Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Nurs > Volume 42(3); 2012 > Article
-
Original Article
- The Effects of Pre-operative Visual Information and Parental Presence Intervention on Anxiety, Delirium, and Pain of Post-Operative Pediatric Patients in PACU
- Je-Bog Yoo, Min-Jung Kim, Soo-Hyun Cho, Yoo-Jung Shin, Nam-Cho Kim
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2012;42(3):333-341.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2012.42.3.333
Published online: June 29, 2012
1Nurse Manager, Samsung Medical Center PACU, Seoul, Korea.
2Nurse, Samsung Medical Center PACU, Seoul, Korea.
3Nurse Director, Samsung Medical Center Operating Room, Seoul, Korea.
4Professor, College of Nursing, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Kim, Nam-Cho. College of Nursing, The Catholic University, 505 Banpo-dong, Seocho-gu, Seoul 137-701, Korea. Tel: +82-2-2258-7405, Fax: +82-2-2258-7772, kncpjo@catholic.ac.kr
© 2012 Korean Society of Nursing Science
- 1,561 Views
- 28 Download
- 18 Crossref
Abstract
-
Purpose
- The purpose of this study was to test whether pre-operative visual information and parental presence had positive effects on anxiety, delirium, and pain in pediatric patients who awoke from general anesthesia in a post-surgical stage.
-
Methods
- This study used a non equivalent control-group post test design (n=76). Independent variables were provision of pre-operative visual information and parental presence for post-surgical pediatric patients in PACU (post anesthesia care unit). Dependent variables were anxiety, delirium, and pain in the pediatric patients measured three times at 10 minute intervals after extubation in the PACU. Measurements included Numerical Rating Scale for assessing state anxiety, Pediatric Anesthesia Emergence Delirium Scale by Sikich & Lerman (2004) for delirium, and Objective Pain Scale by Broadman, Rice & Hannallah (1988) for pain.
-
Results
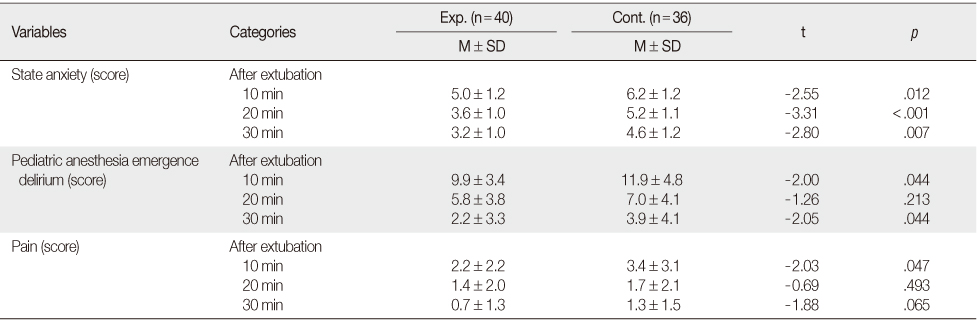
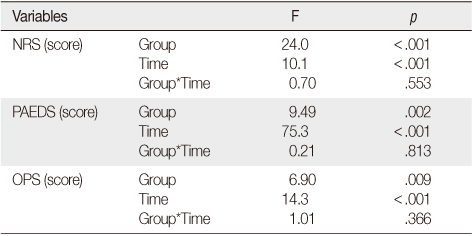
- Experimental group showed significantly decreased state anxiety at time points-10, 20, and 30 minutes after extubation. Delirium was significantly lower at 10 minutes and 30 minutes after extubation in the experimental group. Pain was significantly lower at 10 minutes after extubation in the experimental group.
-
Conclusion
- The results of this study suggest that this intervention can be a safe pre-operative nursing intervention for post-surgical pediatric patients at PACU.
- 1. Bae JY, Song E, Kim JT, Kim HS, Kim JS, Kim SD. Comparison of emergence agitation between sevoflurane, desflurane, and propofol with bispectral index monitoring in pediatric anesthesia. Korean Journal of Anesthesiology. 2008;55:161–165.Article
- 2. Broadman LM, Rice LJ, Hannallah RS. Testing the validity of an objective pain scale for infants and children. Anesthesiology. 1988;69(3A):A770.
