Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Nurs > Volume 43(2); 2013 > Article
-
Original Article
- Evaluation of a Medication Self-management Education Program for Elders with Hypertension Living in the Community
- Jong Kyung Lee
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2013;43(2):267-275.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2013.43.2.267
Published online: April 30, 2013
Department of Nursing, College of Medicine, Dankook University, Cheonan, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Lee, Jong Kyung. Department of Nursing, College of Medicine, Dankook University, San 29 Anseo-dong, Cheonan, Chungnam, Korea. Tel: +82-41-550-3883, Fax: +82-41-550-3888, kyunglee@dankook.ac.kr
© 2013 Korean Society of Nursing Science
Abstract
-
Purpose
- The purpose of this study was to examine the effect of a medication self-management education program on medication awareness, communication with health care provider, medication misuse behavior, and blood pressure in elders with hypertension.
-
Methods
- The research design for this study was a non-equivalent control group quasi-experimental design. Participants were 23 elders for the control group, and 26 elders for the experimental group. The experimental group participated in the medication self-management education program which included the following, verbal education, 1:1 consultation, practice in medication self-management, and discussion over 5 sessions. Data were analyzed using the SPSS 18.0 program.
-
Results
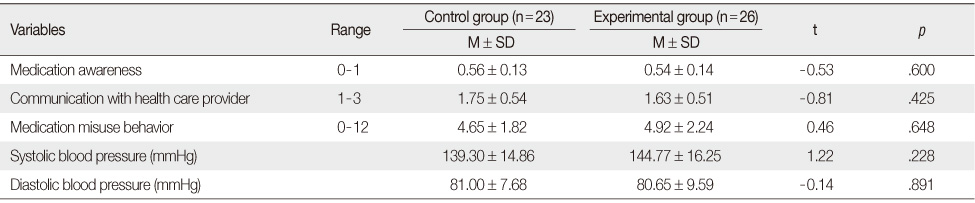
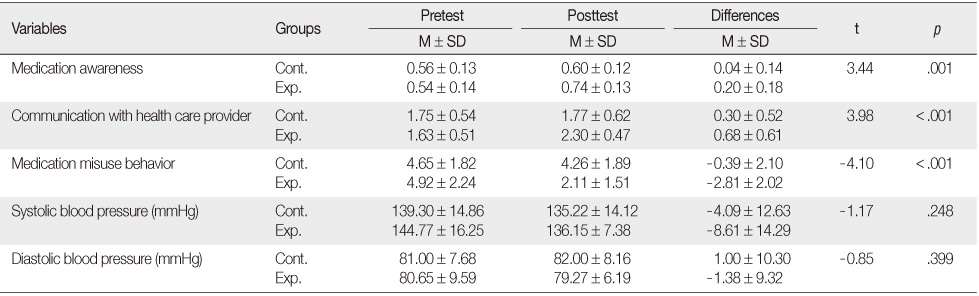
- There were statistically significant differences between the experimental and control group for medication awareness, medication misuse behavior, and communication with health care providers. However, no significant difference was found between the two groups for blood pressure.
-
Conclusion
- The results indicate that the education program is effective in improving medication awareness and communication with health care providers and in decreasing medication misuse behavior. Therefore, it is recommended that this education program be used as an effective intervention for improving medication self-management for elders with hypertension.
- 1. Aguiar PM, Balisa-Rocha BJ, Brito GC, Lyra DP Jr. Pharmaceutical care program for elderly patients with uncontrolled hypertension. J Am Pharm Assoc (2003). 2012;52(4):515–518. http://dx.doi.org/10.1331/JAPhA.2012.11015.ArticlePubMed
- 2. Aguwa CN, Ukwe CV, Ekwunife OI. Effect of pharmaceutical care programme on blood pressure and quality of life in a Nigerian pharmacy. Pharm World Sci. 2008;30(1):107–110. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11096-007-9151-x.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 3. Bergman-Evans B. AIDES to improving medication adherence in older adults. Geriatr Nurs. 2006a;27(3):174–182. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.gerinurse.2006.03.003.ArticlePubMed
- 4. Bergman-Evans B. Evidence-based guideline. Improving medication management for older adult clients. J Gerontol Nurs. 2006b;32(7):6–14.Article
- 5. Carroll CR. Drugs in modern society. 2000;5th ed. Boston, MA, McGraw-Hill Companies.
