Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Nurs > Volume 43(3); 2013 > Article
-
Original Article
- Effect of Kegel Exercise to Prevent Urinary and Fecal Incontinence in Antenatal and Postnatal Women: Systematic Review
- Seong-Hi Park, Chang-Bum Kang, Seon Young Jang, Bo Yeon Kim
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2013;43(3):420-430.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2013.43.3.420
Published online: June 28, 2013
1School of Nursing, Pai Chai University, Daejeon, Korea.
2Research Development Team, Korea Health Promotion Foundation, Seoul, Korea.
3Office of Quality Improvement, Severance Hospital, Yonsei University Health System, Seoul, Korea.
4Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service, Seoul, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Park, Seong-Hi. School of Nursing, Pai Chai University, 155-40, Baejae-ro, Seo-gu, Daejeon 302-735, Korea. Tel: +82-42-520-5104, Fax: +82-70-4362-6291, shpark@pcu.ac.kr
• Received: January 23, 2013 • Accepted: May 17, 2013
© 2013 Korean Society of Nursing Science
Abstract
-
Purpose
- The aim of this study was to review the literature to determine whether intensive pelvic floor muscle training during pregnancy and after delivery could prevent urinary and fecal incontinence.
-
Methods
- Randomized controlled trials (RCT) of low-risk obstetric populations who had done Kegel exercise during pregnancy and after delivery met the inclusion criteria. Articles published between 1966 and 2012 from periodicals indexed in Ovid Medline, Embase, Scopus, KoreaMed, NDSL and other databases were selected, using the following keywords: 'Kegel, pelvic floor exercise'. The Cochrane's Risk of Bias was applied to assess the internal validity of the RCT. Fourteen selected studies were analyzed by meta-analysis using RevMan 5.1.
-
Results
- Fourteen RCTs with high methodological quality, involving 6,454 women were included. They indicated that Kegel exercise significantly reduced the development of urinary and fecal incontinence from pregnancy to postpartum. Also, there was low clinical heterogeneity.
-
Conclusion
- There is some evidence that for antenatal and postnatal women, Kegel exercise can prevent urinary and fecal incontinence. Therefore, a priority task is to develop standardized Kegel exercise programs for Korean pregnant and postpartum women and make efficient use of these programs.
- 1. Bø K, Haakstad LA. Is pelvic floor muscle training effective when taught in a general fitness class in pregnancy? A randomised controlled trial. Physiotherapy. 2011;97(3):190–195. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.physio.2010.08.014ArticlePubMed
- 2. Boyle R, Hay-Smith EJ, Cody JD, Møkved S. Pelvic floor muscle training for prevention and treatment of urinary and faecal incontinence in antenatal and postnatal women. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012;10:CD007471. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD007471.pub2ArticlePubMed
- 3. Chiarelli P, Cockburn J. Promoting urinary continence in women after delivery: Randomised controlled trial. BMJ. 2002;324(7348):1241. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 4. Chiarelli P, Murphy B, Cockburn J. Promoting urinary continence in postpartum women: 12-month follow-up data from a randomised controlled trial. Int Urogynecol J Pelvic Floor Dysfunct. 2004;15(2):99–105. discussion 105. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00192-004-1119-yArticlePubMedPDF
- 5. Choi JB. Urinary incontinence in women. Korean J Fam Med. 2010;31(9):661–671. http://dx.doi.org/10.4082/kjfm.2010.31.9.661Article
- 6. Choi MH, Kim HK, Kim TE, Lee JY, Chung DY, Shin JI, et al. The effects of pregnancy and delivery on stress urinary incontinence. Korean J Obstet Gynecol. 1995;38(9):1572–1576.