- 3. Caumo W, Broenstrub JC, Fialho L, Petry SM, Brathwait O, Bandeira D, et al. Risk factors for postoperative anxiety in children. Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica. 2000;44:782–789. http://dx.doi.org/10.1034/j.1399-6576.2000.440703.x.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 4. Cho SC, Choi JS. Development of the Korean form of the state-trait anxiety inventory for children. Seoul Journal of Psychiatry. 1989;14(3):150–157.
- 5. Cole JW, Murray DJ, McAllister JD, Hirshberg GE. Emergence behaviour in children: Defining the incidence of excitement and agitation following anaesthesia. Paediatric Anaesthesia. 2002;12:442–447. http://dx.doi.org/10.1046/j.1460-9592.2002.00868.x.ArticlePubMed
- 6. Deleskey K. Family visitation in the PACU: The current state of practice in the United States. Journal of PeriAnesthesia Nursing. 2009;24:81–85. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jopan.2009.01.002.ArticlePubMed
- 7. Ely EW, Siegel MD, Inouye SK. Delirium in the intensive care unit; An under-recognized syndrome of organ dysfunction. Seminars in Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. 2001;22:115–126. http://dx.doi.org/10.1055/s-2001-13826.ArticlePubMed
- 8. Francis J. Prevention and treatment of delirium and confusional state. 2011;Retrieved August 30, 2011. from http://www.uptodate.com/contents/prevention-and-treatement-of-delirium-and-confusional-states.
- 9. Hong JY. Effects of sensory information on preoperative anxiety of day-case surgery patients. Korean Journal of Anesthesiology. 2001;40:435–442.Article
- 10. Im JH. Effect of ketorolac and fentanyl on the emergence characteristics after sevoflurane anesthesia in children undergoing tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy. 2003;Seoul, Ewha Womans University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 11. Ji HS. Effects of visual information program on the easing of anxiety of pediatric patients and their parents. 2004;Gongju, Kongju National University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 12. Kamerling SN, Lawler LC, Lynch M, Schwartz AJ. Family-centered care in the pediatric post anesthesia care unit: Changing practice to promote parental visitation. Journal of PeriAnesthesia Nursing. 2008;23:5–16. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jopan.2007.09.011.ArticlePubMed
- 13. Kennedy CM, Riddle II. The influence of the timing of preparation on the anxiety of preschool children experiencing surgery. Maternal-Child Nursing Journal. 1989;18:117–132.PubMed
- 14. Kim YH, Lee HZ. The effects of informational intervention on postoperative pain following tonsillectomy in children. Journal of Korean Academy of Child Health Nursing. 2002;8:400–413.
- 15. Koo HY, Cho YJ, Kim OH, Park HR. The effects of information using photographs on preoperative anxiety in children and their parents. Journal of Korean Academy of Child Health Nursing. 2007;13:273–281.
- 16. Lee SC, Chung CJ, Chin YJ, Lee SI, Lee JH. The effects of anesthetic agents on emergence delirium in pediatrics strabismus surgery. Korean Journal of Anesthesiology. 2007;52:138–142. http://dx.doi.org/10.4097/kjae.2007.52.2.138.
- 17. Lee SH, Chung KW, Park IO. Effects of preoperative nursing information on anxiety and stress in patients undergoing surgery. Journal of the Korean Association of Operating Room Nurses. 2001;9(1):99–111.
- 18. Lee MH. The effects of visual information program on anxiety and role behaviour of pediatric tonsillectomy patients and their mothers. 2008;Seoul, Kyung Hee University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 19. McCaffery M. Nursing management of patient with pain. 1979;Philadelphia, Lippincott.
- 20. O'Kelly SW, Voepel-Lewis T, Tait AR. Postoperative behavior and emergence delirium in pediatric patients: A prospective study. Anesthesiology. 1997;87:A1060.
- 21. Paik HJ, Ahn YM. Measurement of pain following strabismus surgery in children. Journal of the Korean Ophthalmological Society. 2000;41:985–992.
- 22. Potts NL, Mandleco BL. Pediatric nursing: Caring for children and their families. 2002;New York, Delmar.
- 23. Roberts BL. Managing delirium in adult intensive care patient. Critical Care Nurse. 2001;21:48–55.
- 24. Sikich N, Lerman J. Development and psychometric evaluation of the pediatric anesthesia emergence delirium scale. Anesthesiology. 2004;100:1138–1145.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 25. Suh HJ, Yoo YS. Intensive care unit nurse's knowledge, nursing performance and stress about delirium. Korean Journal of Adult Nursing. 2007;19:55–65.