- 6. Case Management Society of America. Korea Research Group of Case Management. CMAG : Case management adherence guidelines 2.0. 2007;Seoul, Hyunmoon. (Original work published 2006).
- 7. Cohen J. Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. 1988;2nd ed. Hillsdale, NJ, Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
- 8. DiMatteo MR, Giordani PJ, Lepper HS, Croghan TW. Patient adherence and medical treatment outcomes: A meta-analysis. Med Care. 2002;40(9):794–811. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/01.mlr.0000024612.61915.2d.PubMed
- 9. Hacihasanoğlu R, Gözüm S. The effect of patient education and home monitoring on medication compliance, hypertension management, healthy lifestyle behaviours and BMI in a primary health care setting. J Clin Nurs. 2011;20(5-6):692–705. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2702.2010.03534.x.ArticlePubMed
- 10. Han JH. The influence of cognitive function, their family support and medication knowledge upon medication adherence in old people. 2007;Seoul, Ewha Womans University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 11. Han JH. Effects of medication education for elderly with low health literacy on medication knowledge and medication misuse & abuse behavior. 2011;Daegu, Keimyung University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 12. Hogan DB, Kwan M. Patient sheet: Tips for avoiding problems with polypharmacy. CMAJ. 2006;175(8):876. http://dx.doi.org/10.1503/cmaj.060888.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 13. Hsu YH, Mao CL, Wey M. Antihypertensive medication adherence among elderly Chinese Americans. J Transcult Nurs. 2010;21(4):297–305. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/1043659609360707.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 14. Kim KH, Park SH, Lee HK. A study on the factors influencing to the medication compliance of the hypertensive patient in one public health center in Seoul. Korean J Health Promot Dis Prev. 2005;5(4):267–274.
- 15. Lee DY. Development and evaluation of preventive education program for medication misuse of the community dwelling elderly. 2002;Seoul, Yonsei University. Unpublished doctoral dissertation.
- 16. Lee JH, Park M. The effects of an education program for safe drug use in the rural elderly. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2007;37(3):295–304.ArticlePDF
- 17. Lee JK. Factors associated with drug misuse behaviors among polypharmacy elderly. Korean J Adult Nurs. 2011;23(6):554–563.
- 18. Ministry of Health & Welfare. Korea national health and nutrition examination survey (KNHANES V-1). 2010;Retrieved April 5, 2012. from http://knhanes.cdc.go.kr/knhanes/index.do.
- 19. Murray MD, Morrow DG, Weiner M, Clark DO, Tu W, Deer MM, et al. A conceptual framework to study medication adherence in older adults. Am J Geriatr Pharmacother. 2004;2(1):36–43.ArticlePubMed
- 20. Opdycke RA, Ascione FJ, Shimp LA, Rosen RI. A systematic approach to educating elderly patients about their medications. Patient Educ Couns. 1992;19(1):43–60.ArticlePubMed
- 21. Park CH. Resistant hypertension: Causes and management. Korean J Med. 2009;76(4):398–401.
- 22. Shen Q, Karr M, Ko A, Chan DK, Khan R, Duvall D. Evaluation of a medication education program for elderly hospital in-patients. Geriatr Nurs. 2006;27(3):184–192. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.gerinurse.2006.03.015.ArticlePubMed
- 23. Shin KR, Kim JS, Kim JY, Yi HR. Effects of a drug misuse and abuse prevention program on knowledge, attitude, and preventive behaviors related to drug misuse and abuse, and depression in low-income elderly women. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2005;35(5):763–773.ArticlePDF
- 24. Suh SR, Lee EH. A path model predicting medication adherence and self-care of low-income older adults with hypertension. Korean J Adult Nurs. 2011;23(4):374–385.
