Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Nurs > Volume 42(4); 2012 > Article
-
Original Article
- Factors Influencing Problem and Pathological Gambling in Participants of Horse Race Gambling
- Mi-Yeul Hyun, Ok-Hee Cho
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2012;42(4):589-598.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2012.42.4.589
Published online: August 31, 2012
College of Nursing, Jeju National University, Jeju-si, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Cho, Ok-Hee. College of Nursing, Jeju National University, 102 Jejudaehakno, Jeju-si, Jeju Special Self-Governing Province 690-756, Korea. Tel: +82-64-754-3887, Fax: +82-64-702-2686, ohcho@jejunu.ac.kr
© 2012 Korean Society of Nursing Science
- 940 Views
- 2 Download
- 1 Crossref
Abstract
-
Purpose
- The purpose of this study was to examine risk factors for pathological gambling of horse race participants.
-
Methods
- The participants, 508 horse race gamblers, completed the DSM-IV criteria of pathological gambling, Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT-K) and Symptom Checklist-47-Revision (SCL-47-R). Data were analyzed using t-test, χ2-test, Fisher's exact test, and logistic regression analyses. Behaviors related to horse racing, alcohol abuse, and mental health were analyzed between problem or pathological gamblers compared to recreational gamblers.
-
Results
- The prevalence rates of recreational, problem, and pathological gambling were 36.6%, 39.4%, and 24.0%, respectively. Frequency of gambling (≥4/day), frequency of racetrack visiting (≥3/month), accompaniment (alone), and mental health (SCL-47-R scores) were all associated with increased risks of problem and pathological gambling. Expenditure on betting (≥200,000 won/day) and alcohol abuse (AUDIT-K 8-20 scores) group members had higher levels of gambling pathology than recreational gamblers.
-
Conclusion
- Problem and pathological gambling are highly associated with alcohol abuse and mental health disorders, suggesting that clinicians should carefully evaluate this population.
- 1. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 1994;4th ed. Washington, DC, Author.
- 2. Barber TF, Hibbins-Biddle JC, Saunders JB, Monteiro MG. The alcohol use disorder identification test(AUDIT): Guidelines for use in primary care. 2001;2nd ed. Geneva, Switzerland, World Health Organization.
- 3. Choi WR. The effects of stress and coping on gambling behaviors: Affinity to pathological gambling and chasing. 2007;Chuncheon, Kangwon National University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 4. Crockford DN, el-Guebaly N. Psychiatric comorbidity in pathological gambling: A critical review. Canadian Journal of Psychiatry. Revue Canadienne de Psychiatrie. 1998;43:43–50.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 5. Derogatis LR, Rickels K, Rock AF. The SCL-90 and the MMPI: A step in the validation of a new self-report scale. British Journal of Psychiatry. 1976;128:280–289. http://dx.doi.org/10.1192/bjp.128.3.280.Article
- 6. Dickerman MG, Baron E, Hong SM, Cottrel D. Estimating the extent and degree of gambling related problems in the Australianpopulation: A national survey. Journal of Gambling Studies. 1996;12:161–178. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/BF01539172.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 7. Han SY, Lee HP, Hur TK, Jang H. The actual condition, participation rate of gambling and prevalence of pathological gamblingin South-Korea. Korean Journal of Health Psychology. 2009;14:255–276.
- 8. Heo JH, Han BS. An analysis of gambling participant addiction. Symposium conducted at the meeting of the 50th Tourism Sciences Society of Korea, Academic Symposium & Research Presentation. 2001;2001, June; 177–188.
- 9. Im SB, Lee JE, Yang S. An analysis of nursing research on addiction in Korea. Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing. 2007;16:5–13.
- 10. Kim HJ. The relationship between perceived social support and the mental health status of persons receiving psychiatric care as outpatient. Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing. 1992;1:51–67.
