Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Nurs > Volume 41(3); 2011 > Article
-
Original Article
- Predictive Bayesian Network Model Using Electronic Patient Records for Prevention of Hospital-Acquired Pressure Ulcers
- In Sook Cho, Eunja Chung
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2011;41(3):423-431.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2011.41.3.423
Published online: June 13, 2011
1Associated Professor, Department of Nursing, Inha University, Incheon, Korea.
2Director, Department of Nursing, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Cho, In Sook. Department of Nursing, Inha University, Yonghyeon 4-dong, Nam-gu, Incheon 402-751, Korea. Tel: +82-32-860-8201, Fax: +82-32-874-5880, insook.cho@inha.ac.kr
© 2011 Korean Society of Nursing Science
Abstract
-
Purpose
- The study was designed to determine the discriminating ability of a Bayesian network (BN) for predicting risk for pressure ulcers.
-
Methods
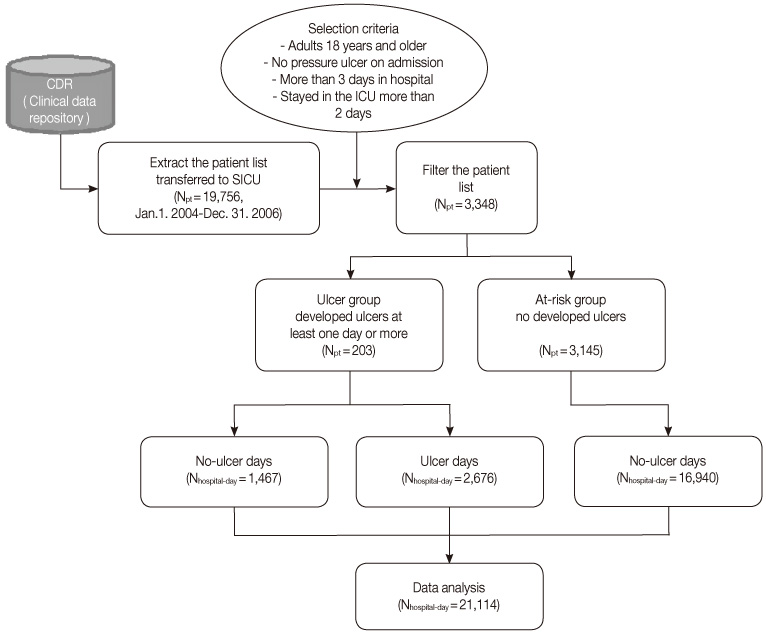
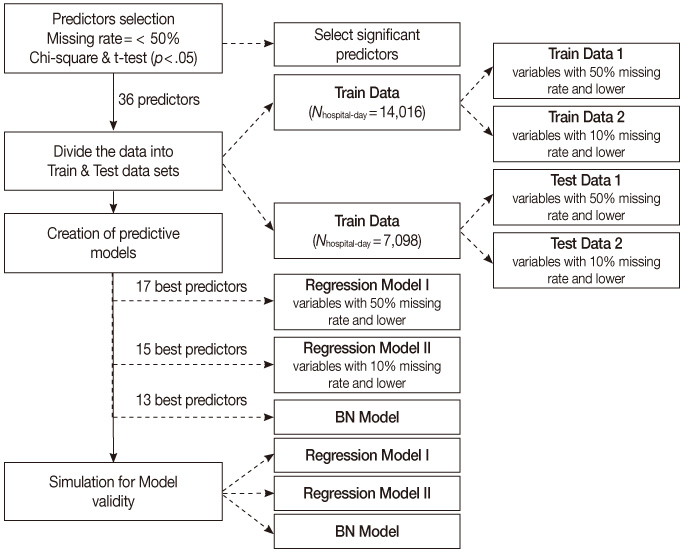
- Analysis was done using a retrospective cohort, nursing records representing 21,114 hospital days, 3,348 patients at risk for ulcers, admitted to the intensive care unit of a tertiary teaching hospital between January 2004 and January 2007. A BN model and two logistic regression (LR) versions, model-I and -II, were compared, varying the nature, number and quality of input variables. Classification competence and case coverage of the models were tested and compared using a threefold cross validation method.
