Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Nurs > Volume 41(5); 2011 > Article
-
Original Article
- Depression Status of Academic High School Students in Seoul: Mediating Role of Entrapment
- Young-Joo Park, Nah-Mee Shin, Kuem Sun Han, Hyun Cheol Kang, Sook-Hee Cheon, Hyunjeong Shin
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2011;41(5):663-672.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2011.41.5.663
Published online: October 31, 2011
1Professor, College of Nursing, Korea University, Seoul, Korea.
2Assistant Professor, College of Nursing, Korea University, Seoul, Korea.
3Associate Professor, Department of Informational Statistics, Hoseo University, Cheonan, Korea.
4Full-time Instructor, Department of Nursing, Sangji University, Wonju, Korea.
5Assistant Professor, College of Nursing, Kyunghee University, Seoul, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Shin, Nah-Mee. Assistant Professor, College of Nursing, Korea University, 126-1 5-ga, Anam-dong, Seongbuk-gu, Seoul 136-701, Korea. Tel: +82-2-3290-4924, Fax: +82-2-927-4676, nshin@korea.ac.kr
© 2011 Korean Society of Nursing Science
Abstract
-
Purpose
- Purpose of this study was to investigate the status of depression in academic high school students and path analysis model for exploring the mediating role of entrapment to depression in relation to academic stress and perceived social support.
-
Methods
- Measurements were four reliable questionnaires measuring academic stress, social support, entrapment, and depression. Data were collected from students in 17 high schools in Seoul.
-
Results
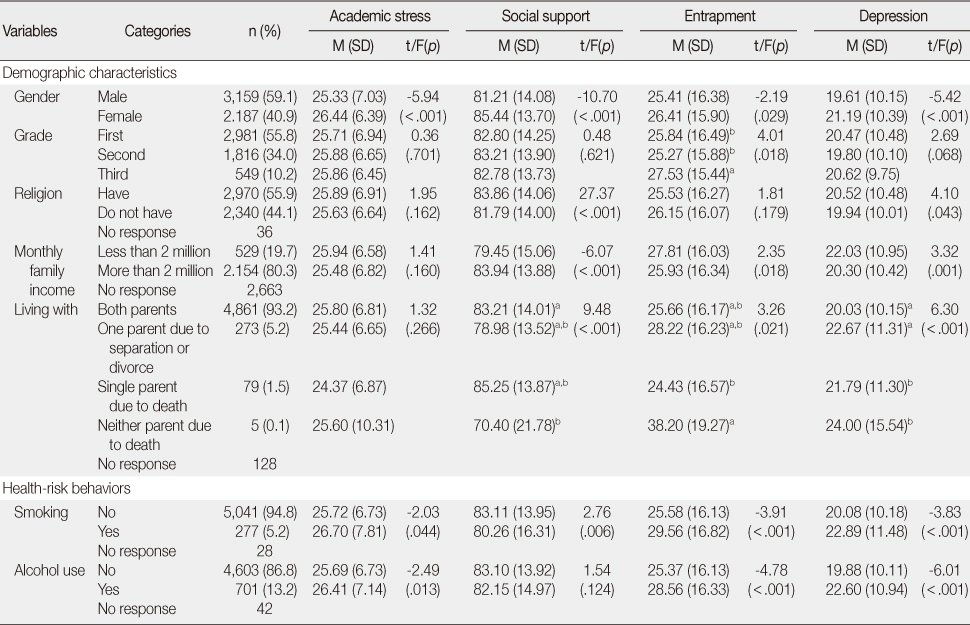
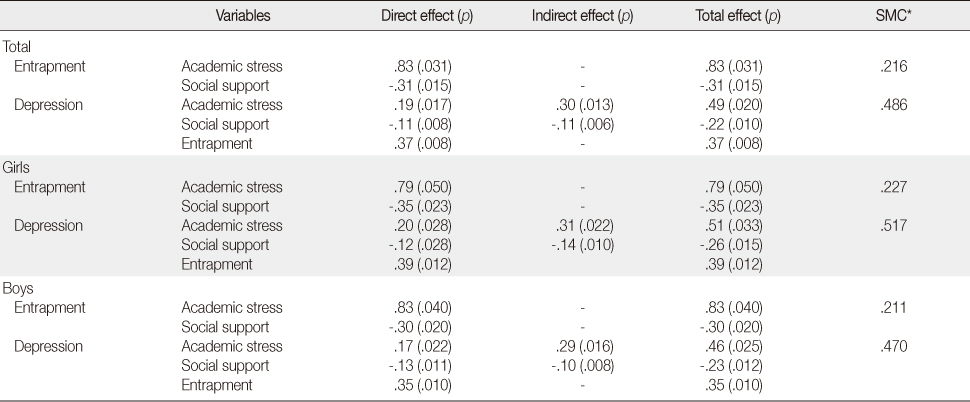
- Students (n=5,346) completing the questionnaires indicated depression & entrapment from academic stress. Depression was more prevalent in girls, those whose parents' household income was less than two million won, who did not live with father or mother or both due to divorce, separation, or death, and those who smoked or used alcohol. Entrapment was more prevalent in students similar to cases of depression and in seniors. According to the proposed path model, 48.6% of depression was explained by academic stress, social support, and entrapment. The indirect effect of entrapment as a mediator between academic stress and depression was verified and larger than the direct effect of academic stress on depression.
