Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Nurs > Volume 42(5); 2012 > Article
-
Original Article
- Optimal Time Interval for Position Change for ICU Patients using Foam Mattress Against Pressure Ulcer Risk
- Hyean Jeong Kim, In Sook Jeong
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2012;42(5):730-737.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2012.42.5.730
Published online: October 31, 2012
1Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan, Republic of Korea.
2College of Nursing, Pusan National University, Yangsan, Republic of Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Jeong, Ihn Sook. College of Nursing, Pusan National University, Beomoe-ri, Mulgeum-eup, Yangsan 626-870, Korea. Tel: +82-51-510-8342, Fax: +82-51-510-8308, jeongis@pusan.ac.kr
© 2012 Korean Society of Nursing Science
- 1,562 Views
- 24 Download
- 11 Crossref
Abstract
-
Purpose
- This study was done to identify the time interval to pressure ulcer and to determine the optimal time interval for position change depending on pressure ulcer risk in patients using foam mattress in intensive care units.
-
Methods
- The Braden scale score, occurrence of pressure ulcers and position change intervals were assessed with 56 patients admitted to an intensive care unit from April to November, 2011. The time to pressure ulcer occurrence by Braden scale risk group was analyzed with Kaplan-Meier survival analysis and log rank test. Then, the optimal time interval for position change was calculated with ROC curve.
-
Results
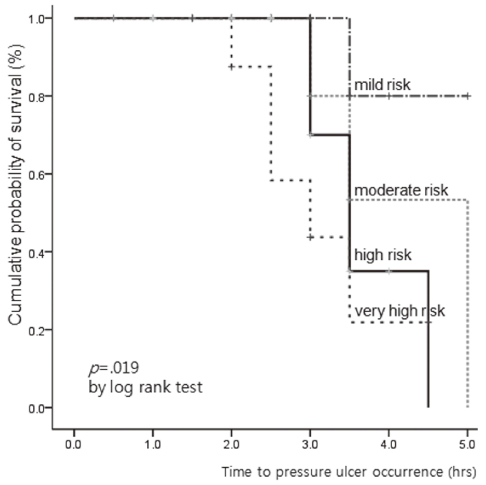
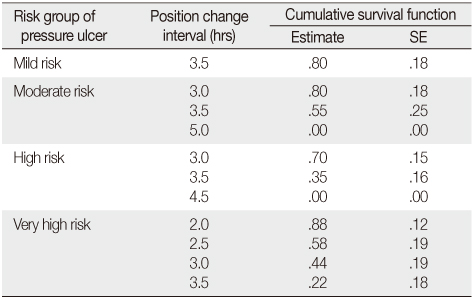
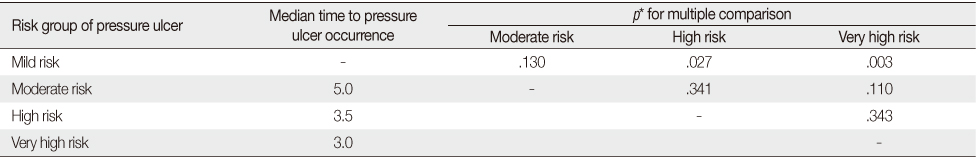
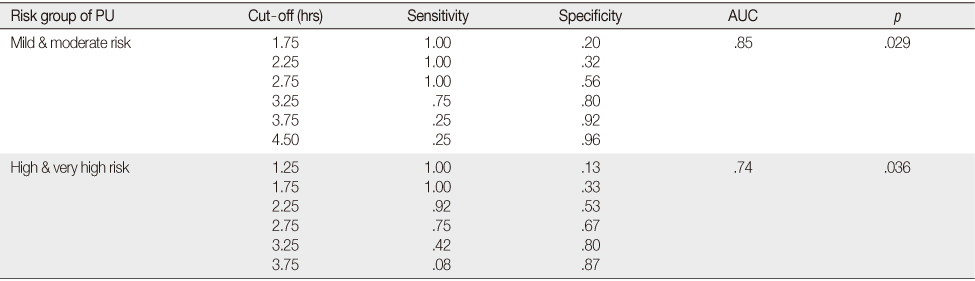
- The median time to pressure ulcer occurrence was 5 hours at mild or moderate risk, 3.5 hours at high risk and 3 hours at very high risk on the Braden scale. The optimal time interval for position change was 3 hours at mild and moderate risk, 2 hours at high and very high risk of Braden scale.