-
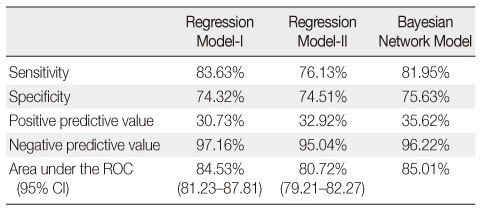
Results
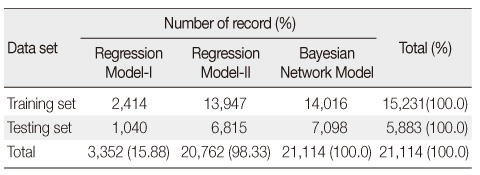
- Average incidence of ulcers was 6.12%. Of the two LR models, model-I demonstrated better indexes of statistical model fits. The BN model had a sensitivity of 81.95%, specificity of 75.63%, positive and negative predictive values of 35.62% and 96.22% respectively. The area under the receiver operating characteristic (AUROC) was 85.01% implying moderate to good overall performance, which was similar to LR model-I. However, regarding case coverage, the BN model was 100% compared to 15.88% of LR.
-
Conclusion
- Discriminating ability of the BN model was found to be acceptable and case coverage proved to be excellent for clinical use.
This work was supported by the Korea Science and Engineering Foundation (KOSEF) grant funded by the Korea government (MOST) (No. 2009-0053032).
- 1. Baumgarten M, Margolis DJ, Localio AR, Kagan SH, Lowe RA, Konsian B, et al. Extrinsic risk factors for pressure ulcers early in the hospital stay: A nested case-control study. The Journals of Gerontology. Series A, Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences. 2008;63:408–413.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 2. Beeckman D, Schoonhoven L, Fletcher J, Furtado K, Gunningberg L, Heyman H, et al. EPUAP classification system for pressure ulcers: European reliability study. Journal of Advanced Nursing. 2007;60:682–691. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2648.2007.04474.x.ArticlePubMed
- 3. Bergstrom N, Braden B, Kemp M, Champagne M, Ruby E. Predicting pressure ulcer risk: A multisite study of the predictive validity of the Braden Scale. Nursing Research. 1998;47:261–269. doi:10.1097/00006199-199809000-00005.ArticlePubMed
- 4. Brown SJ. The Braden Scale: A review of the research evidence. Orthopaedic Nursing. 2004;23:30–38. doi:10.1097/00006416-200401000-00010.ArticlePubMed
- 5. Burnside ES, Rubin DL, Shachter RD. Using a Bayesian network to predict the probability and type of breast cancer represented by microcalcifications on mammography. Studies in Health Technology And Informatics. 2004;107(Pt 1):13–17.PubMed
- 6. Cho I, Noh M. Braden Scale: Evaluation of clinical usefulness in an intensive care unit. Journal of Advanced Nursing. 2010;66:293–302. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2648.2009.05153.x.ArticlePubMed
- 7. Cho I, Yoon HY, Park SI, Lee HS. Availability of nursing data in an electronic nursing record system for a development of a risk assessment. Journal of Korean Society of Medical Informatics. 2008;14:161–168.
- 8. Cios KJ, Moore GW. Uniqueness of medical data mining. Artificial Intelligence in Medicine. 2002;26:1–24. doi:10.1016/S0933-3657(02)00049-0.ArticlePubMed
- 9. Cover TM, Thomas JA. Elements of information theory. 1991;New York, John Wiley & Sons.
- 10. De Laat EH, Pickkers P, Schoonhoven L, Verbeek AL, Feuth T, van Achterberg T. Guideline implementation results in a decrease of pressure ulcer incidence in critically ill patients. Critical Care Medicine. 2007;35:815–820. doi:10.1097/01.CCM.0000257072.10313.56.ArticlePubMed
- 11. Defloor T, Grypdonck MF. Pressure ulcers: Validation of two risk assessment scales. Journal of Clinical Nursing. 2005;14:373–382. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2702.2004.01058.x.ArticlePubMed
- 12. Fernandez G. Statistical data mining using SAS applications. 2010;2nd ed. Minnesota, CRC Press.