-
Conclusion
- Considering levels of depression and entrapment demonstrated by these students, better mental health programs with diverse strategies should be developed for their psychological well-being.
- 1. Brown GW, Harris TO, Hepworth C. Loss, humiliation and entrapment among women developing depression: A patient and non-patient comparison. Psychological Medicine. 1995;25:7–21. doi: 10.1017/S003329170002804X.ArticlePubMed
- 2. Cheon SH, Cha BK. Inferiority, depression and psychosomatic symptoms in female adolescents: The mediating effect of perceived entrapment. Journal of Korean Academy of Child Health Nursing. 2008;14:343–351.
- 3. Chun KK, Lee MK. Preliminary development of Korean version of CES-D. Korean Journal of Clinical Psychology. 1992;11(1):65–76.
- 4. Craig T, Van Natta P. Current medication use and symptoms of depression in a general population. American Journal of Psychiatry. 1978;135:1036–1039.ArticlePubMed
- 5. Dong-A Daily News. Korean adolescents with withered heart. 2008;05 09 Seoul, Author.
- 6. Eom TW, Kang MJ, Choi JS. Gender differences of the stress, hopelessness, depression, suicidal ideation and social support in adolescents. Journal of Human Studies. 2008;22:5–30.
- 7. Gilbert P. Evolution and depression: Issues and implications. Psychological Medicine. 2006;36:287–297. doi: 10.1017/S0033291705006112.ArticlePubMed
- 8. Gilbert P, Allan S. The role of defeat and entrapment (arrested flight) in depression: An exploration of an evolutionary view. Psychological Medicine. 1998;28:585–598. doi: 10.1017/S0033291798006710.ArticlePubMed
- 9. Gilbert P, Gilbert J, Irons C. Life events, entrapments and arrested anger in depression. Journal of Affective Disorders. 2004;79:149–160. doi: 10.1016/S0165-0327(02)00405-6.ArticlePubMed
- 10. Han MH. A study on stress, perceived social supports, and behavior problems of children. 1996;Seoul, Seoul National University. Unpublished doctoral dissertation.
- 11. Han TY. Adolescents' stress at school: Moderation effects of personality and emotional intelligence. Korean Journal of School Psychology. 2005;2(2):177–197.
- 12. Hong YS. The effects of life stress and self-esteem for adolescent suicidal behaviors. Studies on Korean Youth. 2004;15(2):153–182.
- 13. Hong SO, Eum KS, Bae OH. A study on social support and stress of adolescent. Journal of Family Relations. 2003;8(1):139–155.
- 14. Joreskog K, Sorbom D. LISREL 8: User's reference guide. 2001;Chicago, Scientific Software International.
- 15. Kim BJ. Infuence of life stress and social support on school adjustment in junior highschool students. 2003;Daejeon, DaeJeon University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 16. Kim S. The heterogenous developmental trajectories of adolescent depression and their predictors focusing on gender differences. Studies on Korean Youth. 2010;21(1):171–192.
- 17. Kline RB. Principles and practice of structural equation modeling. 1998;New York, The Guilford Press.
- 18. Lee KS, Kim JH. The effects of study stress coping training program on the reduction of study stress and the academic achievements of high school students. Korean Journal of Health Psychology. 2000;5(1):43–59.