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Development and effectiveness of an integrated medication management program centered on senior welfare centers for older adults with hypertension: A cross-sectional study
Heuijeong Moon, Dukyoo Jung
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2023; 25(3): 297. CrossRef - A Knowledge, Attitude, and Practice Survey on Medication Safety in Korean Older Adults: An Analysis of an Ageing Society
Mijin Lee, Kyungim Kim, Kiyon Rhew, Kyung-Hee Choi
Healthcare.2021; 9(10): 1365. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of an Antiviral Agent Medication Adherence Education Program for Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C
Hoo Jeung Cho, Euna Park
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(18): 6518. CrossRef - Evaluation of a group-based hypertension self-management education programme among hypertensive community dwellers
Hanisah Mohd Yatim, Yuet Yen Wong, Seng Hock Lim, Mohamad Azmi Hassali, Yet Hoi Hong, Ahmad Fauzi Dali, Chin Fen Neoh
European Journal of Integrative Medicine.2018; 24: 79. CrossRef - Testing a Middle-Range Theory of Self-Care of Chronic Illness: A Validation for Korean Adult Patients with Severe Hypertension
Eunha Gil, Heeyoung Oh
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2018; 48(5): 521. CrossRef - Medication Status and the Effects of a Medication Management Education Program for the Elderly in a Community
Young-Im Park, Kang-Yi Lee, Dong-Oak Kim, Dong Choon Uhm, Ji-Hyun Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2014; 25(3): 170. CrossRef - The Effects of Long term Osteoporosis Management Education on BMD Level and Medication Compliance in Postmenopausal Women
Dong-Hee Kim, Young-Sil Bae, Sang-Hwa Lee
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2014; 28(1): 102. CrossRef - Effects of an Integrated Case Management Program on Medication Adherence, Pain, Physical Function and Depression among Korean Medical Aid Beneficiaries with Osteoarthritis
Yang Heui Ahn
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2014; 28(1): 32. CrossRef - Effects of an Extreme Heat Adaptation Program in Hypertensive Patients
Seong Hee Jeong, Nam Soon Kim, Sumi Chae, Eun Ju Lee
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2014; 16(3): 164. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Medication Adherence in Patients with Hypertension: Based on the 2008 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Eunhee Cho, Chung Yul Lee, Insook Kim, Taewha Lee, Gwang Suk Kim, Hyeonkyeong Lee, Jisook Ko, Kyongeun Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2013; 24(4): 419. CrossRef - Factors Affecting the Healing of Pressure Ulcers in a Korean Acute Care Hospital
Young Hee Sung, Kyung Hee Park
Journal of Wound, Ostomy & Continence Nursing.2011; 38(1): 38. CrossRef
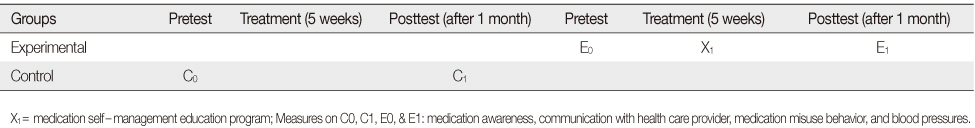
Figure 1
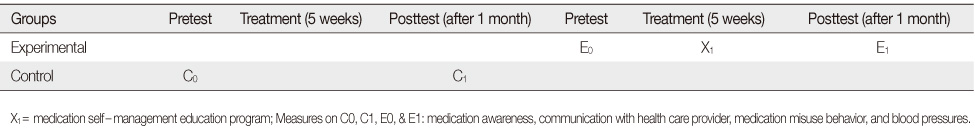
Homogeneity Test for General Characteristics between the Two Groups
*Fisher's exact test.
Cont.=Control group; Exp.=Experimental group; OTC=over-the-counter drug; CCB=calcium channel blocker; ARB=angiotensin receptor blocker; ACEI=angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor; BB=beta blocker.
Homogeneity Test for Dependent Variables between the Two Groups (N=49)
Mean Differences in Dependent Variables between the Two Groups (N=49)
Cont.=Control group (n=23); Exp=Experimental group (n=26).
*Fisher's exact test. Cont.=Control group; Exp.=Experimental group; OTC=over-the-counter drug; CCB=calcium channel blocker; ARB=angiotensin receptor blocker; ACEI=angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor; BB=beta blocker.
Cont.=Control group (n=23); Exp=Experimental group (n=26).
 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION
 Cite
Cite