- 7. Glazener CM, Herbison GP, MacArthur C, Grant A, Wilson PD. Randomised controlled trial of conservative management of postnatal urinary and faecal incontinence: Six year follow up. BMJ. 2005;330(7487):337. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bmj.38320.613461.82ArticlePubMedPMC
- 8. Glazener CM, Herbison GP, Wilson PD, MacArthur C, Lang GD, Gee H, et al. Conservative management of persistent postnatal urinary and faecal incontinence: Randomised controlled trial. BMJ. 2001;323(7313):593–596.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 9. Hay-Smith EJ, Bo Berghmans LC, Hendriks HJ, de Bie RA, van Waalwijk van Doorn ES. Pelvic floor muscle training for urinary incontinence in women. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001;(1):CD001407. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.cd001407ArticlePubMed
- 10. Higgins JPT, Green S. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions version 5.1.0. The Cochrane Collaboration. 2011;updated March 2011. Retrieved March 30, 2011. from www.cochrane-handbook.org.
- 11. Hong JY. The efficacy of pelvic floor muscle exercise in patients with genuine stress incontinence. Korean J Urol. 1997;38(6):639–643.
- 12. Hwang JS, Park TH, Kim DK, Kang MA, Kim SM, Bae CS, et al. The prevalence of female urinary and fecal incontinence. Korean J Obstet Gynecol. 1998;41(6):1552–1559.
- 13. Jeong NO. Effects of an incontinence prevention program on postpartum women. Korean J Women Health Nurs. 2009;15(3):177–185. http://dx.doi.org/10.4069/kjwhn.2009.15.3.177Article
- 14. Kim KS, Suh MJ. A study on prevalence and its relating factors of urinary incontinence in women. J Korean Acad Fundam Nurs. 1997;4(1):73–85.
- 15. Kim SY, Park JS. The effect of pelvic muscle exercise program on women with stress urinary incontinence in the degree and amount of urinary incontinence and maximum vaginal contraction pressure. J Korean Acad Adult Nurs. 2000;12(2):267–277.
- 16. Ko PC, Liang CC, Chang SD, Lee JT, Chao AS, Cheng PJ. A randomized controlled trial of antenatal pelvic floor exercises to prevent and treat urinary incontinence. Int Urogynecol J. 2011;22(1):17–22. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00192-010-1248-4ArticlePubMedPDF
- 17. Lee KS, Lee YS. Pharmacological therapy for urinary incontinence. J Korean Med Assoc. 2007;50(11):1025–1036. http://dx.doi.org/10.5124/jkma.2007.50.11.1025Article
- 18. Lemos A, de Souza AI, Ferreira AL, Figueiroa JN, Cabral-Filho JE. Do perineal exercises during pregnancy prevent the development of urinary incontinence? A systematic review. Int J Urol. 2008;15(10):875–880. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1442-2042.2008.02145.xArticlePubMed
- 19. Møkved S, Bø K. The effect of postpartum pelvic floor muscle exercise in the prevention and treatment of urinary incontinence. Int Urogynecol J Pelvic Floor Dysfunct. 1997;8(4):217–222.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 20. Møkved S, Bø K. Effect of postpartum pelvic floor muscle training in prevention and treatment of urinary incontinence: A one-year follow up. BJOG. 2000;107(8):1022–1028.ArticlePubMed
- 21. Møkved S, Bø K, Schei B, Salvesen KA. Pelvic floor muscle training during pregnancy to prevent urinary incontinence: A single-blind randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol. 2003;101(2):313–319.ArticlePubMed
- 22. Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. Ann Intern Med. 2009;151(4):264–269. W264.ArticlePubMed
- 23. Mon YJ, Lim HS, Jung JE, Cho HH, Kim MR, Lew YO, et al. The effects of the number of normal vaginal deliveries to the function of low urogenital system. Korean J Obstet Gynecol. 2007;50(4):638–644.