-
Conclusion
- When foam mattresses are used a slight extension of the time interval for position change can be considered for the patients with mild or moderate pressure ulcer risk but not for patients with high or very high pressure ulcer risk by Braden scale.
This article is a condensed form of the first author's master's thesis from Pusan National University.
- 1. Agency for Health Care Policy & Research. Clinical practice guideline. 1992;Retrieved November 17, 2011. from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK63910/#A4552.
- 2. Ayello EA, Braden B. How and why to do pressure ulcer risk assessment. Adv Skin Wound Care. 2002;15:125–131.ArticlePubMed
- 3. Bennett G, Dealey C, Posnett J. The cost of pressure ulcers in the UK. Age Ageing. 2004;33:230–235. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/ageing/afh086.ArticlePubMed
- 4. Bergstrom N, Braden BJ. Predictive validity of the Braden scale among black and white subjects. Nurs Res. 2002;51:398–403. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00006199-200211000-00008.ArticlePubMed
- 5. Bergstrom N, Braden B, Kemp M, Champagne M, Ruby E. Predicting pressure ulcer risk: A multisite study of the predictive validity of the Braden scale. Nurs Res. 1998;47:261–269.PubMed
- 6. Bergstrom N, Demuth PJ, Braden BJ. A clinical trial of the Braden scale for predicting pressure sore risk. Nurs Clin North Am. 1987;22:417–428.ArticlePubMed
- 7. Braden BJ, Maklebust J. Preventing pressure ulcers with the Braden scale: An update on this easy-to-use tool that assesses a patient's risk. Am J Nurs. 2005;105:70–72.
- 8. Defloor T. The effect of position and mattress on interface pressure. Appl Nurs Res. 2000;13:2–11. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0897-1897(00)80013-0.ArticlePubMed
- 9. Defloor T, De Bacquer D, Grypdonck MH. The effect of various combinations of turning and pressure reducing devices on the incidence of pressure ulcers. Int J Nurs Stud. 2005;42:37–46. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2004.05.013.ArticlePubMed
- 10. European Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel & National Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel. Pressure ulcer prevention: Quick reference guide. 2009;Retrieved April 7. 2011. from http://www.npuap.org/Final_Quick_Prevention_for_web_2010.pdf.
- 11. Gorecki C, Closs SJ, Nixon J, Briggs M. Patient-reported pressure ulcer pain: A mixed-methods systematic review. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2011;42:443–459. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2010.11.016.ArticlePubMed
- 12. Hagisawa S, Ferguson-Pell M. Evidence supporting the use of two-hourly turning for pressure ulcer prevention. J Tissue Viability. 2008;17:76–81. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jtv.2007.10.001.ArticlePubMed
- 13. Halfens RJ, van Achterberg T, Bal RM. Validity and reliability of the braden scale and the influence of other risk factors: A multi-centre prospective study. Int J Nurs Stud. 2000;37:313–319. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0020-7489(00)00010-9.ArticlePubMed
- 14. Jun Seongsook RN, Jeong Ihnsook RN, Lee Younghee RN. Validity of pressure ulcer risk assessment scales: Cubbin and Jackson, Braden, and Douglas scale. Int J Nurs Stud. 2004;41:199–204. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0020-7489(03)00135-4.ArticlePubMed
- 15. Keller PB, Wille J, van Ramshorst B, van der Werken C. Pressure ulcers in intensive care patients: A review of risks and prevention. Intensive Care Med. 2002;28:1379–1388. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00134-002-1487-z.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 16. Kottner J, Dassen T. Pressure ulcer risk assessment in critical care: Interrater reliability and validity studies of the Braden and Waterlow scales and subjective ratings in two intensive care units. Int J Nurs Stud. 2010;47:671–677. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2009.11.005.ArticlePubMed
- 17. McInnes E, Jammali-Blasi A, Bell-Syer SE, Dumville JC, Cullum N. Support surfaces for pressure ulcer prevention. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011;(4):CD001735. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD001735.pub4.