- 11. Kim KH, Bae JK. The subjective quality of life, self-esteem and social support of amateur gamblers in the cycle and motorboat races. Korean Journal of Health Psychology. 2007;12:367–382.Article
- 12. Kim KH, Kwon SJ. Psychological characteristics and predictors of pathological gamblers. Korean Journal of Health Psychology. 2003;8:261–277.
- 13. Kim KY. A study on the mental health and internet addiction of 2004 freshman at Ansan campus, Hanyang University. Journal of Student Guidance Research. 2004;22:277–300.
- 14. Kim TJ. A study on the Track Fan's behavioral characteristics and emotional features. 2001;Seoul, Yonsei University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 15. Kweon GY, Lee HJ. A study on interrelationship between adolescent mental health and their use internet. Mental Health & Social Work. 2002;13:59–86.
- 16. Lee BH, Kim JH, Choi MK. The association between drinking behavior and mental health in an urban community. Journal of Korean Alcohol Science. 2009;10:141–153.
- 17. Lee BY, Lee CH, Lee PG, Choi MJ, Nam GK. Development of Korean version of AUDIT-K: Its reliability and validity. Journal of Korean academy of Addiction Psychiatry. 2000;4:83–92.
- 18. Lee HP. The effect of irrational gambling belief to the pathological gambling. Korean Journal of Clinical Psychology. 2003;22:415–434.
- 19. Lee HK, Lee KH. A survey on alcohol use of workers. Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing. 2008;17:182–190.ArticlePDF
- 20. Lee IH. Gambling behavior, gambling-related problem, and the satisfaction with life among the residents who live in the location of casinos. Korean Journal of Psychological and Social Issues. 2005;11:67–82.
- 21. Lesieur HR, Rosenthal RJ. Pathological gambling: A review of the literature. Journal of Gambling Studies. 1991;7:5–39. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/BF01019763.PubMed
- 22. Park S, Cho MJ, Jeon HJ, Lee HW, Bae JN, Park JI, et al. Prevalence, clinical correlations, comorbidities, and suicidal tendencies in pathological Korean gamblers: Results from the Korean Epidemiologic Catchment Area Study. Social Psychiatry and Psychiatric Epidemiology. 2010;45:621–629. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00127-009-0102-9.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 23. Park SE. An analysis of satisfaction degree of horse racing participant between the sound and the addicted. 2002;Suwon, Kyonggi University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 24. Potenza MN, Fiellin DA, Heninger GR, Rounsaville BJ, Mazure CM. Gambling: An addictive behavior with health and primary care implications. Journal of General Internal Medicine. 2002;17:721–732. http://dx.doi.org/10.1046/j.1525-1497.2002.10812.x.PubMedPMC
- 25. Potenza MN, Steinberg MA, Wu R. Characteristics of gambling helpline callers with self-reported gambling and alcohol use problems. Journal of Gambling Studies. 2005;21:233–254. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10899-005-3098-4.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 26. Son DS, Jung SY. A study of the issues and impact on pathological gamblers. Mental Health & Social Work. 2007;26:377–407.
- 27. Song HJ, Hyun MY, Lee EJ. Hope, self-care, and mental health in patients with chronic schizophrenia. Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing. 2011;20:180–187.
- 28. The National Gaming Control Commission of Korea. Comprehensive plan of the gaming industry. 2008;11;Seoul, Author.
- 29. Volberg RA. The prevalence and demographic of pathological gamblers: Implications for public health. American Journal of Public Health. 1994;84:237–241.PubMedPMC
- 30. Welte JW, Barns GM, Wieczorek WF, Tidwell MC, Parker J. Gambling participation in the U.S.: Results from a national survey. Journal of Gambling Studies. 2002;18:313–337. http://dx.doi.org/10.1023/A:1021019915591.ArticlePubMedPDF
REFERENCES
OR=odds ratio; 95% CI=95% confidence interval; AUDIT-K=Korean version of alcohol use disorders identification test; SCL-47-R=symptom checklist-47-revision.
