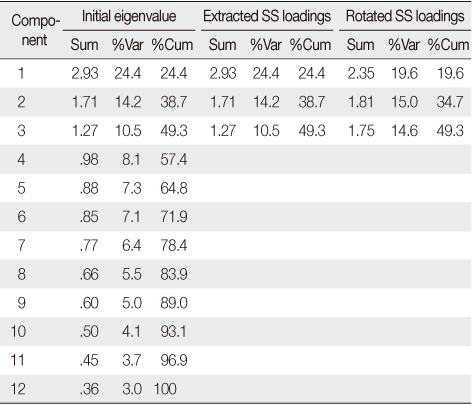
Eigenvalues and Explained Variance (SPSS output)
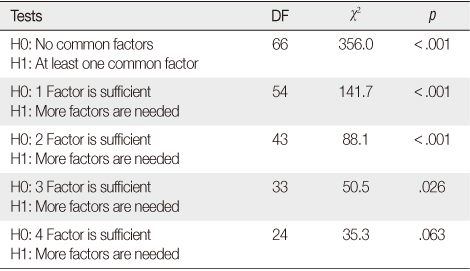
χ2 Test for the Number of Factors (SAS output)
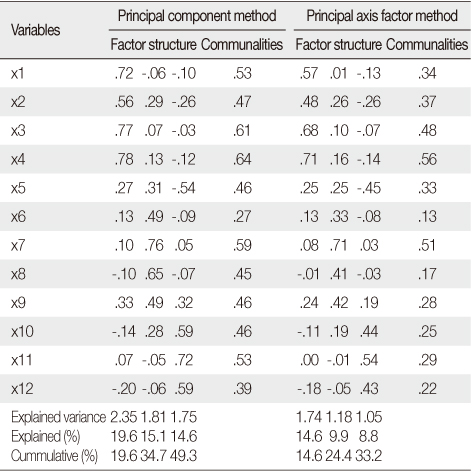
Factor Loadings, Communalities, and Explained Variances
Orthogonal varimax rotation method is used.
Table 1
The Number of Cases, Variables, and Factors in the Papers of JKAN (2010-2012)
Table 2
Descriptive Statistics from an Example
CV=(SD / Mean)×100(%).
Table 3
Eigenvalues and Explained Variance (SPSS output)
Table 4
χ2 Test for the Number of Factors (SAS output)
Table 5
Factor Loadings, Communalities, and Explained Variances
Orthogonal varimax rotation method is used.
 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION
 Cite
Cite