- 13. Fischer JE, Bachmann LM, Jaeschke R. A readers' guide to the interpretation of diagnostic test properties: Clinical example of sepsis. Intensive Care Medicine. 2003;29:1043–1051. doi:10.1007/s00134-003-1761-8.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 14. Fogerty MD, Abumrad NN, Nanney L, Arbogast PG, Poulose B, Barbul A. Risk factors for pressure ulcers in acute care hospitals. Wound Repair and Regeneration. 2008;16:11–18. doi:10.1111/j.1524-475X.2007.00327.x.ArticlePubMed
- 15. Harrison JH. Introduction to the mining of clinical data. Clinics in Laboratory Medicine. 2008;28:1–7. doi:10.1016/j.cll.2007.10.001.ArticlePubMed
- 16. Hatanaka N, Yamamoto Y, Ichihara K, Mastuo S, Nakamura Y, Watanabe M, et al. A new predictive indicator for development of pressure ulcers in bedridden patients based on common laboratory tests results. Journal of Clinical Pathology. 2008;61:514–518. doi:10.1136/jcp.2007.050195.ArticlePubMed
- 17. Jones KR, Fennie K, Lenihan A. Evidence-based management of chronic wounds. Advances in Skin and Wound Care. 2007;20:591–600. doi:10.1097/01.ASW.0000284936.32707.8d.ArticlePubMed
- 18. Korb KB, Nicholson AE. Bayesian artificial intelligence. 2004;London, Chapman & Hall/CRC press.
- 19. Lee KO, Shin HJ, Park HA, Jeong HM, Lee MH, Choi EH, et al. Patient severity classification in a medical ICU using APACHE III and patient severity classification tool. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2000;30:1243–1253.ArticlePDF
- 20. Lee SM, Abbott P, Johantgen M. Logistic regression and Bayesian networks to study outcomes using large data sets. Nursing Research. 2005;54:133–138. doi:10.1097/00006199-200503000-00009.PubMed
- 21. Lee YH, Jeong IS, Jeon SS. A comparative study on the predictive validity among presusre ulcer risk assessment scales. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2003;33:162–169.PubMed
- 22. Lucas PJF, van der Gaag LC, Abu-Hanna A. Bayesian network in biomedicine and health-care. Artificial Intelligence in Medicine. 2004;30:201–214. doi:10.1016/j.artmed.2003.11.001.ArticlePubMed
- 23. Park HS, Park KY, Yu SM. Factors influencing the development of pressure ulcers in surgical patients. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2005;35:125–134.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 24. Pesut D. Weaver C, Delaney C, Weber P, Carr R. 21st century nursing knowledge work: Reasoning into the future. In: Nursing and informatics for the 21st century: Cases, practice, and the future. 2006;Chicago, HIMSS Press. 14–17.
- 25. Russo CA, Steiner C, Spector W. Rep. No. HCUP Statistical Brief #64. Hospitalizations related to pressure ulcers, 2006. 2008;Rockville, MD, Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality.