- 18. Ministry of Health and Welfare, Korea Institute for Healthcare Accreditation. 2011 Healthcare accreditation survey guidebook (ver 1.2)-for large hospitals with 300 and over beds. 2011;Retrieved May 24, 2012. from http://www.koiha.or.kr/home/data/data/doView.act.
- 19. National Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel. Pressure ulcer stage. 2007;Retrieved May 24, 2012. from http://www.npuap.org/pr2.htm.
- 20. National Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel, European Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel (NPUAP & EPUAP). Pressure ulcer treatment recommendations. Prevention and treatment of pressure ulcers: Clinical practice guideline. 2009;Retrieved May 24, 2012. from http://www.guideline.gov/content.aspx?id=25139&search=pressure+ulcer.
- 21. Pancorbo-Hidalgo PL, Garcia-Fernandez FP, Lopez-Medina IM, Alvarez-Nieto C. Risk assessment scales for pressure ulcerprevention: A systematic review. J Adv Nurs. 2006;54:94–110. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2648.2006.03794.x.ArticlePubMed
- 22. Ratliff CR. WOCN's evidence-based pressure ulcer guideline. Adv Skin Wound Care. 2005;18:204–208.ArticlePubMed
- 23. Reddy M, Gill SS, Rochon PA. Preventing pressure ulcers: A systematic review. JAMA. 2006;296:974–984. http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/jama.296.8.974.ArticlePubMed
- 24. Russell LJ, Reynolds TM, Park C, Rithalia S, Gonsalkorale M, Birch J, et al. Randomized clinical trial comparing 2 support surfaces: Results of the prevention of pressure ulcers study. Adv Skin Wound Care. 2003;16:317–327.PubMed
- 25. Theisen S, Drabik A, Stock S. Pressure ulcers in older hospitalised patients and its impact on length of stay: A retrospective observational study. J Clin Nurs. 2012;21(3-4):380–387. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2702.2011.03915.x.ArticlePubMed
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- The effect of support surface on the prevention of pressure injury in acute care settings: A multi-center prospective observational study
Mi-Ock Shim, Chul-Gyu Kim, Ja Kyung Min, So Yeon Kwak, Hyunhee Ghil, Seungmi Park
Journal of Tissue Viability.2024; 33(4): 652. CrossRef - Predicting the cut‐off point for interface pressure in pressure injury according to the standard hospital mattress and polyurethane foam mattress as support surfaces
Mi Yu, Kyung Hee Park, Jiseon Shin, Ji Hyun Lee
International Wound Journal.2022; 19(6): 1509. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Devices for Prevention and Treatment of Pressure Ulcers: A scoping Review