- 26. Vlajkovic GP, Sindjelic RP. Emergence delirium in children: Many questions, few answers. Anesthesia and Analgesia. 2007;104:84–91. http://dx.doi.org/10.1213/01.ane.0000250914.91881.a8.ArticlePubMed
- 27. Yoon HB, Cho KJ. A survey on the nonpharmacologic nursing intervention for children in pain. Journal of Korean Academy of Child Health Nursing. 2000;6:144–157.
- 28. Yoon JR, Kim TK, Yoon SJ, Kim YS, Kim SH, Kim MG, et al. Severe postoperative delirium lasting for three weeks. Korean Journal of Critical Care Medicine. 2004;19:42–46.
- 29. Yu MY, Park JW, Hyun MS, Lee YJ. Factors related to delirium occurrence among the patients in the intensive care units. Journal of Korean Clinical Nursing Research. 2008;14:151–160.
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Virtual Reality Simulation to Improve Postoperative Cardiothoracic Surgical Patient Outcomes
Robert J. Anderson, Philippe R. Bauer, Arman Arghami, Rory M. Haney, Emily M. Reisdorf, Kiersten Baalson
American Journal of Critical Care.2025; 34(2): 111. CrossRef - Nursing experiences and knowledge of paediatric delirium: Analysing knowledge‐practice gaps
Soonyoung Shon, Minkyung Kang
Nursing in Critical Care.2024; 29(5): 923. CrossRef - ASSISTÊNCIA DE ENFERMAGEM PERIOPERATÓRIA AO ADOLESCENTE: SCOPING REVIEW
Layane Cristina Araújo, Danielle Mendonça Oliveira, Taysa de Fátima Garcia, Vanessa de Brito Poveda, Liliane de Lourdes Teixeira Silva
Texto & Contexto - Enfermagem.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - PERIOPERATIVE NURSING CARE FOR ADOLESCENTS: A SCOPING REVIEW
Layane Cristina Araújo, Danielle Mendonça Oliveira, Taysa de Fátima Garcia, Vanessa de Brito Poveda, Liliane de Lourdes Teixeira Silva
Texto & Contexto - Enfermagem.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Impact of Parental Presence on Emergence Delirium in Pediatric Patients After General Anesthesia: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Jihyun Baek, Young Man Kim
Journal of PeriAnesthesia Nursing.2024; 39(3): 475. CrossRef - Sucking lollipop after awakening from sevoflurane anesthesia reduces the degree of emergence agitation in children undergoing ambulatory surgery: A prospective randomized controlled trial
Xiaofei Mo, Jiequn Zeng, Xiaoying Wu, Fa Huang, Kunling Zhang
Medicine.2023; 102(44): e35651. CrossRef - Investigating Non-Pharmacological Stress Reduction Interventions in Pediatric Patients Confirmed with Salivary Cortisol Levels: A Systematic Review
Maria Grigoropoulou, Emmanouil I. Kapetanakis, Achilleas Attilakos, Anestis Charalampopoulos, Anastasia Dimopoulou, Efstratios Vamvakas, Eleftheria Mavrigiannaki, Nikolaos Zavras
Pediatric Reports.2023; 15(2): 349. CrossRef - Intervention to Reduce Anxiety Pre- and Post-Eye Surgery in Pediatric Patients in South Korea: A Preliminary Quasi-Experimental Study
Hyeran Yi, Hanna Lee
Children.2022; 9(1): 65. CrossRef - Effectiveness of preoperative tour to a simulated anaesthesia induction at operating theatre in reducing preoperative anxiety in children and their parents: a pragmatic, single-blinded, randomised controlled trial/ King Fahad Medical City
Hussein Battah, Usamah AlZoraigi, Firas Shubbak