- 26. Schoonhoven L, Haalboom JR, Bousema MT, Algra A, Grobbee DE, Grypdonck MH, et al. Prospective cohort study of routine use of risk assessment scales for prediction of pressure ulcers. British Medical Journal. 2002;325:797–800. doi:10.1136/bmj.325.7368.797.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 27. Thede LQ, Sewell JP. Informatics and nursing: Competencies and applications. 2010;3rd ed. Philadelphia, Wolters Kluwer Health | Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
REFERENCES
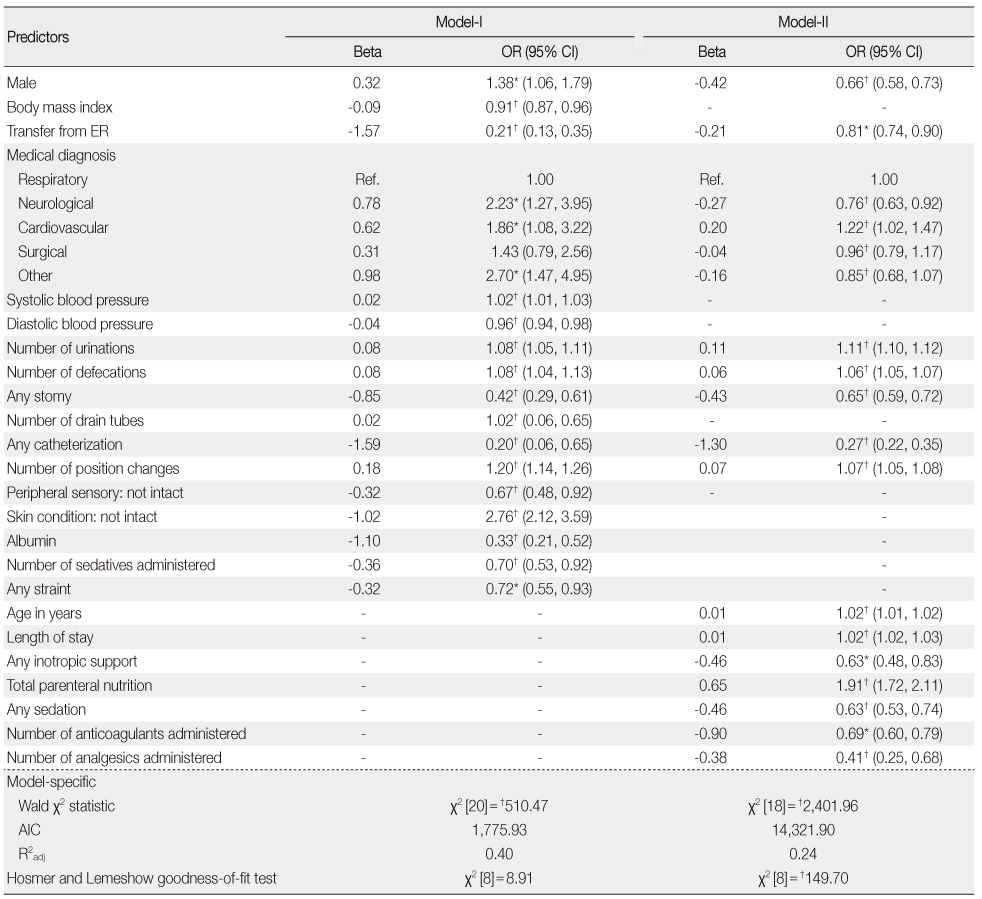
*Confidence intervals (95% CI) not containing the null value (1.00) are statistically significant at p<.05; †p<.001 for χ2 tests; The Akaike information criterion (AIC), a measure of statistical model fit, was used to compare the amount of information explained across the logistic regression models. A lower AIC value indicates a model is a better fit for the observed data.
ER=emergency room; OR=odds ratio; CI=confidence interval.