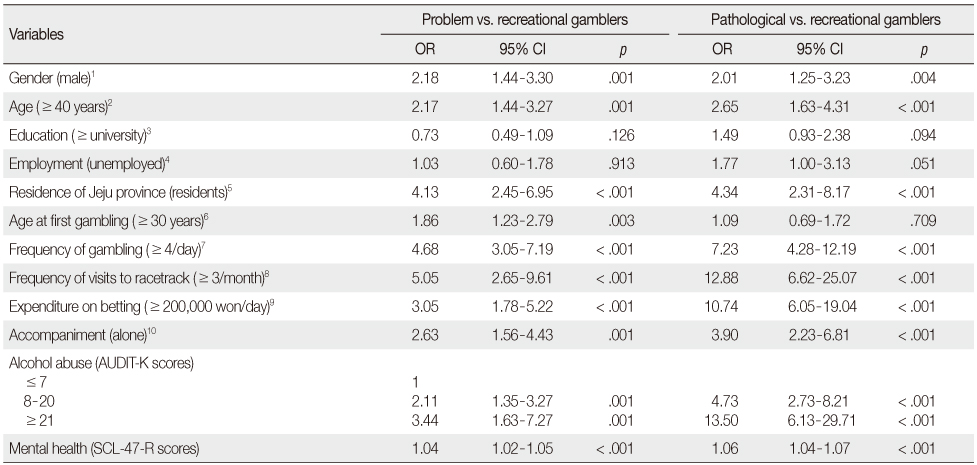
Reference group: 1. gender: female, 2. age: ≤ 40 years, 3. education:< university, 4. employment: employed, 5. residence of Jeju province: non-residents, 6. age at first gambling:< 30 years, 7. frequency of gambling:< 4/day, 8. frequency of visits to racetrack:< 3/month, 9. expenditure on betting:< 200,000 won/day, 10. accompaniment: friend (s)/colleague or family.
OR=odds ratio; 95% CI=95% confidence interval; AUDIT-K=Korean version of alcohol use disorders identification test; SCL-47-R=symptom checklist-47-revision.
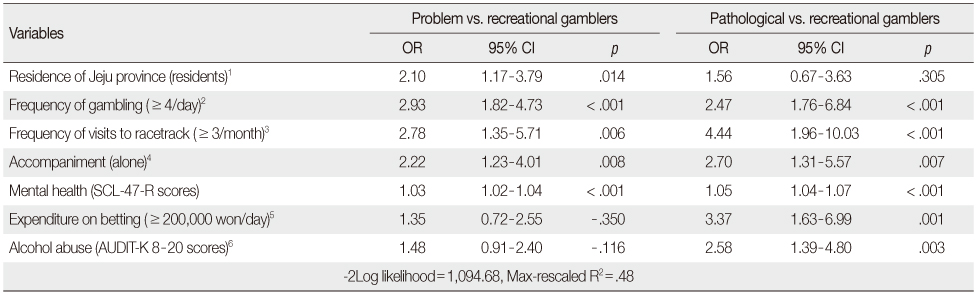
Reference group: 1. residence of Jeju province: non-residents, 2. frequency of gambling:< 4/day, 3. frequency of visits to racetrack:< 3/month, 4. accompaniment: friend (s)/colleague or family, 5. expenditure on betting:< 200,000 won/day, 6. alcohol abuse: AUDIT-K ≤ 7 scores.