- 24. Reilly ET, Freeman RM, Waterfield MR, Waterfield AE, Steggles P, Pedlar F. Prevention of postpartum stress incontinence in primigravidae with increased bladder neck mobility: A randomised controlled trial of antenatal pelvic floor exercises. BJOG. 2002;109(1):68–76.ArticlePubMed
- 25. Sampselle CM. Behavioral intervention for urinary incontinence in women: Evidence for practice. J Midwifery Womens Health. 2000;45(2):94–103.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 26. Sleep J, Grant A. Pelvic floor exercises in postnatal care. Midwifery. 1987;3(4):158–164.ArticlePubMed
- 27. Taskin O, Wheeler JM, Yalcinoglu AI, Coksenim S. The effects of episiotomy and kegel exercises on postpartum pelvic relaxation: A prospective controlled study. J Gynecol Surg. 1996;12(2):123–127.Article
- 28. Thomason AD, Miller JM, Delancey JO. Urinary incontinence symptoms during and after pregnancy in continent and incontinent primiparas. Int Urogynecol J Pelvic Floor Dysfunct. 2007;18(2):147–151. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00192-006-0124-8ArticlePubMedPDF
- 29. Wall LL, Davidson TG. The role of muscular re-education by physical therapy in the treatment of genuine stress urinary incontinence. Obstet Gynecol Surv. 1992;47(5):322–331.ArticlePubMed
- 30. Wilson PD, Herbison GP. A randomized controlled trial of aelvic floor muscle exercise sto treat, postnatal urinary incontinence. Int Urogynecol J Pelvic Floor Dysfunct. 1998;9(5):257–264.PubMed
- 31. Woldringh C, van den Wijngaart M, Albers-Heitner P, Lycklama à Nijeholt AA, Lagro-Janssen T. Pelvic floor muscle training is not effective in women with UI in pregnancy: A randomised controlled trial. Int Urogynecol J Pelvic Floor Dysfunct. 2007;18(4):383–390. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00192-006-0175-xArticlePubMedPDF
- 32. Yoo EH. Pelvic floor muscle rehabilitation. Korean J Obstet Gynecol. 2006;49(9):1838–1843.
- 33. Yoo YJ, Lee EJ. A study on the nursing needs and satosfactions of early postpartum women. J Korean Acad Womens Health Nurs. 1999;5(3):389–409.ArticlePDF
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- Ultrasound Quantitative Assessment of the Effects of Yoga on Early Postpartum Pelvic Organ Position Recovery
Qunfeng Li, Yanhong Liu, Yunli Liu, Qiongzhu Liu, Liping Jiang, Xinling Zhang
International Urogynecology Journal.2025; 36(1): 221. CrossRef - Reliability of Digital Palpation to Perineometeric Scoring for Assessment of Pelvic Floor Muscle Strength: A Comparative Study
Alisha Rai, Sanjeev Kumar Jain, Nidhi Sharma, Astha Lalwani, Sonika Sharma
Gynecology and Minimally Invasive Therapy.2025; 14(3): 223. CrossRef - The Effect of Kegel Exercises and Pelvic Floor Physiotherapy on the
Improvements of Stress Urinary Incontinence and Urge Incontinence in
Women with Normal Vaginal Delivery
Radnia Nahid, Bakhtiari Mahsa, Neda Alimohammadi, Moghadami Samar
Current Womens Health Reviews.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of self-reported ability to perform Kegel’s exercise pre- and post-coital penetration in postpartum women
Chidiebele Petronilla Ojukwu, Ginikachukwu Theresa Nsoke, Stephen Ede, Anne Uruchi Ezeigwe, Sylvester Caesar Chukwu, Emelie Morris Anekwu
Libyan Journal of Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Knowledge, attitudes, and practice of pelvic floor dysfunction and pelvic floor ultrasound among women of childbearing age in Sichuan, China
Xiaoli Wu, Xiaohong Yi, Xiu Zheng, Zeling Chen, Junxi Liu, Xiong Dai
Frontiers in Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Kegel Exercises on Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms in Young Gymnasts: A Prospective Cohort Study
Celia Rodríguez-Longobardo, Amelia Guadalupe-Grau, Miguel Ángel Gómez-Ruano, Olga López-Torres
Urogynecology.2023; 29(8): 670. CrossRef - Improving the Technique of Pelvic Floor Muscle Contraction in Active Nulliparous Women Attending a Structured High–Low Impact Aerobics Program—A Randomized Control Trial
Magdalena Piernicka, Monika Błudnicka, Damian Bojar, Jakub Kortas, Anna Szumilewicz
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(10): 5911. CrossRef - Comparison of postpartum incontinence outcomes after vacuum-assisted and forceps-assisted deliveries in a tertiary maternity unit
Li Shan Sng, Wan Hui Yip, Stella Yan Chai Hong, Stephanie Man Chung Fook-Chong, Wei Keat Andy Tan, Devendra Kanagalingam, Jason Shau Khng Lim
International Urogynecology Journal.2022; 33(6): 1529. CrossRef - Knowledge, Attitude, and Practice of Pregnant Women in Jazan, Saudi Arabia Concerning Pelvic Floor Muscle Exercises
Sarra L Derrar, Fatimah H Dallak, Azhar Alfaifi, Rawan M Alessa, Khawlah A Abbas, Atyaf J Zurayyir, Ahmed A Altraifi, Ibrahim Gosadi
Cureus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effectiveness of Structured teaching programme on knowledge regarding Pelvic floor muscle exercises in prevention of Urinary incontinence among premenopausal women admitted in selected hospital Bangalore
Christina Jose, Christina Rachel C., Della Mathew, Deva Prasanna, Dolma Lhakyi, Dona Elizabeth Mathew, Ethel Deenah Hazel, Grace Ninan, Indumathi Anbalagan, Jismi Thomas, Josmy Jose
Asian Journal of Nursing Education and Research.2021; : 307. CrossRef - What Is Fecal Incontinence That Urologist Need to Know?