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Evaluation of the risk prediction model of pressure injuries in hospitalized patient: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Yuxia Ma, Xiang He, Tingting Yang, Yifang Yang, Ziyan Yang, Tian Gao, Fanghong Yan, Boling Yan, Juan Wang, Lin Han
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2025; 34(6): 2117. CrossRef - Using nursing data for machine learning-based prediction modeling in intensive care units: A scoping review
Yesol Kim, Mihui Kim, Yeonju Kim, Mona Choi
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2025; 169: 105133. CrossRef - Development of a Pressure Injury Machine Learning Prediction Model and Integration into Clinical Practice: A Prediction Model Development and Validation Study
Ju Hee Lee, Jae Yong Yu, So Yun Shim, Kyung Mi Yeom, Hyun A Ha, Se Yong Jekal, Ki Tae Moon, Joo Hee Park, Sook Hyun Park, Jeong Hee Hong, Mi Ra Song, Won Chul Cha
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2024; 36(3): 191. CrossRef - The predictive effect of different machine learning algorithms for pressure injuries in hospitalized patients: A network meta-analyses
Chaoran Qu, Weixiang Luo, Zhixiong Zeng, Xiaoxu Lin, Xuemei Gong, Xiujuan Wang, Yu Zhang, Yun Li
Heliyon.2022; 8(11): e11361. CrossRef - Predictive Modeling of Pressure Injury Risk in Patients Admitted to an Intensive Care Unit
Mireia Ladios-Martin, José Fernández-de-Maya, Francisco-Javier Ballesta-López, Adrián Belso-Garzas, Manuel Mas-Asencio, María José Cabañero-Martínez
American Journal of Critical Care.2020; 29(4): e70. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of Electronic Health Record Data-Driven Predictive Models for Pressure Ulcers
Seul Ki Park, Hyeoun-Ae Park, Hee Hwang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2019; 49(5): 575. CrossRef - Development and Comparison of Predictive Models for Pressure Injuries in Surgical Patients
Seul Ki Park, Hyeoun-Ae Park, Hee Hwang
Journal of Wound, Ostomy & Continence Nursing.2019; 46(4): 291. CrossRef - Automated Pressure Injury Risk Assessment System Incorporated Into an Electronic Health Record System
Yinji Jin, Taixian Jin, Sun-Mi Lee