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Feasibility of a mobile app for traumatic stress management using neurofeedback-based meditation and binaural beat music: A pilot randomized controlled trial
Yun-Jung Choi, Dong-Hee Cho, Na-Rae Lee
DIGITAL HEALTH.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
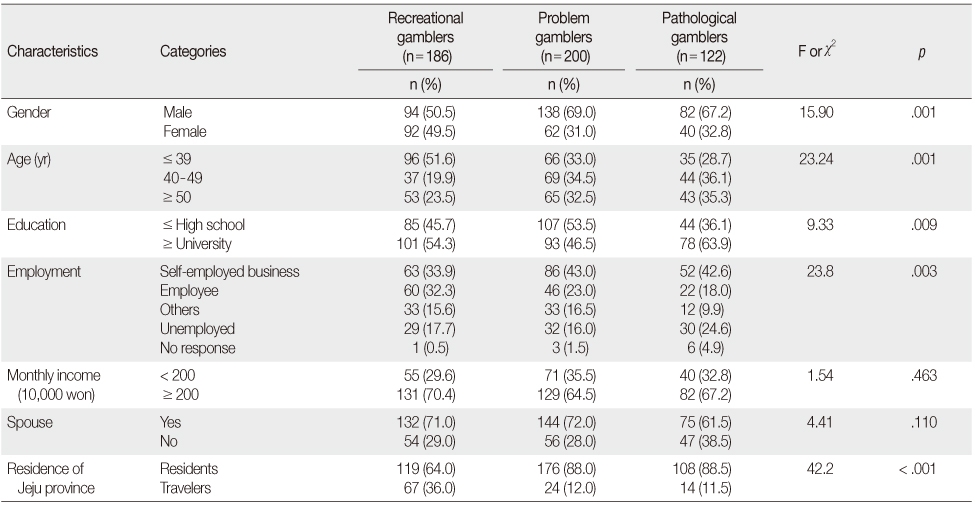
Demographic Characteristics of Recreational, Problem, and Pathological Gamblers (N=508)
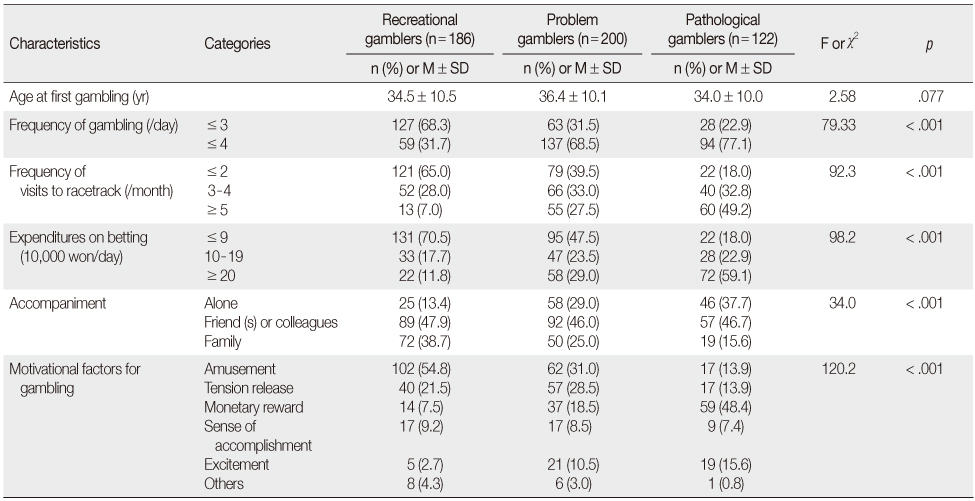
Betting-related Behaviors of Recreational, Problem, and Pathological Gamblers (N=508)
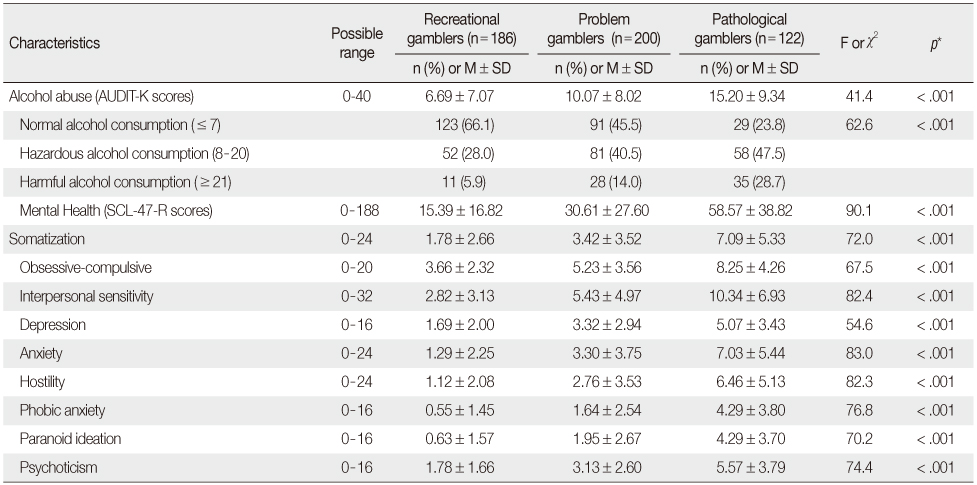
Comparison of Alcohol Abuse and Mental Health among Recreational, Problem, and Pathological Gamblers (N=508)
AUDIT-K=Korean version of alcohol use disorders identification test; SCL-47-R=symptom checklist-47-revision.
*There were significant differences in all results of post-hoc analysis (Bonferroni test) between groups (p < .05).
Risk Factors of Problem and Pathological Gambling by Using Univariate Analysis (N=508)
OR=odds ratio; 95% CI=95% confidence interval; AUDIT-K=Korean version of alcohol use disorders identification test; SCL-47-R=symptom checklist-47-revision.
Reference group: 1. gender: female, 2. age: ≤ 40 years, 3. education:< university, 4. employment: employed, 5. residence of Jeju province: non-residents, 6. age at first gambling:< 30 years, 7. frequency of gambling:< 4/day, 8. frequency of visits to racetrack:< 3/month, 9. expenditure on betting:< 200,000 won/day, 10. accompaniment: friend (s)/colleague or family.
Risk Factors of Problem and Pathological Gambling by Multivariate Analysis (N=508)