- 19. National Youth Commission. White paper of Adolescents. 2007;Seoul, Author.
- 20. Oh MH. Junior highschool students' work related stress factors and symptoms analysis and effects of meditation exercise on reduction of the work related stress. 1993;Daegu, KyungBuk University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 21. Park ES, Park YJ, Ryu HS, Han KS, Hwang RI, Im YJ, et al. A nationwide survey on current conditions of school health education. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2006;36:381–388.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 22. Polit DF, Sherman RE. Statistical power in nursing research. Nursing Research. 1990;39:365–369.PubMed
- 23. Radloff LS. The CES-D scale: A self-report depression scale for research in the general population. Applied Psychological Measurement. 1977;1:385–401. doi: 10.1177/014662167700100306.ArticlePDF
- 24. Saban A, Flisher AJ. The association between psychopathology and substance use in young people: A review of the literature. Journal of Psychoactive Drugs. 2010;42(1):37–47. doi: 10.1080/02791072.2010.10399784.ArticlePubMed
- 25. Seoul Metropolitan Educational Office. Education statistics. 2005;Seoul, Author.
- 26. Vaughan CA, Foshee VA, Ennett ST. Protective effects of maternal and peer support on depressive symptoms during adolescence. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology. 2010;38:261–272. doi: 10.1007/s10802-009-9362-9.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 27. Vaux A, Phillips J, Holly L, Thomson B, Killiams K, Stewart D. The social support appraisal (SS-A) scale: Studies of reliability and validity. American Journal of Community Psychology. 1986;14:195–219. doi: 10.1007/BF00911821.
- 28. Ministry of Health & Welfare. Support for depression screening and treatment for children & adolescents with ADHD. 2009;04 09 Seoul, Author.
- 29. Wilner P, Goldstein RC. Mediation of depression by perceptions of defeat and entrapment in high-stress mothers. The British Journal of Medical Psychology. 2001;74:473–485. doi: 10.1348/000711201161127.ArticlePubMed
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Study on Awareness of Suicide and Suicide Prevention Among Community Youth
Jiyoung Kim, Young-Hoon Ko, Ho-Kyoung Yoon, Boram Chae, Rayoung Han, Nayoung Chae, Jongha Lee
Journal of the Korean Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry.2024; 35(3): 210. CrossRef - The association mental health of adolescents with economic impact during the COVID-19 pandemic: a 2020 Korean nationally representative survey
Hanul Park, Kang-Sook Lee