Nursing Research.2017; 66(6): 462. CrossRef - Recommendation of Personalized Surveillance Interval of Colonoscopy via Survival Analysis
Jayeon Gu, Eun Sun Kim, Seoung Bum Kim
Journal of Korean Institute of Industrial Engineers.2016; 42(2): 129. CrossRef - Medical Data Based Clinical Pathway Analysis and Automatic Ganeration System
Hanna Park, In Ho Bae, Yong Oock Kim
The Journal of Korea Information and Communications Society.2014; 39C(6): 497. CrossRef - Reusability of EMR Data for Applying Cubbin and Jackson Pressure Ulcer Risk Assessment Scale in Critical Care Patients
Eunkyung Kim, Mona Choi, JuHee Lee, Young Ah Kim
Healthcare Informatics Research.2013; 19(4): 261. CrossRef - Using EHR data to predict hospital-acquired pressure ulcers: A prospective study of a Bayesian Network model
Insook Cho, Ihnsook Park, Eunman Kim, Eunjoon Lee, David W. Bates
International Journal of Medical Informatics.2013; 82(11): 1059. CrossRef
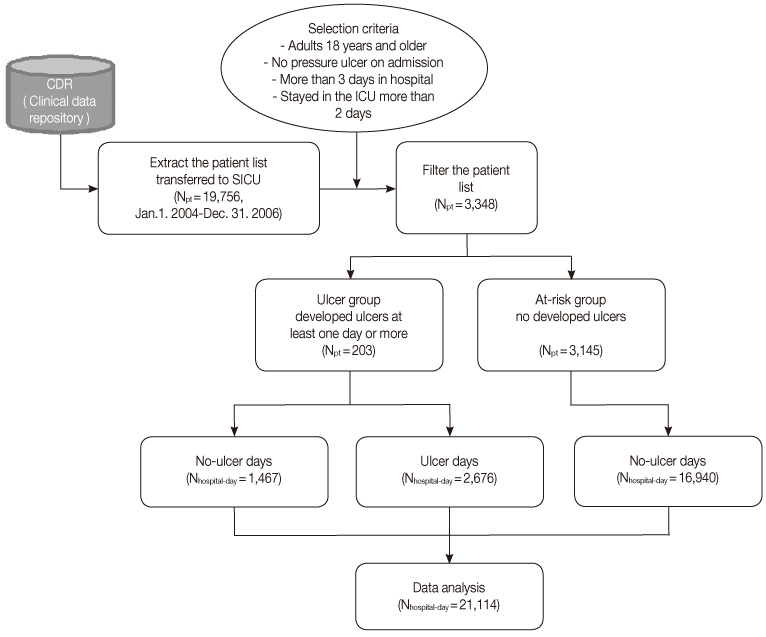
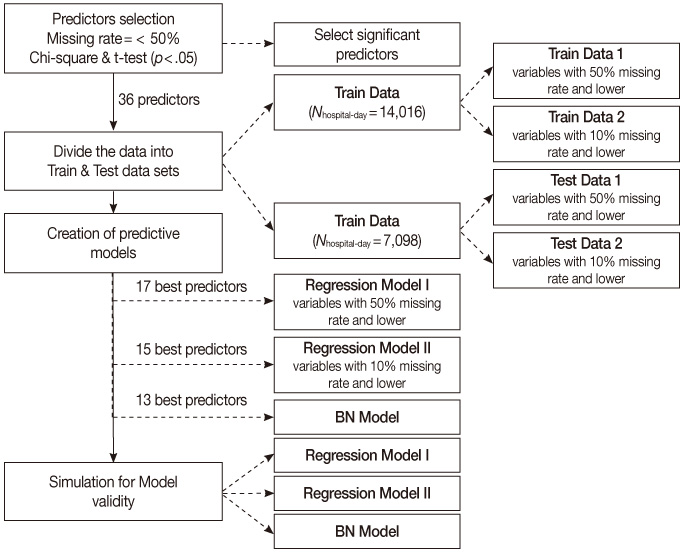
Figure 1
Figure 2
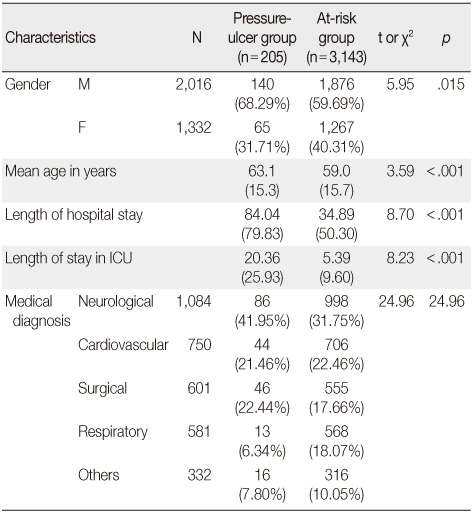
Group Comparison of Demographic Characteristics between Ulcer Group and Risk Group
Multiple Logistic Regression Models Examining Risks of Pressure Ulcers
*Confidence intervals (95% CI) not containing the null value (1.00) are statistically significant at p<.05; †p<.001 for χ2 tests; The Akaike information criterion (AIC), a measure of statistical model fit, was used to compare the amount of information explained across the logistic regression models. A lower AIC value indicates a model is a better fit for the observed data.
ER=emergency room; OR=odds ratio; CI=confidence interval.
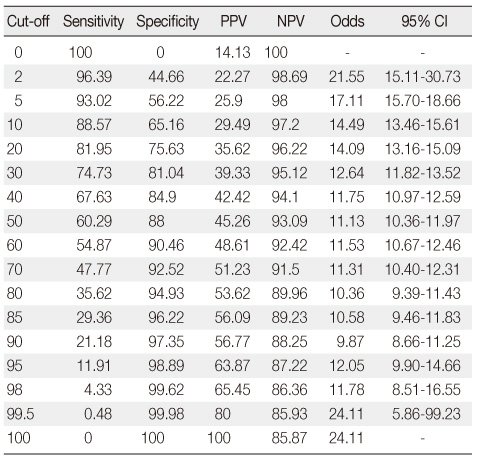
Results of the Sensitivity, Specificity, Positive Predictive Value, and Negative Predictive Value
PPV=positive predictive value; NPV=negative predictive value.
Test Characteristics of the Predictive Models
Case Coverage by the Predictive Models
*Confidence intervals (95% CI) not containing the null value (1.00) are statistically significant at ER=emergency room; OR=odds ratio; CI=confidence interval.
PPV=positive predictive value; NPV=negative predictive value.
 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION
 Cite
Cite