OR=odds ratio; 95% CI=95% confidence interval; AUDIT-K=Korean version of alcohol use disorders identification test; SCL-47-R=symptom checklist-47-revision.
Reference group: 1. residence of Jeju province: non-residents, 2. frequency of gambling:< 4/day, 3. frequency of visits to racetrack:< 3/month, 4. accompaniment: friend (s)/colleague or family, 5. expenditure on betting:< 200,000 won/day, 6. alcohol abuse: AUDIT-K ≤ 7 scores.
AUDIT-K=Korean version of alcohol use disorders identification test; SCL-47-R=symptom checklist-47-revision. *There were significant differences in all results of post-hoc analysis (Bonferroni test) between groups (
OR=odds ratio; 95% CI=95% confidence interval; AUDIT-K=Korean version of alcohol use disorders identification test; SCL-47-R=symptom checklist-47-revision. Reference group: 1. gender: female, 2. age: ≤ 40 years, 3. education:< university, 4. employment: employed, 5. residence of Jeju province: non-residents, 6. age at first gambling:< 30 years, 7. frequency of gambling:< 4/day, 8. frequency of visits to racetrack:< 3/month, 9. expenditure on betting:< 200,000 won/day, 10. accompaniment: friend (s)/colleague or family.
OR=odds ratio; 95% CI=95% confidence interval; AUDIT-K=Korean version of alcohol use disorders identification test; SCL-47-R=symptom checklist-47-revision. Reference group: 1. residence of Jeju province: non-residents, 2. frequency of gambling:< 4/day, 3. frequency of visits to racetrack:< 3/month, 4. accompaniment: friend (s)/colleague or family, 5. expenditure on betting:< 200,000 won/day, 6. alcohol abuse: AUDIT-K ≤ 7 scores.
 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION
 Cite
Cite