HongWook Kim, Jisung Shim, Yumi Seo, Changho Lee, Youngseop Chang
International Neurourology Journal.2021; 25(1): 23. CrossRef - Effects of yoga on the intervention of levator ani hiatus in postpartum women: a prospective study
Qunfeng Li, Xinling Zhang
Journal of Physical Therapy Science.2021; 33(11): 862. CrossRef - High-impact aerobics programme supplemented by pelvic floor muscle training does not impair the function of pelvic floor muscles in active nulliparous women
Magdalena Piernicka, Monika Błudnicka, Jakub Kortas, Barbara Duda-Biernacka, Anna Szumilewicz
Medicine.2021; 100(33): e26989. CrossRef - Development of an exercise attitude scale in Turkish for pregnant women: validity and reliability
Seyda Toprak Celenay, Esra Calik Var, Derya Ozer Kaya
Women & Health.2021; 61(9): 854. CrossRef - Predictors of pelvic muscle exercise on the self‐efficacy of women giving birth
Gisoo Shin, Hye Jin Kim, Miok Kim
International Journal of Urological Nursing.2020; 14(2): 67. CrossRef - Vaginal hyperlaxity syndrome: a new concept and challenge
Santiago Palacios
Gynecological Endocrinology.2018; 34(5): 360. CrossRef - Effect of Pila-dance to Ease Urinary Incontinence of Middle-aged Women
Hye-Jeon Hong
The Korean Journal of Physical Education.2018; 57(2): 431. CrossRef - Faecal incontinence: Current knowledges and perspectives
Alban Benezech
World Journal of Gastrointestinal Pathophysiology.2016; 7(1): 59. CrossRef - Effects of Prenatal Perineal Massage and Kegel Exercises on the Integrity of Postnatal Perine
Sevgul Dönmez, Oya Kavlak
Health.2015; 07(04): 495. CrossRef - A Study on Fecal Incontinence and Depression of Rural Women
Chunmi Kim, Hung Sa Lee, Eun Man Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2014; 25(3): 198. CrossRef
Effect of Kegel Exercise to Prevent Urinary and Fecal Incontinence in Antenatal and Postnatal Women: Systematic Review
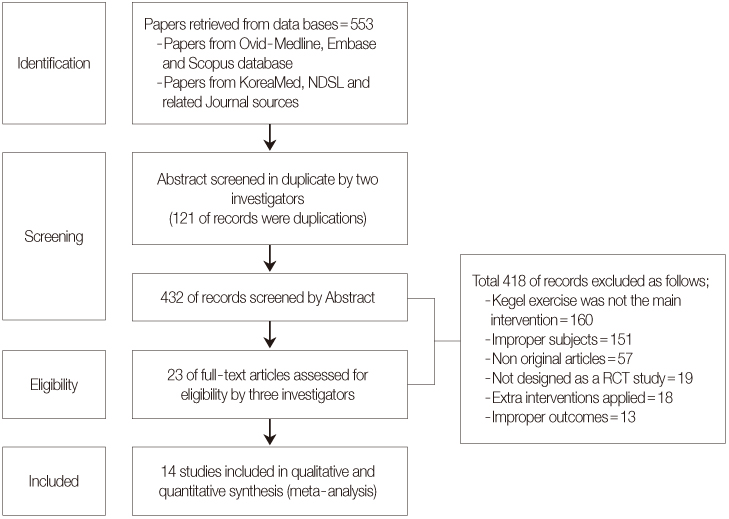
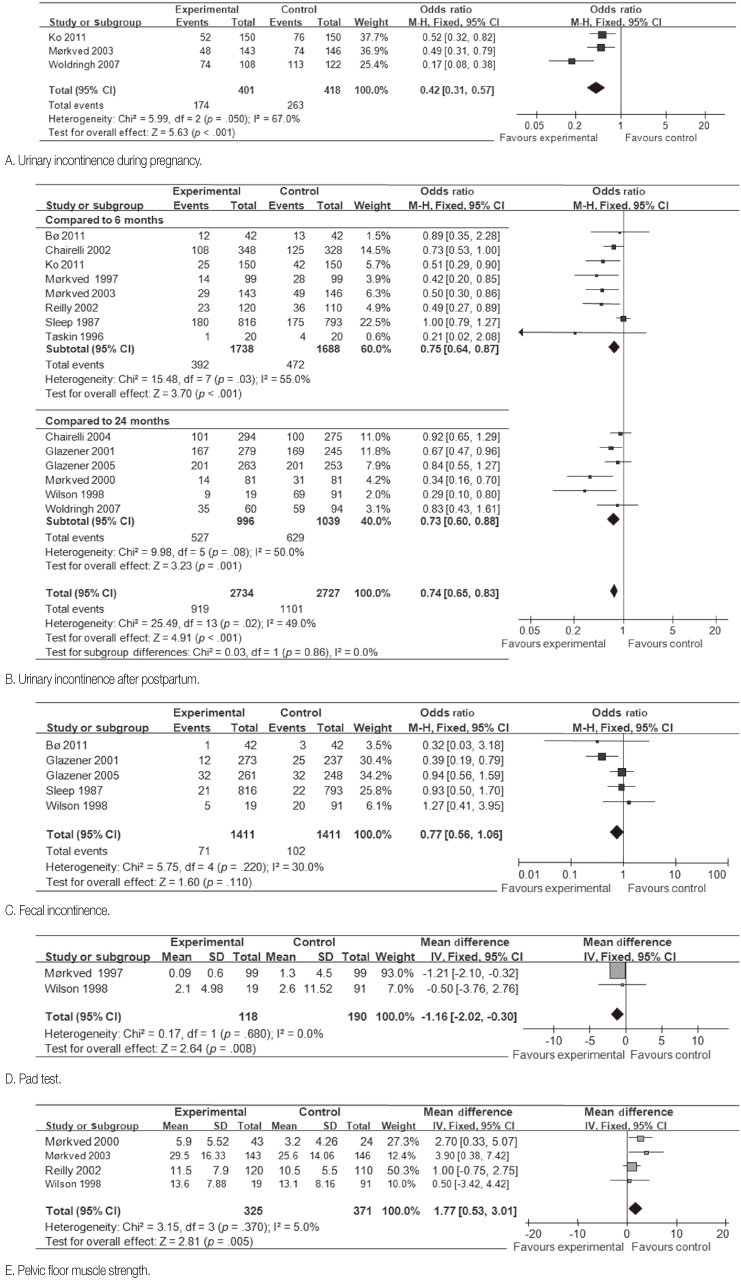
Figure 1
Flow diagram of article selection.
Figure 2
Comparison outcomes of Kegel exercise versus control.