Soo Youn Jung, Mina Park, Kyoung Ja Moon
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2022; 34(2): 123. CrossRef - Comparing Pressure Injury Incidence Based on Repositioning Intervals and Support Surfaces in Acute Care Settings: A Quasi-Experimental Pragmatic Study
Jeong Sil Choi, Seon Young Hyun, Sun Ju Chang
Advances in Skin & Wound Care.2021; 34(8): 1. CrossRef - Perioperative factors and pressure ulcer development in postoperative ICU patients: a retrospective review
Neha Kumta, Fiona Coyer, Michael David
Journal of Wound Care.2018; 27(8): 475. CrossRef - Improving the quality of nurse‐influenced patient care in the intensive care unit
Lynsey J. Sutton, Rebecca J. Jarden
Nursing in Critical Care.2017; 22(6): 339. CrossRef - The Efficacy of a Viscoelastic Foam Overlay on Prevention of Pressure Injury in Acutely Ill Patients
Kyung Hee Park, Joohee Park
Journal of Wound, Ostomy & Continence Nursing.2017; 44(5): 440. CrossRef - Automated Pressure Injury Risk Assessment System Incorporated Into an Electronic Health Record System
Yinji Jin, Taixian Jin, Sun-Mi Lee
Nursing Research.2017; 66(6): 462. CrossRef - Prophylactic Effect of Transparent Film Dressing on Sacrum and Coccyx in SICU Patients*
Heejeong Kim, Sun-Mi Lee, Hee young Choi, Yu Kyung Min, Yoo Jin Jung
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2016; 23(3): 256. CrossRef - A Phenomenological Study on Illness Experience of Patients with Pressure Ulcer
Misoo Yoo, Myungsun Yi
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2015; 27(5): 515. CrossRef - Reusability of EMR Data for Applying Cubbin and Jackson Pressure Ulcer Risk Assessment Scale in Critical Care Patients
Eunkyung Kim, Mona Choi, JuHee Lee, Young Ah Kim
Healthcare Informatics Research.2013; 19(4): 261. CrossRef
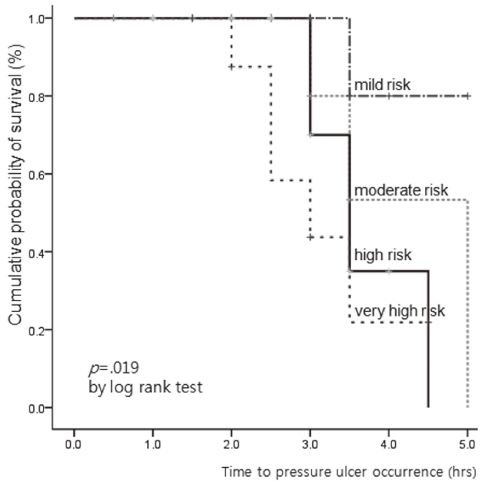
Figure 1
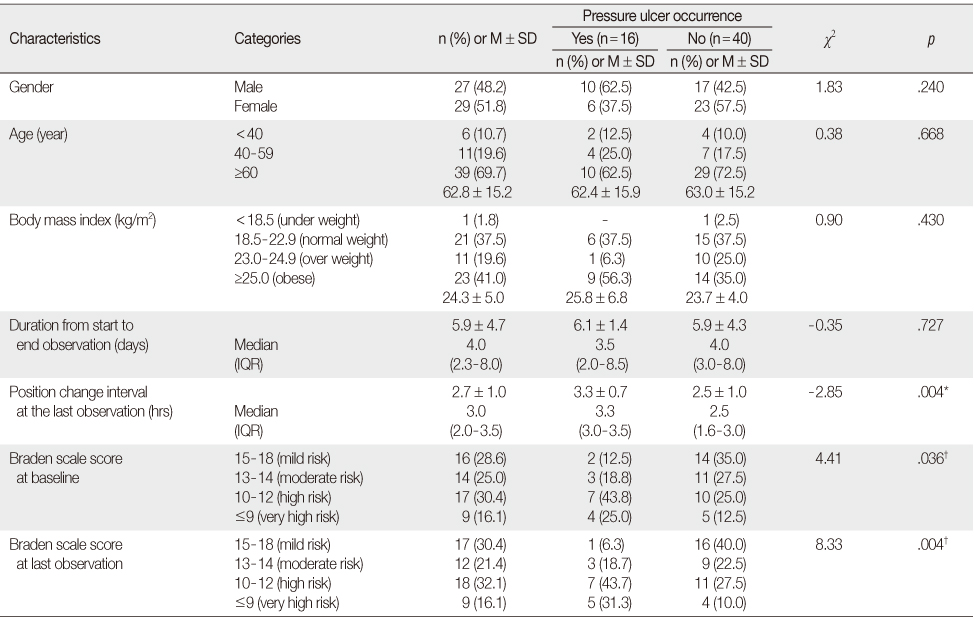
Characteristics of Study Participants (N=56)
*Mann Whitney U test; †χ2 for trend test; IQR=Interquartile range.
Cumulative Survival Function by Pressure Ulcer Risk Group
SE=Standard error.
Median Time to Pressure Ulcer Occurrence by Pressure Ulcer Risk Group
*log-rank test.
Sensitivity and Specificity at a Certain Cut-off Points by Pressure Ulcer Risk Group
PU=Pressure ulcer; AUC=Area under the ROC curve.
*Mann Whitney U test; †χ2 for trend test; IQR=Interquartile range.
SE=Standard error.
*log-rank test.
PU=Pressure ulcer; AUC=Area under the ROC curve.
 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION
 Cite
Cite