BMC Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Adolescent suicide in South Korea: Risk factors and proposed multi-dimensional solution
Chae Woon Kwak, Jeannette R. Ickovics
Asian Journal of Psychiatry.2019; 43: 150. CrossRef - Test anxiety and telomere length: Academic stress in adolescents may not cause rapid telomere erosion
Yaru Zou, Waiian Leong, Mingling Yao, Xuefei Hu, Sixiao Lu, Xiaowei Zhu, Lianxiang Chen, Jianjing Tong, Jingyi Shi, Eric Gilson, Jing Ye, Yiming Lu
Oncotarget.2017; 8(7): 10836. CrossRef - Effects of Anger and Entrapment on Psychological Health of High School Boys: Focused on the Mediating Effects of Social Support
Sun Yi Yang, Yun Hee Oh
Child Health Nursing Research.2017; 23(4): 429. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Emotional and Behavioral Characteristics of High School Students
Kyoung Sun Park, Gyu Young Lee
Journal of the Korean Society of School Health.2014; 27(2): 109. CrossRef - Depression, anxiety, and suicidal ideation among Vietnamese secondary school students and proposed solutions: a cross-sectional study
Dat Tan Nguyen, Christine Dedding, Tam Thi Pham, Pamela Wright, Joske Bunders
BMC Public Health.2013;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk factors of heavy episodic drinking among Korean adolescents
S. S. Chung, K. H. Joung
Journal of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2013; 20(8): 665. CrossRef - Relationships among Daily Hassles, Social Support, Entrapment and Mental Health Status by Gender in University Students
Suk-Hee Cheon
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2012; 18(3): 223. CrossRef - Effects of Adolescent Temperament and Parent-child Attachment on Depression
So-Youn Yim, Myoung-Ok Chae, Ja-Hyung Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Child Health Nursing.2012; 18(4): 207. CrossRef
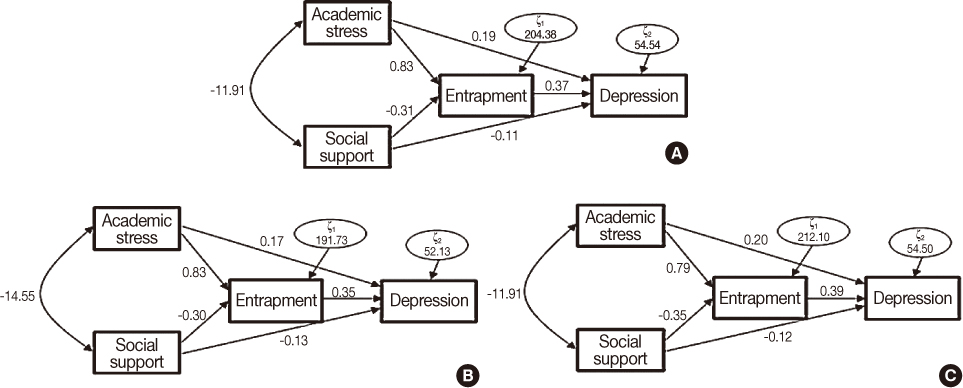
Figure 1
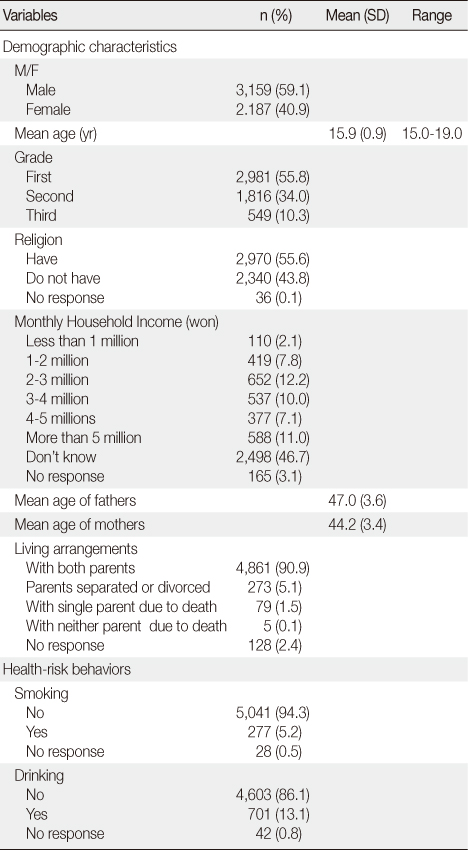
Demographic Characteristics and Health-Risk Behaviors of the Students (N=5,346)
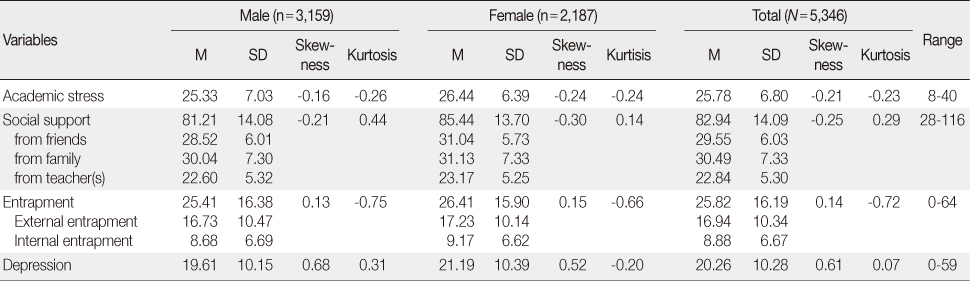
Means of Research Variables for the Students
Research Variables according to Demographic Characteristics and Health-Risk Behaviors of the Students (N=5,346)
Different superscripts mean significant differences by Tukey's multiple comparison test.
Mediating Effect of Entrapment: Standardized Direct, Indirect, and Total Effects and SMC in Depression Path Model
*SMC=Squared multiple correlation.
Different superscripts mean significant differences by Tukey's multiple comparison test.
*SMC=Squared multiple correlation.
 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION
 Cite
Cite