BMJ Simulation and Technology Enhanced Learning.2021; : bmjstel-2020-000707. CrossRef - The Effect of a Parental Visitation Program on Emergence Delirium Among Postoperative Children in the PACU
WooYoung In, Young Man Kim, Hee Soon Kim, SeoHee Hong, YuRi Suh, Yerin Cha, Naeun Kim, JongWon Kim, HyunJi Kang, HyoEun Kwon, YangSoo Kim, Wyunkon Park
Journal of PeriAnesthesia Nursing.2019; 34(1): 108. CrossRef - Factors associated with Pediatric Delirium in the Pediatric Intensive Care Unit
Hyo Jin Kim, Dong Hee Kim
Child Health Nursing Research.2019; 25(2): 103. CrossRef - Stress, Pain, and Nursing Needs of Surgical Patients under General Anesthesia in the Recovery Room
Jihyun Jo, Minkyung Gu, Sohyune Sok
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2019; 31(3): 249. CrossRef - Reduction of Postanesthetic Pediatric Distress: A Coordinated Approach
Simon Hayhoe, Scott Pallett, Juliet Zani, Joanne Trott
Journal of PeriAnesthesia Nursing.2018; 33(3): 312. CrossRef - The effects of maternal presence during anesthesia induction on salivary cortisol levels in children undergoing tonsillectomy and/or adenoidectomy
Hatice K. Ozdogan, Sibel Cetinalp, Gokhan Kuran, Onder Tugal, Murat Tahiroglu, Ummuhan E. Herdem, Suheyl Haytoglu
Journal of Clinical Anesthesia.2017; 39: 64. CrossRef - Effects of Family Presence Intervention on Anxiety, Delirium, Pain and Length of Time in Recovery Room of Post-operative Elderly Patients in Post-anesthesia Care Units
Kyunghee Kim, Sookhee Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2015; 22(2): 149. CrossRef - Preoperative Anxiety Management, Emergence Delirium, and Postoperative Behavior
Richard J. Banchs, Jerrold Lerman
Anesthesiology Clinics.2014; 32(1): 1. CrossRef - The Effect of Hand Holding and Nei-Guan Acupressure on Anxiety and Pain under Local Anesthetic Patients during Surgery
Sun Hee Park, Hee Jung Jang
The Journal of the Korea Contents Association.2014; 14(11): 378. CrossRef - Emergence agitation after sevoflurane anaesthesia in children
A.K. Narayanasamy, A Ghori
British Journal of Anaesthesia.2013; 111(1): 121. CrossRef
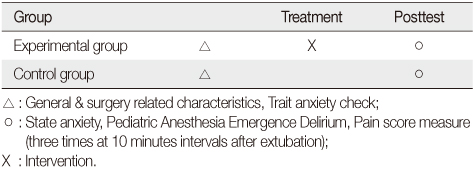
Figure 1
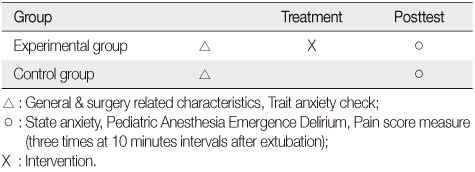
General Characteristics of Participants (N=76)
*Fisher's exact test.
Exp.=Experimental group; Cont.=Control group.
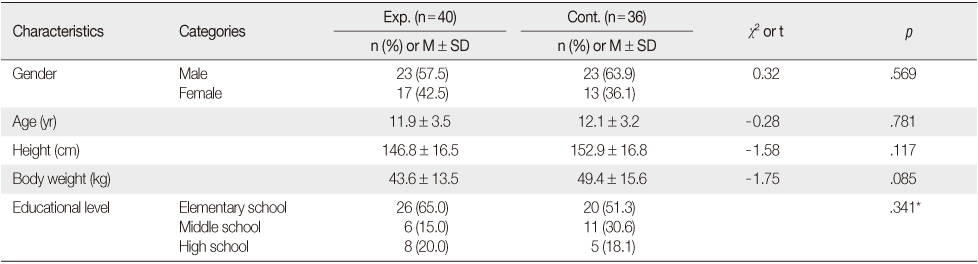
Surgery related Characteristics
*Fisher's exact test.
Exp.=Experimental group; Cont.=Control group.
The Scores of State Anxiety, Pediatric Anesthesia Emergence Delirium and Pain after Intervention
Exp.=Experimental group; Cont.=Control group.
Scores of State Anxiety, Pediatric Anesthesia Emergence Delirium Scale, Pain after Intervention using Repeated Measures ANOVA
NRS=Numerical Rating Scale; PAEDS=Pediatric Anesthesia Emergence Delirium Scale; OPS=Objective Pain Scale.
*Fisher's exact test. Exp.=Experimental group; Cont.=Control group.
*Fisher's exact test. Exp.=Experimental group; Cont.=Control group.
Exp.=Experimental group; Cont.=Control group.
NRS=Numerical Rating Scale; PAEDS=Pediatric Anesthesia Emergence Delirium Scale; OPS=Objective Pain Scale.
 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION
 Cite
Cite