Figure 1
Figure 2
Effect of Kegel Exercise to Prevent Urinary and Fecal Incontinence in Antenatal and Postnatal Women: Systematic Review
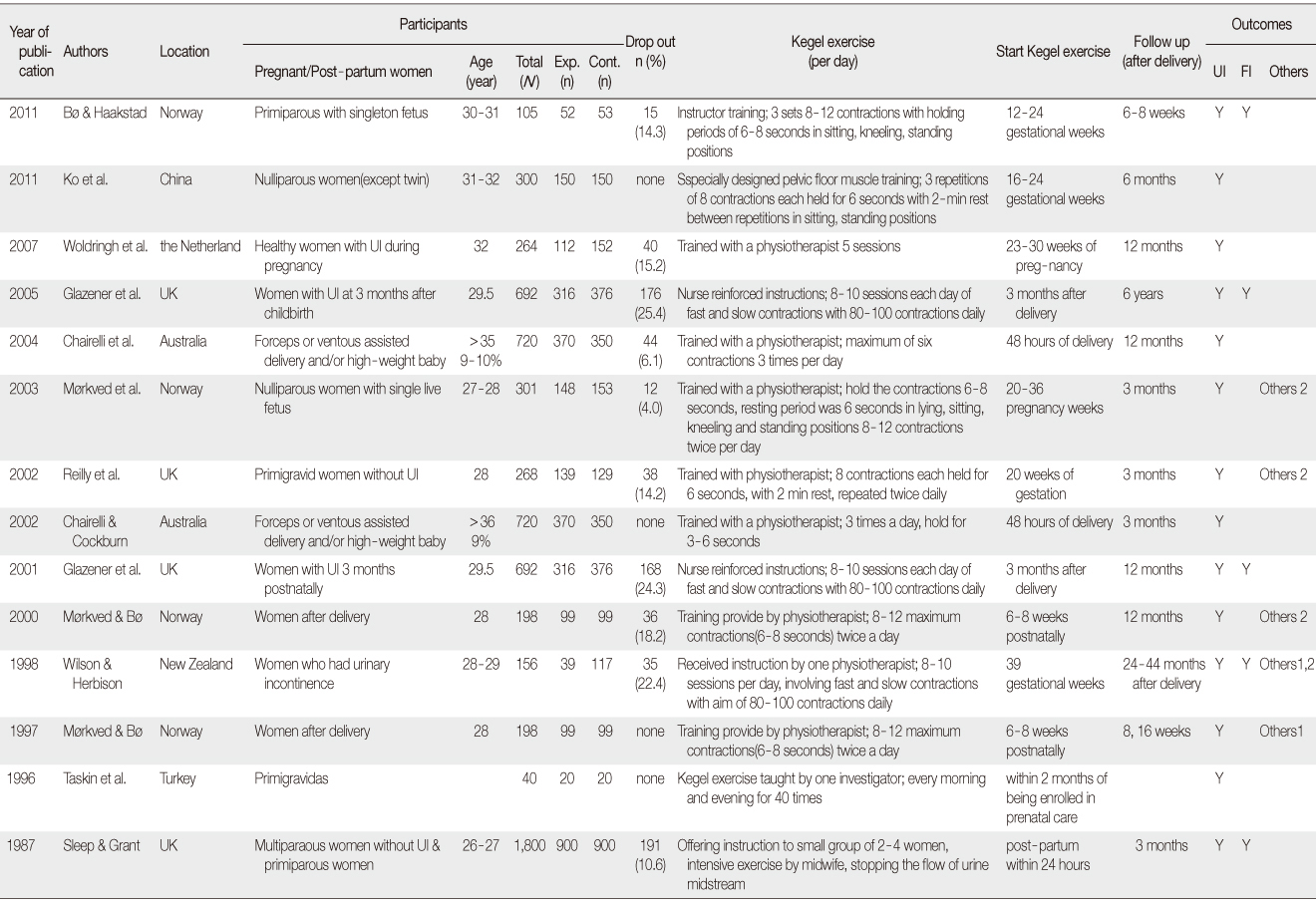
Characteristics of Selected Studies
Exp.=Experimental group; Cont.=Control group; UI=Urinary incontinence; FI=Fecal incontince; Y=Yes; Others 1=Pad test; Others 2=Pelvic floor muscle strength.
Table 1
Characteristics of Selected Studies
Exp.=Experimental group; Cont.=Control group; UI=Urinary incontinence; FI=Fecal incontince; Y=Yes; Others 1=Pad test; Others 2=Pelvic floor muscle strength.
 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION
 Cite
Cite

